- Protect your PC from ransomware
- How can I help keep my PC secure?
- If you suspect you’ve been infected
- If you actually get a ransomware infection
- What to do if you already paid
- Protect important folders with controlled folder access
- What is controlled folder access?
- How does controlled folder access work?
- Why controlled folder access is important
- Windows system folders are protected by default
- Requirements for controlled folder access
- Review controlled folder access events in the Microsoft Defender Security Center
- Review controlled folder access events in Windows Event Viewer
- View or change the list of protected folders
- How to Enable Ransomware Protection in Windows 10
- Ransomware Protection feature
- How to enable Ransomware Protection in Windows 10
Protect your PC from ransomware
Ransomware is malware that encrypts your files or stops you from using your computer until you pay money (a ransom) for them to be unlocked. If your computer is connected to a network the ransomware may also spread to other computers or storage devices on the network.
Some of the ways you can get infected by ransomware include:
Visiting unsafe, suspicious, or fake websites.
Opening file attachments that you weren’t expecting or from people you don’t know.
Opening malicious or bad links in emails, Facebook, Twitter, and other social media posts, or in instant messenger or SMS chats.
You can often recognize a fake email and webpage because they have bad spelling, or just look unusual. Look out for strange spellings of company names (like «PayePal» instead of «PayPal») or unusual spaces, symbols, or punctuation (like «iTunesCustomer Service» instead of «iTunes Customer Service»).
Ransomware can target any PC—whether it’s a home computer, PCs on an enterprise network, or servers used by a government agency.
Caution: Mobile devices can get ransomware too! Learn more
How can I help keep my PC secure?
Make sure your PC is up to date with the latest version of Windows and all the latest patches. Learn more about Windows Update.
Be sure Windows Security is turned on to help protect you from viruses and malware (or Windows Defender Security Center in previous versions of Windows 10).
In Windows 10 turn on Controlled Folder Access to protect your important local folders from unauthorized programs like ransomware or other malware.
Get ransomware detection and recovery with Microsoft 365 advanced protection.
Back up your files with File History if it hasn’t already been turned on by your PC’s manufacturer. Learn more about File History.
Store important files on Microsoft OneDrive. OneDrive includes built in ransomware detection and recovery as well as file versioning so you can restore a previous version of a file. And when you edit Microsoft Office files stored on OneDrive your work is automatically saved as you go.
Use a secure, modern, browser such as Microsoft Edge.
Restart your computer periodically; at least once a week. This can help ensure the applications and operating system are up-to-date and helps your system run better.
Note: If you’re a small business owner consider using Microsoft 365 Business Premium. It includes Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection to help protect your business against online threats.
If you suspect you’ve been infected
Use antimalware programs, such as Windows Security, whenever you’re concerned your PC might be infected. For example, if you hear about new malware in the news or you notice odd behavior on your PC. See Virus & threat protection in Windows Security for how to scan your device.
If you actually get a ransomware infection
Unfortunately, a ransomware infection usually doesn’t show itself until you see some type of notification, either in a window, an app, or a full-screen message, demanding money to regain access to your PC or files. These messages often display after encrypting your files.
Try fully cleaning your PC with Windows Security. You should do this before you try to recover your files. Also see Backup and Restore in Windows 10 for help on backing up and recovering files for your version of Windows.
Don’t pay money to recover your files. Even if you were to pay the ransom, there is no guarantee that you’ll regain access to your PC or files.
What to do if you already paid
If you’ve already paid the ransom, immediately contact your bank and your local authorities. If you paid with a credit card, your bank may be able to block the transaction and return your money.
You can also contact the following government fraud and scam reporting websites:
In Australia, go to the SCAMwatch website.
In Ireland, go to the An Garda Síochána website.
In New Zealand, go to the Consumer Affairs Scams website.
In the United Kingdom, go to the Action Fraud website.
In the United States, go to the On Guard Online website.
If your region isn’t listed here, Microsoft recommends that you contact your region’s federal police or communications authority.
For an illustrated overview about ransomware and what you can do to help protect yourself, see The 5Ws and 1H of ransomware.
If you’re in an enterprise, see the Microsoft Malware Protection Center for in-depth information about ransomware.
Protect important folders with controlled folder access
Applies to:
What is controlled folder access?
