- Объединения сетевых адаптеров NIC Teaming в Windows server 2012 R2
- Настройка
- NIC Teaming в Windows Server 2012
- Настройка NIC Teaming в Windows Server 2012
- Teaming Mode
- Load Balancing mode
- Standby adapter
- Настройка NIC teaming в Windows Server 2012 с помощью Powershell
- NIC Teaming settings
- Teaming modes
- Switch Independent
- Switch Dependent
- Load Balancing modes
- Address Hash
- Hyper-V Port
- Dynamic
- Standby adapter setting
- Primary Team interface property
Объединения сетевых адаптеров NIC Teaming в Windows server 2012 R2
Увеличение пропускной способности — увеличение полосы пропускания пропорционально количеству адаптеров в группе. К примеру, если объединить в NIC Teaming два сетевых адаптера со скоростью 1 Гбит/с, то общая полоса пропускания составит 2 Гбит/с;
Отказоустойчивость — при выходе из строя одного из адаптеров в группе, связь ни на секунду не прерывается и остальные сетевые адаптеры поменяют вышедший из строя.
Технология NIC Teaming не нова, но ранняя ее реализация зависела от производителей сетевого оборудования. Возможность объединять сетевые адаптеры в группу средствами ОС появилась только в редакции начиная с Windows Server 2012. Эта технология позволяет объединять в группу адаптеры разных производителей, единственное ограничение — все они должны работать на одной скорости. Ограничение по количеству объединяемых сетевых адаптеров в NIC Teaming равна 32.
Настройка
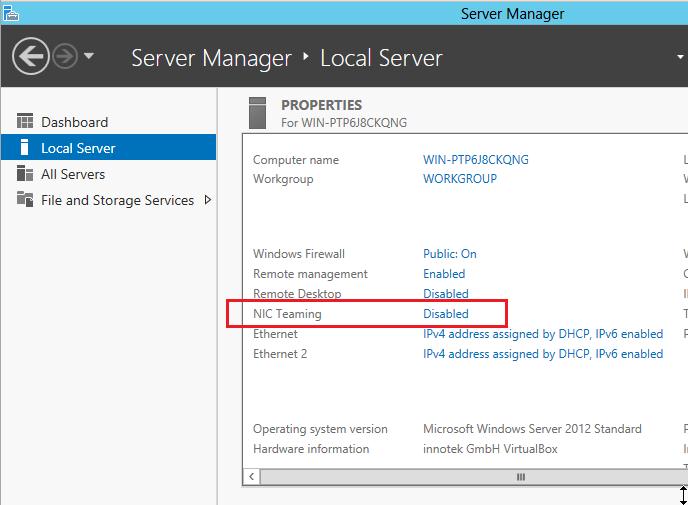
По умолчанию режим «NIC Teaming» в Windows server 2012 R2 отключен. Для его активации открываем «Server Manager» и заходим в свойства сервера, далее нажимаем: Объединение сетевых карт (NIC Teaming).
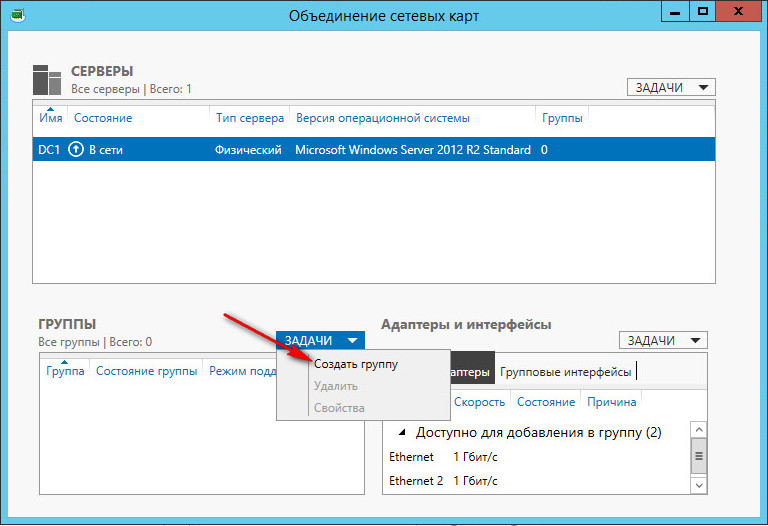
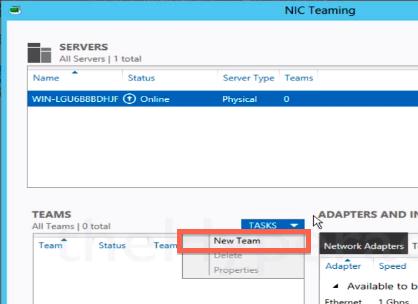
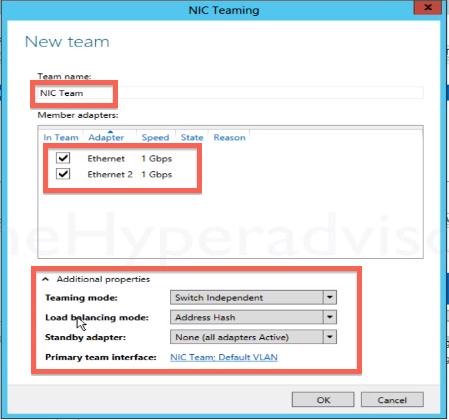
В Задачах (Tasks) выбираем пункт Создать группу (New Team).
