- Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
- Command line syntax
- Options and commands
- Command line argument examples
- Target a specific window
- Open a new profile instance
- Target a directory
- Multiple tabs
- Multiple panes
- Multiple tabs and panes
- Tab title
- Using application title (Preview)
- Tab color
- Color scheme (Preview)
- Tab focus
- Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
- Single quoted parameters
- Escaped quotes
- Using start
- Windows Terminal Preview 1.5 Release
- Full hyperlink support
- Audible bell 🔔
- Profile icon emoji support
- Tab switcher order setting
- Desktop wallpaper background image
- Focus launch modes
- Disable animations
- Command palette improvements
- Reconfigured > prefix
- Back button
- Bold matching search terms
- New actions
- Open tab rename text box
- Toggle pane zoom
- Bug fixes
- Top contributors
Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
You can use wt.exe to open a new instance of Windows Terminal from the command line. You can also use the execution alias wt instead.
If you built Windows Terminal from the source code on GitHub, you can open that build using wtd.exe or wtd .
Command line syntax
The wt command line accepts two types of values: options and commands. Options are a list of flags and other parameters that can control the behavior of the wt command line as a whole. Commands provide the action, or list of actions separated by semicolons, that should be implemented. If no command is specified, then the command is assumed to be new-tab by default.
To display a help message listing the available command line arguments, enter: wt -h , wt —help , wt -? , or wt /? .
Options and commands
Below is the full list of supported commands and options for the wt command line.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| —help , -h , -? , /? | Displays the help message. |
| —maximized , -M | Launches the terminal maximized. |
| —fullscreen , -F | Launches the terminal as full screen. |
| —focus , -f | Launches the terminal in the focus mode. Can be combined with maximized . |
| —window , -w | Launches the terminal in a specific window. |
| Command | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| new-tab , nt | —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , commandline , —title , —tabColor | Creates a new tab. |
| split-pane , sp | -H, —horizontal , -V, —vertical , —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , —title , —tabColor , —size, -s size , commandline , -D, —duplicate | Splits a new pane. |
| focus-tab , ft | —target, -t tab-index | Focuses on a specific tab. |
| move-focus , mf | direction | Move focus between panes in the given direction. Accepts one of up , down , left , right . |
When opening Windows Terminal from cmd (Command Prompt), if you want to use your custom «cmd» profile settings, you will need to use the command wt -p cmd . Otherwise, to run your default profile settings, just use wt cmd .