Controlled folder access helps protect your valuable data from malicious apps and threats, such as ransomware. Controlled folder access protects your data by checking apps against a list of known, trusted apps. Supported on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 clients, controlled folder access can be turned on using the Windows Security App, Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager, or Intune (for managed devices).
Scripting engines are not trusted and you cannot allow them access to controlled protected folders. For example, PowerShell is not trusted by controlled folder access, even if you allow with certificate and file indicators.
Controlled folder access works best with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, which gives you detailed reporting into controlled folder access events and blocks as part of the usual alert investigation scenarios.
Controlled folder access blocks don’t generate alerts in the Alerts queue. However, you can view information about controlled folder access blocks in the device timeline view, while using advanced hunting, or with custom detection rules.
How does controlled folder access work?
Controlled folder access works by only allowing trusted apps to access protected folders. Protected folders are specified when controlled folder access is configured. Typically, commonly used folders, such as those used for documents, pictures, downloads, and so on, are included in the list of controlled folders.
Controlled folder access works with a list of trusted apps. Apps that are included in the list of trusted software work as expected. Apps that are not included in the list are prevented from making any changes to files inside protected folders.
Apps are added to the list based upon their prevalence and reputation. Apps that are highly prevalent throughout your organization and that have never displayed any behavior deemed malicious are considered trustworthy. Those apps are added to the list automatically.
Apps can also be added manually to the trusted list by using Configuration Manager or Intune. Additional actions, such as adding a file indicator for an app, can be performed from the Security Center Console.
Why controlled folder access is important
Controlled folder access is especially useful in helping to protect your documents and information from ransomware. In a ransomware attack, your files can get encrypted and held hostage. With controlled folder access in place, a notification appears on the computer where an app attempted to make changes to a file in a protected folder. You can customize the notification with your company details and contact information. You can also enable the rules individually to customize what techniques the feature monitors.
The protected folders include common system folders (including boot sectors), and you can add more folders. You can also allow apps to give them access to the protected folders.
You can use audit mode to evaluate how controlled folder access would impact your organization if it were enabled. You can also visit the Windows Defender Test ground website at demo.wd.microsoft.com to confirm the feature is working and see how it works.
Controlled folder access is supported on the following versions of Windows:
Windows system folders are protected by default
Windows system folders are protected by default, along with several other folders:
- c:\Users\ \Documents
- c:\Users\Public\Documents
- c:\Users\ \Pictures
- c:\Users\Public\Pictures
- c:\Users\Public\Videos
- c:\Users\ \Videos
- c:\Users\ \Music
- c:\Users\Public\Music
- c:\Users\ \Favorites
You can configure additional folders as protected, but you cannot remove the Windows system folders that are protected by default.
Requirements for controlled folder access
Review controlled folder access events in the Microsoft Defender Security Center
Defender for Endpoint provides detailed reporting into events and blocks as part of its alert investigation scenarios.
You can query Microsoft Defender for Endpoint data by using Advanced hunting. If you’re using audit mode, you can use advanced hunting to see how controlled folder access settings would affect your environment if they were enabled.
Review controlled folder access events in Windows Event Viewer
You can review the Windows event log to see events that are created when controlled folder access blocks (or audits) an app:
- Download the Evaluation Package and extract the file cfa-events.xml to an easily accessible location on the device.
- Type Event viewer in the Start menu to open the Windows Event Viewer.
- On the left panel, under Actions, select Import custom view. .
- Navigate to where you extracted cfa-events.xml and select it. Alternatively, copy the XML directly.
- Select OK.
The following table shows events related to controlled folder access:
| Event ID | Description |
|---|---|
| 5007 | Event when settings are changed |
| 1124 | Audited controlled folder access event |
| 1123 | Blocked controlled folder access event |
View or change the list of protected folders
You can use the Windows Security app to view the list of folders that are protected by controlled folder access.
- On your Windows 10 device, open the Windows Security app.
- Select Virus & threat protection.
- Under Ransomware protection, select Manage ransomware protection.
- If controlled folder access is turned off, you’ll need to turn it on. Select protected folders.
- Do one of the following steps:
- To add a folder, select + Add a protected folder.
- To remove a folder, select it, and then select Remove.
Windows system folders are protected by default, and you cannot remove them from the list.
