- How to free up disk space in Windows 7
- Clear up disk space as fast as possible
- How to free up disk space in Windows 7 32/64 bit
- Additional options to free up disk space in Windows 7
- ① Disable Hibernate
- ② Decrease disk space usage for System Restore
- ③ Move paging file
- ④ Uninstall unused programs
- ⑤ Transfer files and modify program settings
- ⑥ NTFS Compression
- ⑦ Expand C drive to larger size
- How to Clean Up and Make Space on Your Windows 10 “C” Drive
- Delete Temporary Files Manually
- Use Storage Sense
- Scan for Large Files on Your Hard Drive
- Uninstall Windows Shovelware and Space-Hungry Apps
- Use Disk Clean-Up Utility
- Disable Hibernation
- Delete Browser Cache and Cookies
- Remove Old Windows Update Files, Previous Installations
How to free up disk space in Windows 7
by Andy, Updated on: September 3, 2020
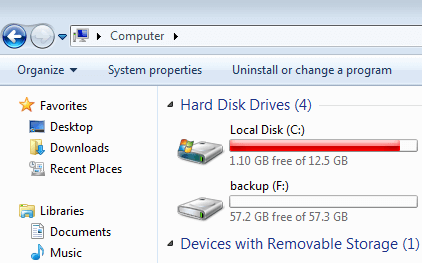
Windows 7 has been released for such a long time, many people insert solid state drive (SSD) when updating computers. The read and write speed of SSD is much faster than traditional mechanical disk, so it is good choice for Operating System and applications. But on the other hand, the size of SSD is much smaller, because it is still expensive.
No matter you use SSD, traditional disk or even hardware RAID array, system C drive is running out of space , because Windows Updates, applications and many other kinds of files write into C drive continuously every day.
What to do when it happens, replace this disk with another new one? HDD manufacturers will be glad if you do that, because you may buy several disks every year. In fact, most of low disk space issue of C drive can be solved except you use a very small disk. In this article, I’ll introduce how to free up disk space in Windows 7 32/64 bit with native Disk Cleanup utility and other methods. In addition, you’d better expand C drive to larger size with free space in other volumes.
Clear up disk space as fast as possible
When the system C drive is filling up, your computer may not perform as well as before. In general, you’ll suffer from computer performance down. If C drive becomes almost full, your computer may stuck, reboot unexpectedly or even crash. It will be too late if the computer cannot boot because of no free disk space in system partition C drive. So try to free up space in Windows 7 as fast as possible.
How to free up disk space in Windows 7 32/64 bit
To reclaim/free up disk space in Windows 7, the first choice and easy way is running the built-in Disk Cleanup tool. Windows 7 Disk Cleanup utility can remove most common types of unnecessary and junk files fast and safely.
Steps to free up disk space in Windows 7 with Disk Cleanup utility:
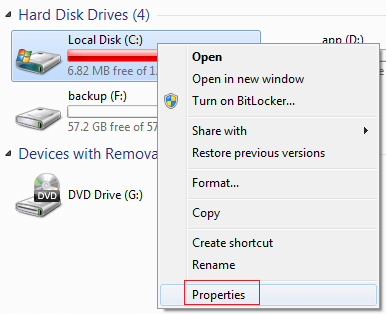
Step 1: Open File Explorer , right click C drive and click Properties :
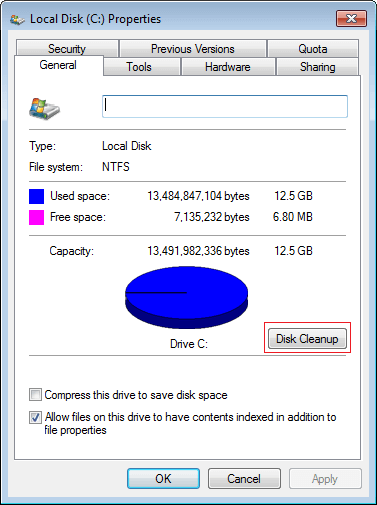
Step 2: Click Disk Cleanup
Another way: press Windows and R keys together, type cleanmgr and press Enter, and then select C: drive in the drop-down list.
