- Change or reset your Windows password
- If you already know your current password and want to change it
- Reset your Windows 10 local account password
- Windows 10 version 1803 and later
- Windows 10 before version 1803
- Reset your Microsoft account password you use to sign in to your computer
- Troubleshoot problems signing in
- Reset your password
- More help with passwords in Windows 8.1
- Reset your password
- My computer is in a workgroup
- Change your password
- Процедуры с учетными данными в проверке подлинности Windows Credentials Processes in Windows Authentication
- Ввод учетных данных для входа пользователя Credential input for user logon
- Ввод учетных данных для входа в приложение и службу Credential input for application and service logon
- Локальная система безопасности Local Security Authority
- Кэшированные учетные данные и проверка Cached credentials and validation
- Хранилище учетных данных и проверка Credential storage and validation
- Процессы для учетных данных удаленного входа Remote logon credential processes
- Процесс автоматического перезапуска учетных данных входа Automatic restart sign-on credential process
- Сохранение имен пользователей и паролей в Windows Vista и Windows XP Stored user names and passwords in Windows Vista and Windows XP
- Хранилище Windows и диспетчер учетных данных Windows Vault and Credential Manager
- База данных диспетчера учетных записей безопасности Security Accounts Manager database
- Локальные домены и доверенные домены Local domains and trusted domains
- Сертификаты в проверке подлинности Windows Certificates in Windows authentication
Change or reset your Windows password
If you forgot or lost your password for Windows 10, Windows 8.1, or Windows 7, you may be able to change or reset it. To get started, choose your version of Windows from the Select Product Version drop-down menu.
If you already know your current password and want to change it
Select Start > Settings > Accounts > Sign-in options . Under Password, select the Change button and follow the steps.
Reset your Windows 10 local account password
If you’ve forgotten or lost your Windows 10 password for a local account and need to sign back in to your device, the below options might help you get up and running. For more info on local standard vs. administrative accounts, see Create a local user or administrator account in Windows 10.
Windows 10 version 1803 and later
If you added security questions when you set up your local account for Windows 10, then you have at least version 1803 and you can answer security questions to sign back in.
After you’ve entered an incorrect password:
Select the Reset password link on the sign-in screen. If you use a PIN instead, see PIN sign-in issues. If you’re using a work device that’s on a network, you may not see an option to reset your password or PIN. In that case, contact your administrator.
Note: If you don’t see security questions after you select the Reset password link, make sure your device name isn’t the same as your local user account name (the name you see when you sign in). To see your device name, right-click Start in the taskbar, select System, andscroll to the Device specifications section. If the device name is the same as your account name, you can create a new administrator account, sign in as an administrator, and then rename your PC (when you view your device name, you can also rename it).
Answer your security questions.
Enter a new password.
Sign in as usual with the new password.
Windows 10 before version 1803
For versions of Windows 10 earlier than 1803, local account passwords can’t be reset because there are no security questions. You can reset your device to choose a new password, however this option will permanently delete your data, programs, and settings. If you’ve backed up your files you’ll be able to restore your deleted files. For more information, see Recovery options in Windows 10.
To reset your device, which will delete data, programs, and settings:
Press the Shift key while you select the Power button > Restart in the lower-right corner of the screen.
On the Choose an option screen, select Troubleshoot > Reset this PC.
Select Remove everything.
Warning: Resetting your device will permanently delete data, programs, and settings.
Reset your Microsoft account password you use to sign in to your computer
On the sign-in screen, type your Microsoft account name if it’s not already displayed. If there are multiple accounts on the computer, choose the one you want to reset. Below the password text box, select I forgot my password. Follow the steps to reset your password.
Troubleshoot problems signing in
If you’re still having trouble signing to your account, see more solutions in Troubleshoot problems signing in.
Reset your password
Note: If you’ve forgotten your Windows 10 password, see Reset your Windows 10 local account password.
If you’ve forgotten your Windows 8.1 password, there are several ways to retrieve or reset it:
If your PC is on a domain, your system administrator must reset your password.
If you’re using a Microsoft account, you can reset your password online. For more info, see How to reset your Microsoft account password.
If you’re using a local account, use your password hint as a reminder.
If you still can’t sign in, you must reinstall Windows. For Windows RT 8.1, contact your PC manufacturer.
More help with passwords in Windows 8.1
If you forget or lose your password, see Reset your password above to reset or recover it.
If you think your Microsoft account password has been compromised or stolen by someone with malicious intent, we can help. For more info, see When you can’t sign in to your Microsoft account.
If you’re signing in to only your local PC, yes. However, we recommend that you keep your PC more secure by using a strong password. When you use a password, only someone who knows it can sign in. If you want to sign in to Windows with a Microsoft account, a password is required. For more info, see Can I sign in to Windows without a password? To learn more about Microsoft accounts and local accounts, see Create a user account.
Stronger passwords contain a variety of characters, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols or spaces. A strong password should also be something that is difficult for a stranger to guess or crack. It shouldn’t contain a complete word, or easy-to-find details like your real name, your user name, or your birth date.
If you’re signing in to a Microsoft account, your password is limited to 16 characters. For more info about Microsoft accounts, see Create a user account.
You can update your password regularly to keep it more secure. If your PC isn’t connected to a domain, follow these steps:
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings.
(If you’re using a mouse, point to the lower-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer up, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings.)
Tap or click Accounts, and then tap or click Sign-in options.
Tap or click Change your password and follow the instructions.
If your PC is connected to a domain, your system administrator might manage how frequently you must change your password. To do so, choose one of the following:
If you’re using a keyboard, press Ctrl+Alt+Delete, tap or click Change a password, and follow the instructions.
If you’re using a tablet, press and hold the Windows button, press the power button, and then tap or click Change a password and follow the instructions.
It depends on whether you’re using a third-party email address. If your email address ends in outlook.com, hotmail.com, live.com, or another Microsoft service, changing the password for your Microsoft account also changes it for that email service.
But you can use any email address for your Microsoft account, even an email address from a third-party web-based mail service like Google Mail or Yahoo! Mail. When you choose a password for your Microsoft account, it doesn’t change the password you might need to use to sign in to web mail on a third-party site.
Create a picture password to sign in with gestures instead of by entering characters.
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, tap Settings, and then tap Change PC settings.
(If you’re using a mouse, point to the lower-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer up, click Settings, and then click Change PC settings.)
Tap or click Accounts, and then tap or click Sign-in options.
Under Picture password, tap or click Add, and then follow the instructions.
When you choose a password for your user account, it’s important to pick something you can remember. You’re going to need it again later!
Of course, you can also write your password down and keep it in a safe place. Taped to the underside of your laptop or the inside of your desk drawer is probably not a good idea, however. If you do write your password down, be sure to keep it separate from your PC.
For added security, use different passwords for different purposes. For example, it’s a good idea to keep distinctly different passwords for a social networking account and your online bank account.
If you do forget or lose your password, there are still several things you can try to reset or recover it. For more info, see Reset your password above to reset or recover it.
Reset your password
My computer is on a domain
Select the Start button 

On the Users tab, under Users for this computer, select the user account name, and then select Reset Password.
Type the new password, confirm the new password, and then select OK.
My computer is in a workgroup
If you type the wrong password when you attempt to log on, Windows displays a message that the password is incorrect. Select OK to close the message.
Select Reset password, and then insert your password reset disk or USB flash drive.
Follow the steps in the Password Reset wizard to create a new password.
Log on with the new password. If you forget your password again, you can use the same password reset disk. You don’t need to make a new one.
Note: If an administrator resets your password, you might lose access to some of your files.
Change your password
Press Ctrl+ Alt+ Delete, and then select Change a password.
Type your old password followed by a new password as indicated, and then type the new password again to confirm it.
Note: If you are logged on as an administrator, you can create and change passwords for all user accounts on the computer.
Warning: If you use an administrator account to change a password for another account, any encrypted files or e mail messages for that other account will no longer be accessible to the person who was using that account.
Процедуры с учетными данными в проверке подлинности Windows Credentials Processes in Windows Authentication
Область применения. Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016 Applies To: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016
В этом справочном разделе для ИТ – специалиста описано, как проверка подлинности Windows обрабатывает учетные данные. This reference topic for the IT professional describes how Windows authentication processes credentials.