How to Enable Ransomware Protection in Windows 10
Mayank Parmar
Windows Defender includes a security feature called «Ransomware Protection» that allows you to enable various protections against ransomware infections. This feature is disabled by default in Windows 10, but with ransomware running rampant, it is important to enable this feature in order to get the most protection you can for your computer.
If you are a regular reader of BleepingComputer, then you have heard about ransomware. For those not familiar with the term, ransomware is a computer malware infection that encrypts the data on your computer and then demands a ransom in bitcoins to decrypt them.
Ransomware Protection feature
Windows 10’s includes a Ransomware Protection feature that is comprised of two components; Controlled Folder Access and Ransomware Data Recovery.
Controlled Folder Access will allow you to specify certain folders that you wish to monitor for and block changes to the files contained in them. This will block all programs, but the ones you allow, from making any modifications to the files within monitored folders, which will protect them from being encrypted by ransomware.
The other component is Ransomware Data Recovery, which will automatically sync your common data folders with your Microsoft OneDrive account in order to backup your files. Ransomware victims with this feature enabled can then use OneDrive to recover their files if they ever become encrypted by ransomware.
In Windows 10 version 1903, Windows Defender’s Ransomware Protection is disabled by default. With this guide we will teach you how to enable it so that it can protect your computer against ransomware attacks.
Unfortunately, if you have a third-party antivirus software installed and Windows Defender’s real-time protection is disabled, the Ransomware Protection features screen and the Controlled Folder Access feature won’t be accessible.
How to enable Ransomware Protection in Windows 10
To enable the full Ransomware Protection capabilities of Windows 10, you should configure both Controlled Folder Access and login to Microsoft OneDrive in order to backup your files.
To do this, just follow these steps:
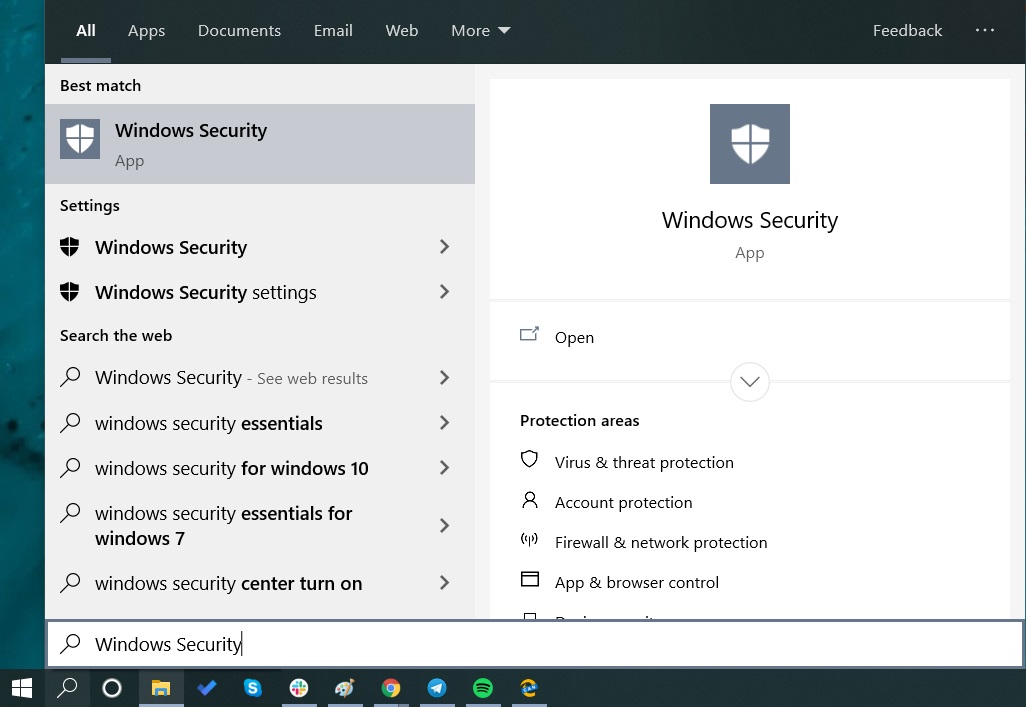
- Click on the Start menu.
- Type Windows Security and select the search result when it appears. You can also access Windows Security by going to the Settings app and navigating to Update & Security—>Windows Security.
