- Delete files from command line
- How to delete a file
- Delete files in bulk
- Delete multiple files
- Delete Read only files
- Как удалить файл или папку через командную строку Windows
- Удаление файлов через командную строку
- Удаление папок через командную строку
- Windows delete file cmd windows
- Errorlevels
- Undeletable Files
- Permanent deletion
- Delete Locked files
- Delete files or folder recursively on Windows CMD
- 12 Answers 12
- Use the Windows rmdir command
Delete files from command line
Deleting files is one of the frequently done operation from Windows command prompt. This post explains how to use ‘del’ command from CMD for different use cases like deleting a single file, deleting files in bulk using wild cards etc. Before we start to look at the syntax, note that the command works only for files and can’t handle folders.
How to delete a file
Run del command with the name of the file to be deleted, you are done!
You do not see message after running the command if the file is deleted successfully. Error message is shown only when something goes wrong.
Delete files in bulk
Del command recognizes wildcard(*) and so can be used to delete files in bulk from CMD. Some examples below.
To delete all the files in current folder
To delete all the files with ‘log’ extension
Delete all files having the prefix ‘abc’
Delete all files having ‘PIC’ somewhere in the file name.
The above are the basic use cases of del command. Continue to read below for non trivial use cases.
Delete multiple files
‘Del’ command can accept multiple files as argument
Delete Read only files
We can’t delete a read-only file using simple‘del’ command. We get access denied error in this scenario.
A read-only file can be deleted by adding /F flag.
Alternatively, we can use the below command too
Is there any batch command to delete all zero byte sized files from cmd.
There is a way to remove folders from the commandline, use “RD” (remove directory), and it has a couple of silent switches, “RD /S /Q C:/Directory” will remove C:/Directory silently, I use this all the time. I think that the directory path has to be in quotations if it contains any spaces.
UAC might want to fight over deleting files, in that case, the command “takeown” to give you ownership of the file first, should get around that.
Sometimes we get an error when we try to delete a File or a folder for no reason , but of course there is a reason.We have many damage file or blocked files.Do not worry if we want to remove the error files or too long path files from our system,here I suggest a smooth way.So use “Long path tool” software and keep yourself.
Well done, I used this when del *1*.*
Will keep this in my reference book. Thanks a lot!
Is there a way to exclude filenames matching a pattern from a delete? For example, I want to delete all files except those whose names are like *xyz*
I am trying to delete csv files in DOS that have a date suffix of earlier
than 2 months ago. I need to do this dynamically, from a batch file.
Is this possible ? Many thanks.
Bethany
I want to delete a file from all the user’s profiles using cmd.
The file is on the desktop.
Name of the file-Hello My Name
I’m writing del %PUBLIC%\Desktop\Hello*My*Name.pdf,but that doesnt seem to work.
I also tried del %PUBLIC%\Desktop\*Hello* but that didnt work too.
Any help is appreciated
c. Using the for loop create 5 text files which start from letter a (ex: a1, a2, a3, a4, a5).
can you help me
create 5 files like this command.
for /l %a in (1 1 5) do mkdir File%a.
Как удалить файл или папку через командную строку Windows
Командная строка – мощный инструмент для автоматизации и упрощения многих задач, которые возникают при администрировании компьютера с операционной системой Windows. В этой статье мы рассмотрим команды DEL, ERASE, RD и RMDIR. С их помощью вы сможете удалять файлы и папки прямо из командной строки.
Удаление файлов через командную строку
Если вам нужно удалить файл через командную строку, то для этого нужно использовать команду DEL или ERASE . Эти команды являются синонимами и работают одинаково. Вы можете получить подробную информацию об этих командах, если введете их в командную строку с параметром « /? ». Например, вы можете ввести « del /? » и в консоль выведется вся основная информация о команде del .
Команда DEL (или ERASE ) предназначена для удаления одного или нескольких файлов и может принимать следующие параметры:
- /P – удаление с запросом подтверждения для каждого файла;
- /F – удаление файлов с атрибутом «только для чтения»;
- /S – удаление указанного файла из всех вложенных папок;
- /Q – удаление без запроса на подтверждение ;
- S — Системные;
- H — Скрытые;
- R – Только для чтения;
- A — Для архивирования
- Также перед атрибутами можно использовать знак минус «-», который имеет значение «НЕ». Например, «-S» означает не системный файл.