Управление учетными данными Windows — это процесс, с помощью которого операционная система получает учетные данные от службы или пользователя и защищает эту информацию для будущего представления целевому объекту, выполняющему проверку подлинности. Windows credentials management is the process by which the operating system receives the credentials from the service or user and secures that information for future presentation to the authenticating target. В случае компьютера, присоединенного к домену, целевой объект, выполняющий проверку подлинности, является контроллером домена. In the case of a domain-joined computer, the authenticating target is the domain controller. Учетные данные, используемые при проверке подлинности, представляют собой цифровые документы, связывающие удостоверение пользователя с какой-либо формой подтверждения подлинности, например сертификатом, паролем или закреплением. The credentials used in authentication are digital documents that associate the user’s identity to some form of proof of authenticity, such as a certificate, a password, or a PIN.
По умолчанию учетные данные Windows проверяются по базе данных диспетчера учетных записей безопасности (SAM) на локальном компьютере или на Active Directory на компьютере, присоединенном к домену, через службу Winlogon. By default, Windows credentials are validated against the Security Accounts Manager (SAM) database on the local computer, or against Active Directory on a domain-joined computer, through the Winlogon service. Учетные данные собираются с помощью пользовательского интерфейса входа в систему или программным путем через интерфейс прикладного программирования (API), который должен быть представлен целевой базе данных для проверки подлинности. Credentials are collected through user input on the logon user interface or programmatically via the application programming interface (API) to be presented to the authenticating target.
Локальная информация о безопасности хранится в реестре в разделе HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SECURITY. Local security information is stored in the registry under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SECURITY. Сохраненные сведения включают параметры политики, значения безопасности по умолчанию и сведения об учетной записи, например кэшированные учетные данные для входа. Stored information includes policy settings, default security values, and account information, such as cached logon credentials. Также хранится копия базы данных SAM, хотя она защищена от записи. A copy of the SAM database is also stored here, although it is write-protected.
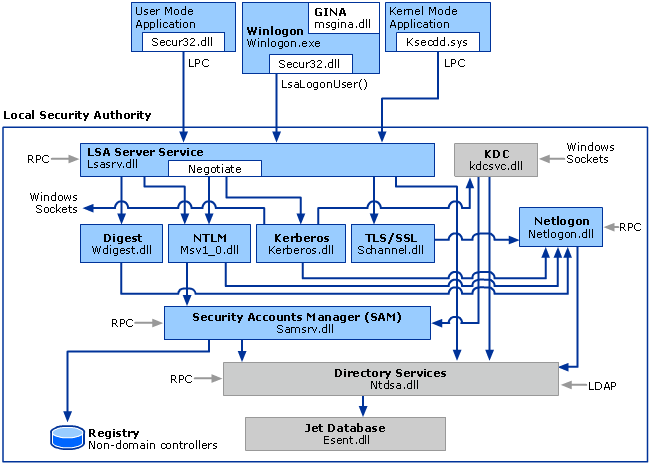
На следующей схеме показаны необходимые компоненты и пути, которые проходят через систему для проверки подлинности пользователя или процесса при успешном входе. The following diagram shows the components that are required and the paths that credentials take through the system to authenticate the user or process for a successful logon.
В следующей таблице описаны все компоненты, управляющие учетными данными в процессе проверки подлинности в момент входа в систему. The following table describes each component that manages credentials in the authentication process at the point of logon.
Компоненты проверки подлинности для всех систем Authentication components for all systems
| Компонент Component | Описание Description |
|---|---|
| Вход пользователя в систему User logon | Winlogon.exe — это исполняемый файл, отвечающий за управление взаимодействием безопасных пользователей. Winlogon.exe is the executable file responsible for managing secure user interactions. Служба Winlogon инициирует процесс входа для операционных систем Windows, передавая учетные данные, собранные действием пользователя на защищенном рабочем столе (в пользовательском интерфейсе входа), в локальный центр безопасности (LSA) через Secur32.dll. The Winlogon service initiates the logon process for Windows operating systems by passing the credentials collected by user action on the secure desktop (Logon UI) to the Local Security Authority (LSA) through Secur32.dll. |
| Вход в приложение Application logon | Вход в приложение или службу, для которых не требуется интерактивный вход. Application or service logons that do not require interactive logon. Большинство процессов, инициированных пользователем, выполняются в пользовательском режиме с помощью Secur32.dll, а процессы, инициированные при запуске, такие как службы, выполняются в режиме ядра с помощью Ksecdd.sys. Most processes initiated by the user run in user mode by using Secur32.dll whereas processes initiated at startup, such as services, run in kernel mode by using Ksecdd.sys. Дополнительные сведения о пользовательском режиме и режиме ядра см. в разделе приложения и пользовательский режим или службы и режим ядра в этой статье. For more information about user mode and kernel mode, see Applications and User Mode or Services and Kernel Mode in this topic. |
| Secur32.dll Secur32.dll | Несколько поставщиков проверки подлинности, образующих основу процесса проверки подлинности. The multiple authentication providers that form the foundation of the authentication process. |
| Lsasrv.dll Lsasrv.dll | Служба LSA Server, которая применяет политики безопасности и выступает в качестве диспетчера пакетов безопасности для LSA. The LSA Server service, which both enforces security policies and acts as the security package manager for the LSA. LSA содержит функцию Negotiate, которая выбирает протокол NTLM или Kerberos после определения того, какой протокол должен быть успешным. The LSA contains the Negotiate function, which selects either the NTLM or Kerberos protocol after determining which protocol is to be successful. |
| Поставщики поддержки безопасности Security Support Providers | Набор поставщиков, которые могут по отдельности вызывать один или несколько протоколов проверки подлинности. A set of providers that can individually invoke one or more authentication protocols. Набор поставщиков по умолчанию может меняться в каждой версии операционной системы Windows, а пользовательские поставщики могут быть написаны. The default set of providers can change with each version of the Windows operating system, and custom providers can be written. |
| Netlogon.dll Netlogon.dll | Служба Net Logon выполняет следующие службы: The services that the Net Logon service performs are as follows: — Обслуживает безопасный канал компьютера (не путать с Schannel) с контроллером домена. — Maintains the computer’s secure channel (not to be confused with Schannel) to a domain controller. |
| Samsrv.dll Samsrv.dll | Диспетчер учетных записей безопасности (SAM), в котором хранятся локальные учетные записи безопасности, обеспечивает применение локально хранимых политик и поддерживает интерфейсы API. The Security Accounts Manager (SAM), which stores local security accounts, enforces locally stored policies and supports APIs. |
| Реестр Registry | Реестр содержит копию базы данных SAM, параметры локальной политики безопасности, значения безопасности по умолчанию и сведения об учетной записи, которые доступны только системе. The Registry contains a copy of the SAM database, local security policy settings, default security values, and account information that is only accessible to the system. |
В этом разделе содержатся следующие подразделы. This topic contains the following sections:
Ввод учетных данных для входа пользователя Credential input for user logon
В Windows Server 2008 и Windows Vista Архитектура графической идентификации и аутентификации (GINA) была заменена моделью поставщика учетных данных, которая позволяет перечислить различные типы входа с помощью плиток входа в систему. In Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, the Graphical Identification and Authentication (GINA) architecture was replaced with a credential provider model, which made it possible to enumerate different logon types through the use of logon tiles. Обе модели описаны ниже. Both models are described below.
Графическая идентификация и архитектура проверки подлинности Graphical Identification and Authentication architecture
Архитектура модели для идентификации и проверки подлинности (GINA) относится к операционным системам Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows 2000 Server, Windows XP и Windows 2000 Professional. The Graphical Identification and Authentication (GINA) architecture applies to the Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows 2000 Server, Windows XP, and Windows 2000 Professional operating systems. В этих системах каждый интерактивный сеанс входа в систему создает отдельный экземпляр службы WinLogon. In these systems, every interactive logon session creates a separate instance of the Winlogon service. Архитектура GINA загружается в пространство процесса, используемое Winlogon, получает и обрабатывает учетные данные и выполняет вызовы интерфейсов проверки подлинности через Лсалогонусер. The GINA architecture is loaded into the process space used by Winlogon, receives and processes the credentials, and makes the calls to the authentication interfaces through LSALogonUser.
Экземпляры Winlogon для интерактивного входа в сеанс 0. The instances of Winlogon for an interactive logon run in Session 0. В сеансе 0 размещаются системные службы и другие критические процессы, в том числе процесс локального центра безопасности (LSA). Session 0 hosts system services and other critical processes, including the Local Security Authority (LSA) process.