The -D, —duplicate parameter for split-pane is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Command line argument examples
Commands may vary slightly depending on which command line you’re using.
Target a specific window
The ability for the —window,-w parameter to accept window names is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Below are examples of how to target specific windows using the —window,-w option.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Open a new profile instance
To open a new terminal instance, in this case the command will open the profile named «Ubuntu-18.04», enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
The -p flag is used to specify the Windows Terminal profile that should be opened. Substitute «Ubuntu-18.04» with the name of any terminal profile that you have installed. This will always open a new window. Windows Terminal is not yet capable of opening new tabs or panes in an existing instance.
Target a directory
To specify the folder that should be used as the starting directory for the console, in this case the d:\ directory, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Multiple tabs
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, in this case a Command Prompt profile and a PowerShell profile, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Multiple panes
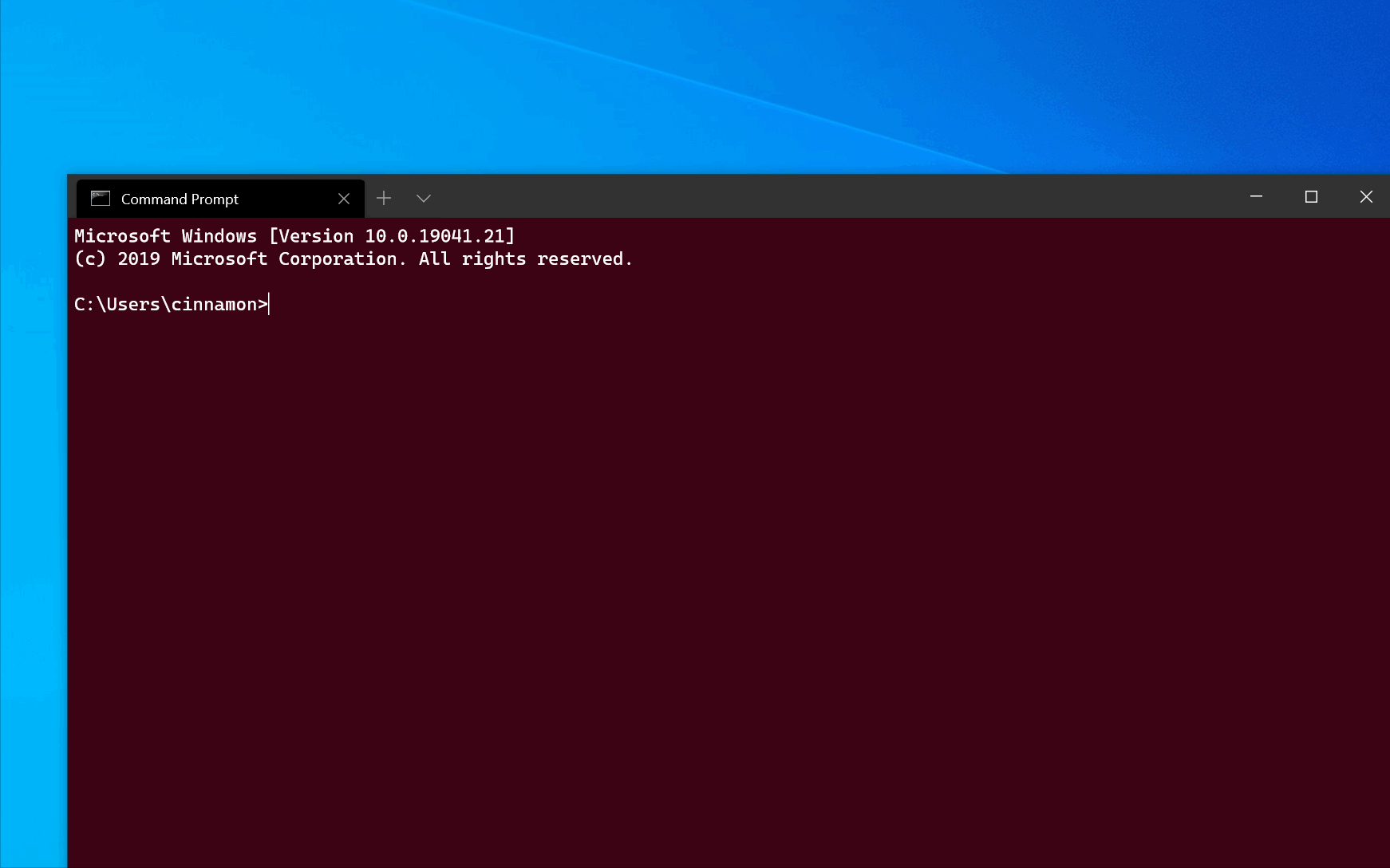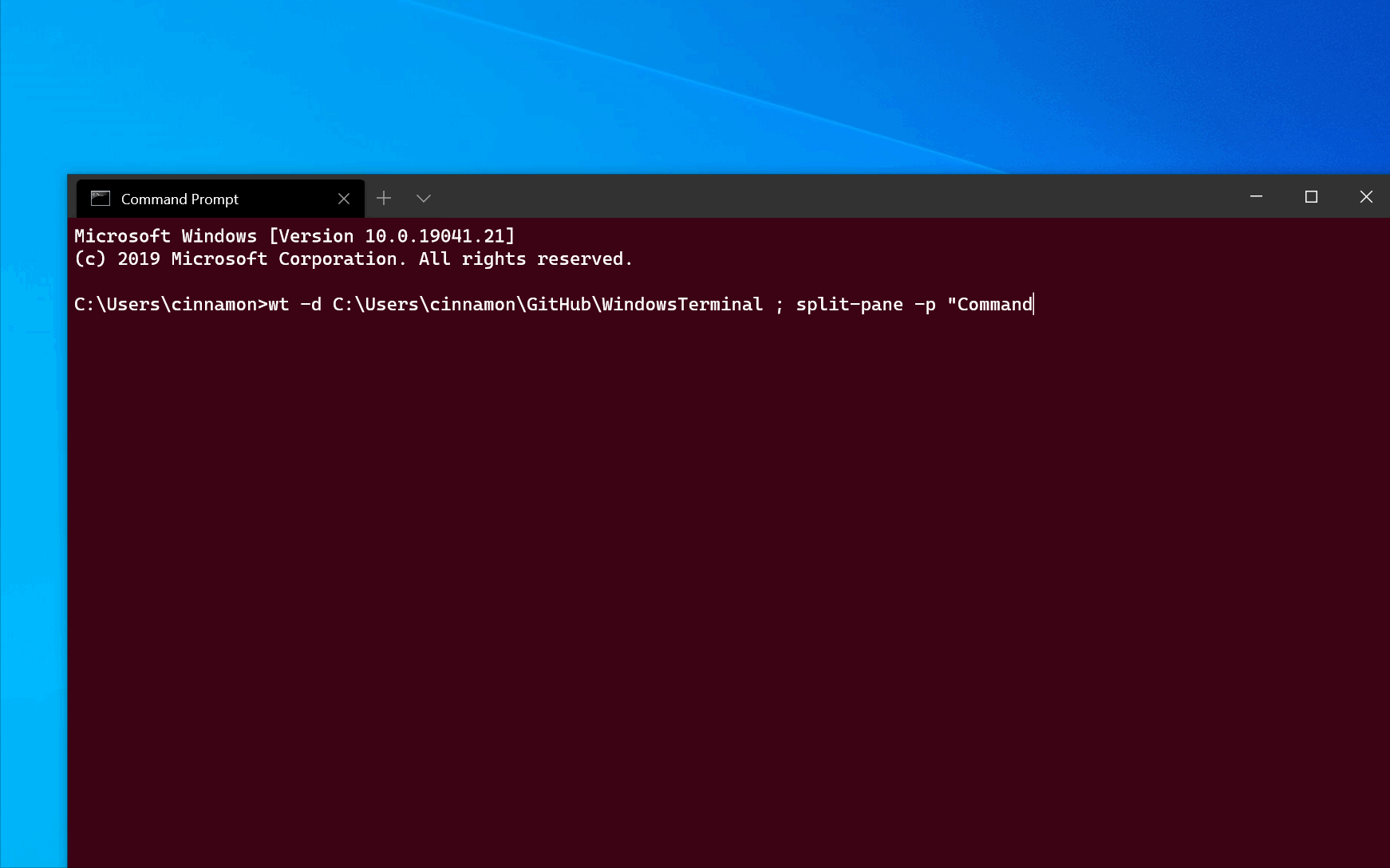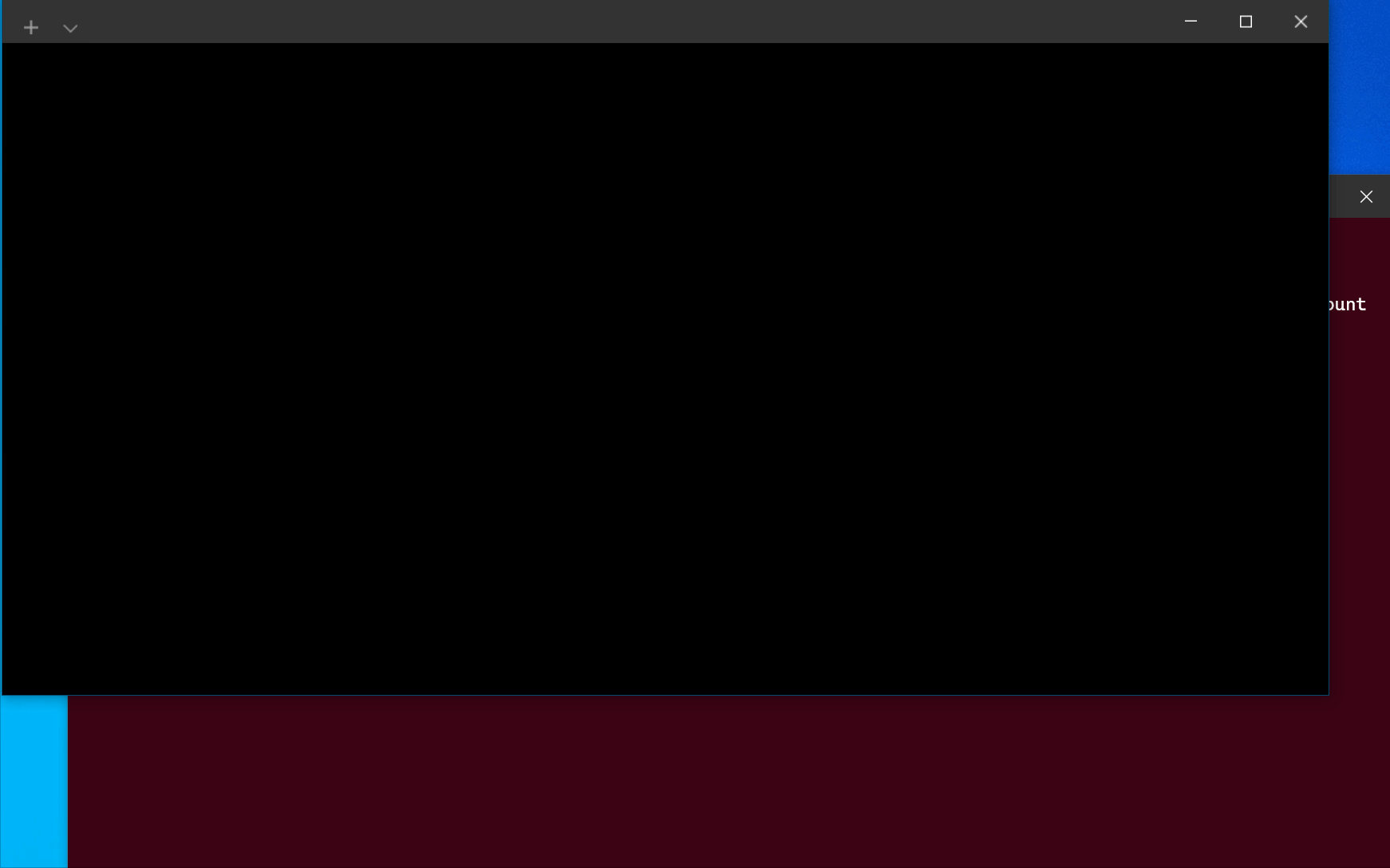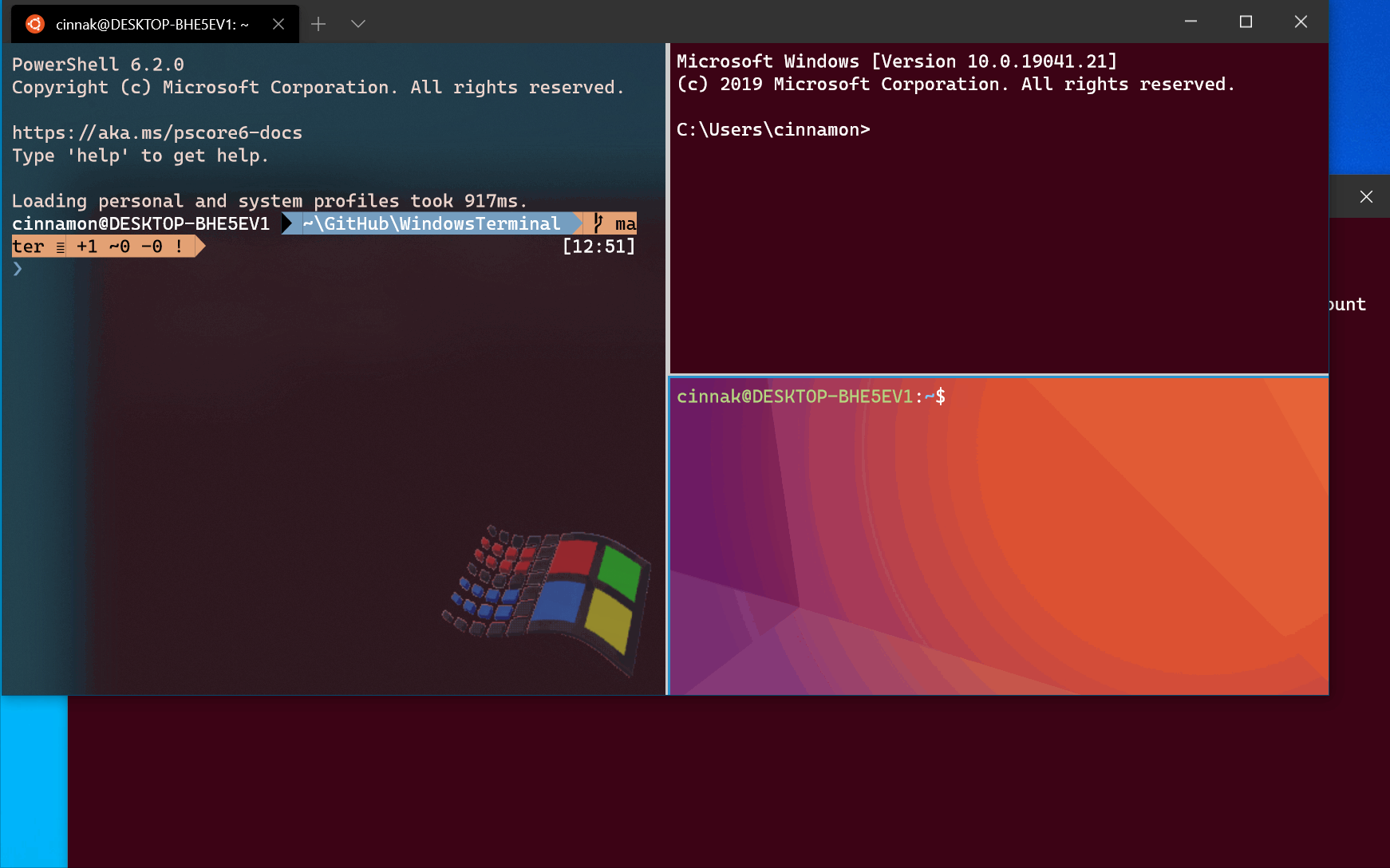
To open a new terminal instance with one tab containing three panes running a Command Prompt profile, a PowerShell profile, and your default profile running a WSL command line, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
The -H flag (or —horizontal ) indicates that you would like the panes to be split horizontally. The -V flag (or —vertical ) indicates that you would like the panes split vertically.
Multiple tabs and panes
The new-tab and split-pane commands can be sequenced to get multiple tabs, each with split panes. To open a new terminal instance with two tabs, each with two panes running a Command Prompt and a WSL command line, with each tab in a different directory, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands. Note to specify a Windows directory as the starting directory for wsl.exe that two backslashes \\ are required.
Tab title
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab titles, use the —title argument. To set the title of each tab when opening two tabs, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; forward-slash + semicolon separates commands.
Using application title (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance allowing applications within it to set the tab title by sending title change messages, use the —useApplicationTitle flag. To suppress these messages, use the —suppressApplicationTitle flag. If none of these flags are provided, the behavior is inherited from the profile’s settings. To open a tab with title tabname that will not be overridden by the application, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab color
