- /* steve jansen */
- // another day in paradise hacking code and more
- Windows Batch Scripting: Getting Started
- Getting Started with Windows Batch Scripting
- Launching the Command Prompt
- Editing Batch Files
- Viewing Batch Files
- Batch File Names and File Extensions
- Saving Batch Files in Windows
- Running your Batch File
- Comments
- Silencing Display of Commands in Batch Files
- Debugging Your Scripts
- Comments
- Guides
- Recent Posts
- Social Stuff
- Windows bat script example
- Написание батников/сценариев (cmd)
- Например:
- Давайте разберем первый пример:
- Второй пример:
- Третий пример:
- Создание bat Файла своими руками
- Основные команды, которые используются для написания батников:
/* steve jansen */
// another day in paradise hacking code and more
Windows Batch Scripting: Getting Started
Getting Started with Windows Batch Scripting
Windows batch scripting is incredibly accessible – it works on just about any modern Windows machine. You can create and modify batch scripts on just about any modern Windows machine. The tools come out of the box: the Windows command prompt and a text editor like Notepad.exe. It’s definitely far from the best shell scripting langauge, but, it gets the job done. It’s my “duct tape” for Windows.
Launching the Command Prompt
Windows gurus launch the command prompt using the keyboard shortcut Windows Logo Key + R (i.e., “Run”) > Type cmd.exe then Enter . This is way faster than navigating the Windows Start Menu to find the Command Prompt.
Editing Batch Files
The universal text editor for batch files is Notepad ( Windows Logo Key + R > Type notepad then Enter ). Since batch files are just ASCII text, you can probably use just about any text editor or word processor. Very few editors do anything special for Batch files like syntax highlighting or keyword support, so notepad is good enough fine and will likely be installed on just about every Windows system you encounter.
Viewing Batch Files
I would stick with Notepad for viewing the contents of a batch file. In Windows Explorer (aka, “My Computer”), you should be able to view a batch file in Notepad by right clicking the file and seleting Edit from the context menu. If you need to view the contents within a command prompt window itself, you can use a DOS command like TYPE myscript.cmd or MORE myscript.cmd or EDIT myscript.cmd
Batch File Names and File Extensions
Assuming you are using Windows XP or newer, I recommend saving your batch files with the file extension .cmd . Some seriously outdated Windows versions used .bat , though I recommend sticking with the more modern .cmd to avoid some rare side effects with .bat files.
With the .cmd file extension, you can use just about filename you like. I recommend avoiding spaces in filenames, as spaces only create headaches in shell scripting. Pascal casing your filenames is an easy way to avoid spaces (e.g., HelloWorld.cmd instead of Hello World.cmd ). You can also use punctuation characters like . or — or _ (e.g. Hello.World.cmd , Hello-World.cmd , Hello_World.cmd ).
Another thing with names to consider is avoiding names that use the same name of any built-in commands, system binaries, or popular programs. For example, I would avoid naming a script ping.cmd since there is a widely used system binary named ping.exe . Things might get very confusing if you try to run ping and inadvertently call ping.cmd when you really wanted ping.cmd . (Stay tuned for how this could happen.) I might called the script RemoteHeartbeat.cmd or something similar to add some context to the script’s name and also avoid any naming collisions with any other executable files. Of course, there could be a very unique circumstance in which you want to modify the default behavior of ping in which this naming suggestion would not apply.
Saving Batch Files in Windows
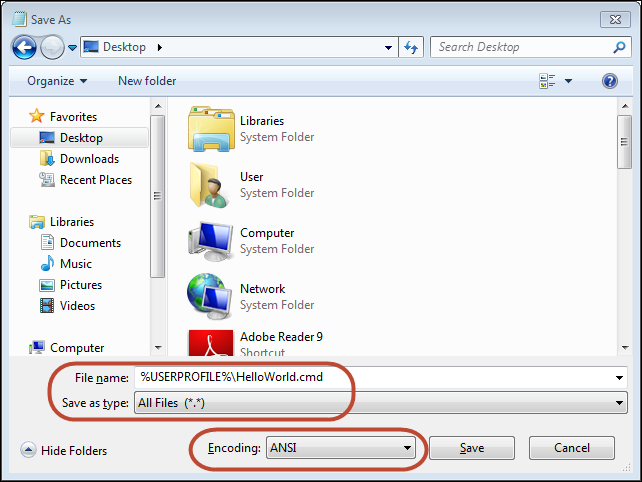
Notepad by default tries to save all files as plain jane text files. To get Notepad to save a file with a .cmd extension, you will need to change the “Save as type” to “All Files (.)”. See the screenshot below for an example of saving a script named “HelloWorld.cmd” in Notepad.