На следующей схеме показан процесс учетных данных для Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows 2000 Server, Windows XP и Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional. The following diagram shows the credential process for Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows 2000 Server, Windows XP, and Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional.
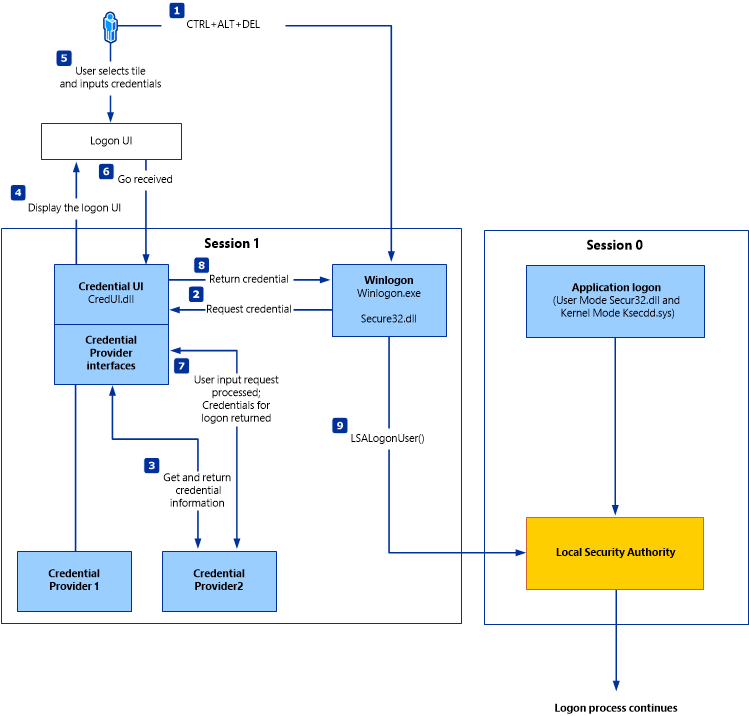
Архитектура поставщика учетных данных Credential provider architecture
Архитектура поставщика учетных данных применяется к версиям, указанным в списке применяется к в начале этого раздела. The credential provider architecture applies to those versions designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic. В этих системах архитектура ввода учетных данных изменилась на расширяемую структуру, используя поставщики учетных данных. In these systems, the credentials input architecture changed to an extensible design by using credential providers. Эти поставщики представлены разными плитками для входа в систему на защищенном рабочем столе, где разрешено любое количество сценариев входа в систему — разные учетные записи одного и того же пользователя и разные методы проверки подлинности, такие как пароль, смарт-карта и биометрия. These providers are represented by the different logon tiles on the secure desktop that permit any number of logon scenarios — different accounts for the same user and different authentication methods, such as password, smart card, and biometrics.
При использовании архитектуры поставщика учетных данных Winlogon всегда запускает пользовательский интерфейс входа после получения события безопасной последовательности. With the credential provider architecture, Winlogon always starts Logon UI after it receives a secure attention sequence event. Пользовательский интерфейс входа запрашивает у каждого поставщика учетных данных количество различных типов учетных данных, для которых настроен поставщик. Logon UI queries each credential provider for the number of different credential types the provider is configured to enumerate. Поставщики учетных данных имеют возможность указать одну из этих плиток по умолчанию. Credential providers have the option of specifying one of these tiles as the default. Когда все поставщики перечисляют плитки, Пользовательский интерфейс входа отображает их пользователю. After all providers have enumerated their tiles, Logon UI displays them to the user. Пользователь взаимодействует с плиткой для предоставления своих учетных данных. The user interacts with a tile to supply their credentials. Пользовательский интерфейс входа отправляет эти учетные данные для проверки подлинности. Logon UI submits these credentials for authentication.
Поставщики учетных данных не являются механизмами принудительного применения. Credential providers are not enforcement mechanisms. Они используются для сбора и сериализации учетных данных. They are used to gather and serialize credentials. Локальный центр безопасности и пакеты проверки подлинности обеспечивают безопасность. The Local Security Authority and authentication packages enforce security.
Поставщики учетных данных регистрируются на компьютере и отвечают за следующее: Credential providers are registered on the computer and are responsible for the following:
Описание учетных данных, необходимых для проверки подлинности. Describing the credential information required for authentication.
Обработка связи и логики с внешними центрами проверки подлинности. Handling communication and logic with external authentication authorities.
Упаковка учетных данных для интерактивного входа в сеть. Packaging credentials for interactive and network logon.
Пакетные учетные данные для интерактивного входа в систему и подключения к сети включают процесс сериализации. Packaging credentials for interactive and network logon includes the process of serialization. Путем сериализации учетных данных плитки для входа в систему могут отображаться в пользовательском интерфейсе входа. By serializing credentials multiple logon tiles can be displayed on the logon UI. Таким образом, ваша организация может управлять отображением входа в систему, таким как пользователи, целевые системы для входа в систему, предварительный доступ к политикам блокировки и разблокировки рабочей станции, используя настроенные поставщики учетных данных. Therefore, your organization can control the logon display such as users, target systems for logon, pre-logon access to the network and workstation lock/unlock policies — through the use of customized credential providers. На одном компьютере может существовать несколько поставщиков учетных данных. Multiple credential providers can co-exist on the same computer.
Поставщики единого входа (SSO) можно разрабатывать как стандартный поставщик учетных данных или как поставщик предварительного доступа для входа. Single sign-on (SSO) providers can be developed as a standard credential provider or as a Pre-Logon-Access Provider.
Каждая версия Windows содержит один поставщик учетных данных по умолчанию и один поставщик предварительного доступа по умолчанию (PLAP), также известный как поставщик единого входа. Each version of Windows contains one default credential provider and one default Pre-Logon-Access Provider (PLAP), also known as the SSO provider. Поставщик единого входа позволяет пользователям устанавливать подключение к сети перед входом на локальный компьютер. The SSO provider permits users to make a connection to a network before logging on to the local computer. При реализации этого поставщика поставщик не перечислит плитки в пользовательском интерфейсе входа. When this provider is implemented, the provider does not enumerate tiles on Logon UI.
Поставщик единого входа предназначен для использования в следующих сценариях: A SSO provider is intended to be used in the following scenarios:
Проверка подлинности сети и вход в систему осуществляется разными поставщиками учетных данных. Network authentication and computer logon are handled by different credential providers. К этому сценарию относятся следующие варианты: Variations to this scenario include:
Пользователь имеет возможность подключиться к сети, например подключение к виртуальной частной сети (VPN), прежде чем войти на компьютер, но это подключение не требуется. A user has the option of connecting to a network, such as connecting to a virtual private network (VPN), before logging on to the computer but is not required to make this connection.
Для получения сведений, используемых во время интерактивной проверки подлинности на локальном компьютере, требуется проверка подлинности сети. Network authentication is required to retrieve information used during interactive authentication on the local computer.
За несколько проверок подлинности сети следует один из других сценариев. Multiple network authentications are followed by one of the other scenarios. Например, пользователь проходит проверку подлинности в поставщике услуг Интернета (ISP), выполняет проверку подлинности в VPN, а затем использует учетные данные учетной записи пользователя для локального входа. For example, a user authenticates to an Internet service provider (ISP), authenticates to a VPN, and then uses their user account credentials to log on locally.
Кэшированные учетные данные отключены, а подключение к службам удаленного доступа через VPN необходимо перед локальным входом для проверки подлинности пользователя. Cached credentials are disabled, and a Remote Access Services connection through VPN is required before local logon to authenticate the user.
У пользователя домена нет локальной учетной записи, настроенной на компьютере, присоединенном к домену, и перед завершением интерактивного входа необходимо установить подключение к службам удаленного доступа через VPN-подключение. A domain user does not have a local account set up on a domain-joined computer and must establish a Remote Access Services connection through VPN connection before completing interactive logon.
Проверка подлинности сети и вход в систему осуществляется с помощью одного и того же поставщика учетных данных. Network authentication and computer logon are handled by the same credential provider. В этом сценарии перед входом в систему пользователь должен подключиться к сети. In this scenario, the user is required to connect to the network before logging on to the computer.
Перечисление плиток входа Logon tile enumeration
Поставщик учетных данных перечисляет плитки входа в следующих экземплярах: The credential provider enumerates logon tiles in the following instances:
Для этих операционных систем, указанных в списке применяется к в начале этого раздела. For those operating systems designated in the Applies to list at the beginning of this topic.
