- Windows commands
- Prerequisites
- Command shell overview
- Command-line reference A-Z
- Синтаксис командной строки компилятора Compiler Command-Line Syntax
- command line option syntax error. Type command /? for help
- Replies (1)
- Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
- Command line syntax
- Options and commands
- Command line argument examples
- Target a specific window
- Open a new profile instance
- Target a directory
- Multiple tabs
- Multiple panes
- Multiple tabs and panes
- Tab title
- Using application title (Preview)
- Tab color
- Color scheme (Preview)
- Tab focus
- Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
- Single quoted parameters
- Escaped quotes
- Using start
Windows commands
All supported versions of Windows (server and client) have a set of Win32 console commands built in.
This set of documentation describes the Windows Commands you can use to automate tasks by using scripts or scripting tools.
Prerequisites
The information that is contained in this topic applies to:
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel)
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows 10
- Windows 8.1
Command shell overview
The Command shell was the first shell built into Windows to automate routine tasks, like user account management or nightly backups, with batch (.bat) files. With Windows Script Host you could run more sophisticated scripts in the Command shell. For more information, see cscript or wscript. You can perform operations more efficiently by using scripts than you can by using the user interface. Scripts accept all Commands that are available at the command line.
Windows has two command shells: The Command shell and PowerShell. Each shell is a software program that provides direct communication between you and the operating system or application, providing an environment to automate IT operations.
PowerShell was designed to extend the capabilities of the Command shell to run PowerShell commands called cmdlets. Cmdlets are similar to Windows Commands but provide a more extensible scripting language. You can run Windows Commands and PowerShell cmdlets in Powershell, but the Command shell can only run Windows Commands and not PowerShell cmdlets.
For the most robust, up-to-date Windows automation, we recommend using PowerShell instead of Windows Commands or Windows Script Host for Windows automation.
You can also download and install PowerShell Core, the open source version of PowerShell.
Incorrectly editing the registry may severely damage your system. Before making the following changes to the registry, you should back up any valued data on the computer.
To enable or disable file and directory name completion in the Command shell on a computer or user logon session, run regedit.exe and set the following reg_DWOrd value:
To set the reg_DWOrd value, use the hexadecimal value of a control character for a particular function (for example, 0 9 is Tab and 0 08 is Backspace). User-specified settings take precedence over computer settings, and command-line options take precedence over registry settings.
Command-line reference A-Z
To find information about a specific command, in the following A-Z menu, click the letter that the command starts with, and then click the command name.
Синтаксис командной строки компилятора Compiler Command-Line Syntax
В командной строке CL используется следующий синтаксис: The CL command line uses the following syntax:
В следующей таблице описаны входные данные для команды CL. The following table describes input to the CL command.
| Ввод Entry | Значение Meaning |
|---|---|
| Параметр option | Один или несколько параметров CL. One or more CL options. Обратите внимание, что все параметры применяются ко всем указанным исходным файлам. Note that all options apply to all specified source files. Параметры задаются символами косой черты (/) или тире (-). Options are specified by either a forward slash (/) or a dash (-). Если параметр принимает аргумент, в описании параметра указывается, разрешено ли пространство между параметром и аргументами. If an option takes an argument, the option’s description documents whether a space is allowed between the option and the arguments. Имена параметров (кроме параметра/HELP) чувствительны к регистру. Option names (except for the /HELP option) are case sensitive. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Порядок параметров CL . See Order of CL Options for more information. |
| file | Имя одного или нескольких исходных файлов, OBJ-файлов или библиотек. The name of one or more source files, .obj files, or libraries. CL компилирует исходные файлы и передает имена OBJ-файлов и библиотек компоновщику. CL compiles source files and passes the names of the .obj files and libraries to the linker. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе синтаксис имени файла cl . See CL Filename Syntax for more information. |
| lib lib | Одно или несколько имен библиотек. One or more library names. CL передает эти имена компоновщику. CL passes these names to the linker. |
| командный файл command-file | Файл, содержащий несколько параметров и имен файлов. A file that contains multiple options and filenames. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Командные файлы CL . See CL Command Files for more information. |
| Ссылка — opt link-opt | Один или несколько параметров компоновщика компилятором MSVC. One or more MSVC Linker Options. CL передает эти параметры компоновщику. CL passes these options to the linker. |
Можно указать любое количество параметров, имен файлов и библиотек, если число символов в командной строке не превышает 1024, ограничение, заданное операционной системой. You can specify any number of options, filenames, and library names, as long as the number of characters on the command line does not exceed 1024, the limit dictated by the operating system.