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab colors, use the —tabColor argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile, but can be overridden as well using the tab color picker. In the following example, a new terminal is created with two tabs of different colors:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
When —tabColor is set for a tab, it is associated with the first pane of this tab. Hence in a tab with multiple panes, the color will be applied only if the first pane is in focus. To set the tab color for additional panes, you will need to add the —tabColor parameter to the split-pane subcommand as well. In the example below, a tab with two panes is created with tab colors specified for each pane:
Color scheme (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance with a specific color scheme (instead of the colorScheme set in the profile), use the —colorScheme argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab focus
To open a new terminal instance with a specific tab in focus, use the -t flag (or —target ), along with the tab-index number. To open your default profile in the first tab and the «Ubuntu-18.04» profile focused in the second tab ( -t 1 ), enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
Windows Terminal uses the semicolon character ; as a delimiter for separating commands in the wt command line. Unfortunately, PowerShell also uses ; as a command separator. To work around this, you can use the following tricks to run multiple wt commands from PowerShell. In all the following examples, a new terminal window is created with three panes — one running Command Prompt, one with PowerShell, and the last one running WSL.
The following examples use the Start-Process command to run wt . For more information on why the terminal uses Start-Process , see Using start below.
Single quoted parameters
In this example, the wt parameters are wrapped in single quotes ( ‘ ). This syntax is useful if nothing is being calculated.
Escaped quotes
When passing a value contained in a variable to the wt command line, use the following syntax:
Note the usage of ` to escape the double-quotes ( » ) around «Windows PowerShell» in the -p parameter to the split-pane parameter.
Using start
All the above examples explicitly used start to launch the terminal.
The following examples do not use start to run the command line. Instead, there are two other methods of escaping the command line:
- Only escaping the semicolons so that PowerShell will ignore them and pass them straight to wt .
- Using —% , so PowerShell will treat the rest of the command line as arguments to the application.
In both of these examples, the newly created Windows Terminal window will create the window by correctly parsing all the provided command-line arguments.