SIDEBAR: I’ve used a shortcut in this screenshot that you will learn more about later. I’ve saved the file to my “user profile folder” by naming the file %USERPROFILE%\HelloWorld.cmd . The %USERPROFILE% keyword is the Windows environmental variable for the full path to your user profile folder. On newer Windows systems, your user profile folder will typically be C:\Users\ . This shortcut saves a little bit of time because a new command prompt will generally default the “working directory” to your user profile folder. This lets you run HelloWorld.cmd in a new command prompt without changing directories beforehand or needing to specify the path to the script.
Running your Batch File
The easy way to run your batch file in Windows is to just double click the batch file in Windows Explorer (aka “My Computer”). Unfortunately, the command prompt will not give you much of a chance to see the output and any errors. The command prompt window for the script will disappear as soon as the script exits. (We will learn how to handle this problem in Part 10 – Advanced Tricks ).
When editing a new script, you will likely need to run the batch file in an existing command window. For newbies, I think the easiest foolproof way to run your script is to drag and drop the script into a command prompt window. The command prompt will enter the full path to your script on the command line, and will quote any paths containing spaces.
Some other tips to running batch files:
- You can recall previous commands using the up arrow and down arrow keys to navigate the command line history.
- I usually run the script as %COMPSPEC% /C /D «C:\Users\User\SomeScriptPath.cmd» Arg1 Arg2 Arg3 This runs your script in a new command prompt child process. The /C option instructs the child process to quit when your script quits. The /D disables any auto-run scripts (this is optional, but, I use auto-run scripts). The reason I do this is to keep the command prompt window from automatically closing should my script, or a called script, call the EXIT command. The EXIT command automatically closes the command prompt window unless the EXIT is called from a child command prompt process. This is annoying because you lose any messages printed by your script.
Comments
The official way to add a comment to a batch file is with the REM (Remark) keyword:
The power user method is to use :: , which is a hack to uses the the label operator : twice, which is almost always ignored.
Most power authors find the :: to be less distracting than REM . Be warned though there are a few places where :: will cause errors.
For example, a FOR loop will error out with :: style comments. Simply fall back to using REM if you think you have a situation like this.
Silencing Display of Commands in Batch Files
The first non-comment line of a batch file is usually a command to turn off printing (ECHO’ing) of each batch file line.
The @ is a special operator to suppress printing of the command line. Once we set ECHO’ing to off, we won’t need the @ operator again in our script commands.
You restore printing of commands in your script with:
Upon exit of your script, the command prompt will automatically restore ECHO to it’s previous state.
Debugging Your Scripts
Batch files invole a lot of trial and error coding. Sadly, I don’t know of any true debugger for Windows batch scripts. Worse yet, I don’t know of a way to put the command processor into a verbose state to help troubleshoot the script (this is the common technique for Unix/Linux scripts.) Printing custom ad-hoc debugging messages is about your only option using the ECHO command. Advanced script writers can do some trickery to selectively print debugging messages, though, I prefer to remove the debugging/instrumentation code once my script is functioning as desired.
Posted by Steve Jansen Mar 1 st , 2013 batch, scripting, shell, windows
Comments
Hi, I’m Steve. I’m a software developer loving life in Charlotte, NC, an (ISC) 2 CSSLP and an avid fan of Crossfit.
And, no, I’m not Steve Jansen the British jazz drummer, though that does sound like a sweet career.
Guides
Recent Posts
Social Stuff
- @steve-jansen on GitHub
- @steve-jansen on StackOverflow
- @steve-jansen ProTips on Coderwall
- @steve-jansen on Microsft Connect
- @steve-jansen on ASP.NET User Voice
- Subscribe via RSS
Copyright © 2015 — Steve Jansen — Powered by Octopress
Windows bat script example
In Windows, the batch file is a file that stores commands in a serial order. Command line interpreter takes the file as an input and executes in the same order. A batch file is simply a text file saved with the .bat file extension. It can be written using Notepad or any other text editor.
