- Troubleshoot problems updating Windows 10
- Have issues installing Windows updates? Start here.
- Still stuck?
- Устранение неполадок обновлений встроенного ПО диска Troubleshooting drive firmware updates
- Распространенные проблемы Common issues
- Определение недопустимого оборудования Identifying inappropriate hardware
- Параметры исправлений Remediation options
- Устранение неполадок сторонних драйверов (SAS) Troubleshooting with 3rd-Party drivers (SAS)
- Параметры исправлений Remediation options
- Дополнительное устранение неполадок в драйверах Microsoft (SATA/NVMe) Additional troubleshooting with Microsoft drivers (SATA/NVMe)
Troubleshoot problems updating Windows 10
In Windows 10, you decide when and how to get the latest updates to keep your device running smoothly and securely. This article will help you answer questions and troubleshoot common problems with your Windows 10 update.
If you’re looking for info on how to activate Windows 10 or to verify that your installation of Windows 10 is activated, see Activate Windows 10.
Have issues installing Windows updates? Start here.
Your device may not be able to update to the latest version of Windows 10 for a few reasons. The following tips can help you pinpoint the issue affecting your device.
Before you begin, make sure your device is plugged into a power source and connected to the internet. Then, try the steps listed below to get your PC to update.
Some updates require administrator access. If your account doesn’t have administrator access, see Create a local user or administrator account in Windows 10. Or if someone else at home or in your office has an administrator account on your device, try asking them to install the updates.
Before trying any of the solutions below, make sure you back up your personal files. You can use File History to back up your files to another drive, or insert a USB drive and use File Explorer to drag and copy important files to the USB drive. If you’re signing into Windows with a Microsoft account, your system settings will be automatically restored after updating, once you’re connected to the internet.
You can also back up your files with OneDrive. For more info, go to Back up your Documents, Pictures, and Desktop folders with OneDrive.
Make sure that your device has enough space. Your device requires at least 16 GB of free space to upgrade a 32-bit OS, or 20 GB for a 64-bit OS. If your device has a small hard drive, you may need to insert a USB drive to update it.
If your PC is running low on storage, try the techniques at Free up drive space in Windows 10.
Many updates require you to restart your device. Save your work and close all open applications. Then, select Start > Power , and select either Update and restart or Update and shut down.
Even if you have downloaded some updates, there may be more available. After trying the preceding steps, run Windows Update again by selecting Start > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates. Download and install any new updates.
Remove any external storage devices and drives, docks, and other hardware plugged into your device that aren’t needed for basic functionality. Then try to run updates again and see if this resolved your issue. If it didn’t, continue to the next tip.
If you’ve added hardware to your device, check for third-party driver updates and installation instructions on the hardware manufacturer’s website. Update any drivers, then try to run updates again and see if this resolved your issue. If it didn’t, continue to the next tip.
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select Device Manager from the list of results.
In the window that appears, look for any device with a yellow exclamation mark next to it. (You may have to select each category to view the list of devices.) Select the device name.
Select Action, and then choose either Update driver or Uninstall to correct the errors.
Common troubleshooting questions
If you are receiving an error message with a specific error code, try running the Windows Update Troubleshooter. If that doesn’t resolve the issue, see Fix Windows Update errors and follow the instructions to help resolve common update issues.
The time required to download and install updates depends on connection speed, network settings, and the size of the update. If the installation remains stuck at the same percentage, try checking for updates again or running the Windows Update Troubleshooter.
To check for updates, select Start > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates.
To get help, in the search box on the task bar, type get help, then select Get Help from the list of results. To leave feedback if you run into further problems, in the search box on the taskbar, type feedback hub, then select Feedback Hub from the list of results.
Windows 10 is the most secure Windows ever, and we recommend you stay updated to protect your PC from security risks and to keep it running smoothly. However, you can temporarily pause updates as well as schedule a restart to install updates at a time that’s convenient for you.
Learn how to temporarily pause updates
Find out how to schedule a restart to install updates at a convenient time
You will only receive a notification when it’s time to restart your computer to apply the installed updates.
If you need to know where you left off in your work after an update, use Timeline to jump back in.
