- How to: View certificates with the MMC snap-in
- View certificates in the MMC snap-in
- View certificates with the Certificate Manager tool
- To view certificates for the local device
- To view certificates for the current user
- Цифровые сертификаты: Как посмотреть и удалить их в Windows 10
- Как посмотреть установленные цифровые сертификаты в Windows 10
- Как удалить сертификат в Windows 10
- Certify your desktop application
- Step 1: Prepare for certification
- Step 2: Test your app with the Windows App Certification Kit
- Step 3: Use the Windows Certification Dashboard
- Step 4: Promote your desktop app
- See also:
- How to manage Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10
- Manage Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10
- Требования к сертификатам и их перечисление Certificate Requirements and Enumeration
- Поддержка сертификатов для совместимости About Certificate support for compatibility
- Поток входов смарт-карт в Windows Smart card sign-in flow in Windows
- Сертификат KDC KDC certificate
- Требования и сопоставления сертификатов клиентов Client certificate requirements and mappings
- Требования к сертификатам Certificate requirements
- Сопоставления сертификатов клиента Client certificate mappings
- Вход смарт-карты для одного пользователя с одним сертификатом на несколько учетных записей Smart card sign-in for a single user with one certificate into multiple accounts
- Вход смарт-карты для нескольких пользователей в одну учетную запись Smart card sign-in for multiple users into a single account
- Вход смарт-карты в лесах Smart card sign-in across forests
- Поддержка OCSP для PKINIT OCSP support for PKINIT
- Требования к корневому сертификату смарт-карты для использования при входе в домен Smart card root certificate requirements for use with domain sign-in
How to: View certificates with the MMC snap-in
When you create a secure client or service, you can use a certificate as the credential. For example, a common type of credential is the X.509 certificate, which you create with the X509CertificateInitiatorClientCredential.SetCertificate method.
There are three different types of certificate stores that you can examine with the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) on Windows systems:
Local computer: The store is local to the device and global to all users on the device.
Current user: The store is local to the current user account on the device.
Service account: The store is local to a particular service on the device.
View certificates in the MMC snap-in
The following procedure demonstrates how to examine the stores on your local device to find an appropriate certificate:
Select Run from the Start menu, and then enter mmc.
The MMC appears.
From the File menu, select Add/Remove Snap In.
The Add or Remove Snap-ins window appears.
From the Available snap-ins list, choose Certificates, then select Add.
In the Certificates snap-in window, select Computer account, and then select Next.
Optionally, you can select My user account for the current user or Service account for a particular service.
If you’re not an administrator for your device, you can manage certificates only for your user account.
In the Select Computer window, leave Local computer selected, and then select Finish.
In the Add or Remove Snap-in window, select OK.
Optional: From the File menu, select Save or Save As to save the MMC console file for later use.
To view your certificates in the MMC snap-in, select Console Root in the left pane, then expand Certificates (Local Computer).
A list of directories for each type of certificate appears. From each certificate directory, you can view, export, import, and delete its certificates.
View certificates with the Certificate Manager tool
You can also view, export, import, and delete certificates by using the Certificate Manager tool.
To view certificates for the local device
Select Run from the Start menu, and then enter certlm.msc.
The Certificate Manager tool for the local device appears.
To view your certificates, under Certificates — Local Computer in the left pane, expand the directory for the type of certificate you want to view.
To view certificates for the current user
Select Run from the Start menu, and then enter certmgr.msc.
The Certificate Manager tool for the current user appears.
To view your certificates, under Certificates — Current User in the left pane, expand the directory for the type of certificate you want to view.
Цифровые сертификаты: Как посмотреть и удалить их в Windows 10
Цифровые сертификаты — это небольшие файлы, которые содержат ряд личной и частной информации, как наши данные, учетные данные для доступа и т. п. Цифровые сертификаты используется для идентификации нас через Интернет, чтобы мы могли подтвердить свою личность и выполнять все виды запросов и Интернет-менеджменте. Когда мы устанавливаем сертификат в Windows 10, он устанавливается в защищенном разделе операционной системы, и когда приложение будет нуждаться в каком-либо сертификате, то оно будет запрашивать доступ к нему, чтобы использовать его.
Одним из наиболее распространенных применений этих сертификатов является их использование в Google Chrome. К примеру, на государственных сайтов для личного доступа к базам данным нужен сертификат. Этот сертификат вам выдает гос. сайт и его нужно будет установить. Без него вы не сможете получить доступ к базе, функциям, или даже к самому сайту. Многие приложения устанавливают собственные сертификаты для внесения изменений в оборудование. Они служат для обеспечения того, чтобы приложение было законным и надежным. Они также используются для подписи трафика, которым обмениваются серверы. Даже Windows имеет свои собственные корневые сертификаты, которые обеспечивают нормальную работу операционной системы, и такие функции, как Центр обновления Windows, можно безопасно использовать.
Как посмотреть установленные цифровые сертификаты в Windows 10
1. Посмотрим сертификаты для оборудования, сгенерированными Microsoft и другими разработчиками для правильного функционирования компьютера. Они доступны для всех пользователей.
Нажмите сочетание клавиш Win + R и введите certlm.msc, чтобы открыть сертификаты.
Далее вы увидите сертификаты и разные категории. В зависимости от назначения каждого сертификата они будут храниться в том или ином каталоге.
2. Если вы хотите просмотреть личные сертификаты, которые доступны только текущему пользователю на данной учетной записи, то нажмите Win + R и введите certmgr.msc, чтобы открыть этот персональный менеджер сертификатов. Мы найдем все личные сертификаты, которые являются эксклюзивными для нашего пользователя. В частности, в папке «Личное» мы найдем все это.
Как удалить сертификат в Windows 10
Если вам нужно удалить какой-либо сертификат, что я не рекомендую, то просто найдите его и нажмите на нем правой кнопкой мыши, после чего «Удалить». Иногда бывает так, что сертификаты становятся криво или повреждаются, в этом случае нужно будет удалить и заново установить.
Certify your desktop application
Certification for Win32 desktop apps is deprecated. Instead, submit files here.
Follow these steps to get your desktop app certified for Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, and Windows 10.
If you wish to convert your desktop app to be compatible with the Universal Windows Platform and Windows Store, you will use the Windows Desktop Bridge, in which case you should follow the Desktop Bridge guidance for certification steps.
If you are developing and certifying a UWP app from the start, see Guidance for Windows App Certification in UWP for info on certification.