Далее именуем группу, выбираем отмечаем адаптеры и настраиваем дополнительные свойства группы. Далее подробней рассмотрим дополнительные параметры настройки «NIC Teaming» в Windows server 2012 R2:
Режим поддержки групп (Teaming mode) определяет режим взаимодействия группы с сетевым оборудованием:
1. Не зависит от коммутатора (Switch Independent) — группа работает независимо от коммутатора, никакой дополнительной настройки сетевого оборудования не требуется. Этот режим позволяет подключать адаптеры одной тиминговой группы к разным свичам для защиты от сбоя одного из них. настройка по умолчанию;
2. Статическая поддержка групп (Static Teaming) — режим с зависимостью от сетевого оборудования. Все адаптеры группы должны быть подключены к одному коммутатору. Порты коммутатора, к которым подключены адаптеры группы, настраиваются на использование статической агрегации каналов;
3. LACP — режим с зависимостью от сетевого оборудования. Коммутатор настраивается на использование динамической агрегации каналов с использованием протокола «Link Aggregation Control Protocol» (LACP).
Режим балансировки нагрузки (Load Balancing mode) определяет, каким образом распределять сетевой трафик между адаптерами группы:
1. Хэш адреса (Address Hash) — при передаче сетевого трафика на основании MAC или IP-адресов отправителя и получателя вычисляется хеш (некое число). Это число привязывается к определенному физическому адаптеру и в дальнейшем весь трафик от этого отправителя будет идти через этот адаптер;
2. Порт Hyper-V (Hyper-V Port) — в этом режиме осуществляется привязка адаптера teaming группы к определенному порту виртуального свича в Hyper-V. Этот режим используется в том случае, если на сервере активирована роль Hyper-V.
Резервный адаптер (Standby adapter) позволяет назначить один из адаптеров группы в качестве резервного. В нормальном состоянии резервный адаптер не используется для передачи трафика, но при выходе любого адаптера группы из строя сразу занимает его место и трафик продолжает передаваться без перерывов. Но даже без резервирования выход из строя одного адаптера в NIC Teaming не приведет к прерыванию сетевого соединения, потому что, нагрузка будет автоматически распределена по оставшимся адаптерам.