To get started with Timeline, select Task View on the taskbar, or press the Windows logo key +Tab and select the activity you want to resume.
Monthly quality updates on Windows 10 are quite small and have a minimal impact on data usage. Feature updates typically happen twice per year, and you can control when to install them. They require more data but are less frequent.
If you’re on a metered connection, some updates for Windows won’t be installed automatically. Metered connections in Windows 10
Your computer might be slow for a number of reasons, but updating to the latest version of Windows 10 can improve its performance. For help with a slow computer, see Tips to improve PC performance in Windows 10.
If you’re having trouble finding your files after an upgrade, see Find lost files after the upgrade to Windows 10 for other things to try.
Warning: Microsoft only recommends trying the procedures in this section if you’re comfortable working in the command line. These procedures require administrator permissions on your device.
In the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt, then select Run as administrator from the list of options. Select Yes. Next, in the window that appears, type the following commands one at a time, including the spaces as shown. After you type each command, press Enter. Then let each command complete before you type the next command.
net stop wuauserv
ren %systemroot%\softwaredistribution softwaredistribution.bak
ren %systemroot%\system32\catroot2 catroot2.bak
net start wuauserv
After all these commands are completed, close the Command Prompt window and restart your computer.
In some instances, third-party antivirus or security software can cause errors when you try to update to the latest version of Windows 10. You can temporarily uninstall this software, update your PC, and then reinstall the software after your device is up to date. We recommend using third-party antivirus or security software that’s compatible with the latest version of Windows 10. You can check compatibility by visiting the software manufacturer’s website.
Note: Before uninstalling software, make sure you know how to reinstall your programs and that you have any necessary product keys.
In the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt, and then select Run as administrator from the list of options. Select Yes. In the window that appears, type the following command, including the space as shown:
chkdsk/f C:
and then press Enter. Repairs will automatically start on your hard drive, and you’ll be asked to restart your device.
A clean restart starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. This helps eliminate software conflicts that occur when you install a program or an update that may cause issues updating your PC.
Learn how to do a clean restart
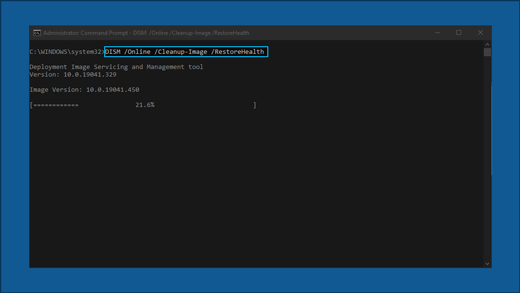
In the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt, then select Run as administrator from the list of options.
In the window that appears, type this command including spaces as shown:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth
Press Enter. When the command operation has run successfully, you’ll see a confirmation message from Command Prompt that says, “The restore operation completed successfully” or “The operation completed successfully”.
Note: If you don’t see a confirmation message, retype the command and try again.
Next, type this command, including the space as shown:
sfc /scannow
Press Enter. Wait until the sfc scan verification reaches 100% completion, and then close Command Prompt.
Try running the Windows Update again.
Go to the software download page and select Download tool now to download the clean installation tool. Make sure to carefully read the notes on the software download page before using the tool.
Still stuck?
Contact Microsoft support if you continue to have problems with your Windows updates.
Устранение неполадок обновлений встроенного ПО диска Troubleshooting drive firmware updates
Область применения: Windows 10, Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Applies to: Windows 10, Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel),
В Windows 10 версии 1703 и более поздних версиях, а также в Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel) имеется возможность обновлять встроенное ПО жестких дисков и дисков SSD, которые были сертифицированы с помощью дополнительного квалификатора обновляемого встроенного ПО через PowerShell. Windows 10, version 1703 and newer, and Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel) include the capability to update firmware of HDDs and SSDs that have been certified with the Firmware Upgradeable AQ (Additional Qualifier) via PowerShell.
Дополнительные сведения об этом компоненте можно найти здесь: You can find more information about this feature here:
Обновление встроенного ПО может завершиться с ошибкой по различным причинам. Firmware updates may fail for various reasons. Эта статья предназначена помочь при выполнении расширенных действий по устранению неполадок. The purpose of this article is to help with advanced troubleshooting.