Step 1: Prepare for certification
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| What are the benefits? | Certifying your desktop app provides several benefits for you and your customers. |
| Read the requirements | Review the technical requirements and eligibility qualifications that a desktop app must meet. |
Step 2: Test your app with the Windows App Certification Kit
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Get the Kit | To certify your app, you have to install and run the Windows App Certification Kit (included in the Windows SDK). |
| Using the Kit | Before you can submit your app, you must test it for readiness. You can also download a copy of the app certification white paper. |
| Review test details | Get the list of the tests your app needs to pass to qualify for compatibility with the latest Windows operating system. |
Step 3: Use the Windows Certification Dashboard
To submit your app for certification, you’ll need to log in or register a company account on the Windows Certification Dashboard. Once you do, not only will you be able to get your app certified, but you’ll also gain access to tools to review and manage your app at all stages of the process.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Set up your account | If your company isn’t already registered, you must register it through the Windows Certification Dashboard. |
| Get a code signing certificate | Before you can establish a Windows Certification Dashboard account, you need to get a code signing certificate to secure your digital information. |
| Test locally and upload the results | After your run the Windows App Certification Kit tests, upload the results to the Windows Certification Dashboard. |
| Manage your submission | After you submit your app for certification, you can review your submission through the Windows Certification Dashboard. |
Step 4: Promote your desktop app
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Check app compatibility | If you are building an app for Windows 8.1, investigate compatibility concerns. |
| Use the logo with your app | Display the logo on packaging and in ads and other promotional materials according to the guidelines. For Windows 7 only. |
See also:
App compatibility forum: Find support from the community about compatibility and logo certification.
Windows SDK blog: Find tips and news related to app certification.
Windows Server forum: Visit the Certification forum to get answers.
Compatibility cookbook: Get info about what’s new or changed in the latest version of Windows.
How to manage Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10
In one of our earlier posts, we have seen what Root Certificates are. There may be times, when some companies or users may feel the need to manage and configure Trusted Root Certificates, to prevent other users in the domain from configuring their own set. In this post, we will see how to manage Trusted Root Certificates & add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store in Windows 10/8/7.
Manage Trusted Root Certificates in Windows 10
To add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for a local computer, from the WinX Menu in Windows 10/8.1, open Run box, type mmc , and hit Enter to open the Microsoft Management Control.
Press the File menu link and select Add/Remove Snap-in. Now under Available snap-ins, click Certificates, and then click Add.
Click OK. In the next dialog box, select Computer account and then on Next.
Now select Local computer and click on Finish.
Now, back in MMC, in the console tree, double-click on Certificates and then right-click on Trusted Root Certification Authorities Store. Under All tasks, select Import.
The Certificate Import Wizard will open.
Follow the instructions in the wizard to complete the process.
Now let us see how to configure and manage trusted root certificates for a local computer. Open MMC and press the File menu link and select Add/Remove Snap-in. Now under Available snap-ins, click Group Policy Object Editor, and then click Add. Select the computer whose local GPO you want to edit, and click Finish / OK.
Now, back in the MMC console tree, navigate to Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings. Next Public Key Policies. Double-click Certificate Path Validation Settings, and then select the Stores tab.
Read: Manage certificates using Certificate Manager or Certmgr.msc.
Here, select the Define these policy settings, Allow user trusted root CAs to be used to validate certificates and Allow users to trust peer trust certificates checkboxes.
Finally, under Stores tab > Root certificate stores, select one option under Root CAs that the client computers can trust and click OK. If in doubt, go with the recommended option.
To see how you can manage trusted root certificates for a domain and how to add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for a domain, visit Technet.
RCC is a free Root Certificates Scanner that can help you scan Windows Root Certificates for untrusted ones.
Требования к сертификатам и их перечисление Certificate Requirements and Enumeration
Применяется к: Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 Applies To: Windows 10, Windows Server 2016
В этом разделе для ИТ-специалистов и разработчиков смарт-карт описывается, как управляются сертификаты и используются для регистрации смарт-карт. This topic for the IT professional and smart card developers describes how certificates are managed and used for smart card sign-in.
При вставке смарт-карты выполняются следующие действия. When a smart card is inserted, the following steps are performed.
**** Примечание Если иное не указано, все операции выполняются безмолвно (CRYPT_SILENT передается CryptAcquireContext). Note Unless otherwise mentioned, all operations are performed silently (CRYPT_SILENT is passed to CryptAcquireContext).
База данных диспетчера ресурсов смарт-карт ищет поставщика криптографических служб смарт-карты (CSP). The smart card resource manager database searches for the smart card’s cryptographic service provider (CSP).
Квалифицированное имя контейнера строится с помощью имени читателя смарт-карт и передается в CSP. A qualified container name is constructed by using the smart card reader name, and it is passed to the CSP. Формат \\\\ читателя The format is \\.\ \
CryptAcquireContext вызван для получения контекста в контейнер по умолчанию. CryptAcquireContext is called to retrieve a context to the default container. Если произойдет сбой, смарт-карта будет непригодной для регистрации смарт-карты. If a failure occurs, the smart card will be unusable for smart card sign-in.
Имя контейнера извлекают с помощью параметра PP_CONTAINER CryptGetProvParam. The name of the container is retrieved by using the PP_CONTAINER parameter with CryptGetProvParam.
С помощью контекста, приобретенного в шаге 3, CSP запрашивается для параметра PP_USER_CERTSTORE (добавлен в Windows Vista). Using the context acquired in Step 3, the CSP is queried for the PP_USER_CERTSTORE parameter (added in Windows Vista). Дополнительные сведения см. в см. в «Архитектуре смарт-карт». For more information, see Smart Card Architecture. Если операция будет успешной, возвращается имя магазина сертификатов, а поток программы пропускает шаг 8. If the operation is successful, the name of a certificate store is returned, and the program flow skips to Step 8.
Если операция в шаге 5 не удалась, по умолчанию для ключа AT_KEYEXCHANGE запрашивается контекст контейнера по умолчанию из шага 3. If the operation in Step 5 fails, the default container context from Step 3 is queried for the AT_KEYEXCHANGE key.
Затем сертификат запрашивается из контекста ключа с помощью KP_CERTIFICATE. The certificate is then queried from the key context by using KP_CERTIFICATE. Сертификат добавляется в хранилище сертификатов в памяти. The certificate is added to an in-memory certificate store.
Для каждого сертификата в хранилище сертификатов с 5-го или 7-го этапов выполняются следующие проверки: For each certificate in the certificate store from Step 5 or Step 7, the following checks are performed:
Сертификат должен быть действительным на основе системных часов компьютера (не истек и не действителен с будущей датой). The certificate must be valid, based on the computer system clock (not expired or valid with a future date).
Сертификат не должен быть в at_SIGNATURE части контейнера. The certificate must not be in the AT_SIGNATURE part of a container.
Сертификат должен иметь действительное имя пользователя (UPN). The certificate must have a valid user principal name (UPN).
Сертификат должен иметь использование ключа цифровой подписи. The certificate must have the digital signature key usage.
Сертификат должен иметь EKU с логотипом смарт-карты. The certificate must have the smart card logon EKU.