Команда создания группы «NIC Teaming» в powerShell:
New-NetLbfoTeam -Name First-team -TeamMembers ″Ethernet″,″Ethernet 2″ ` -TeamingMode SwitchIndependent -LoadBalansingAlgorithm TransportPorts
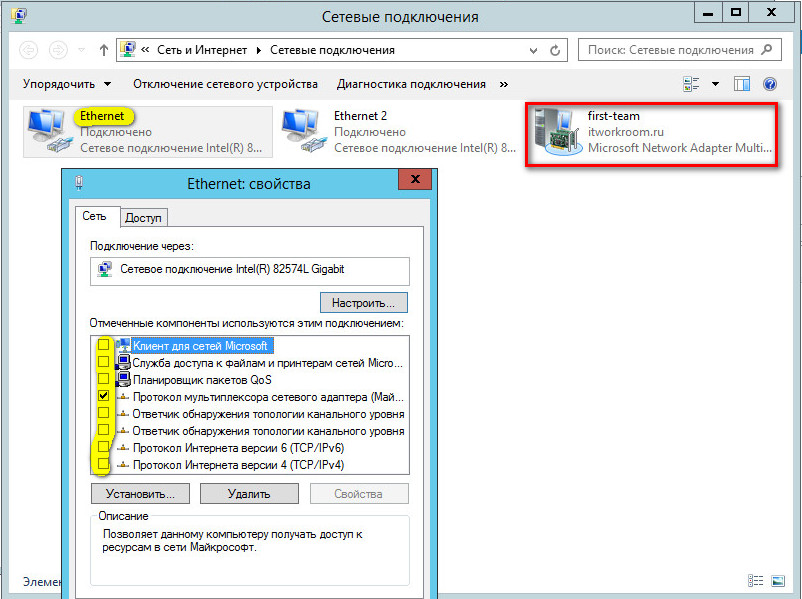
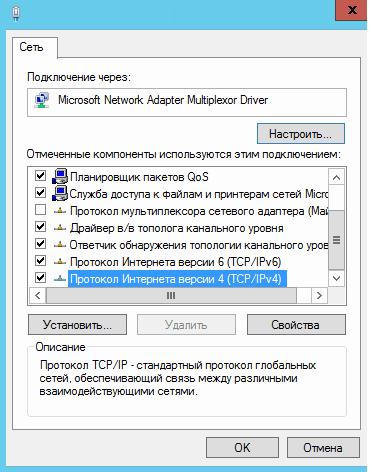
После создания группы, в окне «Сетевые подключения» появиться еще один сетевой адаптер, который как раз и является виртуальным адаптером созданной группы, при этом если посмотреть свойства физического сетевого адаптера, то мы увидим, что все компоненты кроме протокола мультиплексора сетевого адаптера отключены (выделено желтым).
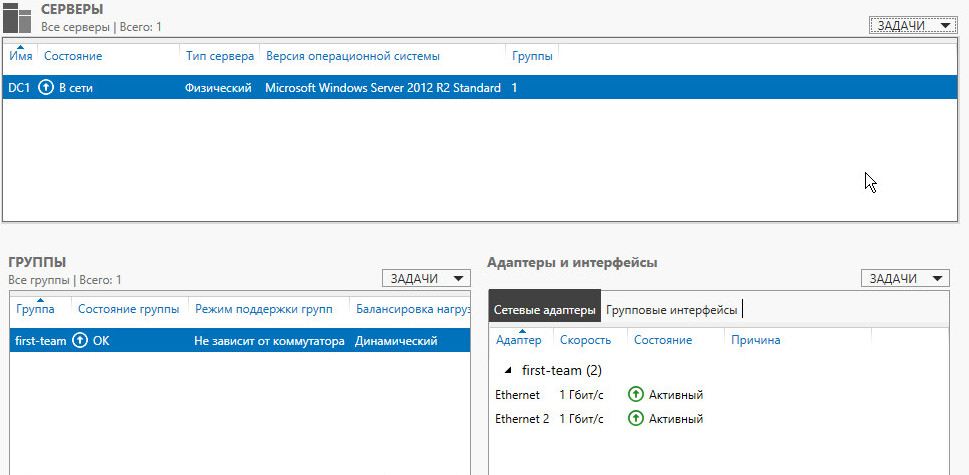
Удалить группу можно также командой power shell: Remove-NetLbfoTeam -Name First-team или в графическом интерфейсе:
NIC Teaming в Windows Server 2012
Функция NIC teaming в ОС Windows Server 2012 позволяет администратору объединить несколько физических сетевых карточек (NIC) в одну логическую сетевую карту. В этой статье мы узнаем, для каких целей можно использовать данную возможность и на практическом примере разберем настройку NIC Teaming на Windows Server 2012 для двух сетевых карт.
NIC teaming технология не новая, но в предыдущих версиях серверной ОС от MS, ее можно было настроить только с помощью специального программного обеспечения, разрабатываемого производителем сервера. В ОС Windows Server 2012 технология ОС Windows Server 2012 является стандартным средством ОС (поддерживает широкий диапазон аппаратного обеспечения) и поставляется «в коробке».
Следует отметить, что NIC Teaming в Server 2012 позволяет объединить в группу до 32 сетевых карточек, возможно даже различных производителей, главное, чтобы они работали на одной скорости.
В каких же целях можно использовать технологию NIC teaming
- Объединение пропускной способности и балансировка нагрузки. Это означает, что имея две сетевые 1 Гб сетевые карты, и объединив их в одну «команду», можно добиться увеличения общей полосы пропускания до 2 Гб/с.