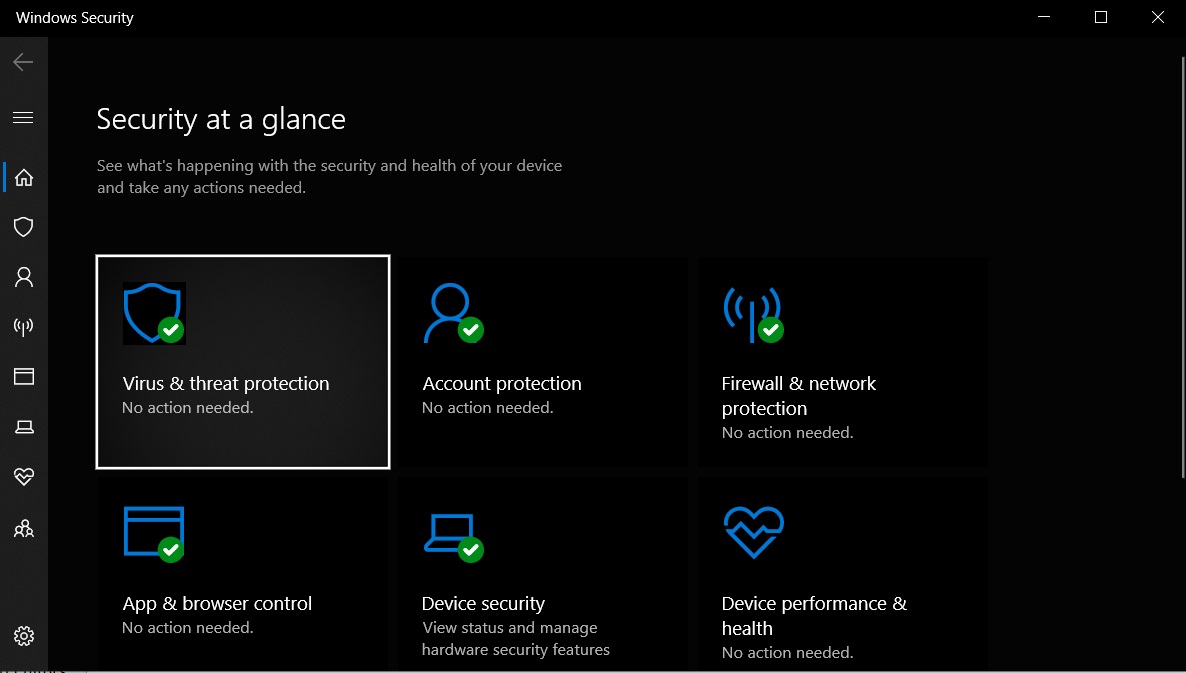
After opening Windows Security, click on Virus & Threat Protection option.
Scroll down and locate Ransomware Protection and click on the Manage ransomware protection option.
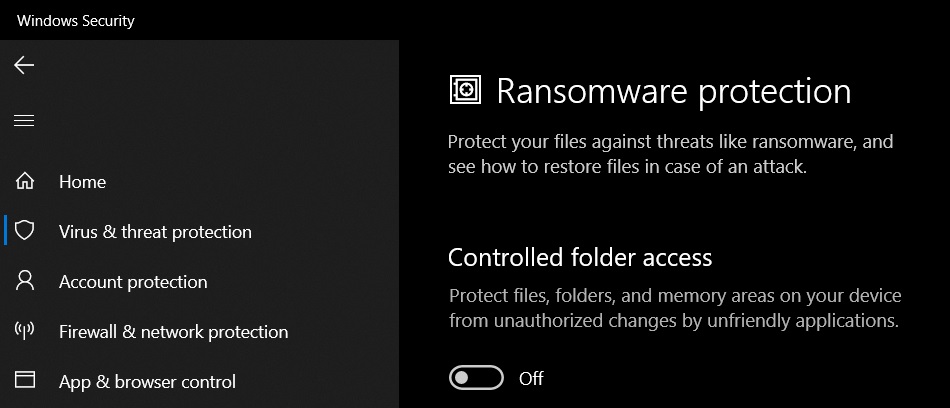
On the next page, you will find a brief description of Controlled folder access and a toggle to enable it.
To enable Ransomware Protection. turn on Controlled Folder Access and login to OneDrive so that both features are enabled as seen below.
You can now configure Controlled Folder Access and choose any folder you want to monitor and block from malicious programs.