Любой сертификат, отвечающий этим требованиям, отображается пользователю с upN сертификата (или адресом электронной почты или субъектом, в зависимости от наличия расширений сертификата). Any certificate that meets these requirements is displayed to the user with the certificate’s UPN (or e-mail address or subject, depending on the presence of the certificate extensions).
**** Примечание Эти требования такие же, как и в Windows Server 2003, но выполняются до ввода ПИН-кода пользователем. Note These requirements are the same as those in Windows Server 2003, but they are performed before the user enters the PIN. Многие из них можно переопрепредить с помощью параметров групповой политики. You can override many of them by using Group Policy settings.
Затем процесс выбирает сертификат, и пин-код вошел. The process then chooses a certificate, and the PIN is entered.
LogonUI.exe пакеты данных и отправляет их в Lsass.exe для обработки попытки регистрации. LogonUI.exe packages the information and sends it to Lsass.exe to process the sign-in attempt.
В случае успешного LogonUI.exe закрывается. If successful, LogonUI.exe closes. Это приводит к релизу контекста, приобретенного в шаге 3. This causes the context acquired in Step 3 to be released.
Поддержка сертификатов для совместимости About Certificate support for compatibility
Хотя версии Windows раньше Windows Vista включают поддержку смарт-карт, типы сертификатов, которые могут содержать смарт-карты, ограничены. Although versions of Windows earlier than Windows Vista include support for smart cards, the types of certificates that smart cards can contain are limited. Ограничения: The limitations are:
Каждый сертификат должен иметь основное имя пользователя (UPN) и идентификатор объекта для регистрации смарт-карты (также известный как OID) в поле атрибутов расширенного использования ключей (EKU). Each certificate must have a user principal name (UPN) and the smart card sign-in object identifier (also known as OID) in the enhanced key usage (EKU) attribute field. Существует параметр групповой политики, позволяющий использовать сертификаты ECC для логоса и проверки подлинности, чтобы сделать EKU необязательным. There is a Group Policy setting, Allow ECC certificates to be used for logon and authentication, to make the EKU optional.
Каждый сертификат должен храниться в at_KEYEXCHANGE части контейнера CryptoAPI по умолчанию, а контейнеры CryptoAPI по умолчанию не поддерживаются. Each certificate must be stored in the AT_KEYEXCHANGE portion of the default CryptoAPI container, and non-default CryptoAPI containers are not supported.
В следующей таблице перечислены поддержка сертификатов в старых версиях операционной системы Windows. The following table lists the certificate support in older Windows operating system versions.
| Операционная система Operating system | Поддержка сертификатов Certificate support |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7 Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 | Поддержка регистрации смарт-карт с помощью сертификатов на основе ECC. Support for smart card sign-in with ECC-based certificates. Вход в смарт-карты ECC включен через групповую политику. ECC smart card sign-in is enabled through Group Policy. ECDH_P256 ECDH_P256 ECDSA_P256 ECDSA_P256 ECDH_P384 ECDH_P384 ECDH_P521 ECDH_P521 ECDSA_P256 ECDSA_P256 ECDSA_P384 ECDSA_P384 ECDSA_P521 ECDSA_P521 |
| Windows Server 2008 и Windows Vista Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista | Допустимые сертификаты отображаются со всех смарт-карт и представляются пользователю. Valid certificates are enumerated and displayed from all smart cards and presented to the user. Ключи больше не ограничиваются контейнером по умолчанию, и могут быть выбраны сертификаты в разных контейнерах. Keys are no longer restricted to the default container, and certificates in different containers can be chosen. Сертификаты криптографии на основе эллиптической кривой (ECC) не поддерживаются для регистрации смарт-карт Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC)-based certificates are not supported for smart card sign-in |
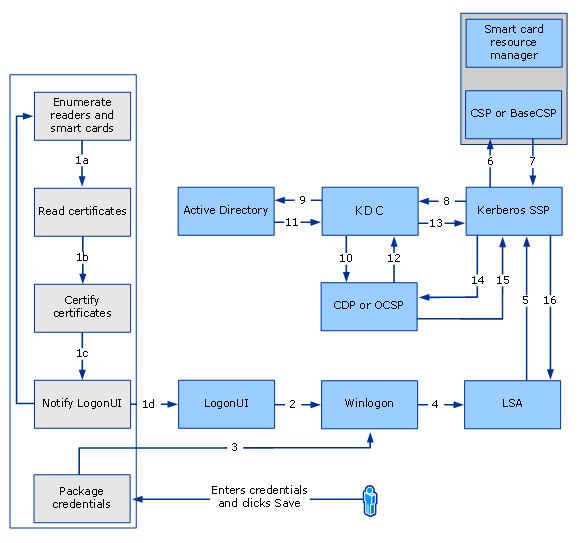
Поток входов смарт-карт в Windows Smart card sign-in flow in Windows
Большинство проблем при проверке подлинности возникают из-за изменений поведения сеанса. Most issues during authentication occur because of session behavior changes. Когда происходят изменения, Служба локальной безопасности (LSA) не перезахотряет контекст сеанса; вместо этого он полагается на поставщика криптографических служб для обработки изменения сеанса. When changes occur, the Local Security Authority (LSA) does not reacquire the session context; it relies instead on the Cryptographic Service Provider to handle the session change.
В поддерживаемых версиях Windows, указанных в списке Applies To в начале этого раздела, клиентские сертификаты, не содержащие upN в поле subjectAltName (SAN) сертификата, могут быть включены для входа, который поддерживает более широкий спектр сертификатов и поддерживает несколько сертификатов входа на одной и той же карте. In the supported versions of Windows designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic, client certificates that do not contain a UPN in the subjectAltName (SAN) field of the certificate can be enabled for sign-in, which supports a wider variety of certificates and supports multiple sign-in certificates on the same card.
Поддержка нескольких сертификатов на одной и той же карте включена по умолчанию. Support for multiple certificates on the same card is enabled by default. Новые типы сертификатов должны быть включены с помощью групповой политики. New certificate types must be enabled through Group Policy.
Если вы включаете допустимые ключи подписи для политики поставщика учетных данных Logon, все сертификаты, доступные на смарт-карте с ключом только для подписи, перечислены на экране входа. If you enable the Allow signature keys valid for Logon credential provider policy, any certificates that are available on the smart card with a signature-only key are listed on the sign-in screen. Это позволяет пользователям выбирать опытом входных данных. This allows users to select their sign-in experience. Если политика отключена или не настроена, сертификаты на основе подписи смарт-карт не перечислены на экране регистрации. If the policy is disabled or not configured, smart card signature-key-based certificates are not listed on the sign-in screen.
На следующей схеме показано, как работает вход смарт-карты в поддерживаемых версиях Windows. The following diagram illustrates how smart card sign-in works in the supported versions of Windows.