However, these methods are not recommended currently, as PowerShell will wait for the newly-created terminal window to be closed before returning control to PowerShell. By default, PowerShell will always wait for Windows Store applications (like Windows Terminal) to close before returning to the prompt. Note that this is different than the behavior of Command Prompt, which will return to the prompt immediately.
Windows Terminal Preview 1.5 Release
November 11th, 2020
We’re back with another Windows Terminal release! Windows Terminal has moved to version 1.4 and includes the features described in the 1.4 release blog post. Windows Terminal Preview has moved to version 1.5 and includes the features described below. You can download both versions from the Microsoft Store or from the GitHub releases page. Let’s dive into what’s new!
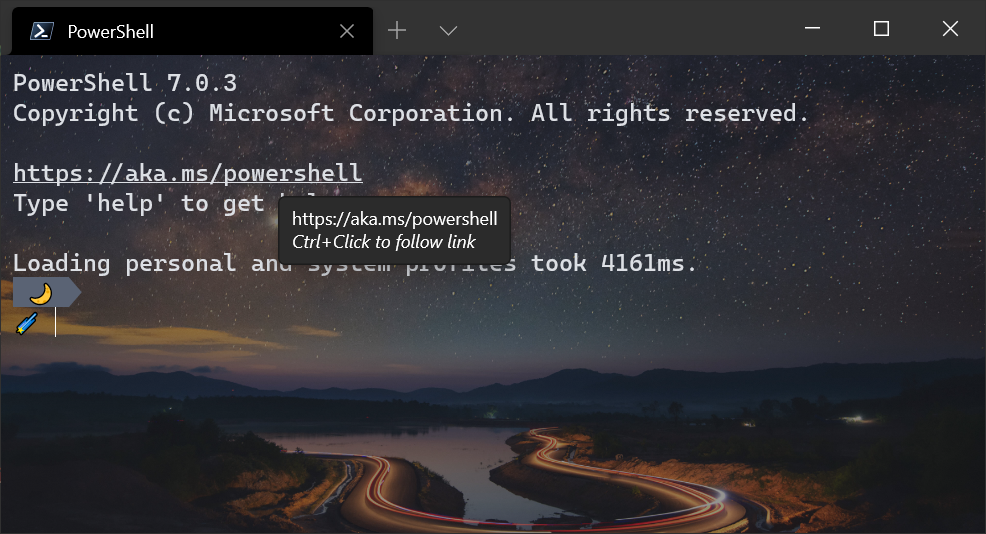