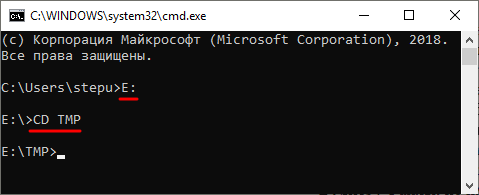
Обычно, для того чтобы воспользоваться командной DEL нужно сначала перейти в папку, в которой находится файл для удаления, и после этого выполнить команду. Для того чтобы сменить диск нужно просто ввести букву диска и двоеточие. А для перемещения по папкам нужно использовать команду « CD ».
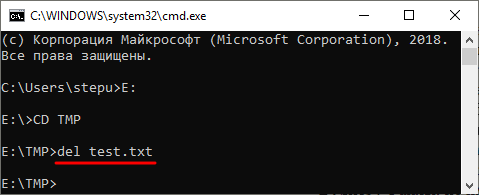
После того как вы попали в нужную папку можно приступать к удалению файлов. Для этого просто введите команду DEL и название файла.
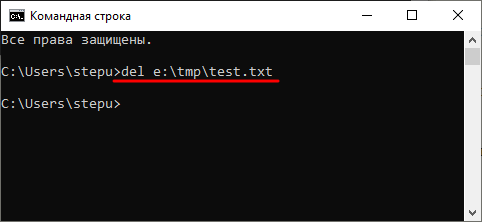
Также, при необходимости вы можете удалять файлы, не перемещаясь по папкам. В этом случае нужно указывать полный путь к документу.
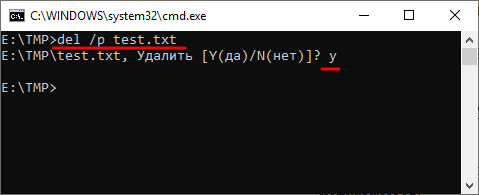
Если есть необходимость выполнить запрос на подтверждение удаления каждого их файлов, то к команде DEL нужно добавить параметр « /p ». В этом случае в командной строке будет появляться запрос на удаление файла и пользователю нужно будет ввести букву «Y» для подтверждения.
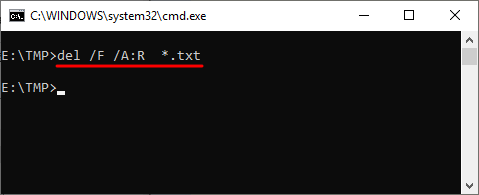
Нужно отметить, что при использовании параметра «/a», отвечающие за атрибуты буквы нужно вводить через двоеточие. Например, для того чтобы удалить все файлы с атрибутом «только для чтения» и с расширением «txt» нужно ввести команду « del /F /A:R *.txt ».
Аналогичным образом к команде DEL можно добавлять и другие параметры. Комбинируя их вы сможете создавать очень мощные команды для удаления файлов через командную строку Windows. Ниже мы приводим еще несколько примеров:
- del D:\ — уничтожение всех файлов в корне диска D;
- del D:\*.txt – уничтожение всех файлов с расширением txt в корне диска D;
- del D:\doc – уничтожение всех файлов в папке d:\doc (документы с атрибутами будут пропущены);
- del /A:r d:\doc\*.txt – уничтожение всех файлов с атрибутом «только для чтения» и расширением «txt» в папке d:\doc;
Удаление папок через командную строку
Если вам нужно удалить папку через командную строку Windows, то указанные выше команды вам не помогут. Для удаления папок существует отдельная команда RD или RMDIR (сокращение от английского Remove Directory).