Поток входов смарт-карт Smart card sign-in flow
Ниже пишите действия, выполняемые во время регистрации смарт-карты: Following are the steps that are performed during a smart card sign-in:
Winlogon запрашивает сведения о учетных данных пользовательского интерфейса входа. Winlogon requests the sign-in UI credential information.
Асинхронно запускается менеджер ресурсов смарт-карт, и поставщик учетных данных смарт-карт делает следующее: Asynchronously, smart card resource manager starts, and the smart card credential provider does the following:
Получает сведения о учетных данных (список известных учетных данных или, если нет учетных данных, сведения о считывателье смарт-карт, обнаруженные Windows). Gets credential information (a list of known credentials, or if no credentials exist, the smart card reader information that Windows detected).
Получает список считывателей смарт-карт (с помощью API WinSCard) и список смарт-карт, вставленных в каждой из них. Gets a list of smart card readers (by using the WinSCard API) and the list of smart cards inserted in each of them.
При этом каждая карта передается, чтобы убедиться в том, что сертификат регистрации, контролируемый групповой политикой, присутствует. Enumerates each card to verify that a sign-in certificate that is controlled by Group Policy is present. Если сертификат присутствует, поставщик учетных данных смарт-карт копирует его во временный защищенный кэш на компьютере или терминале. If the certificate is present, the smart card credential provider copies it into a temporary, secure cache on the computer or terminal.
**** Примечание Записи кэша smartcard создаются для сертификатов с именем субъекта или с идентификатором ключа субъекта. Note Smartcard cache entries are created for certificates with a subject name or with a subject key identifier. Если сертификат имеет имя субъекта, он хранится с индексом, основанным на имени субъекта и эмитенте сертификата. If the certificate has a subject name, it is stored with an index that is based on the subject name and certificate issuer. Если используется другой сертификат с тем же именем субъекта и эмитентом сертификата, он заменит существующую кэшную запись. If another certificate with the same subject name and certificate issuer is used, it will replace the existing cached entry. Изменение этого поведения после Windows Vista позволяет создать условие, при котором у сертификата нет имени субъекта, кэш создается с индексом, основанным на идентификаторе ключа субъекта и эмитенте сертификатов. A change in this behavior after Windows Vista, allows for the condition when the certificate does not have a subject name, the cache is created with an index that is based on the subject key identifier and certificate issuer. Если другой сертификат имеет тот же идентификатор ключа субъекта и эмитент сертификата, запись кэша заменяется. If another certificate has the same the subject key identifier and certificate issuer, the cache entry is replaced. Если сертификаты не имеют ни имени субъекта, ни идентификатора ключа субъекта, кэшная запись не создается. When certificates have neither a subject name nor subject key identifier, a cached entry is not created.
- Сообщает пользовательскому интерфейсу входа, что у него есть новые учетные данные. Notifies the sign-in UI that it has new credentials.
Пользовательский интерфейс входа запрашивает новые учетные данные у поставщика учетных данных смарт-карт. The sign-in UI requests the new credentials from the smart card credential provider. В ответ поставщик учетных данных смарт-карты предоставляет каждому входу сертификат пользовательского интерфейса входа, и отображаются соответствующие плитки входа. As a response, the smart card credential provider provides each sign-in certificate to the sign-in UI, and corresponding sign-in tiles are displayed. Пользователь выбирает плитку сертификата на основе смарт-карт, а в Windows отображается диалоговое окно PIN-кода. The user selects a smart card-based sign-in certificate tile, and Windows displays a PIN dialog box.
Пользователь вводит ПИН-код, а затем нажимает ВВОД. The user enters the PIN, and then presses ENTER. Поставщик учетных данных смарт-карт шифрует ПИН-код. The smart card credential provider encrypts the PIN.
Поставщик учетных данных, который находится в системе LogonUI, собирает ПИН-код. The credential provider that resides in the LogonUI system collects the PIN. В рамках упаковки учетных данных в поставщике учетных данных смарт-карт данные упаковываются в структуру KERB_CERTIFICATE_LOGON. As part of packaging credentials in the smart card credential provider, the data is packaged in a KERB_CERTIFICATE_LOGON structure. Основным содержимым структуры KERB_CERTIFICATE_LOGON являются ПИН-код смарт-карты, CSP-данные (например, имя читателя и имя контейнера), имя пользователя и доменное имя. The main contents of the KERB_CERTIFICATE_LOGON structure are the smart card PIN, CSP data (such as reader name and container name), user name, and domain name. Имя пользователя необходимо, если домен входной записи находится не в одном лесу, так как позволяет соотнося сертификат с несколькими учетными записями пользователей. User name is required if the sign-in domain is not in the same forest because it enables a certificate to be mapped to multiple user accounts.
Поставщик учетных данных заворачивает данные (например, зашифрованный ПИН-код, имя контейнера, имя читателя и спецификацию ключа карты) и отправляет их обратно в LogonUI. The credential provider wraps the data (such as the encrypted PIN, container name, reader name, and card key specification) and sends it back to LogonUI.
Winlogon представляет данные из LogonUI в LSA с данными пользователей в LSALogonUser. Winlogon presents the data from LogonUI to the LSA with the user information in LSALogonUser.
LSA вызывает пакет проверки подлинности Kerberos (Kerberos SSP) для создания запроса службы проверки подлинности Kerberos (KRB_AS_REQ), содержащего предавентикатор (как указано в RFC 4556: шифрование общедоступных ключей для начальной проверки подлинности в Kerberos (PKINIT)). LSA calls the Kerberos authentication package (Kerberos SSP) to create a Kerberos authentication service request (KRB_AS_REQ), which containing a preauthenticator (as specified in RFC 4556: Public Key Cryptography for Initial Authentication in Kerberos (PKINIT)).
Если проверка подлинности выполняется с помощью сертификата, использующего цифровую подпись, данные предварительной проверки состоят из открытого сертификата пользователя и сертификата, подписанного цифровой подписью с соответствующим закрытым ключом. If the authentication is performed by using a certificate that uses a digital signature, the preauthentication data consists of the user’s public certificate and the certificate that is digitally signed with the corresponding private key.
Если проверка подлинности выполняется с помощью сертификата, использующего шифрование ключей, данные предварительной проверки состоят из открытого сертификата пользователя и сертификата, шифруемого с помощью соответствующего закрытого ключа. If the authentication is performed by using a certificate that uses key encipherment, the preauthentication data consists of the user’s public certificate and the certificate that is encrypted with the corresponding private key.
Чтобы подписать запрос в цифровом формате (по RFC 4556), в соответствующий CSP для операции частного ключа будет выполнен вызов. To sign the request digitally (as per RFC 4556), a call is made to the corresponding CSP for a private key operation. Так как частный ключ в этом случае хранится в смарт-карте, подсистема смарт-карт называется, и необходимая операция завершена. Because the private key in this case is stored in a smart card, the smart card subsystem is called, and the necessary operation is completed. Результат отправляется обратно поставщику поддержки безопасности Kerberos (SSP). The result is sent back to the Kerberos security support provider (SSP).