Дополнительные сведения о возвращаемом значении cl.exe см. в разделе возвращаемое значение cl.exe . For information about the return value of cl.exe, see Return Value of cl.exe .
Длина входных данных командной строки в 1024 символов не гарантируется в будущих выпусках Windows. The command-line input limit of 1024 characters is not guaranteed to remain the same in future releases of Windows.
command line option syntax error. Type command /? for help
I’m trying to install MATLAB but every time I initiate the installation there is «command line option syntax error» for Microsoft visual C++ 2005 Redistributable. I have installed » Microsoft visual C++ 2005 Redistributable» but still this error continues. I have also modified variable value but still problem continues. I am facing above problem since 1709 update of windows 10.
Moved from: (Windows / Windows 10 / Performance & system failures)
Replies (1)
Issues with installing an application are usually occurring due to software incompatibility issues. Your concern might need an in-depth technical assistance and we might need to redirect you to our Microsoft TechNet forums. For us to direct you to the correct forum category, we would need you to answer the following questions:
- Which build and edition of Windows 10 is installed on your computer?
- Is your device connected to a domain network?
- Is the same issue occurring even when you are using other user profiles?
In the meantime, we suggest performing a clean boot before installing the program. Let us know if the same issue persists.
We are looking forward to your response.
6 people found this reply helpful
Was this reply helpful?
Sorry this didn’t help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
You can use wt.exe to open a new instance of Windows Terminal from the command line. You can also use the execution alias wt instead.
If you built Windows Terminal from the source code on GitHub, you can open that build using wtd.exe or wtd .
Command line syntax
The wt command line accepts two types of values: options and commands. Options are a list of flags and other parameters that can control the behavior of the wt command line as a whole. Commands provide the action, or list of actions separated by semicolons, that should be implemented. If no command is specified, then the command is assumed to be new-tab by default.
To display a help message listing the available command line arguments, enter: wt -h , wt —help , wt -? , or wt /? .
Options and commands
Below is the full list of supported commands and options for the wt command line.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| —help , -h , -? , /? | Displays the help message. |
| —maximized , -M | Launches the terminal maximized. |
| —fullscreen , -F | Launches the terminal as full screen. |
| —focus , -f | Launches the terminal in the focus mode. Can be combined with maximized . |
| —window , -w | Launches the terminal in a specific window. |
| Command | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| new-tab , nt | —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , commandline , —title , —tabColor | Creates a new tab. |
| split-pane , sp | -H, —horizontal , -V, —vertical , —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , —title , —tabColor , —size, -s size , commandline , -D, —duplicate | Splits a new pane. |
| focus-tab , ft | —target, -t tab-index | Focuses on a specific tab. |
| move-focus , mf | direction | Move focus between panes in the given direction. Accepts one of up , down , left , right . |
When opening Windows Terminal from cmd (Command Prompt), if you want to use your custom «cmd» profile settings, you will need to use the command wt -p cmd . Otherwise, to run your default profile settings, just use wt cmd .
The -D, —duplicate parameter for split-pane is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Command line argument examples
Commands may vary slightly depending on which command line you’re using.