Команды RD и RMDIR являются синонимами и предназначены для удаления папок. Они могу принимать следующие параметры:
- /S — удаление всего дерева каталогов, при использовании данного параметра будет удалена не только сама папка, но и все ее содержимое;
- /Q – удаление дерева папок без запроса на подтверждение;
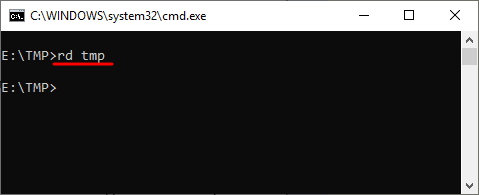
Например, для того чтобы удалить папку достаточно ввести команду RD и название папки.
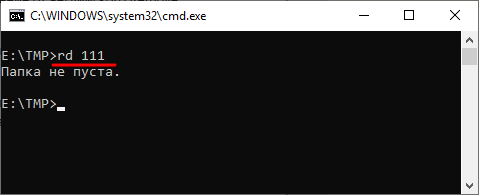
Если папка содержит вложенные папки или файлы, то при ее удалении будет выведена ошибка».
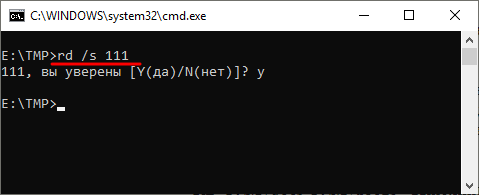
Для решения этой проблемы к команде RD нужно добавить параметр « /s ». В этом случае удаление проходит без проблем, но появляется запрос на подтверждение удаления.
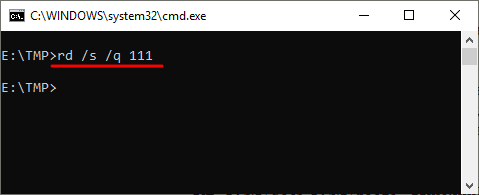
Для того чтобы удаление дерева папок прошло без появления запроса на подтверждение к команде нужно добавить параметр « /q ». В этом случае папка удаляется без лишних вопросов.
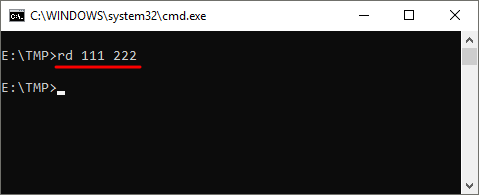
Также команда RD может принимать сразу несколько папок, для этого их нужно просто разделить пробелом. Например, если выполнить « rd 111 222 », то за один раз можно удалить папки с названиями « 111 » и « 222 ».
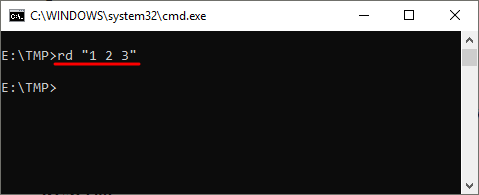
Если же вам нужно удалить через командную строку папку, которая сама содержит пробел, то в этом случае ее название нужно взять в двойные кавычки.
Комбинируя команды DEL и RD , можно создавать мощные скрипты для очистки и удаления папок в операционной системе Windows.
Windows delete file cmd windows
Delete one or more files.
If a folder name is given instead of a file, all files in the folder will be deleted, but the folder itself will not be removed.
Errorlevels: DEL will return an Errorlevel of 0, irrespective if the delete succeeds or fails for any reason.
Also a deletion failure will not fire for || unless the DEL arguments are invalid.
If you delete files using PowerShell then a True/False return code ( $? ) will be set correctly.
Errorlevels
If the files were successfully deleted %ERRORLEVEL% = 0
If the files failed to delete, or don’t exist to be deleted %ERRORLEVEL% = 0
Bad or no parameters given %ERRORLEVEL% = 1
Undeletable Files
Files are sometimes created with a very long filename or a trailing period or with reserved names (CON, AUX, COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, LPT1, LPT2, LPT3, PRN, NUL) and as a result they become impossible to delete with Windows Explorer.
To delete such files use the syntax: DEL «\\?\path to file»
You can also use «\\.\path to device «
e,g,
DEL «\\?\C:\some folder\AZH64GT.»