Сведения в этой статье, в зависимости от проблемы, могут быть недостаточными для полной отладки всех возможных сбоев. Information in this article, depending on the issue, may not be sufficient to fully debug all possible failure cases.
Распространенные проблемы Common issues
С точки зрения архитектуры эта новая возможность опирается на API, реализованные в стеке хранилища Windows, в который PowerShell направляет вызовы. Architecturally, this new capability relies on APIs implemented in the Windows storage stack, which PowerShell calls into. Стек хранилища зависит от драйверов и оборудования, чтобы правильно реализовывать определенные в отрасли команды. The storage stack relies on drivers and hardware to properly implement industry defined commands. Вследствие этого создаются несколько точек, в которых возникают сбои. This yields several points at which failures can occur. Далее перечислены наиболее частые проблемы. The most commonly observed issues are:
- Определенный диск не реализует стандартные команды надлежащим образом (у него отсутствует ДК) A given drive does not properly implement the industry-standard commands (does not have the AQ)
- API, необходимые для выполнения обновления, не реализованы или работают со сбоями (если используются драйверы других производителей) The APIs needed to perform the update are not implemented or faulty (if 3rd party drivers are used)
- API работают, но существует проблема с самым встроенным ПО (недопустимый или поврежденный образ, …) The APIs work, but there is an issue with the firmware itself (invalid/corrupt image, …)
В следующих разделах описываются сведения об устранении неполадок, связанных с использованием драйверов Microsoft или сторонних драйверов. The following sections outline troubleshooting information, depending on whether Microsoft or 3rd party drivers are used.
Определение недопустимого оборудования Identifying inappropriate hardware
Самый быстрый способ определить, поддерживает ли устройство правильный набор команд, — просто запустить PowerShell и передать объект PhysicalDisk, представляющий диск, в командлет Get-StorageFirmwareInfo. The quickest way to identify if a device supports the correct command set is to simply launch PowerShell and pass a disk’s representing PhysicalDisk object into the Get-StorageFirmwareInfo cmdlet. Например: Here is an example:
Вот пример выходных данных: And here’s example output:
Поле SupportsUpdate, по крайней мере для устройств SATA и NVMe, будет указывать, может ли использоваться встроенная функция PowerShell для обновления встроенного ПО. The SupportsUpdate field, at least for SATA and NVMe devices, will indicate if the built-in PowerShell functionality can be used to update firmware.
Поле SupportsUpdate всегда будет отображать значение True для последовательно подключенных устройств SAS, так как запросы на поддержку соответствующей команды невозможны с помощью стандартных отраслевых команд. The SupportsUpdate field will always report “True” for SAS-attached devices, as querying for the appropriate command support is not possible with industry-standard commands.
Чтобы проверить, поддерживает ли устройство SAS набор необходимых команд, существует два варианта: To validate if a SAS device supports the required command set, two options exist:
- Попробуйте воспользоваться командлетом Update-StorageFirmware с изображением соответствующего образа, или Try it out via the Update-StorageFirmware cmdlet with an appropriate firmware image, or
- Просмотрите каталог Windows Server, чтобы узнать, какие устройства SAS успешно получили обновление FW AQ (https://www.windowsservercatalog.com/) Consult the Windows Server Catalogue to identify which SAS devices have successfully gained the FW Update AQ (https://www.windowsservercatalog.com/)
Параметры исправлений Remediation options
Если тестируемое вами устройство не поддерживает соответствующий набор команд, обратитесь к поставщику, чтобы узнать о наличии обновленного встроенного ПО с набором необходимых команд, или обратитесь к Каталогу Windows Server для определения устройств, способных реализовать набор соответствующих команд. If a given device you are testing does not support the appropriate command set, either query your vendor to see if an updated firmware is available that provides the needed command set, or consult the Windows Server Catalogue to identify devices for sourcing that implement the appropriate command set.