Поставщик учетных данных перечисляет плитки для входа на рабочую станцию. The credential provider enumerates the tiles for workstation logon. Поставщик учетных данных обычно сериализует учетные данные для проверки подлинности в локальном центре безопасности. The credential provider typically serializes credentials for authentication to the local security authority. Этот процесс отображает сведения о плитках для каждого пользователя и конкретных целевых систем каждого пользователя. This process displays tiles specific for each user and specific to each user’s target systems.
Архитектура входа и аутентификации позволяет пользователю использовать плитки, перечисленные поставщиком учетных данных для разблокировки рабочей станции. The logon and authentication architecture lets a user use tiles enumerated by the credential provider to unlock a workstation. Как правило, пользователь, выполнивший вход в систему, является плиткой по умолчанию, но при входе в систему нескольких пользователей отображается множество плиток. Typically, the currently logged-on user is the default tile, but if more than one user is logged on, numerous tiles are displayed.
Поставщик учетных данных перечисляет плитки в ответ на запрос пользователя на изменение пароля или другой частной информации, такой как ПИН-код. The credential provider enumerates tiles in response to a user request to change their password or other private information, such as a PIN. Как правило, пользователь, выполнивший вход в систему, является плиткой по умолчанию; Однако при входе в систему нескольких пользователей отображается множество плиток. Typically, the currently logged-on user is the default tile; however, if more than one user is logged on, numerous tiles are displayed.
Поставщик учетных данных перечисляет плитки на основе сериализованных учетных данных, которые будут использоваться для проверки подлинности на удаленных компьютерах. The credential provider enumerates tiles based on the serialized credentials to be used for authentication on remote computers. Пользовательский интерфейс учетных данных не использует тот же экземпляр поставщика, что и пользовательский интерфейс входа, разблокируйте рабочую станцию или смените пароль. Credential UI does not use the same instance of the provider as the Logon UI, Unlock Workstation, or Change Password. Поэтому сведения о состоянии не могут храниться в поставщике между экземплярами пользовательского интерфейса учетных данных. Therefore, state information cannot be maintained in the provider between instances of Credential UI. Эта структура приводит к одной плитке для каждого удаленного входа в систему, предполагая, что учетные данные правильно сериализованы. This structure results in one tile for each remote computer logon, assuming the credentials have been correctly serialized. Этот сценарий также используется в контроле учетных записей (UAC), который может помочь предотвратить несанкционированные изменения на компьютере, запрашивая у пользователя разрешение или пароль администратора перед тем, как разрешить действия, которые могут повлиять на работу компьютера, или изменить параметры, влияющие на работу других пользователей компьютера. This scenario is also used in User Account Control (UAC), which can help prevent unauthorized changes to a computer by prompting the user for permission or an administrator password before permitting actions that could potentially affect the computer’s operation or that could change settings that affect other users of the computer.
На следующей схеме показан процесс учетных данных для операционных систем, указанных в списке применимые к в начале этого раздела. The following diagram shows the credential process for the operating systems designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic.
Ввод учетных данных для входа в приложение и службу Credential input for application and service logon
Проверка подлинности Windows предназначена для управления учетными данными для приложений или служб, которые не нуждаются в взаимодействии с пользователем. Windows authentication is designed to manage credentials for applications or services that do not require user interaction. Приложения в пользовательском режиме ограничены с точки зрения доступа к системным ресурсам, в то время как службы могут иметь неограниченный доступ к системной памяти и внешним устройствам. Applications in user mode are limited in terms of what system resources they have access to, while services can have unrestricted access to the system memory and external devices.
Системные службы и приложения уровня транспорта обращаются к поставщику поддержки безопасности (SSP) через интерфейс поставщика поддержки безопасности (SSPI) в Windows, который предоставляет функции для перечисления пакетов безопасности, доступных в системе, выбора пакета и использования этого пакета для получения проверенного соединения. System services and transport-level applications access an Security Support Provider (SSP) through the Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) in Windows, which provides functions for enumerating the security packages available on a system, selecting a package, and using that package to obtain an authenticated connection.
При проверке подлинности подключения клиента или сервера: When a client/server connection is authenticated:
Приложение на клиентской стороне соединения отправляет учетные данные на сервер с помощью функции SSPI InitializeSecurityContext (General) . The application on the client side of the connection sends credentials to the server by using the SSPI function InitializeSecurityContext (General) .
Приложение на стороне сервера соединения отвечает с помощью функции SSPI AcceptSecurityContext (General) . The application on the server side of the connection responds with the SSPI function AcceptSecurityContext (General) .
Функции SSPI InitializeSecurityContext (General) и AcceptSecurityContext (General) повторяются до тех пор, пока все необходимые сообщения проверки подлинности не будут передаваться на успешную или неудачную проверку подлинности. The SSPI functions InitializeSecurityContext (General) and AcceptSecurityContext (General) are repeated until all the necessary authentication messages have been exchanged to either succeed or fail authentication.
После проверки подлинности подключения LSA на сервере использует сведения от клиента для создания контекста безопасности, содержащего маркер доступа. After the connection has been authenticated, the LSA on the server uses information from the client to build the security context, which contains an access token.
Затем сервер может вызвать функцию SSPI, ImpersonateSecurityContext чтобы присоединить маркер доступа к потоку олицетворения для службы. The server can then call the SSPI function ImpersonateSecurityContext to attach the access token to an impersonation thread for the service.
Приложения и пользовательский режим Applications and user mode
Пользовательский режим в Windows состоит из двух систем, способных передавать запросы ввода-вывода в соответствующие драйверы режима ядра: систему среды, которая запускает приложения, написанные для множества различных типов операционных систем, и целую систему, которая использует системные функции от имени системы среды. User mode in Windows is composed of two systems capable of passing I/O requests to the appropriate kernel-mode drivers: the environment system, which runs applications written for many different types of operating systems, and the integral system, which operates system-specific functions on behalf of the environment system.
Целая система управляет функциями систем’спеЦифик от имени системы среды и состоит из процесса системы безопасности (LSA), службы рабочей станции и службы сервера. The integral system manages operating system’specific functions on behalf of the environment system and consists of a security system process (the LSA), a workstation service, and a server service. Процесс системы безопасности работает с маркерами безопасности, предоставляет или запрещает доступ к учетным записям пользователей на основе разрешений для ресурсов, обрабатывает запросы на вход и инициирует проверку подлинности входа, а также определяет системные ресурсы, которые должны быть проверены операционной системой. The security system process deals with security tokens, grants or denies permissions to access user accounts based on resource permissions, handles logon requests and initiates logon authentication, and determines which system resources the operating system needs to audit.
Приложения могут работать в пользовательском режиме, где приложение может запускаться как любой участник, в том числе в контексте безопасности локальной системы (SYSTEM). Applications can run in user mode where the application can run as any principal, including in the security context of Local System (SYSTEM). Приложения также могут работать в режиме ядра, где приложение может запускаться в контексте безопасности локальной системы (SYSTEM). Applications can also run in kernel mode where the application can run in the security context of Local System (SYSTEM).
ИНТЕРФЕЙС SSPI доступен через модуль Secur32.dll, который используется для получения интегрированных служб безопасности для проверки подлинности, целостности сообщений и конфиденциальности сообщений. SSPI is available through the Secur32.dll module, which is an API used for obtaining integrated security services for authentication, message integrity, and message privacy. Он обеспечивает уровень абстракции между протоколами уровня приложения и протоколами безопасности. It provides an abstraction layer between application-level protocols and security protocols. Поскольку различным приложениям требуются различные способы идентификации пользователей и проверки подлинности, а также различные способы шифрования данных по сети, SSPI предоставляет способ доступа к динамическим библиотекам (DLL), содержащим различные функции проверки подлинности и шифрования. Because different applications require different ways of identifying or authenticating users and different ways of encrypting data as it travels across a network, SSPI provides a way to access dynamic-link libraries (DLLs) that contain different authentication and cryptographic functions. Эти библиотеки DLL называются поставщиками поддержки безопасности (SSP). These DLLs are called Security Support Providers (SSPs).