- Отказоустойчивость – при выходе из строя любой из сетевых карт, объединённых при помощи NIC teaming, остальные подхватывают ее функции, и связь с сервером не прерывается. Для критически-важных серверов этот механизм может защитить от простоя сервиса во время выхода из строя сетевого коммутатора. Для реализации такой возможности, достаточно подключить сетевые карты в разные физические коммутаторы.
Технология не будет работать с технологиями SR-IOV и Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA), т.к. при их использовании трафик посылается непосредственно на сетевой адаптер и сетевой стек игнорируется. TCP Chimney также не поддерживается.
Настройка NIC Teaming в Windows Server 2012
Объединить несколько сетевых карт в одну крайне просто. По умолчанию, режим NIC Teaming в Win 2012 отключен. Для его активации откройте консоль управления Server Manager, выберите локальный сервер (Local Server) и в его свойствах выберите пункт «NIC Teaming: Disabled».
В появившемся окне в левой нижней панели выберите пункт Tasks->New Team (Создать группу).
Далее нужно указать имя группы (Team Name) и выбрать сетевые адаптеры, которые будут входить в состав данной группы.
Ниже можно настроить специальные параметры группы. От данных параметров зависит методика работы и эффективность NIC Teaming. Рассмотрим эти настройки подробнее.
Teaming Mode
Режим поддержки групп. Данный параметр определяет способ взаимодействия группы с сетевым оборудованием (коммутатором)
- StaticTeaming — статический режим работы с зависимостью от сетевого оборудования. Все адаптеры группы должны быть подключены к одному коммутатору, порты которого настроены на использование статической агрегации каналов.
- SwitchIndependent – группа работает независимо от свитча, настраивать который дополнительно не нужно. В этом режиме разные адаптеры группы можно подключить к разным коммутаторам для защиты системы от сбоев в любом из них. Это режим работы по –умолчанию.
- LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) – режим также зависит от сетевого оборудования. Свитч в этом случае конфигурируется на использование динамической агрегации каналов по протоколу LACP.
Load Balancing mode
Режим балансировки нагрузки. Определяет способ распределения трафика по сетевым картам в группе.
• Address Hash — для каждого из адаптеров вычисляется специальный хэш (на основании MAC или IP-адресов отправителя и получателя). В дальнейшем весь сетевой трафик от данного отправителя идет через данный адаптер.
• Hyper-V Port — режим можно использовать для сервера с ролью Hyper-V. В данном режиме можно привязать конкретный порт в группе Nic teaming к конкретному порту на виртуальном коммутаторе Hyper-V.
Standby adapter
Один из адаптеров в группе можно назначить резервным (standby). Т.е. при нормальном режиме работы данный порт для передачи трафика не используется, но при неполадке на любом другом адаптере в группе, он тут-же занимает его место. Стоит отметить, что и без данной функции при выходе из строя любой сетевой карты, простоя сервиса не будет, т.к. ее нагрузка автоматически распределится между оставшимися картами.
Выбрав все нужные параметры можно нажать ОК и новая группа Nic Teaming будет создана.
Перейдем в окно «Сетевые подключения» панели управления и убедимся, что у нас появился новый сетевой адаптер (его иконка немного отличается). Это и есть виртуальный адаптер для нашей группы.
Дальнейшая настройка параметров сетевой карты (протоколы, ipv4/v6 адрес) осуществляется теперь в свойствах данного адаптера.
Настройка NIC teaming в Windows Server 2012 с помощью Powershell
Указанные операции можно выполнить не только из графического интерфейса Windows, но и с помощью команд Powershell, в котором для этого есть специальный модуль NetLbfo.
Создадим новую группу с именем team0 из адаптеров с именами Ethernet0 и Ethernet1, зададим режим работы Switch Independent и балансировку по хэшу адреса.