DEL «\\.\C:\Work\LPT1 «
Alternatively for long filenames, you can reduce the total path length by using SUBST to map a drive letter to the folder containing the file.
It is also possible to delete long paths using RoboCopy — Copy/Move the required files to a temporary folder and then delete the folder, one gotcha with that technique is RoboCopy’s tendency to follow symbolic links which can cause files outside the source folder to be moved/ deleted.
If a file is still ‘undeletable’ this may be caused by the indexing service, temporarily stop the service and then delete the file.
Permanent deletion
Deleting a file will not prevent third party utilities from un-deleting it again. Secure file deletion utilities are available, however for casual use, you can turn any file into a zero-byte file to destroy the file allocation chain like this:
TYPE nul > C:\examples\MyFile.txt
DEL C:\examples\MyFile.txt
Delete Locked files
Typically this is caused by the Offline Cache or Internet Explorer temp files.
Close all applications
Open a command prompt
Click Start, and then Shut Down
Simultaneously press CTRL+SHIFT+ALT.
While you keep these keys pressed, click Cancel in the Shut Down Windows dialog box.
In the command prompt window, navigate to the cache location, and delete all files from the folder (DEL /s)
At the command prompt, type explorer, and then press ENTER.
DELTREE — Older versions of Windows had the DELTREE command to delete all files and sub folders. This can be replicated with a script as shown on the DELTREE page.
Delete «Hello World.txt»
DEL «Hello World.txt»
Delete 3 named files:
DEL file1.txt file2.txt «C:\demo\file3.txt»
Delete all files that start with the letter A
Delete all files that end with the letter A
Delete all files with a .doc extension:
Delete all read only files:
Delete all files including any that are read only:
Normally DEL will display a list of the files deleted, if Command Extensions are disabled; it will instead display a list of any files it cannot find.
DEL is an internal command. ERASE is a synonym for DEL
“But over all things brooding slept, The quiet sense of something lost”
DELPROF — Delete user profiles.
DELTREE — Script to Delete a folder and all subfolders/files.
RD — Delete folders or entire folder trees.
CleanMgr — Automated cleanup of Temp files, Internet files, downloaded files, recycle bin.
FORFILES — Delete files older than X days.
INUSE — updated file replacement utility (may not preserve file permissions)
Q120716 — Remove Files with Reserved Names.
Q320081 — You cannot delete a file or folder.
Q159199 — A file cannot be deleted (NTFS)
PowerShell: Remove-Item — Delete the specified items.
Equivalent bash command (Linux): rmdir / rm — Remove folders/ files.
Delete files or folder recursively on Windows CMD
How do I delete files or folders recursively on Windows from the command line?
I have found this solution where path we drive on the command line and run this command.
I have given an example with a .svn file extension folder:
12 Answers 12
The other answers didn’t work for me, but this did:
/q disables Yes/No prompting
/s means delete the file(s) from all subdirectories.
Please execute the following steps:
- Open the command prompt
- Change directory to the required path
Give the following command
You can use this in the bat script:
Now, just change c:\folder a to your folder’s location. Quotation is only needed when your folder name contains spaces.
ex. RMDIR «C:\tmp» /S
Note that you’ll be prompted if you’re really going to delete the «C:\tmp» folder. Combining it with /Q switch will remove the folder silently (ex. RMDIR «C:\tmp» /S /Q )
For file deletion, I wrote following simple batch file which deleted all .pdf’s recursively:
Even for the local directory we can use it as:
The same can be applied for directory deletion where we just need to change del with rmdir.
If you want to delete a specific extension recursively, use this:
You could also do:
The /p will prompt you for each found file, if you’re nervous about deleting something you shouldn’t.
After the blog post How Can I Use Windows PowerShell to Delete All the .TMP Files on a Drive?, you can use something like this to delete all .tmp for example from a folder and all subfolders in PowerShell:
Use the Windows rmdir command
That is, rmdir /S /Q C:\Temp
I’m also using the ones below for some years now, flawlessly.
Check out other options with: forfiles /?
Delete SQM/Telemetry in windows folder recursively
Delete windows TMP files recursively
Delete user TEMP files and folders recursively