Управляемые учетные записи служб и виртуальные учетные записи появились в Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7 для предоставления важных приложений, таких как Microsoft SQL Server и службы IIS (IIS), с изоляцией собственных доменных учетных записей, одновременно устраняя необходимость администратора вручную администрировать имя участника-службы (SPN) и учетные данные для этих учетных записей. Managed service accounts and virtual accounts were introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to provide crucial applications, such as Microsoft SQL Server and Internet Information Services (IIS), with the isolation of their own domain accounts, while eliminating the need for an administrator to manually administer the service principal name (SPN) and credentials for these accounts. Дополнительные сведения об этих функциях и их роли в проверке подлинности см. в документации по управляемым учетным записям служб для Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2 и групповых управляемых учетных записей служб. For more information about these features and their role in authentication, see Managed Service Accounts Documentation for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 and Group Managed Service Accounts Overview.
Службы и режим ядра Services and kernel mode
Несмотря на то, что большинство приложений Windows выполняются в контексте безопасности пользователя, запустившего его, это не относится к службам. Even though most Windows applications run in the security context of the user who starts them, this is not true of services. Многие службы Windows, такие как службы сети и печати, запускаются контроллером служб при запуске компьютера пользователем. Many Windows services, such as network and printing services, are started by the service controller when the user starts the computer. Эти службы могут работать как локальная служба или локальная система и могут продолжать работать после выхода последнего пользователя. These services might run as Local Service or Local System and might continue to run after the last human user logs off.
Обычно службы выполняются в контекстах безопасности, известных как «Локальная система», «Сетевая служба» или «Локальная служба». Services normally run in security contexts known as Local System (SYSTEM), Network Service, or Local Service. В Windows Server 2008 R2 появились службы, работающие под управляемой учетной записью службы, которая является субъектами домена. Windows Server 2008 R2 introduced services that run under a managed service account, which are domain principals.
Перед запуском службы контроллер службы входит в систему с помощью учетной записи, назначенной для службы, а затем представляет учетные данные службы для проверки подлинности LSA. Before starting a service, the service controller logs on by using the account that is designated for the service, and then presents the service’s credentials for authentication by the LSA. Служба Windows реализует программный интерфейс, который диспетчером контроллеров служб может использовать для управления службой. The Windows service implements a programmatic interface that the service controller manager can use to control the service. Служба Windows может запускаться автоматически при запуске системы или вручную с помощью программы управления службами. A Windows service can be started automatically when the system is started or manually with a service control program. Например, когда клиентский компьютер Windows присоединяется к домену, служба сообщений на компьютере подключается к контроллеру домена и открывает защищенный канал. For example, when a Windows client computer joins a domain, the messenger service on the computer connects to a domain controller and opens a secure channel to it. Для получения подключения, прошедшего проверку подлинности, служба должна иметь учетные данные, которым доверяет локальный администратор безопасности удаленного компьютера. To obtain an authenticated connection, the service must have credentials that the remote computer’s Local Security Authority (LSA) trusts. При взаимодействии с другими компьютерами в сети LSA использует учетные данные учетной записи домена локального компьютера, так же как и все остальные службы, работающие в контексте безопасности локальной системы и сетевой службы. When communicating with other computers in the network, LSA uses the credentials for the local computer’s domain account, as do all other services running in the security context of the Local System and Network Service. Службы на локальном компьютере работают от имени системы, поэтому учетные данные не нужно предоставлять LSA. Services on the local computer run as SYSTEM so credentials do not need to be presented to the LSA.
Файл Ksecdd.sys управляет и шифрует эти учетные данные и использует вызов локальной процедуры в LSA. The file Ksecdd.sys manages and encrypts these credentials and uses a local procedure call into the LSA. Файл имеет тип DRV (driver) и известен как поставщик поддержки безопасности в режиме ядра (SSP), и в этих версиях, указанных в списке применимо к в начале этого раздела, используется соответствие стандарту FIPS 140-2 уровня 1. The file type is DRV (driver) and is known as the kernel-mode Security Support Provider (SSP) and, in those versions designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic, is FIPS 140-2 Level 1-compliant.
Режим ядра имеет полный доступ к оборудованию и системным ресурсам компьютера. Kernel mode has full access to the hardware and system resources of the computer. Режим ядра останавливает службы и приложения пользовательского режима на доступ к критическим областям операционной системы, к которым у них нет доступа. The kernel mode stops user-mode services and applications from accessing critical areas of the operating system that they should not have access to.
Локальная система безопасности Local Security Authority
Локальный администратор безопасности (LSA) — это защищенный системный процесс, который выполняет проверку подлинности и регистрирует пользователей на локальном компьютере. The Local Security Authority (LSA) is a protected system process that authenticates and logs users on to the local computer. Кроме того, LSA сохраняет информацию обо всех аспектах локальной безопасности на компьютере (эти аспекты совместно называются локальной политикой безопасности) и предоставляют различные службы для перевода между именами и идентификаторами безопасности (SID). In addition, LSA maintains information about all aspects of local security on a computer (these aspects are collectively known as the local security policy), and it provides various services for translation between names and security identifiers (SIDs). Процесс системы безопасности, служба локального центра безопасности (LSASS), отслеживает политики безопасности и учетные записи, действующие на компьютерную систему. The security system process, Local Security Authority Server Service (LSASS), keeps track of the security policies and the accounts that are in effect on a computer system.
LSA проверяет удостоверение пользователя на основе того, какие из следующих двух сущностей выдавали учетную запись пользователя: The LSA validates a user’s identity based on which of the following two entities issued the user’s account:
Локальный центр безопасности. Local Security Authority. LSA может проверить сведения о пользователе, проверив базу данных диспетчера учетных записей безопасности (SAM), расположенную на том же компьютере. The LSA can validate user information by checking the Security Accounts Manager (SAM) database located on the same computer. На любой рабочей станции или рядовом сервере могут храниться локальные учетные записи пользователей и сведения о локальных группах. Any workstation or member server can store local user accounts and information about local groups. Тем не менее эти учетные записи можно использовать только для доступа к рабочей станции или компьютеру. However, these accounts can be used for accessing only that workstation or computer.
Центр безопасности для локального домена или для доверенного домена. Security authority for the local domain or for a trusted domain. LSA обращается к сущности, выдавшей учетную запись, и запрашивает проверку действительности учетной записи и запрос, полученный от владельца учетной записи. The LSA contacts the entity that issued the account and requests verification that the account is valid and that the request originated from the account holder.
Служба LSASS сохраняет в памяти учетные данные пользователей с активными сеансами Windows. The Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) stores credentials in memory on behalf of users with active Windows sessions. Сохраненные учетные данные позволяют пользователям легко обращаться к сетевым ресурсам, таким как общие файловые ресурсы, почтовые ящики Exchange Server и сайты SharePoint, без повторного ввода учетных данных для каждой удаленной службы. The stored credentials let users seamlessly access network resources, such as file shares, Exchange Server mailboxes, and SharePoint sites, without re-entering their credentials for each remote service.
Служба LSASS способна хранить учетные данных в различных форматах, включая LSASS can store credentials in multiple forms, including:
Зашифрованный обычный текст с возможностью дешифровки Reversibly encrypted plaintext
Билеты Kerberos (билеты на предоставление билета (TGT), билеты службы) Kerberos tickets (ticket-granting tickets (TGTs), service tickets)
Хэш диспетчера LAN (LM) LAN Manager (LM) hash
Если пользователь входит в систему Windows с помощью смарт-карты, LSASS не сохраняет пароль в виде открытого текста, но сохраняет соответствующее значение хэша NT для учетной записи и ПИН-код в виде открытого текста для этой карты. If the user logs on to Windows by using a smart card, LSASS does not store a plaintext password, but it stores the corresponding NT hash value for the account and the plaintext PIN for the smart card. Если для смарт-карты, необходимой для интерактивного входа, включается атрибут учетной записи, то для соответствующего профиля происходит автоматическая генерация произвольного NT-хэша, который используется вместо изначального хэша пароля. If the account attribute is enabled for a smart card that is required for interactive logon, a random NT hash value is automatically generated for the account instead of the original password hash. Хэш пароля, автоматически сгенерированный при установке атрибута, не изменяется. The password hash that is automatically generated when the attribute is set does not change.
Если пользователь входит в систему на компьютере под управлением Windows с паролем, совместимым с хэшами LAN Manager (LM), это средство проверки подлинности находится в памяти. If a user logs on to a Windows-based computer with a password that is compatible with LAN Manager (LM) hashes, this authenticator is present in memory.
Хранение учетных данных в памяти в виде обычного текста нельзя выключить, даже если этого требуют поставщики учетных данных. The storage of plaintext credentials in memory cannot be disabled, even if the credential providers that require them are disabled.