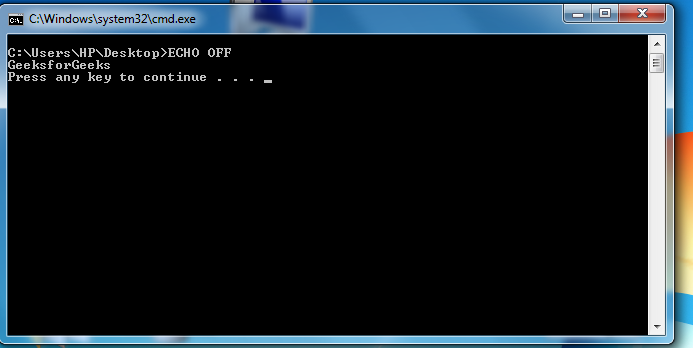
A simple batch file will be
After saving it with .bat extension. Double click it to run the file. It prints shows
In above script, ECHO off cleans up the console by hiding the commands from being printed at the prompt, ECHO prints the text “GeeksforGeeks” to the screen, and then waits for the user to press a key so program can be ceased.
Some basic commands of batch file
- echo – Prints out the input string. It can be ON or OFF, for ECHO to turn the echoing feature on or off. If ECHO is ON, the command prompt will display the command it is executing.
- cls – Clears the command prompt screen.
- title: Changes the title text displayed on top of prompt window.
- EXIT – To exit the Command Prompt.
- pause – Used to stop the execution of Windows batch file.
- :: – Add a comment in the batch file.
- COPY – Copy a file or files
Types of “batch” files in Windows
- INI (*.ini) – Initialization file. These set the default variables for the system and programs.
- CFG (*.cfg) – These are the configuration files.
- SYS (*.sys) – System files, can sometimes be edited, mostly compiled machine code in new versions.
- COM (*.com) – Command files. These are the executable files for all the DOS commands. In early versions there was a separate file for each command. Now, most are inside COMMAND.COM.
- CMD (*.cmd) – These were the batch files used in NT operating systems.
Lets take another example,
Suppose we need to list down all the files/directory names inside a particular directory and save it to a text file, so batch script for it will be,
Now when we run this batch script, it will create a file name geeks_list.txt in your C:\ directory, displaying all the files/folder names in C:\Program Files
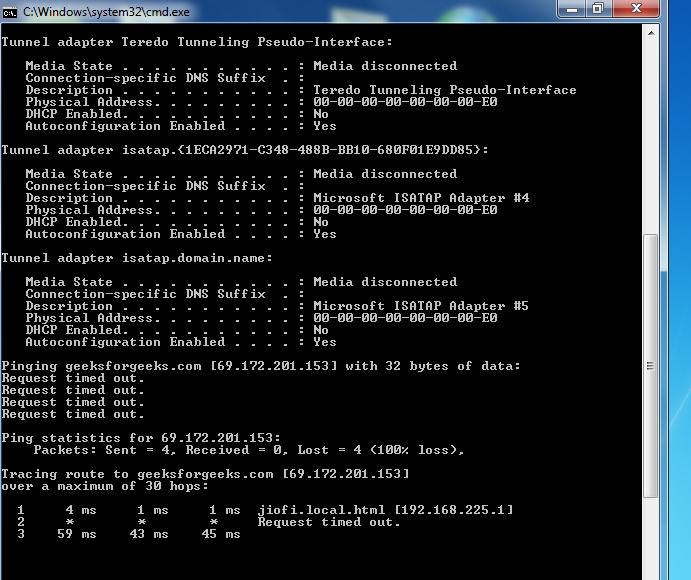
Another useful batch script that can be written to diagnose your network and check performance of it.
This script displays,
This script gives information about the current network and some network packet information. ‘ipconfig /all’ helps to view the network information and ‘ping’ & ‘tracert’ to get each packet info. Learn about ping and traceroute here.
Написание батников/сценариев (cmd)

Всем нам, приходилось сталкиваться с рутинными задачами изо дня в день на работе, и не только.