Full hyperlink support
We have improved the hyperlink functionality to automatically detect links inside your terminal. These links are clickable and will open in your default browser using Ctrl + Click .
Audible bell 🔔
Windows Terminal now supports the BEL character. You can enable or disable the bell with the «bellStyle» profile setting.
Profile icon emoji support
Have you ever wanted to set your profile icon to an emoji? Well today is your lucky day! You can now use emojis as profile icons throughout your terminal by setting your profile’s «icon» to an emoji.
👉 Note: The jump list does not support emojis as icons, so your profiles will be listed without the emojis.
Tab switcher order setting
The «useTabSwitcher» setting has received an upgrade! You can now specify «mru» or «inOrder» , which will enable the tab switcher with the tabs listed either in most recently used order or in order of their layout in the terminal.
Desktop wallpaper background image
A new option has been added to the «backgroundImage» setting! You can set your background image to «desktopWallpaper» , which will set your terminal background image to your desktop wallpaper. Thanks @bennettnicholas!
Focus launch modes
New launch modes have been added to the «launchMode» setting. You can now specify the terminal to launch in focused mode or maximized focus mode. Focus mode hides the tabs and the title bar. Thanks @Don-Vito!
Disable animations
We added animations for when you create and close panes. If you would like to disable animations throughout the terminal application, you can use the «disableAnimations» global setting.
👉 Note: If you have animations disabled at the OS level, you will not see animations inside your terminal unless you set «disableAnimations» to false .