Служба SSP Kerberos отправляет запрос на проверку подлинности для билета-билета (TGT) (за RFC 4556) в службу Key Distribution Center (KDC), которая работает на контроллере домена. The Kerberos SSP sends an authentication request for a ticket-granting-ticket (TGT) (per RFC 4556) to the Key Distribution Center (KDC) service that runs on a domain controller.
KDC находит объект учетной записи пользователя в Службе домена Active Directory (AD DS), как описано в требованиях и сопоставлениях сертификата клиента,и использует сертификат пользователя для проверки подписи. The KDC finds the user’s account object in Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), as detailed in Client certificate requirements and mappings, and uses the user’s certificate to verify the signature.
KDC проверяет сертификат пользователя (время, путь и состояние отзыва), чтобы убедиться, что сертификат из надежного источника. The KDC validates the user’s certificate (time, path, and revocation status) to ensure that the certificate is from a trusted source. KDC использует CryptoAPI для построения пути сертификации от сертификата пользователя до сертификата корневого органа сертификации (CA), который находится в корневом хранилище на контроллере домена. The KDC uses CryptoAPI to build a certification path from the user’s certificate to a root certification authority (CA) certificate that resides in the root store on the domain controller. Затем KDC использует CryptoAPI для проверки цифровой подписи на подписанной проверке подлинности, которая была включена в поля данных предварительной проверки. The KDC then uses CryptoAPI to verify the digital signature on the signed authenticator that was included in the preauthentication data fields. Контроллер домена проверяет подпись и использует общедоступный ключ из сертификата пользователя, чтобы доказать, что запрос исходил от владельца закрытого ключа, соответствующего общественному ключу. The domain controller verifies the signature and uses the public key from the user’s certificate to prove that the request originated from the owner of the private key that corresponds to the public key. Кроме того, KDC проверяет доверие эмитента и появляется в хранилище сертификатов NTAUTH. The KDC also verifies that the issuer is trusted and appears in the NTAUTH certificate store.
Служба KDC извлекает сведения об учетных записях пользователей из AD DS. The KDC service retrieves user account information from AD DS. KDC строит TGT, основанный на данных учетных записей пользователей, полученных из AD DS. The KDC constructs a TGT, which is based on the user account information that it retrieves from AD DS. Поля данных авторизации TGT включают идентификатор безопасности пользователя (SID), siD-коды для универсальных и глобальных доменных групп, к которым принадлежит пользователь, и (в многодомной среде) siD для всех универсальных групп, членом которых является пользователь. The TGT’s authorization data fields include the user’s security identifier (SID), the SIDs for universal and global domain groups to which the user belongs, and (in a multidomain environment) the SIDs for any universal groups of which the user is a member.
Контроллер домена возвращает TGT клиенту в рамках ответа KRB_AS_REP. The domain controller returns the TGT to the client as part of the KRB_AS_REP response.
**** Примечание Пакет KRB_AS_REP состоит из: Note The KRB_AS_REP packet consists of:
- Сертификат атрибута привилегий (PAC) Privilege attribute certificate (PAC)
- SID пользователя User’s SID
- SID-данные всех групп, членом которых является пользователь SIDs of any groups of which the user is a member
- Запрос на службу предоставления билетов (TGS) A request for ticket-granting service (TGS)
- Данные предварительной оценки Preauthentication data
TGT шифруется главным ключом KDC, а ключ сеанса шифруется временным ключом. TGT is encrypted with the master key of the KDC, and the session key is encrypted with a temporary key. Этот временный ключ получен на основе RFC 4556. This temporary key is derived based on RFC 4556. С помощью CryptoAPI временный ключ расшифровываются. Using CryptoAPI, the temporary key is decrypted. В рамках процесса расшифровки, если частный ключ находится на смарт-карте, в подсистему смарт-карты делается вызов с помощью указанного CSP для извлечения сертификата, соответствующего общественному ключу пользователя. As part of the decryption process, if the private key is on a smart card, a call is made to the smart card subsystem by using the specified CSP to extract the certificate corresponding to the user’s public key. (Программные вызовы сертификата включают CryptAcquireContext, CryptSetProvParam с ПИН-кодом, CryptgetUserKey и CryptGetKeyParam.) После того, как временный ключ будет получен, SSP Kerberos расшифровка ключа сеанса. (Programmatic calls for the certificate include CryptAcquireContext, CryptSetProvParam with the PIN, CryptgetUserKey, and CryptGetKeyParam.) After the temporary key is obtained, the Kerberos SSP decrypts the session key.
Клиент проверяет ответ из состояния KDC (время, путь и отзыв). The client validates the reply from the KDC (time, path, and revocation status). Сначала он проверяет подпись KDC путем строительства пути сертификации от сертификата KDC до доверенного корневого центра, а затем использует общедоступный ключ KDC для проверки подписи ответа. It first verifies the KDC’s signature by the construction of a certification path from the KDC’s certificate to a trusted root CA, and then it uses the KDC’s public key to verify the reply signature.
После получения TGT клиент получает талон службы, который используется для регистрации на локальном компьютере. Now that a TGT has been obtained, the client obtains a service ticket, which is used to sign in to the local computer.
С успехом LSA сохраняет билеты и возвращает сообщение об успехе в LSALogonUser. With success, LSA stores the tickets and returns a success message to LSALogonUser. После выпуска этого сообщения об успехе выбирается и задан профиль пользователя для устройства, выполняется мгновенное обновление групповой политики и выполняются другие действия. After this success message is issued, user profile for the device is selected and set, Group Policy refresh is instantiated, and other actions are performed.
После загрузки профиля пользователя служба распространения сертификации (CertPropSvc) обнаруживает это событие, считывает сертификаты с смарт-карты (включая корневые сертификаты), а затем заполняет их в хранилище сертификатов пользователя (MYSTORE). After the user profile is loaded, the Certification Propagation Service (CertPropSvc) detects this event, reads the certificates from the smart card (including the root certificates), and then populates them into the user’s certificate store (MYSTORE).
Связь CSP с диспетчером ресурсов смарт-карт происходит на канале LRPC. CSP to smart card resource manager communication happens on the LRPC Channel.
При успешной проверке подлинности сертификаты распространяются в хранилище пользователя асинхронно службой распространения сертификатов (CertPropSvc). On successful authentication, certificates are propagated to the user’s store asynchronously by the Certificate Propagation Service (CertPropSvc).
При удалении карты удаляются сертификаты в хранилище временного безопасного кэша. When the card is removed, certificates in the temporary secure cache store are removed. Сертификаты больше не доступны для регистрации, но они остаются в хранилище сертификатов пользователя. The Certificates are no longer available for sign-in, but they remain in the user’s certificate store.