Сохраненные учетные данные напрямую связываются с сеансами входа служба LSASS (LSASS), которые были запущены после последнего перезапуска и не закрываются. The stored credentials are directly associated with the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) logon sessions that have been started after the last restart and have not been closed. Например, сеансы с сохраненными учетными данными LSA создаются, когда пользователь выполняет одно из следующих действий. For example, LSA sessions with stored LSA credentials are created when a user does any of the following:
Выполняет вход в локальный сеанс или сеанс протокол удаленного рабочего стола (RDP) на компьютере. Logs on to a local session or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) session on the computer
Запускает задание с помощью команды RunAs Runs a task by using the RunAs option
Запускает на компьютере активную службу Windows Runs an active Windows service on the computer
Запускает назначенное или пакетное задание Runs a scheduled task or batch job
Запускает на локальном компьютере задание с помощью средства удаленного администрирования. Runs a task on the local computer by using a remote administration tool
В некоторых обстоятельствах секреты LSA, являющиеся секретными частями данных, которые доступны только для СИСТЕМНЫХ процессов, хранятся на жестком диске. In some circumstances, the LSA secrets, which are secret pieces of data that are accessible only to SYSTEM account processes, are stored on the hard disk drive. Некоторые из этих секретов представляют собой учетные данные, которые должны сохраниться после перезагрузки и хранящиеся на жестком диске в зашифрованном виде. Some of these secrets are credentials that must persist after reboot, and they are stored in encrypted form on the hard disk drive. Учетные данные, хранящиеся в виде секретов LSA, могут включать Credentials stored as LSA secrets might include:
Пароль учетной записи домен Active Directory служб компьютера (AD DS) Account password for the computer’s Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) account
Пароли учетных записей служб Windows, настроенных на компьютере Account passwords for Windows services that are configured on the computer
Пароли учетных записей настроенных назначенных заданий Account passwords for configured scheduled tasks
Пароли учетных записей для пулов приложений IIS и веб-сайтов. Account passwords for IIS application pools and websites
Пароли для учетных записей Майкрософт Passwords for Microsoft accounts
Операционная система клиента, появившаяся в Windows 8.1, обеспечивает дополнительную защиту для LSA, чтобы предотвратить чтение памяти и внедрение кода незащищенными процессами. Introduced in Windows 8.1, the client operating system provides additional protection for the LSA to prevent reading memory and code injection by non-protected processes. Эта защита повышает безопасность для учетных данных, которые LSA хранит и управляет. This protection increases security for the credentials that the LSA stores and manages.
Дополнительные сведения об этих дополнительных целях защиты см. в разделе Настройка дополнительной защиты LSA. For more information about these additional protections, see Configuring Additional LSA Protection.
Кэшированные учетные данные и проверка Cached credentials and validation
Механизмы проверки полагаются на представление учетных данных во время входа в систему. Validation mechanisms rely on the presentation of credentials at the time of logon. Однако если компьютер отключен от контроллера домена и пользователь выполняет показ учетных данных домена, Windows использует процесс кэшированных учетных данных в механизме проверки. However, when the computer is disconnected from a domain controller, and the user is presenting domain credentials, Windows uses the process of cached credentials in the validation mechanism.
Каждый раз, когда пользователь входит в домен, Windows кэширует предоставленные учетные данные и сохраняет их в кусте безопасности в реестре операционной системы. Each time a user logs on to a domain, Windows caches the credentials supplied and stores them in the security hive in the registry of the operation system.
С помощью кэшированных учетных данных пользователь может войти в домен, не подключаясь к контроллеру домена в этом домене. With cached credentials, the user can log on to a domain member without being connected to a domain controller within that domain.
Хранилище учетных данных и проверка Credential storage and validation
Не всегда желательно использовать один набор учетных данных для доступа к различным ресурсам. It is not always desirable to use one set of credentials for access to different resources. Например, администратор может использовать администратора, а не учетные данные пользователя при доступе к удаленному серверу. For example, an administrator might want to use administrative rather than user credentials when accessing a remote server. Аналогично, если пользователь обращается к внешним ресурсам, таким как банковский счет, он может использовать только учетные данные, которые отличаются от учетных данных домена. Similarly, if a user accesses external resources, such as a bank account, he or she can only use credentials that are different than their domain credentials. В следующих разделах описываются различия в управлении учетными данными между текущими версиями операционных систем Windows и операционными системами Windows Vista и Windows XP. The following sections describe the differences in credential management between current versions of Windows operating systems and the Windows Vista and Windows XP operating systems.
Процессы для учетных данных удаленного входа Remote logon credential processes
Протокол удаленного рабочего стола (RDP) управляет учетными данными пользователя, подключающегося к удаленному компьютеру с помощью клиента удаленный рабочий стол, который появился в Windows 8. The Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) manages the credentials of the user who connects to a remote computer by using the Remote Desktop Client, which was introduced in Windows 8. Учетные данные в форме с открытым текстом отправляются на целевой узел, где узел пытается выполнить процесс проверки подлинности, и при успешном подключении подключает пользователя к разрешенным ресурсам. The credentials in plaintext form are sent to the target host where the host attempts to perform the authentication process, and, if successful, connects the user to allowed resources. Протокол RDP не сохраняет учетные данные на клиенте, но учетные данные домена пользователя хранятся в LSASS. RDP does not store the credentials on the client, but the user’s domain credentials are stored in the LSASS.
В Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows 8.1 Ограниченный административный режим обеспечивает дополнительную защиту сценариев удаленного входа в систему. Introduced in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, Restricted Admin mode provides additional security to remote logon scenarios. Этот режим удаленный рабочий стол приводит к тому, что клиентское приложение выполняет запрос входа в сеть с помощью одностороннего функции NT (НТОВФ) или использует билет службы Kerberos при проверке подлинности на удаленном узле. This mode of Remote Desktop causes the client application to perform a network logon challenge-response with the NT one-way function (NTOWF) or use a Kerberos service ticket when authenticating to the remote host. После проверки подлинности администратора администратор не имеет соответствующих учетных данных в LSASS, так как они не были предоставлены удаленному узлу. After the administrator is authenticated, the administrator does not have the respective account credentials in LSASS because they were not supplied to the remote host. Вместо этого у администратора есть учетные данные учетной записи компьютера для сеанса. Instead, the administrator has the computer account credentials for the session. Учетные данные администратора не предоставляются удаленному узлу, поэтому действия выполняются в качестве учетной записи компьютера. Administrator credentials are not supplied to the remote host, so actions are performed as the computer account. Ресурсы также ограничены учетной записью компьютера, и администратор не может получить доступ к ресурсам с собственной учетной записью. Resources are also limited to the computer account, and the administrator cannot access resources with his own account.
Процесс автоматического перезапуска учетных данных входа Automatic restart sign-on credential process
Когда пользователь входит на устройство Windows 8.1, LSA сохраняет учетные данные пользователя в зашифрованной памяти, доступ к которой возможен только LSASS.exe. When a user signs in on a Windows 8.1 device, LSA saves the user credentials in encrypted memory that are accessible only by LSASS.exe. Если Центр обновления Windows инициирует автоматический перезапуск без присутствия пользователя, эти учетные данные используются для настройки автоматического входа пользователя в систему. When Windows Update initiates an automatic restart without user presence, these credentials are used to configure Autologon for the user.
При перезапуске пользователь автоматически входит в систему с помощью механизма автоматического входа, а затем компьютер дополнительно блокируется для защиты сеанса пользователя. On restart, the user is automatically signed in via the Autologon mechanism, and then the computer is additionally locked to protect the user’s session. Блокировка инициируется с помощью Winlogon, в то время как управление учетными данными выполняется с помощью LSA. The locking is initiated through Winlogon whereas the credential management is done by LSA. Автоматически войдя в систему и блокируя сеанс пользователя на консоли, приложения блокировки экрана пользователя перезапускаются и доступны. By automatically signing in and locking the user’s session on the console, the user’s lock screen applications is restarted and available.
Сохранение имен пользователей и паролей в Windows Vista и Windows XP Stored user names and passwords in Windows Vista and Windows XP
В Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista и Windows XP, сохраненные имена пользователей и пароли на панели управления, упрощают управление и использование нескольких наборов учетных данных для входа в систему, включая сертификаты X. 509, используемые со смарт-картами и учетные данные Windows Live (теперь называется учетная запись Майкрософт). In Windows Server 2008 , Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows XP, Stored User Names and Passwords in Control Panel simplifies the management and use of multiple sets of logon credentials, including X.509 certificates used with smart cards and Windows Live credentials (now called Microsoft account). Учетные данные — часть профиля пользователя хранятся до тех пор, пока они не понадобятся. The credentials — part of the user’s profile — are stored until needed. Это действие может повысить уровень безопасности для каждого отдельного ресурса, гарантируя, что при компрометации одного пароля он не подвергается безопасности. This action can increase security on a per-resource basis by ensuring that if one password is compromised, it does not compromise all security.