Устранение неполадок сторонних драйверов (SAS) Troubleshooting with 3rd-Party drivers (SAS)
Компонентами программного обеспечения, наиболее тесно взаимодействующими с оборудованием, являются драйверы мини-портов в стеке хранилища Windows. The software components that most closely interact with hardware are mini-port drivers in the Windows storage stack. Для некоторых протоколов хранилища, например SATA и NVMe, корпорация Майкрософт предоставляет собственные драйверы для Windows. For some storage protocols, such as SATA and NVMe, Microsoft provides native Windows drivers. Эти драйверы предоставляют дополнительную информацию об отладке. These drivers allow for additional debug information. Однако поставщики стороннего оборудования и программного обеспечения имеют полную свободу написания собственных драйверов мини-порта для своих устройств. При этом уровень их поддержки для информации об отладке может быть разным. 3rd party hardware and software vendors however are free to write their own miniport drivers for their devices and their support level for debug information may vary.
Чтобы определить, что произошло со встроенным ПО, скачайте и активируйте API, отправленные в стек хранилища, независимо от драйвера мини-порта. Обратитесь к следующему каналу журнала: To identify what happened to the firmware download and activate APIs sent down the storage stack, regardless of miniport driver, consult the following event log channel:
Просмотр событий — Журналы приложений и служб — Microsoft — Windows — StorDiag — Microsoft-Windows-Storage-ClassPnP/Operational Event Viewer — Application and Services Logs — Microsoft — Windows — StorDiag — Microsoft-Windows-Storage-ClassPnP/Operational
Этот канал записывает сведения об API Windows, отправляемых драйверам мини-порта, а также их ответы. This channel records information about the Windows APIs sent down to the miniport drivers and what their responses are. Например, состояние ошибки, показанное непосредственно ниже, проявляется при попытке скачать образ встроенного ПО на устройство SATA, подключенное через HBA SAS, которое не реализует надлежащим образом необходимый перевод из SAS в SATA: For example, the error condition shown directly below is exhibited when attempting to download a firmware image to a SATA device, which is connected through a SAS HBA that does not properly implement the needed translation from SAS to SATA:
Ниже приведен пример выхода. Here’s an example of the output:
PowerShell вызовет ошибку и получит информацию о том, что вызванная функция (то есть Kernel API) является неправильной. PowerShell will throw an error and has received the information that the function called (i.e. Kernel API) was incorrect. Это может означать, что API не реализован драйвером мини-порта стороннего устройства SAS (значение true в этом случае) или сбой API произошел по другой причине, например из-за рассогласования сегментов скачивания. This could mean that either the API was not implemented by the 3rd party SAS mini-port driver (true in this case), or that the API was failed for another reason, such as a misalignment of download segments.
Событие трассировки событий Windows 507 из канала показывает, что сбой запроса SCSI СРБ и предоставление дополнительных сведений, которые Сенсекэй был «5» (недопустимый запрос), а Аддитионалсенсе сведения были «36» (недопустимое поле в CDB). The ETW event 507 from the channel shows that a SCSI SRB request failed and provides the additional information that SenseKey was ‘5′ (Illegal Request), and that AdditionalSense information was ‘36′ (Illegal Field in CDB).
Эта информация предоставляется непосредственно соответствующим мини-портом, и точность этих сведений будут зависеть от реализации и усовершенствования драйвера мини-порта. This information is provided directly by the miniport in question and the accuracy of this information will depend on the implementation and sophistication of the miniport driver.
Возможно, разные состояния ошибки будут вызывать одинаковые коды ошибок, если драйвер мини-порта не разграничит их. It is possible that different error condition exhibit the same error codes, if the miniport driver does not disambiguate between them. Например, попытка скачать недопустимый образ встроенного ПО через SAS HBA на устройство SATA (на котором ожидается ошибка) может быть переведена в аналогичные коды ошибок. For example, trying to download an invalid firmware image through a SAS HBA to a SATA device (which the device is expected to fail) may be translated to the same failure codes.
В случаях, в которых смешиваются протоколы и происходят переводы, т. е. SATA за SAS, лучше всего проверять устройство SATA с прямым подключением к контроллеру SATA, чтобы исключить его потенциальные проблемы. In cases where protocols are mixed and translations occur, i.e. SATA behind SAS, it is best to test the SATA device directly connected to a SATA controller to rule it out as a potential problem.