**** Примечание Sid создается для каждого пользователя или группы в момент создания учетной записи пользователя или учетной записи группы в локальной базе данных учетных записей безопасности или в AD DS. Note A SID is created for each user or group at the time a user account or a group account is created within the local security accounts database or within AD DS. Sid никогда не изменяется, даже если пользователь или учетная запись группы переименована. The SID never changes, even if the user or group account is renamed.
Дополнительные сведения о протоколе Kerberos см. в сайте Microsoft Kerberos. For more information about the Kerberos protocol, see Microsoft Kerberos.
По умолчанию KDC проверяет, что сертификат клиента содержит проверку подлинности клиента смарт-карты EKU szOID_KP_SMARTCARD_LOGON. By default, the KDC verifies that the client’s certificate contains the smart card client authentication EKU szOID_KP_SMARTCARD_LOGON. Однако, если включено, сертификаты Allow без атрибута атрибута групповой политики сертификата расширенного ключевого использования позволяют KDC не требовать EKU SC-LOGON. However, if enabled, the Allow certificates with no extended key usage certificate attribute Group Policy setting allows the KDC to not require the SC-LOGON EKU. SC-LOGON EKU не требуется для сопоставлений учетных записей, основанных на общедоступных ключах. SC-LOGON EKU is not required for account mappings that are based on the public key.
Сертификат KDC KDC certificate
Службы сертификатов Active Directory предоставляют три типа шаблонов сертификатов: Active Directory Certificate Services provides three kinds of certificate templates:
Контроллер домена Domain controller
Проверка подлинности контроллера домена Domain controller authentication
Проверка подлинности Kerberos Kerberos authentication
В зависимости от конфигурации контроллера домена один из этих типов сертификатов отправляется в составе пакета AS_REP. Depending on the configuration of the domain controller, one of these types of certificates is sent as a part of the AS_REP packet.
Требования и сопоставления сертификатов клиентов Client certificate requirements and mappings
Требования к сертификатам перечислены в версиях операционной системы Windows. Certificate requirements are listed by versions of the Windows operating system. Сопоставление сертификатов описывает сопоставление сведений из сертификата с учетной записью пользователя. Certificate mapping describes how information from the certificate is mapped to the user account.
Требования к сертификатам Certificate requirements
Сертификат смарт-карты имеет определенные требования к формату при его работе с Windows XP и более ранними операционными системами. The smart card certificate has specific format requirements when it is used with Windows XP and earlier operating systems. Вы можете включить любой сертификат, который будет виден поставщику учетных данных смарт-карт. You can enable any certificate to be visible for the smart card credential provider.
| Компонент Component | Требования к Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista и Windows 10 Requirements for Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows 10 | Требования к Windows XP Requirements for Windows XP |
|---|---|---|
| Расположение точки распространения CRL CRL distribution point location | Не требуется Not required | Расположение должно быть указано, в Интернете и доступно, например: The location must be specified, online, and available, for example: [1]Точка распространения CRL [1]CRL Distribution Point Имя точки распространения: Distribution Point Name: Полное имя: Full Name: URL= URL= http://server1.contoso.com/CertEnroll/caname.crl |
| Использование ключей Key usage | Цифровая подпись Digital signature | Цифровая подпись Digital signature |
| Основные ограничения Basic constraints | Не требуется Not required | [Subject Type=End Entity, Path Length Constraint=None] (необязательный) [Subject Type=End Entity, Path Length Constraint=None] (Optional) |
| Расширенное использование ключей (EKU) Enhanced key usage (EKU) | Идентификатор объекта для регистрации смарт-карты не требуется. The smart card sign-in object identifier is not required. **** Примечание Если EKU присутствует, он должен содержать EKU для регистрации смарт-карты. Note If an EKU is present, it must contain the smart card sign-in EKU. Сертификаты без EKU можно использовать для регистрации. Certificates with no EKU can be used for sign-in. | — Проверка подлинности клиента (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) — Client Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) Идентификатор объекта проверки подлинности клиента требуется только в том случае, если сертификат используется для проверки подлинности SSL. The client authentication object identifier is required only if a certificate is used for SSL authentication. — Вход смарт-карты (1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.2) — Smart Card Sign-in (1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.2) |
| Альтернативное имя субъекта Subject alternative name | Для регистрации смарт-карт не требуется удостоверение электронной почты. E-mail ID is not required for smart card sign-in. | Другое имя: Основное имя=(UPN), например: Other Name: Principal Name=(UPN), for example: UPN=user1@contoso.com UPN=user1@contoso.com Идентификатор объекта UpN OtherName — 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.3. The UPN OtherName object identifier is 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.3. Значение UPN OtherName должно быть строкой UTF8 с кодом ASN1. The UPN OtherName value must be an ASN1-encoded UTF8 string. |
| Субъект Subject | Не требуется Not required | Отличительное имя пользователя. Distinguished name of user. Это поле является обязательным расширением, но население этого поля является необязательным. This field is a mandatory extension, but the population of this field is optional. |
| Обмен ключами (поле AT_KEYEXCHANGE) Key exchange (AT_KEYEXCHANGE field) | Не требуется для сертификатов входа смарт-карт, если включен параметр групповой политики. Not required for smart card sign-in certificates if a Group Policy setting is enabled. (По умолчанию параметры групповой политики не включены.) (By default, Group Policy settings are not enabled.) | Не требуется Not required |
| CRL CRL | Не требуется Not required | Не требуется Not required |
| UPN UPN | Не требуется Not required | Не требуется Not required |
| Примечания Notes | Вы можете включить любой сертификат, который будет виден поставщику учетных данных смарт-карт. You can enable any certificate to be visible for the smart card credential provider. | Существует два предопределяемого типа закрытых ключей. There are two predefined types of private keys. Это только подписи (AT_SIGNATURE) и Key Exchange (AT_KEYEXCHANGE). These keys are Signature Only (AT_SIGNATURE) and Key Exchange (AT_KEYEXCHANGE). Сертификаты для регистрации смарт-карт должны иметь частный тип ключа Exchange (AT_KEYEXCHANGE). Smart card sign-in certificates must have a Key Exchange (AT_KEYEXCHANGE) private key type. |
Сопоставления сертификатов клиента Client certificate mappings
Сопоставление сертификатов основано на поле UPN, которое содержится в поле subjectAltName (SAN) сертификата. Certificate mapping is based on the UPN that is contained in the subjectAltName (SAN) field of the certificate. Кроме того, поддерживаются клиентские сертификаты, не содержащие сведений в поле SAN. Client certificates that do not contain information in the SAN field are also supported.