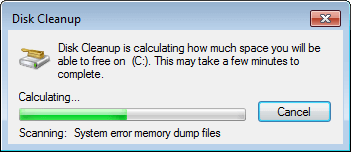
Wait for Disk Cleanup to calculate how much space can be cleaned up safely. This process can last for a few seconds to a few minutes. The time depends on your computer performance and the amount of junk files.
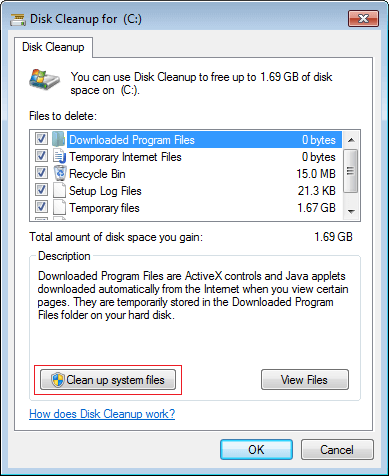
Step 3: Select the files that you want to delete and click OK to proceed. Highlight each option you’ll see corresponding description. (Make sure that you’ve clicked the check-boxes for each type of files that you want to clear up.)
Step 4: Repeat to clean up system files in the same window. Within one minute or two, the same Disk cleanup menu will appear with additional types of files to delete.
- Service Pack Backup : Windows keeps old versions of files updated by service packs. Be aware that if you clear these files, you’ll be unable to uninstall the service pack.
- Temporary Windows installation : These installation files are used by Windows setup and left over from the installation process, feel free to delete these files.
- Windows Updates : Windows retains a copy of each newly-installed Windows Update, deletes older versions of updates that you no longer need.
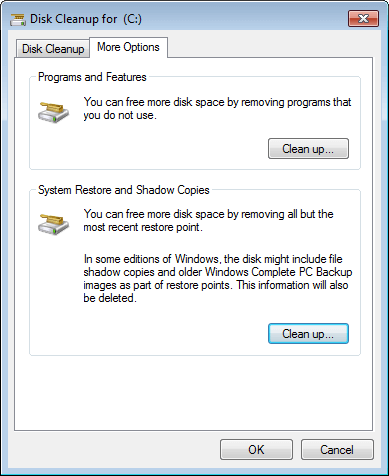
Step 5: To get more free space, you may switch to More Options tab, where you can clean up installed programs and System Restore points.
This native Disk Cleanup utility is very useful to the computers that never free up space in Windows 7.
Additional options to free up disk space in Windows 7
If Windows 7 Disk Cleanup cannot free up enough disk space, there are additional options for you:
① Disable Hibernate
Hibernation uses large amount of disk space. From administrative command prompt, type «powercfg -h off» to get that space back. (Don’t turn it off if you use the feature).
② Decrease disk space usage for System Restore
Windows 7 keeps backups of lots of system files every time something major such as driver installation and software installations happens, and after a while this can take up lots of space. You may completely turn it off to release all disk space or decrease the space usage for System Restore.