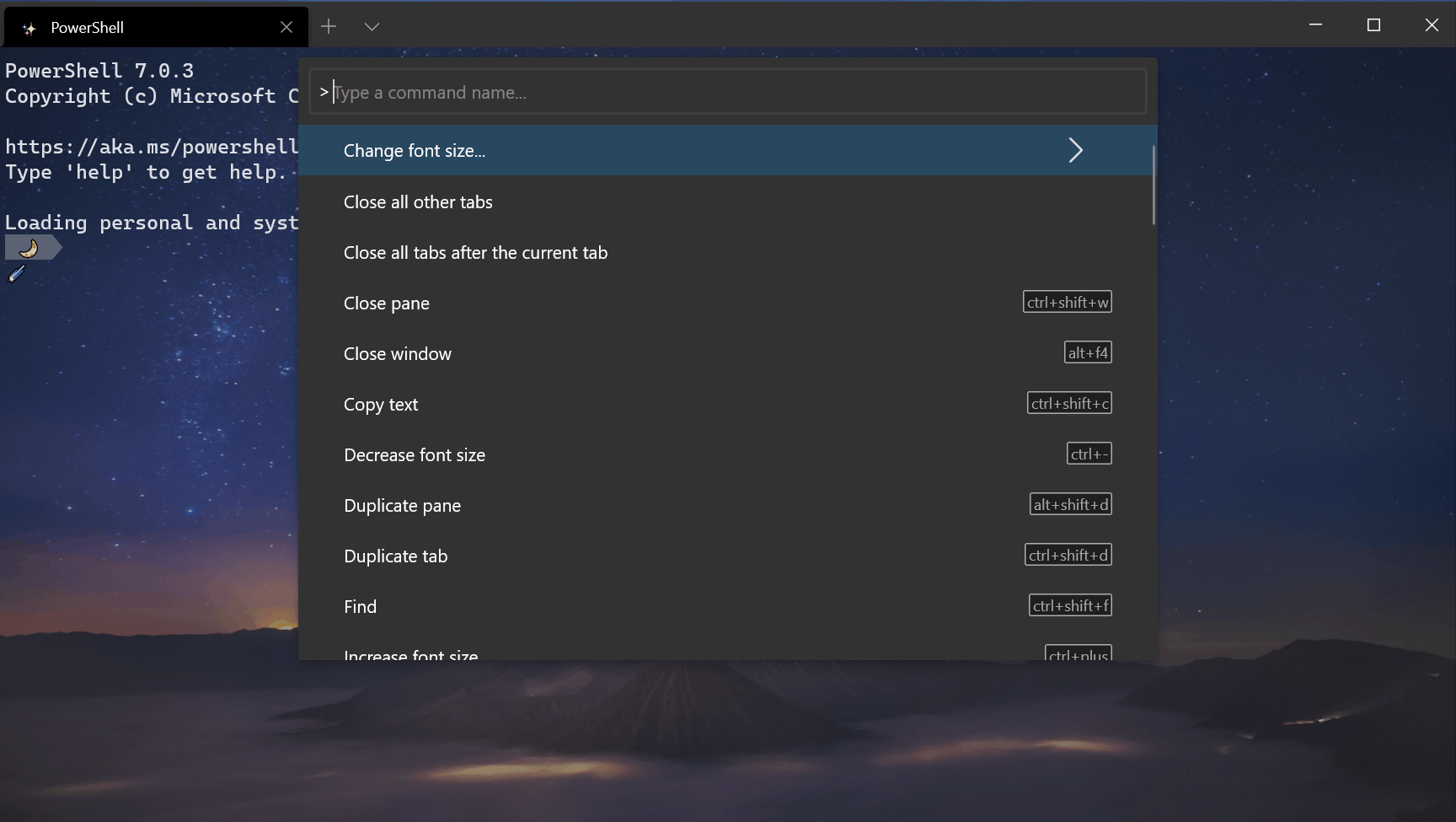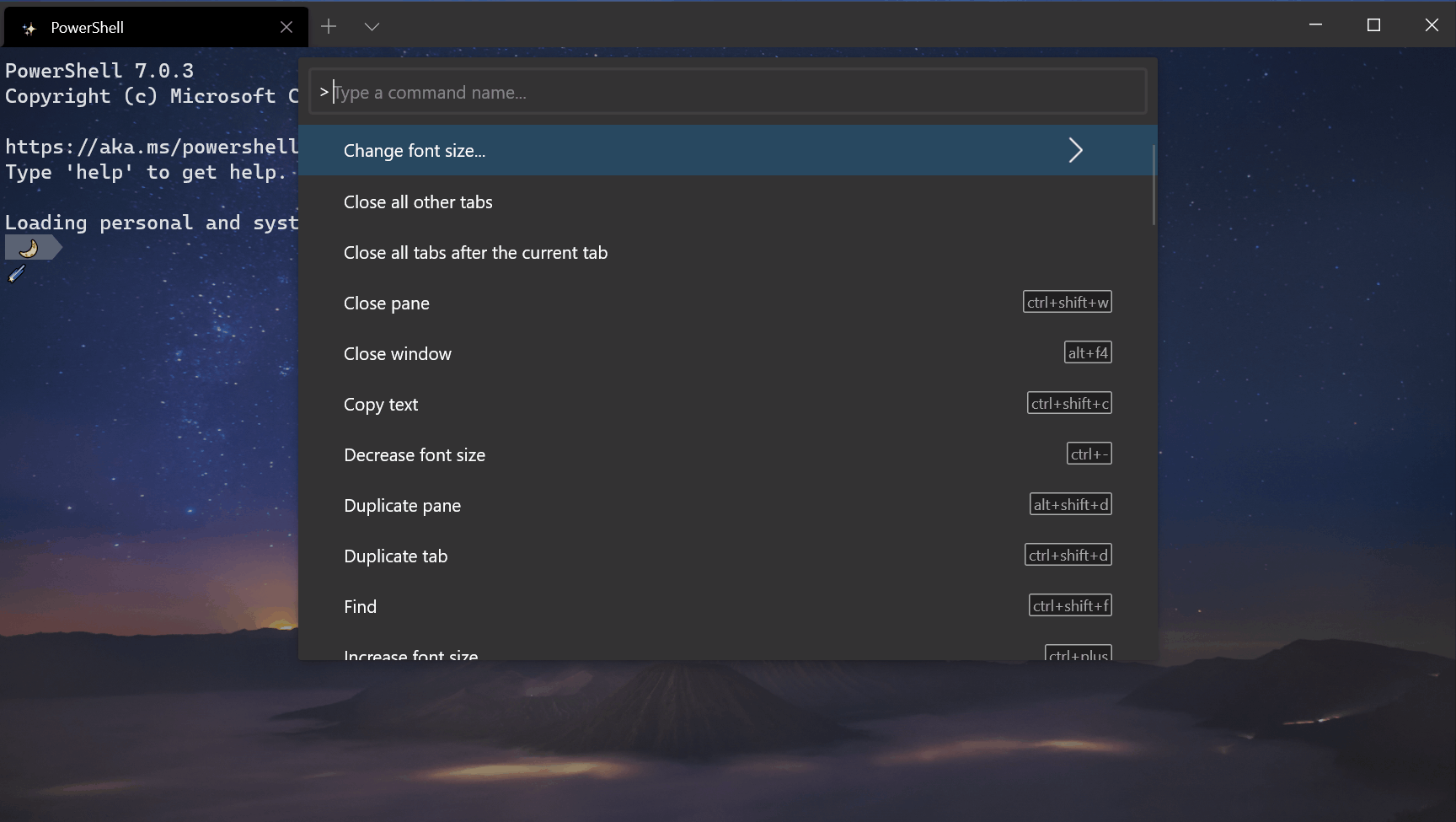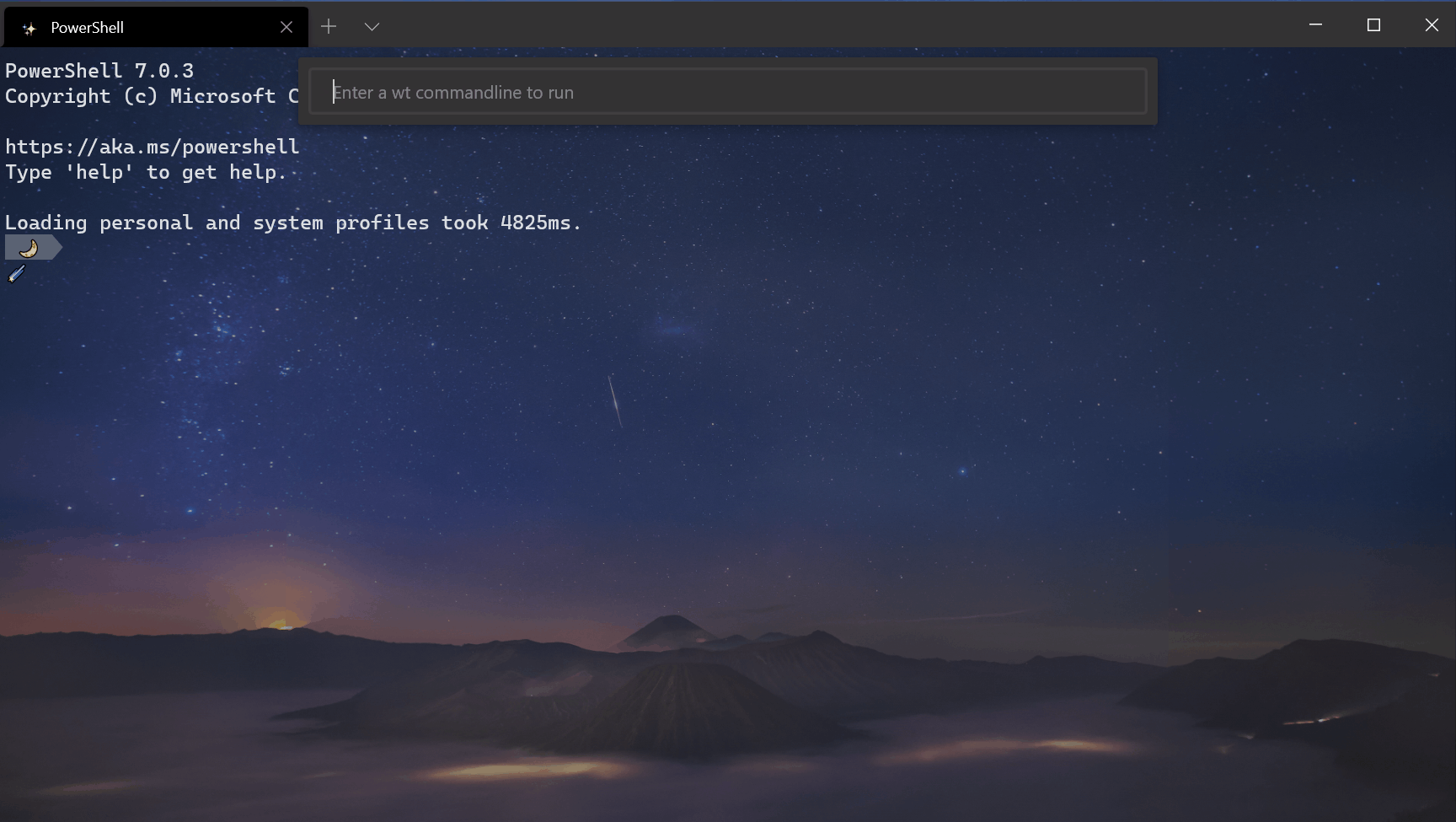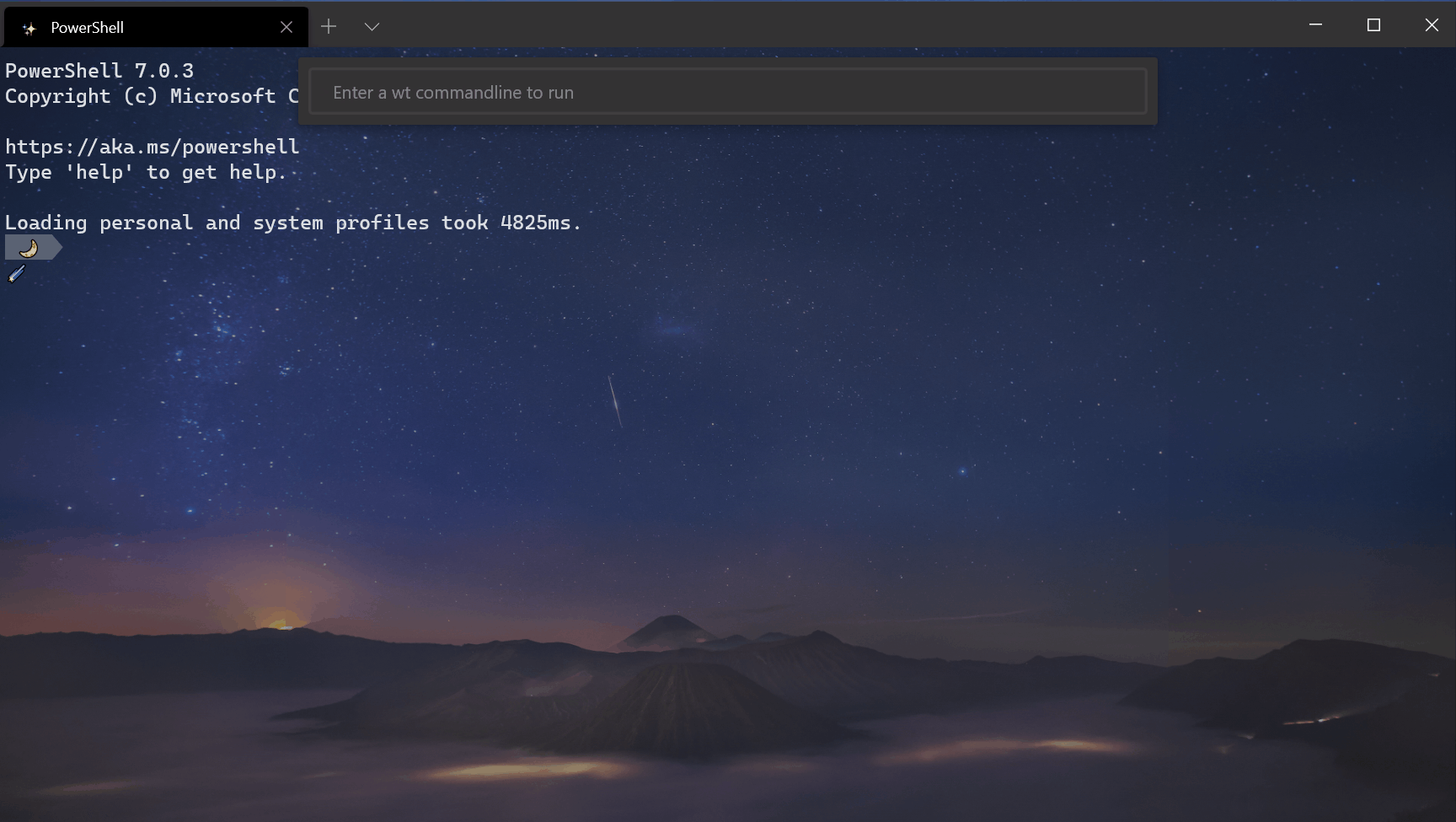
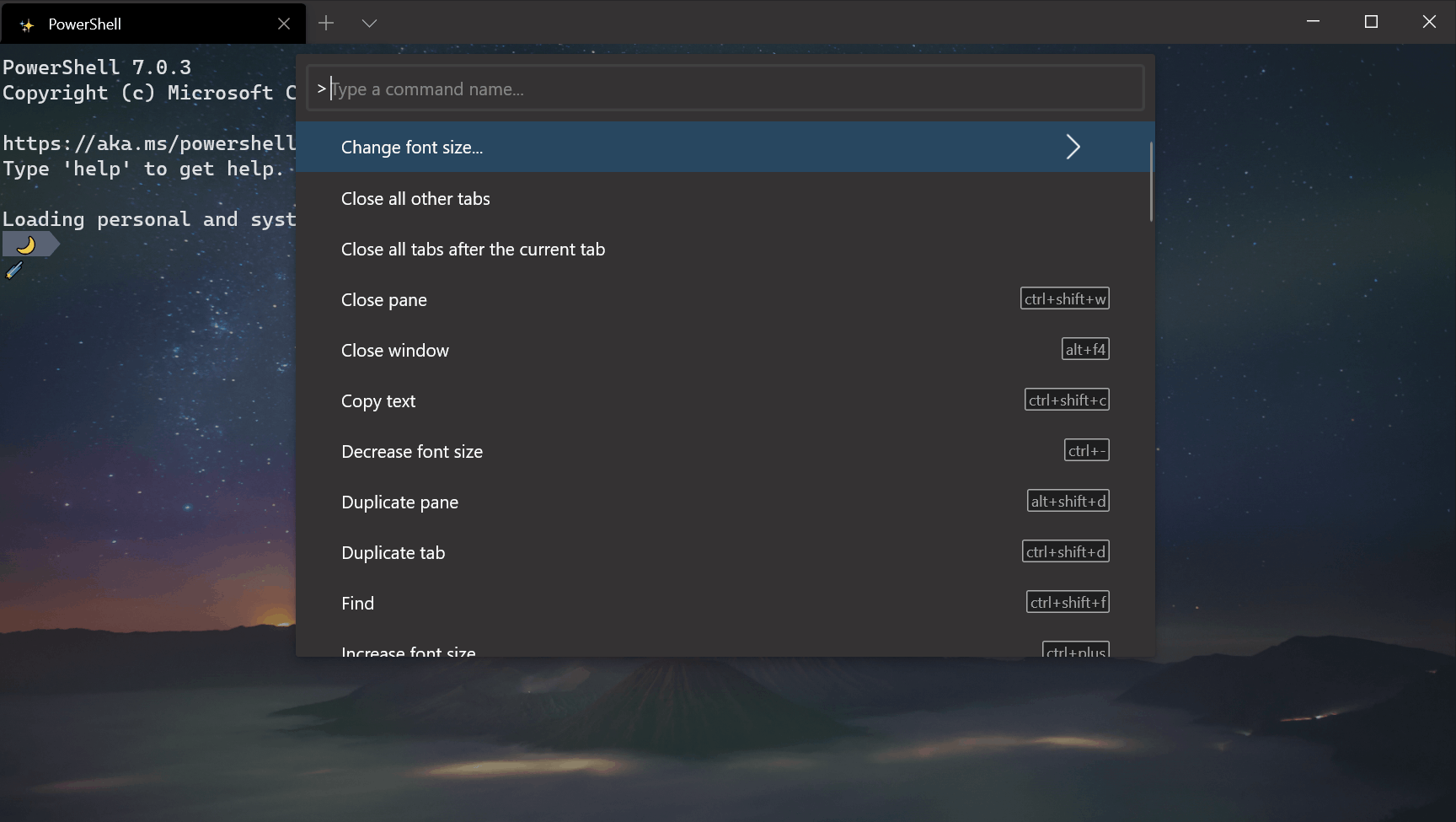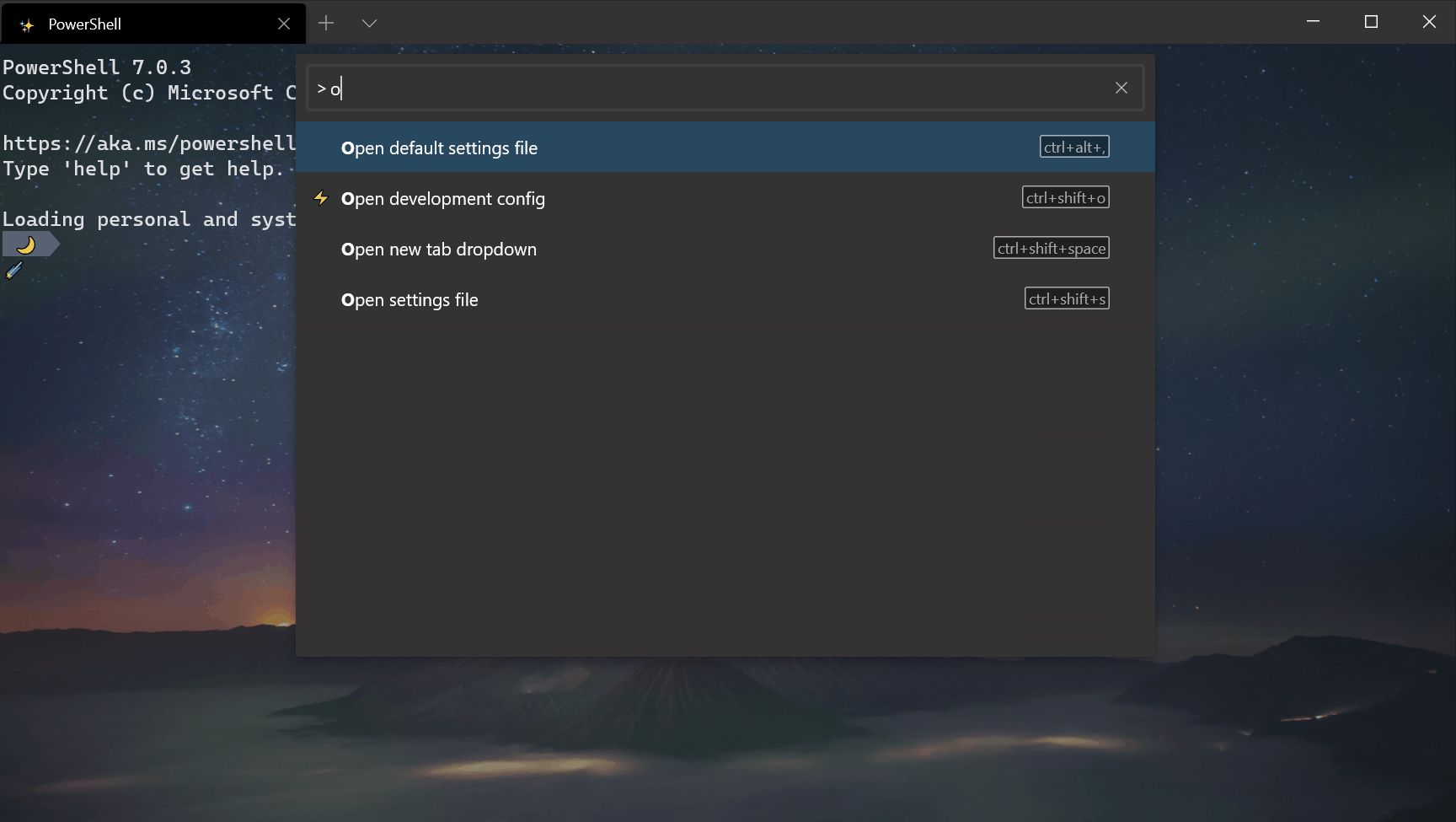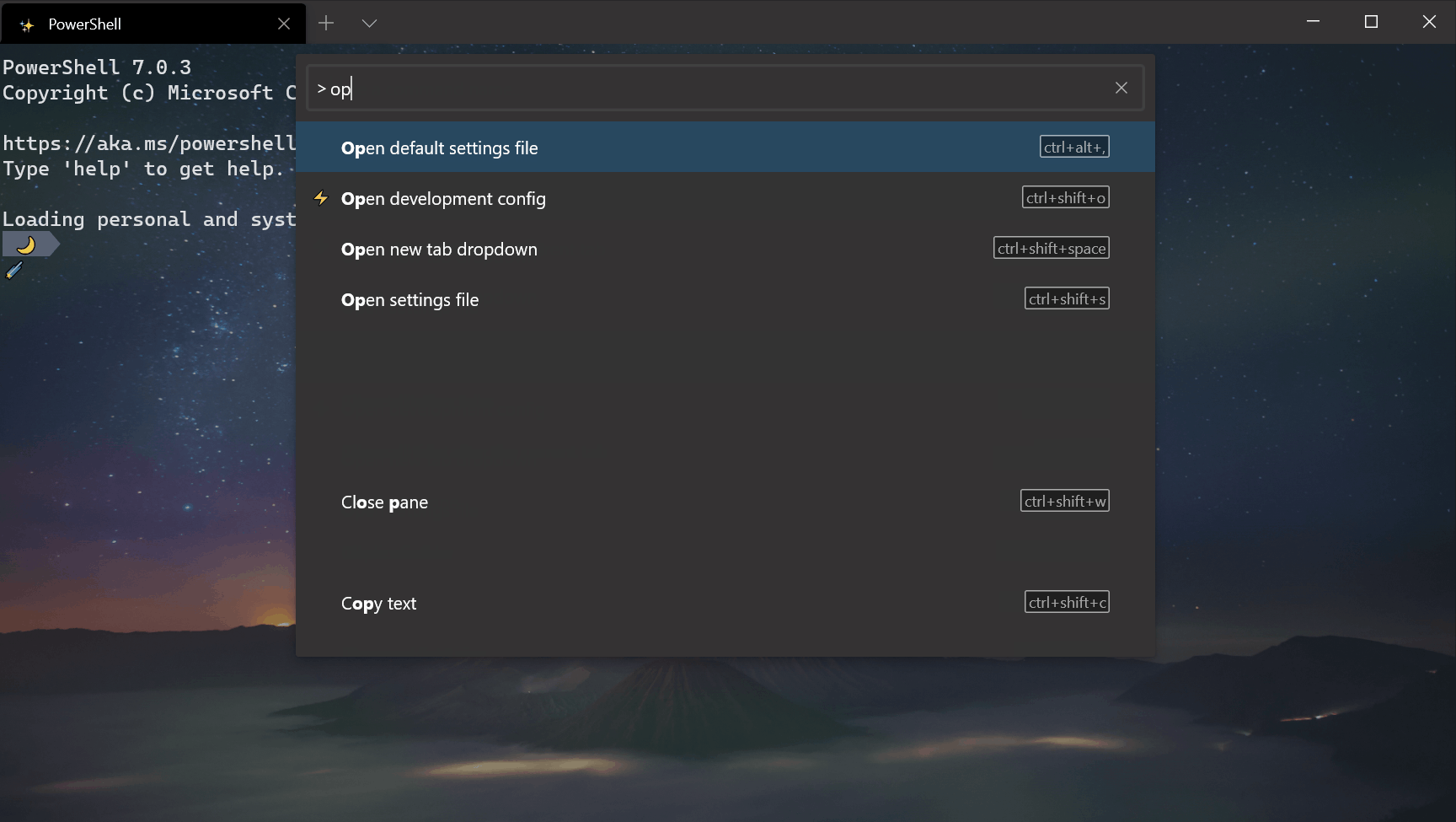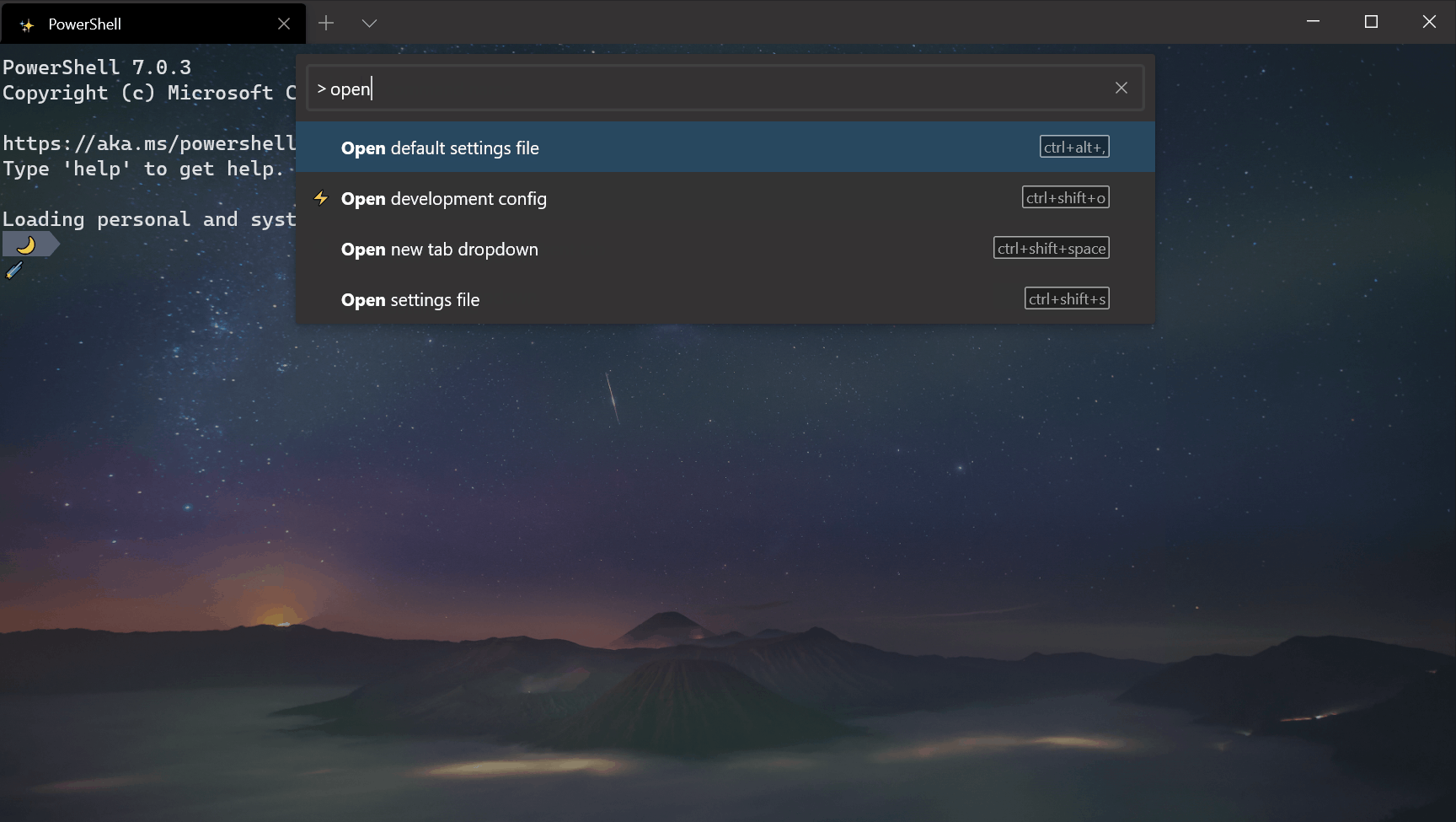
Command palette improvements
Reconfigured > prefix
We switched the > prefix to action mode inside the command palette, thus matching VS Code’s command palette functionality. Backspacing will remove the > character and place you in command line mode, allowing you to run command line arguments.
Back button
When entering a nested menu from the command palette, you can now navigate back to the root menu without having to exit the command palette. Thanks @Hegunumo!
Bold matching search terms
When searching for commands in the command palette, the results will bold the matching text to make it easier to find your desired command. Thanks @Don-Vito!
New actions
Open tab rename text box
You can now open the tab renaming text box using the «openTabRenamer» action. Thanks @Coridyn!
Toggle pane zoom
You can use the «togglePaneZoom» action to expand a pane to fit the entire contents of the terminal window.
Bug fixes
🐛 The terminal is much faster when launching, opening tabs, and closing tabs when you have a lot of profiles.
🐛 Clicking links inside the terminal will no longer hang.
🐛 The jump list will now display icons that use forward slashes in their file paths.
🐛 Failure to write to your settings file will now display a warning.
🐛 When using a screen reader, it is much faster when moving to the next word.
Top contributors
We had a ton of wonderful contributions for this release and we would love to recognize those who have especially made an impact!