После того как пользователь войдет в систему и попытается получить доступ к дополнительным ресурсам, защищенным паролем, например к общему ресурсу на сервере, и если учетные данные пользователя по умолчанию не достаточны для получения доступа, будут запрошены сохраненные имена пользователей и пароли . After a user logs on and attempts to access additional password-protected resources, such as a share on a server, and if the user’s default logon credentials are not sufficient to gain access, Stored User Names and Passwords is queried. Если в сохраненных именах пользователей и паролях были сохранены альтернативные учетные данные с правильными регистрационными данными, эти учетные данные используются для получения доступа. If alternate credentials with the correct logon information have been saved in Stored User Names and Passwords, these credentials are used to gain access. В противном случае пользователю предлагается ввести новые учетные данные, которые затем можно сохранить для повторного использования в сеансе входа в систему или во время следующего сеанса. Otherwise, the user is prompted to supply new credentials, which can then be saved for reuse, either later in the logon session or during a subsequent session.
Применяются следующие ограничения: The following restrictions apply:
Если сохраненные имена пользователей и пароли содержат недопустимые или неверные учетные данные для определенного ресурса, доступ к ресурсу будет запрещен, а диалоговое окно сохраненные имена пользователей и пароли не появится. If Stored User Names and Passwords contains invalid or incorrect credentials for a specific resource, access to the resource is denied, and the Stored User Names and Passwords dialog box does not appear.
Сохраненные имена пользователей и пароли хранят учетные данные только для NTLM, протокола Kerberos, учетная запись Майкрософт (ранее Windows Live ID) и проверки подлинности SSL (SSL). Stored User Names and Passwords stores credentials only for NTLM, Kerberos protocol, Microsoft account (formerly Windows Live ID), and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) authentication. Некоторые версии Internet Explorer поддерживают собственный кэш для обычной проверки подлинности. Some versions of Internet Explorer maintain their own cache for basic authentication.
Эти учетные данные становятся зашифрованными частью локального профиля пользователя в каталоге \Documents and Сеттингс\усернаме\аппликатион Дата\микрософт\кредентиалс. These credentials become an encrypted part of a user’s local profile in the \Documents and Settings\Username\Application Data\Microsoft\Credentials directory. В результате эти учетные данные могут перемещаться с пользователем, если политика сети пользователя поддерживает перемещаемые профили пользователей. As a result, these credentials can roam with the user if the user’s network policy supports Roaming User Profiles. Однако если пользователь копирует сохраненные имена пользователей и пароли на два разных компьютера и изменяет учетные данные, связанные с ресурсом на одном из этих компьютеров, это изменение не распространяется на сохраненные имена пользователей и пароли на втором компьютере. However, if the user has copies of Stored User Names and Passwords on two different computers and changes the credentials that are associated with the resource on one of these computers, the change is not propagated to Stored User Names and Passwords on the second computer.
Хранилище Windows и диспетчер учетных данных Windows Vault and Credential Manager
Диспетчер учетных данных появился в Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7 как функция панели управления для хранения имен пользователей и паролей и управления ими. Credential Manager was introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 as a Control Panel feature to store and manage user names and passwords. Диспетчер учетных данных позволяет пользователям хранить учетные данные, относящиеся к другим системам и веб-сайтам, в безопасном хранилище Windows. Credential Manager lets users store credentials relevant to other systems and websites in the secure Windows Vault. Некоторые версии Internet Explorer используют эту функцию для проверки подлинности на веб-сайтах. Some versions of Internet Explorer use this feature for authentication to websites.
Управление учетными данными с помощью диспетчера учетных данных контролируется пользователем локального компьютера. Credential management by using Credential Manager is controlled by the user on the local computer. Чтобы пользователям было удобно регистрироваться в поддерживаемых браузерах и Windows-приложениях, они могут сохранять и хранить учетные данные с этих ресурсов. Users can save and store credentials from supported browsers and Windows applications to make it convenient when they need to sign in to these resources. Учетные данные сохраняются в специальных зашифрованных папках на компьютере в профиле пользователя. Credentials are saved in special encrypted folders on the computer under the user’s profile. Приложения, поддерживающие эту функцию (с помощью API диспетчера учетных данных), такие как веб-браузеры и приложения, могут предоставлять правильные учетные данные другим компьютерам и веб-сайтам в процессе входа в систему. Applications that support this feature (through the use of the Credential Manager APIs), such as web browsers and apps, can present the correct credentials to other computers and websites during the logon process.
Когда веб-сайт, приложение или другой компьютер запрашивают проверку подлинности с помощью NTLM или протокола Kerberos, появляется диалоговое окно, в котором можно установить флажок обновить учетные данные по умолчанию или Сохранить пароль . When a website, an application, or another computer requests authentication through NTLM or the Kerberos protocol, a dialog box appears in which you select the Update Default Credentials or Save Password check box. Это диалоговое окно, позволяющее пользователю сохранять учетные данные локально, создается приложением, которое поддерживает API-интерфейсы диспетчера учетных данных. This dialog box that lets a user save credentials locally is generated by an application that supports the Credential Manager APIs. Если пользователь устанавливает флажок Сохранить пароль , диспетчер учетных данных отслеживает имя пользователя, пароль и связанные сведения для используемой службы проверки подлинности. If the user selects the Save Password check box, Credential Manager keeps track of the user’s user name, password, and related information for the authentication service that is in use.
При следующем использовании службы Диспетчер учетных данных автоматически предоставляет учетные данные, хранящиеся в хранилище Windows. The next time the service is used, Credential Manager automatically supplies the credential that is stored in the Windows Vault. Если данные не принимаются, пользователю предлагается ввести правильную информацию для получения доступа. If it is not accepted, the user is prompted for the correct access information. Если доступ предоставляется с новыми учетными данными, то диспетчер учетных данных перезаписывает предыдущие учетные данные с новым, а затем сохраняет новые учетные данные в хранилище Windows. If access is granted with the new credentials, Credential Manager overwrites the previous credential with the new one and then stores the new credential in the Windows Vault.
База данных диспетчера учетных записей безопасности Security Accounts Manager database
Диспетчер учетных записей безопасности (SAM) — это база данных, в которой хранятся локальные учетные записи пользователей и группы. The Security Accounts Manager (SAM) is a database that stores local user accounts and groups. Он имеется в каждой операционной системе Windows; Однако при присоединении компьютера к домену Active Directory управляет учетными записями домена в Active Directory доменах. It is present in every Windows operating system; however, when a computer is joined to a domain, Active Directory manages domain accounts in Active Directory domains.
Например, клиентские компьютеры под управлением операционной системы Windows участвуют в сетевом домене, взаимодействующем с контроллером домена, даже если никто из пользователей не вошел в систему. For example, client computers running a Windows operating system participate in a network domain by communicating with a domain controller even when no human user is logged on. Чтобы инициировать обмен данными, компьютер должен иметь активную учетную запись в домене. To initiate communications, the computer must have an active account in the domain. Прежде чем принимать подключения от компьютера, LSA на контроллере домена проверяет подлинность удостоверения компьютера, а затем конструирует контекст безопасности компьютера так же, как и для участника безопасности. Before accepting communications from the computer, the LSA on the domain controller authenticates the computer’s identity and then constructs the computer’s security context just as it does for a human security principal. Этот контекст безопасности определяет удостоверение и возможности пользователя или службы на определенном компьютере или пользователя, службы или компьютера в сети. This security context defines the identity and capabilities of a user or service on a particular computer or a user, service, or computer on a network. Например, маркер доступа, содержащийся в контексте безопасности, определяет ресурсы (такие как файловый ресурс или принтер), к которым можно получить доступ, и действия (например, чтение, запись или изменение), которые могут быть выполнены этим участником, пользователем, компьютером или службой на этом ресурсе. For example, the access token contained within the security context defines the resources (such as a file share or printer) that can be accessed and the actions (such as Read, Write, or Modify) that can be performed by that principal — a user, computer, or service on that resource.