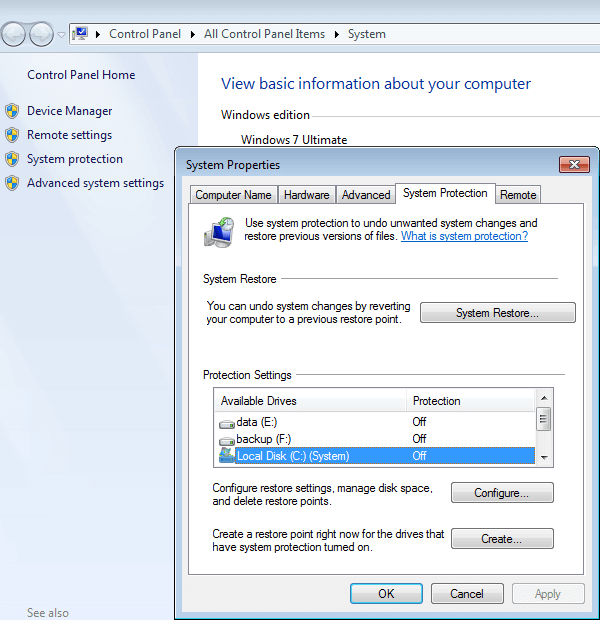
To open Windows 7 System Restore:
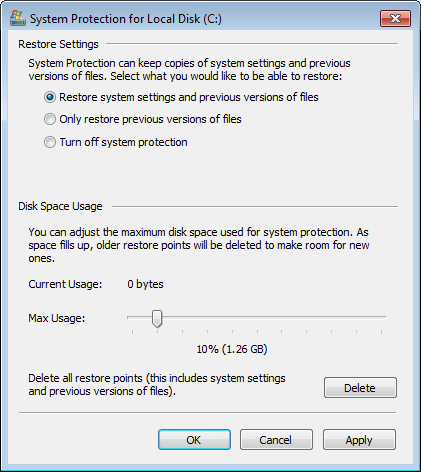
Click Windows > Control Panel > System > System protection
To turn off or decrease disk space usage:
Click Configure in System Protection tab, there are 3 options and select one, you can adjust the maximum disk space usage or system protection by dragging on Max Usage bar.
Turning off system protection won’t delete all restore points automatically, to do this, you should click the Delete button on the bottom.
③ Move paging file
Page file is used by Windows as RAM and it’s located in C drive by default, you can decrease it or set it to other volume.
- Press Windows and R on keyboard to start Run.
- Input sysdm.cpl ,3 and press Enter.
- Click Settings under Performance in Advanced tab.
- Click Change under Virtual Memory.
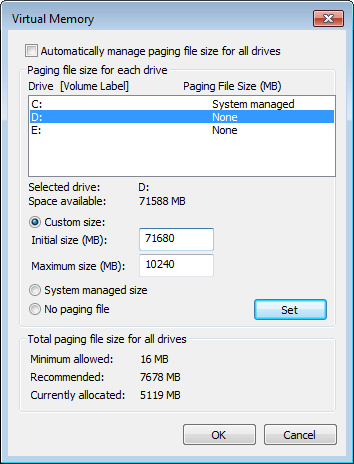
- Uncheck Automatically manage paging file size for all drives on the top.
- Select D: or other drive, enter amount of Initial size and Maximum size in Customer size radio box, and then click Set.
- Select C: drive and select No paging file radio box, then click Set.
- Click OK. (It requires reboot to take affect)
④ Uninstall unused programs
Consider uninstall the programs that you no longer or seldom use, the more program uninstalled, the more disk space will be released.
⑤ Transfer files and modify program settings
Some program such as Games, Projects and Videos output very large files, you may modify the default output path to other volume and transfer these files to new locations.
⑥ NTFS Compression
This is a great feature of NTFS files system. If you’ve got a bunch of folders with old crap in them, but you don’t want to delete them, then consider compressing them to save disk space.
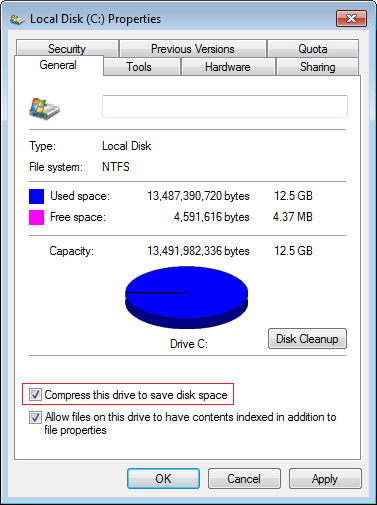
To do this, right click C drive and click Properties, click the check-box of Compress this drive to save disk space.
To a Windows 7 computer that never free up disk space, you may reclaim over 10 Gigabytes disk space, however, this is not the final step.