С текущими группами портов, их настройками и состоянием можно познакомится при помощи команды:
Name : team0
Members :
TeamNics : team0
TeamingMode : SwitchIndependent
LoadBalancingAlgorithm : TransportPorts
Status : Up
NIC Teaming settings
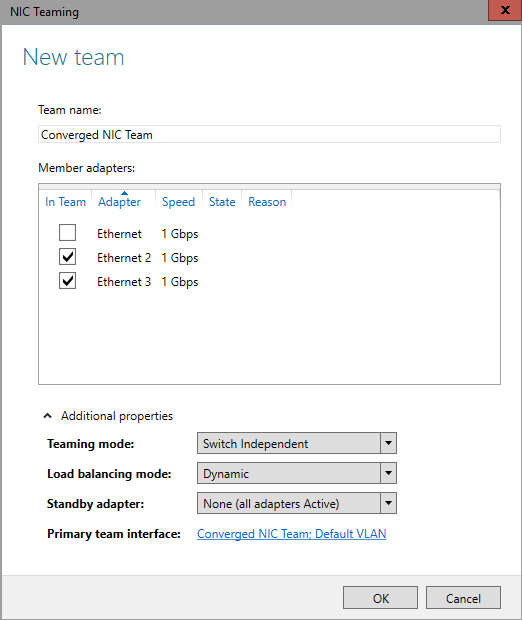
In this topic, we give you an overview of the NIC Team properties such as teaming and load balancing modes. We also give you details about the Standby adapter setting and the Primary team interface property. If you have at least two network adapters in a NIC Team, you do not need to designate a Standby adapter for fault tolerance.
Teaming modes
The options for Teaming mode are Switch Independent and Switch Dependent. The Switch Dependent mode includes Static Teaming and Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP).
For best NIC Team performance, we recommend that you use a Load Balancing mode of Dynamic distribution.
Switch Independent
With Switch Independent mode, the switch or switches to which the NIC Team members are connected are unaware of the presence of the NIC team and do not determine how to distribute network traffic to NIC Team members — instead, the NIC Team distributes inbound network traffic across the NIC Team members.
When you use Switch Independent mode with Dynamic distribution, the network traffic load is distributed based on the TCP Ports address hash as modified by the Dynamic load balancing algorithm. The Dynamic load balancing algorithm redistributes flows to optimize team member bandwidth utilization so that individual flow transmissions can move from one active team member to another. The algorithm takes into account the small possibility that redistributing traffic could cause out-of-order delivery of packets, so it takes steps to minimize that possibility.
Switch Dependent
With Switch Dependent modes, the switch to which the NIC Team members are connected determines how to distribute the inbound network traffic among the NIC Team members. The switch has complete independence to determine how to distribute the network traffic across the NIC Team members.
Switch dependent teaming requires that all team members are connected to the same physical switch or a multi-chassis switch that shares a switch ID among the multiple chassis.
Static Teaming. Static Teaming requires you to manually configure both the switch and the host to identify which links form the team. Because this is a statically configured solution, there is no additional protocol to assist the switch and the host to identify incorrectly plugged cables or other errors that could cause the team to fail to perform. This mode is typically supported by server-class switches.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP). Unlike Static Teaming, LACP Teaming mode dynamically identifies links that are connected between the host and the switch. This dynamic connection enables the automatic creation of a team and, in theory but rarely in practice, the expansion and reduction of a team simply by the transmission or receipt of LACP packets from the peer entity. All server-class switches support LACP, and all require the network operator to administratively enable LACP on the switch port. When you configure a Teaming mode of LACP, NIC Teaming always operates in LACP’s Active mode with a short timer. No option is presently available to modify the timer or change the LACP mode.
When you use Switch Dependent modes with Dynamic distribution, the network traffic load is distributed based on the TransportPorts address hash as modified by the Dynamic load balancing algorithm. The Dynamic load balancing algorithm redistributes flows to optimize team member bandwidth utilization. Individual flow transmissions can move from one active team member to another as part of the dynamic distribution. The algorithm takes into account the small possibility that redistributing traffic could cause out-of-order delivery of packets, so it takes steps to minimize that possibility.
As with all switch dependent configurations, the switch determines how to distribute the inbound traffic among the team members. The switch is expected to do a reasonable job of distributing the traffic across the team members but it has complete independence to determine how it does so.
Load Balancing modes
The options for Load Balancing distribution mode are Address Hash, Hyper-V Port, and Dynamic.
Address Hash
With Address Hash, this mode creates a hash based on address components of the packet, which then get assigned to one of the available adapters. Usually, this mechanism alone is sufficient to create a reasonable balance across the available adapters.
Use Windows PowerShell to specify values for the following hashing function components.
Source and destination TCP ports and source and destination IP addresses. This is the default when you select Address Hash as the Load Balancing mode.
Source and destination IP addresses only.
Source and destination MAC addresses only.
The TCP ports hash creates the most granular distribution of traffic streams, resulting in smaller streams that can be independently moved between NIC team members. However, you cannot use the TCP ports hash for traffic that is not TCP or UDP-based, or where the TCP and UDP ports are hidden from the stack, such as with IPsec-protected traffic. In these cases, the hash automatically uses the IP address hash or, if the traffic is not IP traffic, the MAC address hash is used.