SSL/TLS может сопоставление сертификатов, не использующих SAN, и сопоставление делается с помощью атрибутов AltSecID на клиентских учетных записях. SSL/TLS can map certificates that do not have SAN, and the mapping is done by using the AltSecID attributes on client accounts. X509 AltSecID, который используется для проверки подлинности клиента SSL/TLS, имеет форму «X509: * Имя*эмитента » * *. The X509 AltSecID, which is used by SSL/TLS client authentication is of the form «X509: » » » . Имя * имя* * * субъекта эмитента взяты из клиентского сертификата, а «\r» и «\n» заменены на «,». The and are taken from the client certificate, with ‘\r’ and ‘\n’ replaced with ‘,’.
Точки рассылки списков отзыва сертификатов Certificate revocation list distribution points
UPN в поле Альтернативное имя субъекта UPN in Subject Alternative Name field
Поля Subject и Issuer Subject and Issuer fields
Это сопоставление учетных записей поддерживается KDC в дополнение к шести другим методам сопоставления. This account mapping is supported by the KDC in addition to six other mapping methods. На следующем рисунке демонстрируется поток логики сопоставления учетных записей пользователей, используемый KDC. The following figure demonstrates a flow of user account mapping logic that is used by the KDC.
Высокоуровневый поток обработки сертификатов для регистрации High-level flow of certificate processing for sign-in
Объект сертификата выполняет анализ содержимого для выполнения сопоставления учетных записей пользователей. The certificate object is parsed to look for content to perform user account mapping.
Когда имя пользователя предоставляется сертификатом, имя пользователя используется для поиска объекта учетной записи. When a user name is provided with the certificate, the user name is used to locate the account object. Эта операция является самой быстрой, так как происходит соответствие строкам. This operation is the fastest, because string matching occurs.
Когда предоставляется только объект сертификата, выполняется серия операций, чтобы найти имя пользователя, чтобы соотоставить имя пользователя с объектом учетной записи. When only the certificate object is provided, a series of operations are performed to locate the user name to map the user name to an account object.
Если для проверки подлинности нет сведений о домене, локальный домен используется по умолчанию. When no domain information is available for authentication, the local domain is used by default. Если какой-либо другой домен будет использоваться для lookup, для выполнения сопоставления и привязки должен быть предоставлен подсказка доменного имени. If any other domain is to be used for lookup, a domain name hint should be provided to perform the mapping and binding.
Сопоставление на основе общих атрибутов невозможно, так как нет универсального API для получения атрибутов из сертификата. Mapping based on generic attributes is not possible because there is no generic API to retrieve attributes from a certificate. В настоящее время первый метод, который находит учетную запись, успешно останавливает поиск. Currently, the first method that locates an account successfully stops the search. Но ошибка конфигурации возникает, если два метода соотносят один и тот же сертификат с разными учетными записьми пользователей, когда клиент не сообщает имя клиента через подсказки сопоставления. But a configuration error occurs if two methods map the same certificate to different user accounts when the client does not supply the client name through the mapping hints.
На следующем рисунке иллюстрируется процесс сопоставления учетных записей пользователей для входов в каталог, просматривая различные записи в сертификате. The following figure illustrates the process of mapping user accounts for sign-in in the directory by viewing various entries in the certificate.
Логика обработки сертификатов Certificate processing logic
Политика NT_AUTH лучше всего описана в разделе CERT_CHAIN_POLICY_NT_AUTH параметра функции CertVerifyCertificateChainPolicy. NT_AUTH policy is best described in the CERT_CHAIN_POLICY_NT_AUTH parameter section of the CertVerifyCertificateChainPolicy function. Дополнительные сведения см. в дополнительных сведениях в certVerifyCertificateChainPolicy. For more information, see CertVerifyCertificateChainPolicy.
Вход смарт-карты для одного пользователя с одним сертификатом на несколько учетных записей Smart card sign-in for a single user with one certificate into multiple accounts
Один сертификат пользователя можно соотнося с несколькими учетной записью. A single user certificate can be mapped to multiple accounts. Например, пользователь может войти в учетную запись пользователя, а также войти в качестве администратора домена. For example, a user might be able to sign in to a user account and also to sign in as a domain administrator. Сопоставление делается с помощью построенного AltSecID на основе атрибутов из клиентских учетных записей. The mapping is done by using the constructed AltSecID based on attributes from client accounts. Сведения о том, как оценивается это сопоставление, см. в справке о требованиях к сертификатам клиента и сопоставлениях. For information about how this mapping is evaluated, see Client certificate requirements and mappings.
**** Примечание Поскольку каждая учетная запись имеет свое имя **** пользователя, рекомендуется включить параметр Групповой политики намека на имя пользователя (ключ реестра X509HintsNeeded), чтобы предоставить необязательные поля, позволяющие пользователям вводить имена пользователей и сведения о домене для входа. Note Because each account has a different user name, we recommend that you enable the Allow user name hint Group Policy setting (X509HintsNeeded registry key) to provide the optional fields that allow users to enter their user names and domain information to sign in.
На основе сведений, доступных в сертификате, условия регистрации: Based on the information that is available in the certificate, the sign-in conditions are:
Если в сертификате нет upN: If no UPN is present in the certificate:
Вход может происходить в локальном лесу или в другом лесу, если одному пользователю с одним сертификатом необходимо войти в различные учетные записи. Sign-in can occur in the local forest or in another forest if a single user with one certificate needs to sign in to different accounts.
Подсказка должна быть предоставлена, если сопоставление не является уникальным (например, если несколько пользователей сопоставлены с одним и тем же сертификатом). A hint must be supplied if mapping is not unique (for example, if multiple users are mapped to the same certificate).
Если в сертификате присутствует upN: If a UPN is present in the certificate:
Сертификат не может быть соедан нескольким пользователям в одном лесу. The certificate cannot be mapped to multiple users in the same forest.
Сертификат может быть соедан нескольким пользователям в разных лесах. The certificate can be mapped to multiple users in different forests. Чтобы пользователь въехал в другие леса, пользователю должен быть предоставлен подсказка X509. For a user to sign in to other forests, an X509 hint must be supplied to the user.
Вход смарт-карты для нескольких пользователей в одну учетную запись Smart card sign-in for multiple users into a single account
Группа пользователей может войти в одну учетную запись (например, учетную запись администратора). A group of users might sign in to a single account (for example, an administrator account). Для этой учетной записи сертификаты пользователей соотносят так, чтобы они были включены для входа. For that account, user certificates are mapped so that they are enabled for sign-in.
Несколько различных сертификатов можно соотносять с одной учетной записью. Several distinct certificates can be mapped to a single account. Чтобы это работало должным образом, сертификат не может иметь upNs. For this to work properly, the certificate cannot have UPNs.
Например, если в Certificate1 есть CN=CNName1, у Certificate2 есть CN=User1, а у Certificate3 есть CN=User2, AltSecID этих сертификатов можно сопоставлено с одной учетной записью с помощью сопоставления имен Пользователей и компьютеров Active Directory. For example, if Certificate1 has CN=CNName1, Certificate2 has CN=User1, and Certificate3 has CN=User2, the AltSecID of these certificates can be mapped to a single account by using the Active Directory Users and Computers name mapping.