Many people feedback that C drive becomes full again after freeing up disk space. Because new junk files are generated continuously, so 10GB free space will be eaten up quickly. To completely solve this problem, you’d better expand C drive as large as possible.
⑦ Expand C drive to larger size
Disk partitions are created while installing Windows or built by OEM manufacturers, but you can change size of each partitions without reinstalling OS/programs or losing data, of course with safe partitioning software.
Better than other software, NIUBI Partition Editor has unique 1 Second Rollback , Virtual Mode and Cancel-at-well technologies to protect system and data. In addition, it is much faster because of its special file-moving algorithm. It has free edition for Windows 7/8/10 home computer users.
This step is very important if you cannot reclaim enough free space with Disk Cleanup utility and to the computers that C drive are created small.
Download NIUBI Partition Editor Free and follow the steps in the video to resize and extend C drive in Windows 7.
Besides resizing allocated partition, this tool helps you do many other disk partition management operations such as merge, copy, convert, defrag, wipe, hide, scan partition, etc.
After expanding system partition C, you still need to consider following steps:
- Install new programs to separate drive such as D.
- Change file output path of installed programs to other large drives, especially to the programs for games, videos, photos and projects.
- Run Windows 7 Disk Cleanup once a month to delete new generated junk files.
How to Clean Up and Make Space on Your Windows 10 “C” Drive
The all-important “C” drive is, for most people, the core of the PC, where their operating system is installed and all the crucial system files are kept. Inevitably, this is also the drive that gets filled up most easily due to endless Windows updates, downloaded files that you forget about, and the fact that by default, everything saves to the “C” drive.
Here we show you how to clean up your drive, recover some space, and subsequently get it running nicely and quickly again.
Delete Temporary Files Manually
Below, we show you some tricks that clean out your various temporary files automatically, but those methods (like Storage Sense and Disk Clean-up) won’t do a complete job of clearing out temporary files, and there’s a good chance that the biggest, most hard-drive-hogging temporary files will remain in your Temp folder for a bit longer. (The automatic methods will wait for files to reach a certain age – one week, usually – before deleting them.)
Note: make sure you’re not running anything when deleting temporary files manually. If you delete temporary files related to an app you’re currently running, it may crash, and you may lose whatever you were working on at that moment.
To find your main temporary files folder, the default directory is “C:\Users\Rob\AppData\Local\Temp” (or you can hit Win + R , then enter %temp% ).
To see how much space the Temp folder is taking up, select everything in it using Ctrl + A , then right-click any file and click Properties. If you’re happy to go ahead with the delete, make sure everything is selected using Ctrl + A , right-click, then click Delete.
Use Storage Sense
Windows 10 has a handy feature called Storage Sense, which monitors the storage space on your PC, then jumps in and cleans things up if you’re running low. It does basic things like clean your Recycle Bin, remove old files in your Downloads folder, and delete temporary files on your PC.
To turn this feature on, go to “Settings -> System,” then click “Storage” in the pane on the left.
Click “Configure Storage Sense or run it now,” then in the new window click the slider under Storage Sense so that it’s “On.” You can then use the drop-down menu below to choose whether you want it to run when you’re low on space, daily, weekly or monthly.
In Storage Sense, you’ll also see that you can get it to automatically delete files in your Recycle Bin that have been there for a certain amount of time, and even files in your Downloads folder (which, from my experience, is definitely a place where unused files tend to outstay their welcome).
Scan for Large Files on Your Hard Drive
Using Windows Explorer, you can scan your entire hard drive for files based on their size. The amount of times I’ve found hefty redundant files sitting around for years is unbelievable.
To do this search, open a Windows Explorer window, select your “C” drive, then click the “Search (C:)” search box at the top-right of the window.
Type “size:” and you’ll get a bunch of autofill options showing varying sizes of files to filter for. You can use one of these presets, or if you want to get more specific about the size of file you’re looking for, you can type “size:>1gb” to look for files over 1GB in size and so on.