Например:
- Необходимо раз в месяц удалять все файлы из папки обмен.
- «Добросовестные» пользователи не выключают компьютеры, и уходят домой, а вам потом по голове дают за то, что компьютер работал, и жрал электроэнергию.
- У вас 20 человек в кабинете, принтер один и всем нужно выводить на него печать. Можно написать батник закинуть его в обмен зайти в кабинет и всем пользователям сказать зайдите туда-туда, нажмите то-то, и можете печатать, а если у Вас есть active directory, то можно распространить с помощью неё.
Можно еще привести множество примеров обыкновенных задач, на которые лучше не тратить свое время, а автоматизировать процесс. Сегодня хочу рассказать, как пишутся элементарные bat скрипты.
Давайте разберем первый пример:
Необходимо раз в месяц удалять все файлы из папки обмен.
- Открываем WordPad, блокнот не подойдет, он не умеет сохранять в кодировке 866.
- Пишем:
Команда del- удаляет файлы, ключ q говорит, удалять файлы без подтверждения пользователя, дальше идет путь до папки обмен, команда pause – это для вашего удобства, что бы окно не закрылось автоматически после выполнения работы скрипта, можно её не писать.
- Дальше выбираем Файл => Сохранить как => в строке Имя файла пишем допустим, del_obmen.bat, жмем Ок, запускаем и наслаждаемся.
Второй пример:
«Добросовестные» пользователи не выключают компьютеры, и уходят домой, а вам потом по голове дают за то, что компьютер работал, и жрал электроэнергию.
Пояснения я думаю ни к чему.
3. Дальше выбираем Файл => Сохранить как => в строке Имя файла пишем допустим, shutdown.bat, жмем Ок, запускаем и наслаждаемся.
4. Дальше открываем панель управления => планировщик заданий, создаем задание в 20 00, думаю понятно для чего.
Третий пример:
У вас 20 человек в кабинете, принтер один и всем нужно выводить на него печать. Можно написать батник закинуть его в обмен зайти в кабинет и всем пользователям сказать зайдите туда-туда, нажмите то-то, и можете печатать, а если у Вас есть active directory, то можно распространить с помощью неё.
Start – запуск, \\192.168.0.37 – ip адрес, \SamsungU – имя принтера.
Если у вас ip адреса раздаются по DHCP, то лучше ввести не ip адрес, а имя компьютера.
3. Дальше выбираем Файл => Сохранить как => в строке Имя файла пишем допустим, print.bat, жмем Ок, запускаем и наслаждаемся.
Создание bat Файла своими руками
Основные команды, которые используются для написания батников:
ASSOC — Отображает или модифицирует связи расширений файлов
AT — Планирует команды и программы для выполнения на компьютере.
ATTRIB — Отображает или изменяет атрибуты файла.
BREAK — Устанавливает или отменяет проверку комбинации [Ctrl+C].
CACLS — Отображает или модифицирует списки управления доступом (ACLs) для файлов.
CALL — Вызывает один *.BAT-файл из другого.
CD — Отображает имя или изменяет имя текущей директории.
CHCP — Отображает или устанавливает номер активной кодовой страницы.
CHDIR — Отображает имя или изменяет имя текущей директории.
CHKDSK — Проверяет диск и отображает отчет о состоянии.
CLS — Очищает экран.
CMD — Стартует новый экземпляр интерпретатора команд Windows NT.
COLOR — Устанавливает цвета по умолчанию для переднего и заднего плана консоли.
COMMAND — Стартует новую копию интерпретатора команд Windows.
COMP — Сравнивает содержимое двух файлов или установки файлов.
COMPACT — Отображает или видоизменяет сжатие файлов на патрициях Windows NT(NTFS).
CONVERT — Конвертирует FAT томов к формату файловой системы Windows NT(NTFS). Вы не можете конвертировать текущий диск.
COPY — Копирует один или больше файлов на другое место.
CTTY — Изменяет терминальное устройство, используемое для управления вашей системой.
DATE — Отображает или устанавливает дату.
DEL — Удаляет один или более файлов.
DEBUG — Выполняет отладку, тестирование программ и редактирование инструментальных средств.