Hyper-V Port
With Hyper-V Port, NIC Teams configured on Hyper-V hosts give VMs independent MAC addresses. The VMs MAC address or the VM ported connected to the Hyper-V switch, can be used to divide network traffic between NIC Team members. You cannot configure NIC Teams that you create within VMs with the Hyper-V Port load balancing mode. Instead, use the Address Hash mode.
Because the adjacent switch always sees a particular MAC address on one port, the switch distributes the ingress load (the traffic from the switch to the host) on multiple links based on the destination MAC (VM MAC) address. This is particularly useful when Virtual Machine Queues (VMQs) are used, because a queue can be placed on the specific NIC where the traffic is expected to arrive.
However, if the host has only a few VMs, this mode might not be granular enough to achieve a well-balanced distribution. This mode will also always limit a single VM (i.e., the traffic from a single switch port) to the bandwidth that is available on a single interface. NIC Teaming uses the Hyper-V Virtual Switch Port as the identifier instead of using the source MAC address because, in some instances, a VM might be configured with more than one MAC address on a switch port.
Dynamic
With Dynamic, outbound loads are distributed based on a hash of the TCP ports and IP addresses. Dynamic mode also rebalances loads in real time so that a given outbound flow may move back and forth between team members. Inbound loads, on the other hand, get distributed the same way as Hyper-V Port. In a nutshell, Dynamic mode utilizes the best aspects of both Address Hash and Hyper-V Port and is the highest performing load balancing mode.
The outbound loads in this mode are dynamically balanced based on the concept of flowlets. Just as human speech has natural breaks at the ends of words and sentences, TCP flows (TCP communication streams) also have naturally occurring breaks. The portion of a TCP flow between two such breaks is referred to as a flowlet.
When the dynamic mode algorithm detects that a flowlet boundary has been encountered — such as when a break of sufficient length has occurred in the TCP flow — the algorithm automatically rebalances the flow to another team member if appropriate. In some circumstances the algorithm might also periodically rebalance flows that do not contain any flowlets. Because of this, the affinity between TCP flow and team member can change at any time as the dynamic balancing algorithm works to balance the workload of the team members.
Whether the team is configured with Switch Independent or one of the Switch Dependent modes, it is recommended that you use Dynamic distribution mode for best performance.
There is an exception to this rule when the NIC Team has just two team members, is configured in Switch Independent mode, and has Active/Standby mode enabled, with one NIC active and the other configured for Standby. With this NIC Team configuration, Address Hash distribution provides slightly better performance than Dynamic distribution.
Standby adapter setting
The options for Standby Adapter are None (all adapters Active) or your selection of a specific network adapter in the NIC Team that acts as a Standby adapter. When you configure a NIC as a Standby adapter, all other unselected team members are Active, and no network traffic is sent to or processed by the adapter until an Active NIC fails. After an Active NIC fails, the Standby NIC becomes active and processes network traffic. When all team members get restored to service, the standby team member returns to standby status.
If you have a two-NIC team and you choose to configure one NIC as a Standby adapter, you lose the bandwidth aggregation advantages that exist with two active NICs. You do not need to designate a Standby Adapter to achieve fault tolerance; fault tolerance is always present whenever there are at least two network adapters in a NIC Team.
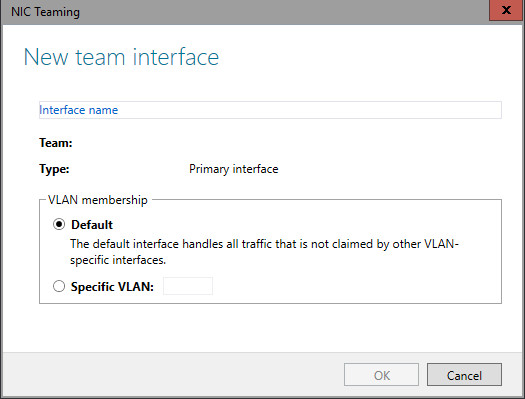
Primary Team interface property
To access the Primary Team Interface dialog box, you must click the link that is highlighted in the illustration below.
After you click the highlighted link, the following New Team Interface dialog box opens.
If you are using VLANs, you can use this dialog box to specify a VLAN number.
Whether or not you are using VLANs, you can specify a NIC name for the NIC Team.