You can delete files directly from the results or right-click, then select “Sort by -> Size” to order them by size and quickly see which ones need deleting. Just by testing this, I’ve discovered an old Android 7.1 VM that I really don’t need any more. Just don’t delete anything that looks important. (For example, stuff from the “C:Windows folder” or game files that tend to be quite large.)
Uninstall Windows Shovelware and Space-Hungry Apps
In the “Apps & Features” window (you’ll find it by right-clicking the Start button), you can sort the list by “Size” to see which applications are the most HDD-hungry. You may be surprised by the results and may wish to remove apps as appropriate. Think about whether you really need all those space-hungry apps and delete as appropriate.
Another thing that may surprise you is that you’re the proud owner of games like Bubble Witch 3 Saga and Minecraft, which you never wanted in the first place! Simply uninstalling them from the “Apps & Features” list won’t suffice, however, and you will need to remove them using the Powershell. To do this, read our guide on how to uninstall pre-installed Windows apps.
Use Disk Clean-Up Utility
You’re probably aware of Windows’s built-in Disk Clean-Up utility but have not been using it. This is the first place to look to free up some space. To start using it, launch Windows Explorer, right-click on the C drive and select “Properties” from the list.
Once the Properties window is open, click “Disk Cleanup” to open the utility. Here, in the “files to delete” box, select all the checkboxes like System memory error dump files, Recycle Bin, set up log files, etc.
Once you have selected all the checkboxes you want, click on “OK” to free up the disk space occupied by the above files. How much space you free up depends on how badly you’ve neglected your “C” drive. As you can see below, I haven’t taken good care of the C drive at all. Shame on me.
Disable Hibernation
Hibernation is a handy feature you can use to easily turn off your computer while saving the current state so you can resume your work when you power it on. That said, it can take up a huge amount of disk space, as it reserves the amount of space on your hard drive equal to how much content is saved in your RAM. (So potentially, the more RAM you have, the more disk space it uses.)
To disable hibernation, open your Windows Control Panel by pressing Win + X and selecting “Control Panel” from the list. Once the control panel is opened, select “Power Options.”
2. Click on the “choose what the power buttons do” link in the pane on the left. This action will take you to the system settings window.
3. Click “Change settings that are currently unavailable.” This action will enable all the disabled options.
4. Scroll down and un-check the “Hibernate” checkbox to disable hibernation in Windows 10.
Delete Browser Cache and Cookies
Temporary Internet files like the browser cache and cookies take up a little bit of your C drive space, so clearing those temporary files will grant you some free space.
In Chrome, go to “Settings -> Advanced -> Privacy and security,” then “Clear browsing data.”
In Firefox, go to “Options -> Privacy & Security,” then under “History,” select “clear your recent history.”
In Microsoft Edge, go to “Settings -> Clear browsing data -> Choose what to clear,” and make sure to select the “Cached data” and “Cookies” options.
Remove Old Windows Update Files, Previous Installations
Windows has a tendency to hold onto old (and mostly redundant) system files. For the most part you can delete these files, particularly if you installed your current version of Windows over a previous version. To do this:
1. Open Windows Explorer, right-click the C drive and select “Properties.”
2. Click “Disk CleanUp,” then in the new window click “Clean up system files” to open the advanced disk cleanup window.
4. Select the “Windows upgrade log files” checkbox and, if you have anything there, the “Previous Windows installation(s)” checkbox. Unbeknownst to me, my secondhand laptop still has the “Windows.old” folder from the previous user, using up a whopping 31.5GB of hard drive real estate.
There are other checkboxes here, but for the most part they don’t use up a ton of space and can be left alone. When you’re ready, click “OK” to clean up your hard drive.
It’s good to go through this routine every now and then, but it’s advisable to make sure it doesn’t fill up in the first place. If you want to keep streamlining your Windows setup, see how to install Chromium on Windows 10. We also have a guide on how you can view network adapter details in Windows 10.
Related:
Content Manager at Make Tech Easier. Enjoys Android, Windows, and tinkering with retro console emulation to breaking point.