Target a specific window
The ability for the —window,-w parameter to accept window names is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Below are examples of how to target specific windows using the —window,-w option.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Open a new profile instance
To open a new terminal instance, in this case the command will open the profile named «Ubuntu-18.04», enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
The -p flag is used to specify the Windows Terminal profile that should be opened. Substitute «Ubuntu-18.04» with the name of any terminal profile that you have installed. This will always open a new window. Windows Terminal is not yet capable of opening new tabs or panes in an existing instance.
Target a directory
To specify the folder that should be used as the starting directory for the console, in this case the d:\ directory, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Multiple tabs
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, in this case a Command Prompt profile and a PowerShell profile, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Multiple panes
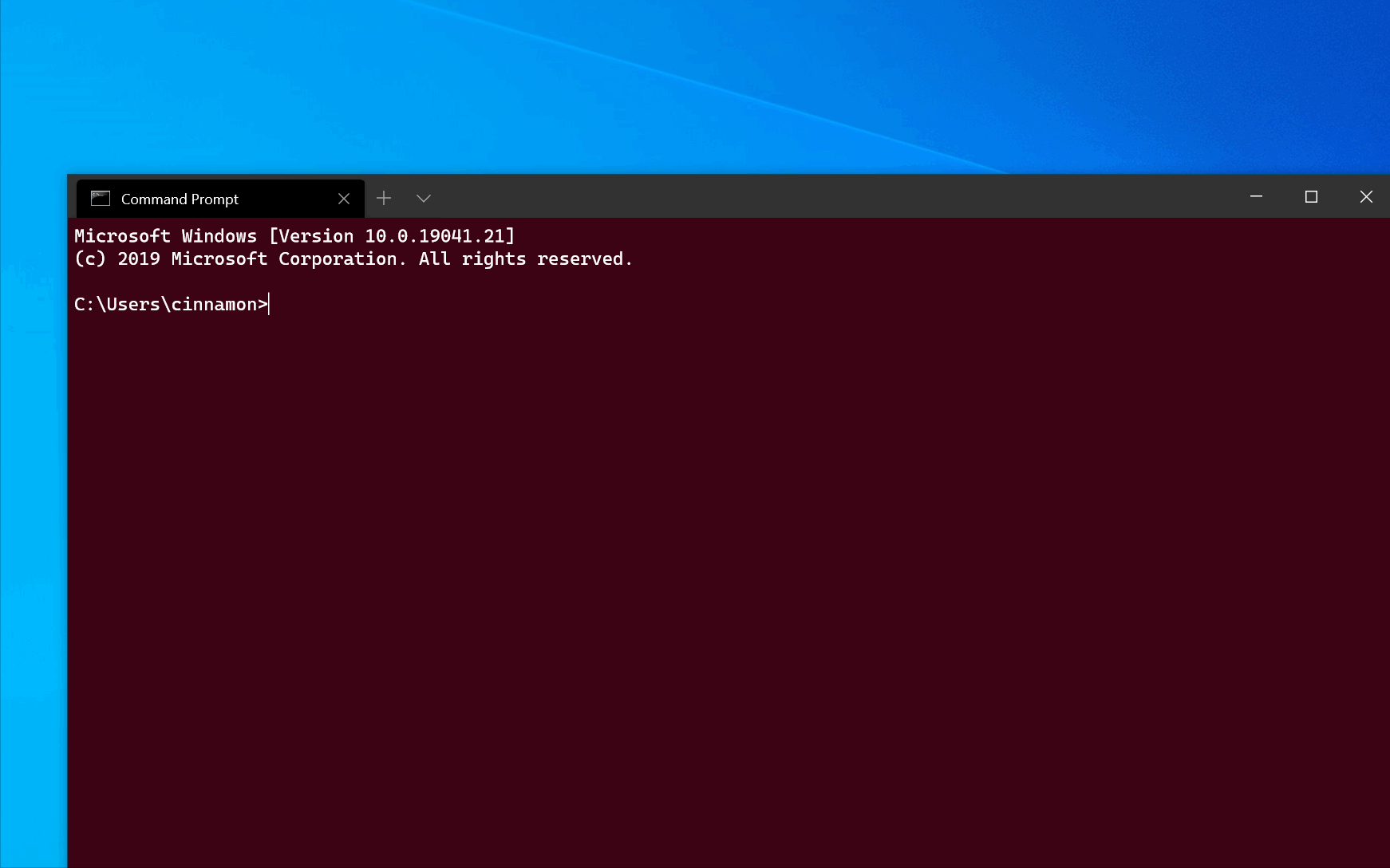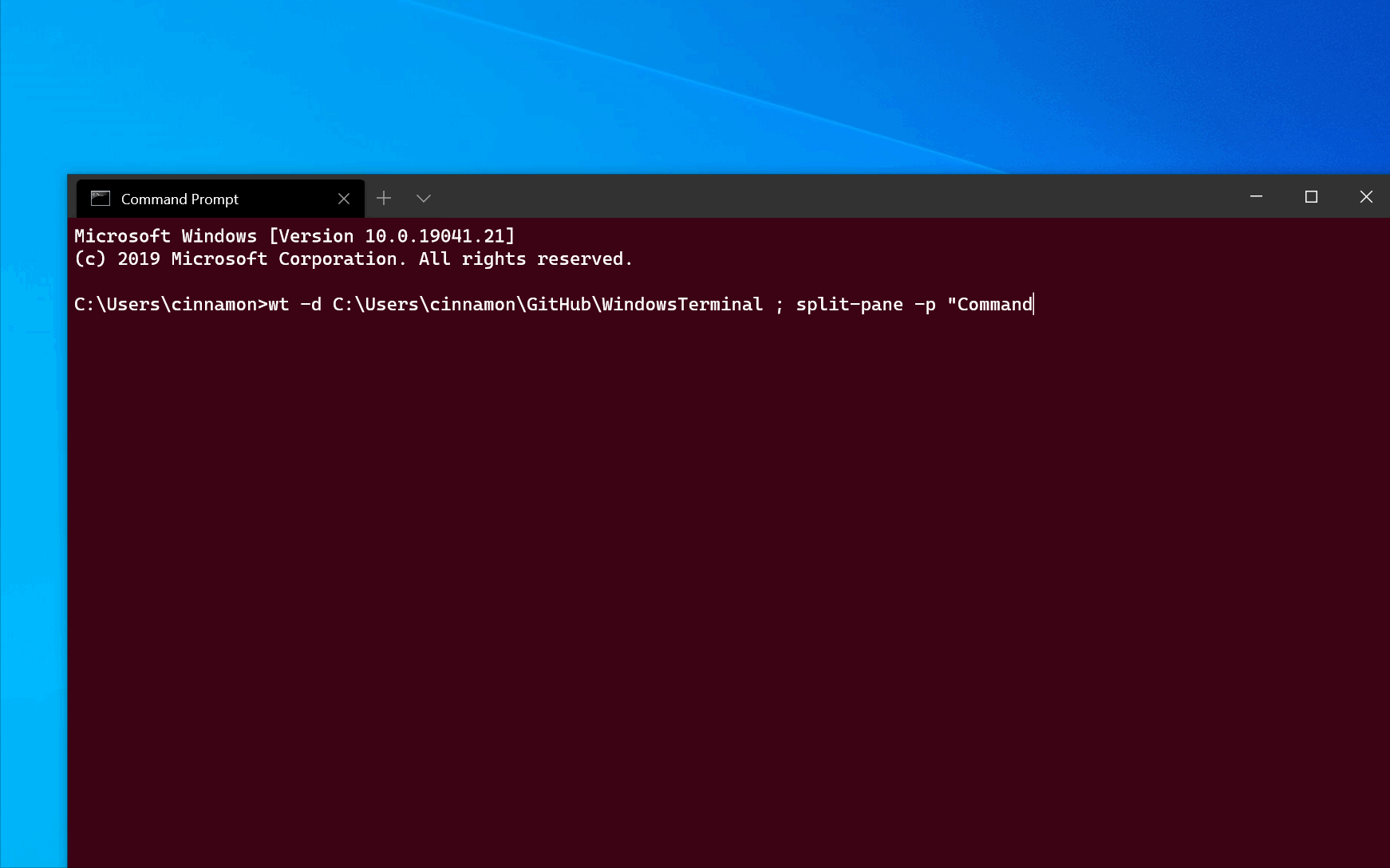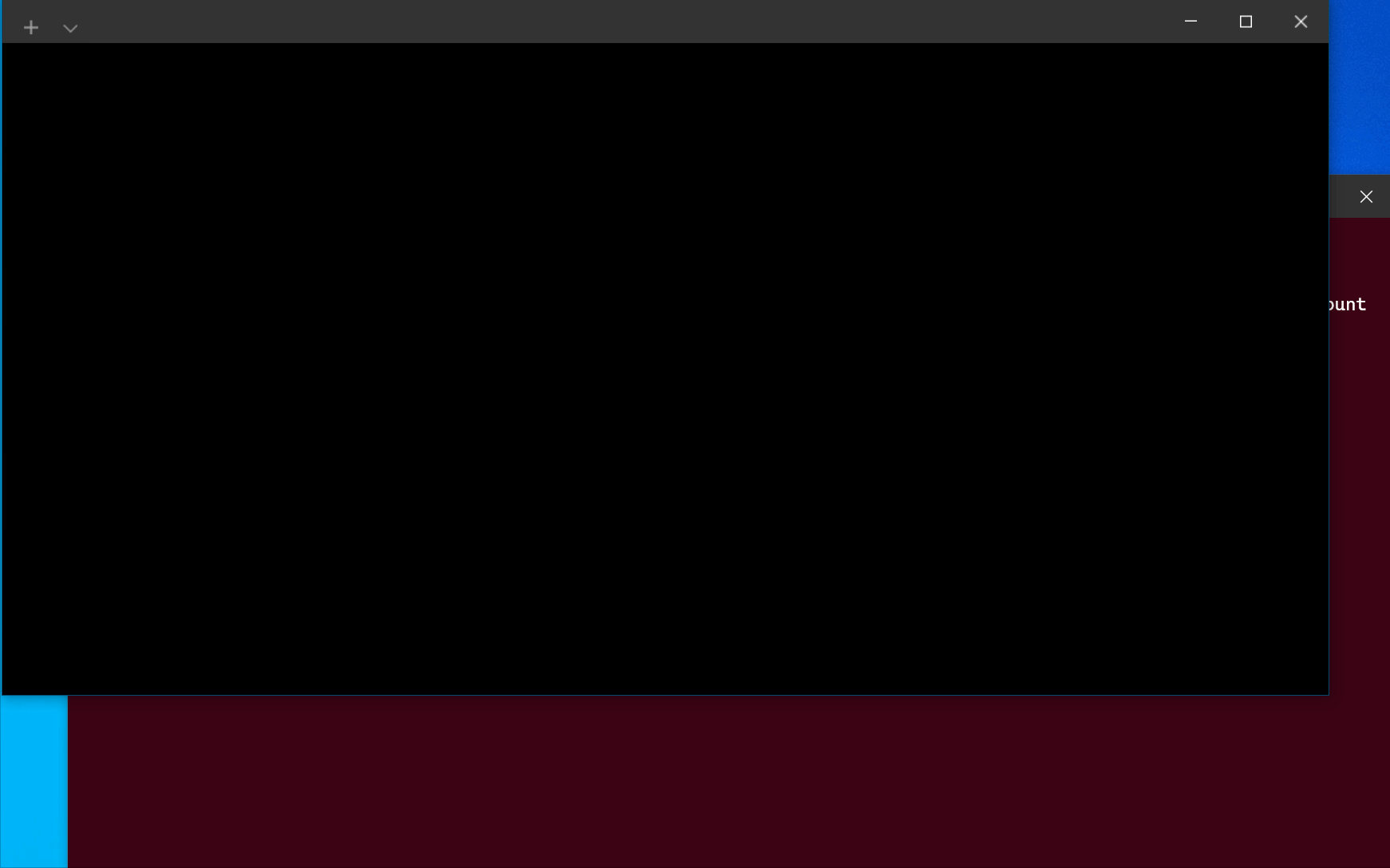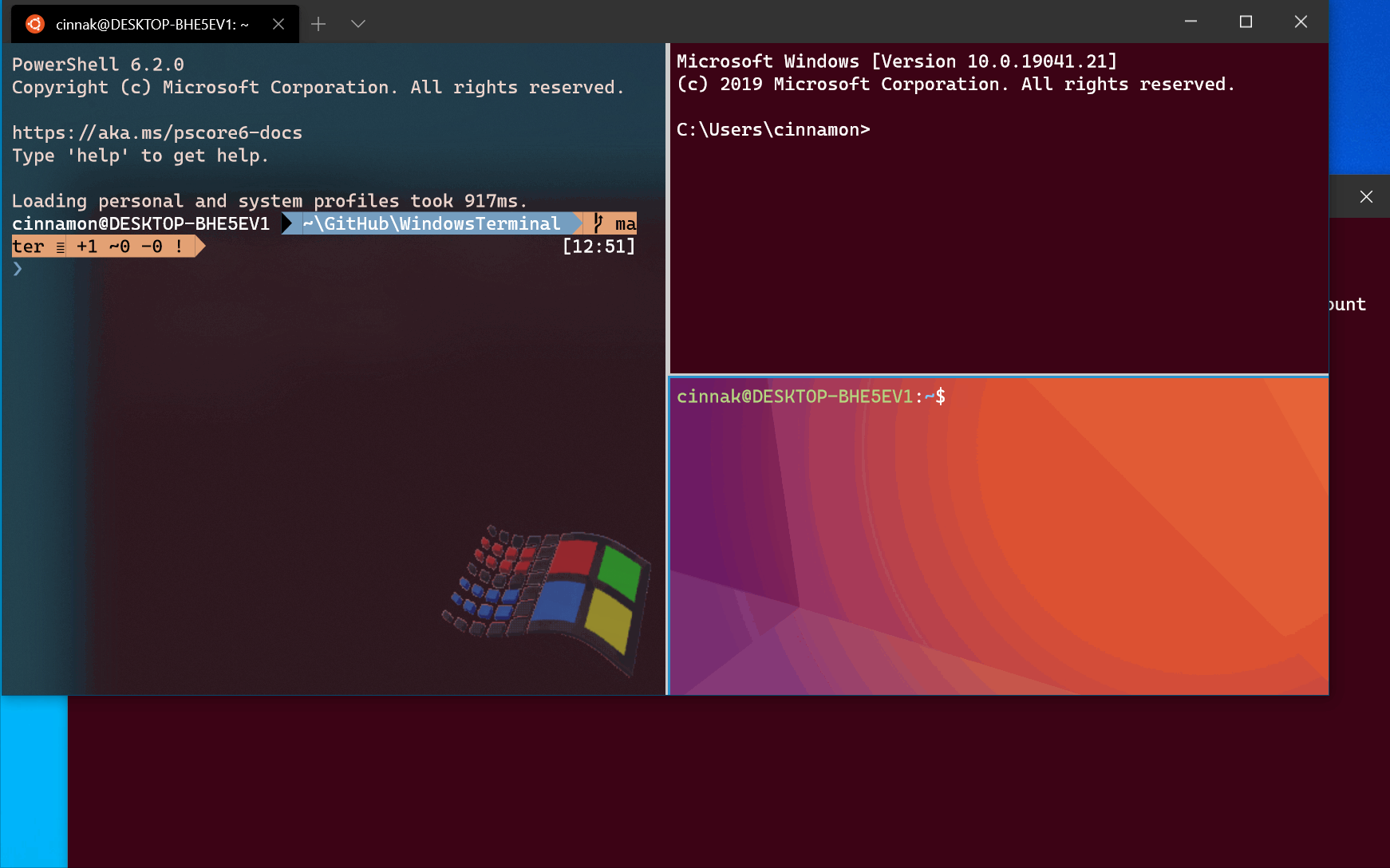
To open a new terminal instance with one tab containing three panes running a Command Prompt profile, a PowerShell profile, and your default profile running a WSL command line, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
The -H flag (or —horizontal ) indicates that you would like the panes to be split horizontally. The -V flag (or —vertical ) indicates that you would like the panes split vertically.