Вход смарт-карты в лесах Smart card sign-in across forests
Чтобы сопоставление учетных записей работало в лесах, особенно в тех случаях, когда в сертификате недостаточно сведений, пользователь может ввести подсказку в виде имени пользователя, например домена\пользователя, или полностью квалифицированного upN, например user@contoso.com . For account mapping to work across forests, particularly in cases where there is not enough information available on the certificate, the user might enter a hint in the form of a user name, such as domain\user, or a fully qualified UPN such as user@contoso.com.
**** Примечание Чтобы поле подсказки появлялось во время **** входа в смарт-карточку, необходимо включить в клиенте параметр Разрешить параметр групповой политики подсказки пользователя (ключ реестра X509HintsNeeded). Note For the hint field to appear during smart card sign-in, the Allow user name hint Group Policy setting (X509HintsNeeded registry key) must be enabled on the client.
Поддержка OCSP для PKINIT OCSP support for PKINIT
Протокол состояния сертификата в Интернете (OCSP), определенный в RFC 2560, позволяет приложениям получать сведения о состоянии отзыва сертификата вовремя. Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP), which is defined in RFC 2560, enables applications to obtain timely information about the revocation status of a certificate. Так как ответы OCSP являются небольшими и хорошо связанными, ограниченные клиенты могут использовать OCSP для проверки действительности сертификатов kerberos на KDC, чтобы избежать передачи больших crLs и сохранить пропускную способность в ограниченных сетях. Because OCSP responses are small and well bound, constrained clients might want to use OCSP to check the validity of the certificates for Kerberos on the KDC, to avoid transmission of large CRLs, and to save bandwidth on constrained networks. Сведения о ключах реестра CRL см. в группе smart Card Policy and Registry Settings. For information about CRL registry keys, see Smart Card Group Policy and Registry Settings.
KDCs в Windows пытаются получить ответы OCSP и использовать их при наличии. The KDCs in Windows attempt to get OCSP responses and use them when available. Это поведение нельзя отключить. This behavior cannot be disabled. CryptoAPI для кэшей OCSP ответов OCSP и состояния ответов. CryptoAPI for OCSP caches OCSP responses and the status of the responses. KDC поддерживает только ответы OCSP для сертификата подписавщика. The KDC supports only OCSP responses for the signer certificate.
Клиентские компьютеры Windows пытаются запрашивать ответы OCSP и использовать их в ответе, когда они доступны. Windows client computers attempt to request the OCSP responses and use them in the reply when they are available. Это поведение нельзя отключить. This behavior cannot be disabled.
Требования к корневому сертификату смарт-карты для использования при входе в домен Smart card root certificate requirements for use with domain sign-in
Чтобы войти в домен на основе смарт-карт, сертификат смарт-карты должен соответствовать следующим условиям: For sign-in to work in a smart card-based domain, the smart card certificate must meet the following conditions:
Корневой сертификат KDC на смарт-карте должен иметь пункт рассылки HTTP CRL, указанный в сертификате. The KDC root certificate on the smart card must have an HTTP CRL distribution point listed in its certificate.
Сертификат регистрации смарт-карты должен иметь точку распространения HTTP CRL, указанную в сертификате. The smart card sign-in certificate must have the HTTP CRL distribution point listed in its certificate.
Точка распространения CRL должна иметь допустимый crL опубликованный и дельта CRL, если применимо, даже если точка распространения CRL пуста. The CRL distribution point must have a valid CRL published and a delta CRL, if applicable, even if the CRL distribution point is empty.
Сертификат смарт-карты должен содержать один из следующих: The smart card certificate must contain one of the following:
Поле субъекта, содержаще доменное имя DNS в имени. A subject field that contains the DNS domain name in the distinguished name. Если этого не происходит, разрешение соответствующего домена не удается, поэтому удаленные службы настольных компьютеров и вход домена с помощью смарт-карты не удается. If it does not, resolution to an appropriate domain fails, so Remote Desktop Services and the domain sign-in with the smart card fail.
UpN, в котором доменное имя решается на фактический домен. A UPN where the domain name resolves to the actual domain. Например, если доменное имя — Engineering.Corp.Contoso, upN username@engineering.corp.contoso.com. For example, if the domain name is Engineering.Corp.Contoso, the UPN is username@engineering.corp.contoso.com. Если какой-либо части доменного имени не будет опущен, клиент Kerberos не сможет найти соответствующий домен. If any part of the domain name is omitted, the Kerberos client cannot find the appropriate domain.
Хотя точки распространения HTTP CRL по умолчанию включены в Windows Server 2008, последующие версии операционной системы Windows Server не включают точки распространения HTTP CRL. Although the HTTP CRL distribution points are on by default in Windows Server 2008, subsequent versions of the Windows Server operating system do not include HTTP CRL distribution points. Чтобы разрешить вход смарт-карты в домен в этих версиях, сделайте следующее: To allow smart card sign-in to a domain in these versions, do the following:
Включить точки распространения HTTP CRL в ЦС. Enable HTTP CRL distribution points on the CA.
Перезапустите ЦС. Restart the CA.
Переоценка сертификата KDC. Reissue the KDC certificate.
Выпуск или переоценка сертификата регистрации смарт-карты. Issue or reissue the smart card sign-in certificate.
Распространение обновленного корневого сертификата на смарт-карту, которую необходимо использовать для регистрации домена. Propagate the updated root certificate to the smart card that you want to use for the domain sign-in.
Обходной путь — включить **** параметр Групповой политики подсказки пользователя (ключ реестра X509HintsNeeded), который позволяет пользователю предоставить подсказку в пользовательском интерфейсе учетных данных для входа в домен. The workaround is to enable the Allow user name hint Group Policy setting (X509HintsNeeded registry key), which allows the user to supply a hint in the credentials user interface for domain sign-in.
Если клиентский компьютер не присоединяется к домену или присоединяется к другому домену, клиентский компьютер может разрешить домен сервера, только глядя на отличительное имя в сертификате, а не на upN. If the client computer is not joined to the domain or if it is joined to a different domain, the client computer can resolve the server domain only by looking at the distinguished name on the certificate, not the UPN. Чтобы этот сценарий работал, сертификат требует полного субъекта, включая DC=* *для разрешения доменных имен. For this scenario to work, the certificate requires a full subject, including DC= , for domain name resolution.
Чтобы развернуть корневые сертификаты на смарт-карте для в настоящее время присоединимых доменов, можно использовать следующую команду: To deploy root certificates on a smart card for the currently joined domain, you can use the following command:
certutil -scroots update certutil -scroots update
Дополнительные сведения об этом параметре для средства командной строки см. в пункте -SCRoots. For more information about this option for the command-line tool, see -SCRoots.