Контекст безопасности пользователя или компьютера может отличаться от одного компьютера к другому, например, когда пользователь входит в систему на сервере или на рабочую станцию, отличную от основной рабочей станции пользователя. The security context of a user or computer can vary from one computer to another, such as when a user logs on to a server or a workstation other than the user’s own primary workstation. Он также может отличаться от одного сеанса к другому, например, когда администратор изменяет права и разрешения пользователя. It can also vary from one session to another, such as when an administrator modifies the user’s rights and permissions. Кроме того, контекст безопасности обычно отличается, если пользователь или компьютер работает на автономной основе, в сети или в составе домена Active Directory. In addition, the security context is usually different when a user or computer is operating on a stand-alone basis, in a network, or as part of an Active Directory domain.
Локальные домены и доверенные домены Local domains and trusted domains
Если между двумя доменами существует отношение доверия, механизмы проверки подлинности для каждого домена полагаются на допустимость проверки подлинности, поступающих из другого домена. When a trust exists between two domains, the authentication mechanisms for each domain rely on the validity of the authentications coming from the other domain. Отношения доверия помогают предоставить контролируемый доступ к общим ресурсам в домене ресурсов (доверяющем домене), убедившись, что входящие запросы на аутентификацию поступают от доверенного центра (доверенного домена). Trusts help to provide controlled access to shared resources in a resource domain (the trusting domain) by verifying that incoming authentication requests come from a trusted authority (the trusted domain). Таким образом, отношения доверия действуют как мосты, позволяющие проходить только проверенные запросы проверки подлинности между доменами. In this way, trusts act as bridges that let only validated authentication requests travel between domains.
Как конкретное отношение доверия проходит проверку подлинности, зависит от того, как оно настроено. How a specific trust passes authentication requests depends on how it is configured. Отношения доверия могут быть односторонними, предоставляя доступ из доверенного домена к ресурсам в доверяющем домене или двусторонним образом, предоставляя доступ из каждого домена к ресурсам в другом домене. Trust relationships can be one-way, by providing access from the trusted domain to resources in the trusting domain, or two-way, by providing access from each domain to resources in the other domain. Отношения доверия также являются нетранзитивными. в этом случае доверие существует только между двумя доменами партнерских партнеров или транзитивным. в этом случае доверие автоматически распространяется на любые другие домены, которым доверяет любой из партнеров. Trusts are also either nontransitive, in which case a trust exists only between the two trust partner domains, or transitive, in which case a trust automatically extends to any other domains that either of the partners trusts.
Сведения о доверительных отношениях доменов и лесов в отношении проверки подлинности см. в разделе делегированная проверка подлинности и доверительные отношения. For information about domain and forest trust relationships regarding authentication, see Delegated Authentication and Trust Relationships.
Сертификаты в проверке подлинности Windows Certificates in Windows authentication
Инфраструктура открытых ключей (PKI) — это сочетание программного обеспечения, технологий шифрования, процессов и служб, которые позволяют Организации защищать свои коммуникации и бизнес-транзакции. A public key infrastructure (PKI) is the combination of software, encryption technologies, processes, and services that enable an organization to secure its communications and business transactions. Возможности PKI для защиты связи и бизнес-транзакций основаны на обмене цифровыми сертификатами между прошедшими проверку подлинности пользователями и доверенными ресурсами. The ability of a PKI to secure communications and business transactions is based on the exchange of digital certificates between authenticated users and trusted resources.
Цифровой сертификат — это электронный документ, содержащий сведения о сущности, которой он принадлежит, сущности, которой он был выдан, уникальный серийный номер или другая уникальная идентификация, даты выдачи и срока действия, а также цифровой отпечаток. A digital certificate is an electronic document that contains information about the entity it belongs to, the entity it was issued by, a unique serial number or some other unique identification, issuance and expiration dates, and a digital fingerprint.
Проверка подлинности — это процесс определения того, может ли удаленный узел быть доверенным. Authentication is the process of determining if a remote host can be trusted. Чтобы установить надежность, удаленный узел должен предоставить приемлемый сертификат проверки подлинности. To establish its trustworthiness, the remote host must provide an acceptable authentication certificate.
Удаленные узлы устанавливают надежность, получая сертификат из центра сертификации (ЦС). Remote hosts establish their trustworthiness by obtaining a certificate from a certification authority (CA). Центр сертификации может, в свою очередь, иметь сертификацию от более высокого центра, что создает цепочку доверия. The CA can, in turn, have certification from a higher authority, which creates a chain of trust. Чтобы определить, является ли сертификат надежным, приложение должно определить удостоверение корневого центра сертификации, а затем определить, является его надежным. To determine whether a certificate is trustworthy, an application must determine the identity of the root CA, and then determine if it is trustworthy.
Аналогичным образом удаленный узел или локальный компьютер должен определить, является ли сертификат, представленный пользователем или приложением, подлинным. Similarly, the remote host or local computer must determine if the certificate presented by the user or application is authentic. Сертификат, представленный пользователем с помощью LSA и SSPI, оценивается на подлинность на локальном компьютере для локального входа в сеть или в домене через хранилища сертификатов в Active Directory. The certificate presented by the user through the LSA and SSPI is evaluated for authenticity on the local computer for local logon, on the network, or on the domain through the certificate stores in Active Directory.
Для создания сертификата данные проверки подлинности проходят через алгоритмы хэширования, например алгоритм SHA-1 (SHA1), для создания дайджеста сообщений. To produce a certificate, authentication data passes through hash algorithms, such as Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (SHA1), to produce a message digest. Затем дайджест сообщения подписывается с помощью закрытого ключа отправителя, чтобы подтвердить, что дайджест сообщения был создан отправителем. The message digest is then digitally signed by using the sender’s private key to prove that the message digest was produced by the sender.
SHA1 используется по умолчанию в Windows 7 и Windows Vista, но был изменен на SHA2 в Windows 8. SHA1 is the default in Windows 7 and Windows Vista, but was changed to SHA2 in Windows 8.
Аутентификация по смарт-карте Smart card authentication
Технология смарт-карт — это пример проверки подлинности на основе сертификатов. Smart card technology is an example of certificate-based authentication. Вход в сеть со смарт-картой обеспечивает строгую форму проверки подлинности, так как она использует идентификацию и подтверждение владения при проверке подлинности пользователя в домене. Logging on to a network with a smart card provides a strong form of authentication because it uses cryptography-based identification and proof of possession when authenticating a user to a domain. Службы сертификации Active Directory (AD CS) обеспечивают идентификацию на основе криптографии путем выдачи сертификата входа для каждой смарт-карты. Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) provides the cryptographic-based identification through the issuance of a logon certificate for each smart card.
Дополнительные сведения о проверке подлинности смарт-карт см. в статье техническое руководство по смарт-картам Windows. For information about smart card authentication, see the Windows Smart Card Technical Reference.
Технология виртуальных смарт-карт появилась в Windows 8. Virtual smart card technology was introduced in Windows 8. Он сохраняет сертификат смарт-карты на компьютере, а затем защищает его с помощью микросхемы безопасности доверенный платформенный модуль (TPM) на устройстве (TPM). It stores the smart card’s certificate in the PC, and then protects it by using the device’s tamper-proof Trusted Platform Module (TPM) security chip. Таким образом, ПК фактически превращается в смарт-карту, которая должна получать ПИН-код пользователя для проверки подлинности. In this way, the PC actually becomes the smart card which must receive the user’s PIN in order to be authenticated.
Удаленная и беспроводная аутентификация Remote and wireless authentication
Проверка подлинности удаленных и беспроводных сетей — еще одна технология, использующая сертификаты для аутентификации. Remote and wireless network authentication is another technology that uses certificates for authentication. Служба проверки подлинности в Интернете (IAS) и виртуальные частные сетевые серверы используют расширяемую проверку подлинности Protocol-Transport уровня безопасности (EAP-TLS), защищенный протокол PEAP или протокол IPsec для проверки подлинности на основе сертификатов для многих типов сетевого доступа, включая VPN и беспроводные подключения. The Internet Authentication Service (IAS) and virtual private network servers use Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Level Security (EAP-TLS), Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP), or Internet Protocol security (IPsec) to perform certificate-based authentication for many types of network access, including virtual private network (VPN) and wireless connections.
Сведения о проверке подлинности на основе сертификатов в сети см. в разделе Проверка подлинности доступа к сети и сертификаты. For information about certificate-based authentication in networking, see Network access authentication and certificates.