Multiple tabs and panes
The new-tab and split-pane commands can be sequenced to get multiple tabs, each with split panes. To open a new terminal instance with two tabs, each with two panes running a Command Prompt and a WSL command line, with each tab in a different directory, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands. Note to specify a Windows directory as the starting directory for wsl.exe that two backslashes \\ are required.
Tab title
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab titles, use the —title argument. To set the title of each tab when opening two tabs, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; forward-slash + semicolon separates commands.
Using application title (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance allowing applications within it to set the tab title by sending title change messages, use the —useApplicationTitle flag. To suppress these messages, use the —suppressApplicationTitle flag. If none of these flags are provided, the behavior is inherited from the profile’s settings. To open a tab with title tabname that will not be overridden by the application, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab color
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab colors, use the —tabColor argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile, but can be overridden as well using the tab color picker. In the following example, a new terminal is created with two tabs of different colors:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
When —tabColor is set for a tab, it is associated with the first pane of this tab. Hence in a tab with multiple panes, the color will be applied only if the first pane is in focus. To set the tab color for additional panes, you will need to add the —tabColor parameter to the split-pane subcommand as well. In the example below, a tab with two panes is created with tab colors specified for each pane:
Color scheme (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance with a specific color scheme (instead of the colorScheme set in the profile), use the —colorScheme argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab focus
To open a new terminal instance with a specific tab in focus, use the -t flag (or —target ), along with the tab-index number. To open your default profile in the first tab and the «Ubuntu-18.04» profile focused in the second tab ( -t 1 ), enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
Windows Terminal uses the semicolon character ; as a delimiter for separating commands in the wt command line. Unfortunately, PowerShell also uses ; as a command separator. To work around this, you can use the following tricks to run multiple wt commands from PowerShell. In all the following examples, a new terminal window is created with three panes — one running Command Prompt, one with PowerShell, and the last one running WSL.
The following examples use the Start-Process command to run wt . For more information on why the terminal uses Start-Process , see Using start below.
Single quoted parameters
In this example, the wt parameters are wrapped in single quotes ( ‘ ). This syntax is useful if nothing is being calculated.
Escaped quotes
When passing a value contained in a variable to the wt command line, use the following syntax:
Note the usage of ` to escape the double-quotes ( » ) around «Windows PowerShell» in the -p parameter to the split-pane parameter.
Using start
All the above examples explicitly used start to launch the terminal.
The following examples do not use start to run the command line. Instead, there are two other methods of escaping the command line:
- Only escaping the semicolons so that PowerShell will ignore them and pass them straight to wt .
- Using —% , so PowerShell will treat the rest of the command line as arguments to the application.
In both of these examples, the newly created Windows Terminal window will create the window by correctly parsing all the provided command-line arguments.
However, these methods are not recommended currently, as PowerShell will wait for the newly-created terminal window to be closed before returning control to PowerShell. By default, PowerShell will always wait for Windows Store applications (like Windows Terminal) to close before returning to the prompt. Note that this is different than the behavior of Command Prompt, which will return to the prompt immediately.