Параметры исправлений Remediation options
Если сторонний драйвер будет определен как таковой, что не реализует необходимые API или переводы, можно перейти на предоставленные корпорацией Майкрософт альтернативы для SATA (StorAHCI.sys) и NVMe (StorNVMe.sys) или обратиться к изготовителю OEM или HBA, который предоставил драйвер SAS, и спросить о существовании более новой версии с надлежащей поддержкой. If the 3rd party driver is identified as not implementing the needed APIs or translations, it is possible to either swap to the Microsoft provided alternatives for SATA (StorAHCI.sys) and NVMe (StorNVMe.sys), or reach out to the OEM or HBA vendor that provided the SAS driver and query if a newer version with the proper support exists.
Дополнительное устранение неполадок в драйверах Microsoft (SATA/NVMe) Additional troubleshooting with Microsoft drivers (SATA/NVMe)
Когда встроенные драйверы Windows, например StorAHCI.sys или StorNVMe.sys, используются для хранения данных устройства управления питанием, можно получить дополнительные сведения о возможных случаях сбоев во время обновления встроенного ПО. When Windows-native drivers, such as StorAHCI.sys or StorNVMe.sys are used to power storage devices, it is possible to get additional information about possible failure cases during firmware update operations.
Помимо операционного канала Класспнп, СторахЦи и Сторнвме будут регистрировать коды возврата, относящиеся к протоколу устройства, в следующем канале ETW: Beyond the ClassPnP Operational channel, StorAHCI and StorNVMe will log the device’s protocol specific return codes in the following ETW channel:
Просмотр событий — Журналы приложений и служб — Microsoft — Windows — StorDiag — Microsoft-Windows-Storage-StorPort/Diagnose Event Viewer — Application and Services Logs — Microsoft — Windows — StorDiag — Microsoft-Windows-Storage-StorPort/Diagnose
Журналы диагностики не отображаются по умолчанию и могут быть активированы или показаны выбором команды «Просмотр» в EventViewer и элемента «Показать журналы аналитики и отладки» из раскрывающего меню. The diagnostic logs are not shown by default and can be activated/shown by clicking on “View” in EventViewer and selecting “Show Analytics and Debug Logs” from the drop-down menu.
Для сбора этих расширенных записей журнала включите журнал, воспроизведите сбой обновления встроенного ПО и сохраните журнал диагностики. To gather these advanced log entries, enable the log, reproduce the firmware update failure, and save the diagnostic log.
Вот пример обновления встроенного ПО на неисправном устройстве SATA из-за недопустимого образа для скачивания (код события: 258): Here is an example of a firmware update on a SATA device failing, because the image to be downloaded was invalid (Event ID: 258):
Указанное выше событие содержит подробные сведения об устройстве в значениях параметров 2–6. The above event contains detailed device information in parameter values 2 through 6. Здесь мы рассматриваем различные значения регистров ATA. Here we are looking at various ATA register values. Спецификации ACS ATA можно использовать для декодирования указанных ниже значений для сбоя команды Download Microcode: The ATA ACS specification can be used to decode the below values for failure of a Download Microcode command:
- Код возврата: 0 (0000 0000) (Н/Д — бессмысленно, так как не передавалась рабочая нагрузка) Return Code: 0 (0000 0000) (N/A — meaningless since no payload was transferred)
- Функции: 15 (0000 1111) (бит 1 имеет значение «1» и указывает «Abort») Features: 15 (0000 1111) (Bit 1 is set to ‘1′ and indicates “abort”)
- SectorCount: 0 (0000 0000) (Н/Д) SectorCount: 0 (0000 0000) (N/A)
- DriveHead: 160 (1010 0000) (Н/Д — настраиваются только устаревшие биты) DriveHead: 160 (1010 0000) (N/A – only obsolete bits are set)
- Команда: 146 (1001 0010) (бит 1 имеет значение «1», указывающее на доступность осмысленных данных) Command: 146 (1001 0010) (Bit 1 is set to ‘1′ indicating the availability of sense data)
Это сообщает нам, что операция обновления встроенного ПО была прервана устройством. This tells us that the firmware update operation was aborted by the device.