DIR — Отображает список файлов и поддиректорий в директории.
DISKCOMP — Сравнивает содержимое двух дискет.
DISKCOPY — Копирует содержимое одной дискеты на другую.
DOSKEY — Редактирует командные строки, восстанавливает команды Windows и создает макрос.
ECHO — Отображает сообщения, или включает/выключает вывод команд.
EMM386 — Включает/выключает поддержку расширенной памяти EMM386.
ENDLOCAL — Заканчивает локализацию изменений окружающей среды в *.BAT-файле.
ERASE — Удаляет один или более файлов.
EXIT — Прекращает выполнение программы «CMD.EXE» (интерпретатор команд).
EXTRACT — Средство извлечения информации из CAB — файлов.
FC — Сравнивает два файла или установки файлов, и отображает различие между ними.
FIND — Ищет текстовую строку в файле или файлах.
FINDSTR — Поиск строк в файлах.
FOR — Выполняет указанную команду для каждого файла в наборе файлов.
FORMAT — Форматирует диск для использования с Windows.
FTYPE — Отображает или модифицирует типы файлов, используемых в связях расширений.
GOTO — Направляет интерпретатор команд Windows NT к помеченной строке в *.BAT-файле.
GRAFTABL — Способность Windows отображать символы псевдографики, вставленные в графическом режиме.
HELP — Обеспечивает информацию Help для команд Windows.
IF — Выполняет обработку условия в *.BAT-файле.
KEYB — Конфигурирует клавиатуру для заданного языка.
LABEL — Создает, изменяет, или удаляет метку тома на диске.
LOADHIGH(LH) — Загружает программу в верхние адреса памяти.
MD — Создает директорию.
MEM — Отображает величину используемой и свободной памяти в вашей системе.
MKDIR — Создает директорию.
MODE — Конфигурирует системное устройство.
MORE — Отображает вывод одного экрана за раз.
MOVE — Перемещает один или более файлов из одной директории в другую на том же диске.
NETSTAT — Отображает статистики протоколов и текущих сетевых соединений TCP/IP.
NLSFUNC — Загружает информацию, специфическую для страны.
PATH — Отображает или устанавливает путь поиска для выполняемых файлов.
PAUSE — Приостанавливает обработку *.BAT-файла и отображает сообщение.
POPD — Восстанавливает предыдущее значение текущей директории, сохраненной по PUSHD.
PRINT — Печатает текстовый файл.
PROMPT — Изменяет подсказку к командам Windows.
PUSHD — Сохраняет текущую директорию, потом изменяет.
RD — Удаляет директорию.
RECOVER — Восстанавливает читаемую информацию с плохого или дефектного диска.
REM — Записывает комментарии (примечания) в *.BAT-файлы или CONFIG.SYS.
REN — Переименует файл или файлы.
RENAME — Переименует файл или файлы.
REPLACE — Заменяет файлы.
RESTORE — Восстанавливает файлы, которые были архивированы с использованием команды BACKUP.
RMDIR — Удаляет директорию.
SET — Отображает, устанавливает или удаляет переменные среды Windows.
SETLOCAL — Начинает локализацию изменений среды в *.BAT-файле.
SETVER — Устанавливает номер версии MS-DOS, который Windows сообщает программе.
SHIFT — Сдвигает позицию замещаемых параметров в *.BAT-файле.
SMARTDRV — Инсталлирует и конфигурирует утилиту кэширования диска SMART — драйва.
SORT — Сортирует входной поток.
START — Стартует отдельное окно для выполнения указанной программы или команды.
SUBST — Связывает путь с литерой диска.
SYS — Копирует файлы системы MS-DOS и интерпретатор команд на указанный вами диск.
TIME — Отображает или устанавливает системное время.
TITLE — Устанавливает заголовок окна для сеанса «CMD.EXE» .
TREE — Графически отображает структуру директория в драйве или путь.
TYPE — Отображает содержимое текстового файла.
VER — Отображает версию Windows.
VERIFY — Сообщает Windows, проверять ли правильность записи файлов на диск.
VOL — Отображает метку дискового тома и серийный номер.
XCOPY — Копирует файлы и деревья директории.
Также есть очень хороший форум, где куча готовых скриптов.