- Windows Errors, System Error Messages and Codes: Complete List and Meaning
- Windows Error Codes
- System Error Codes
- Events and Errors Message Center
- 7 Ways to Copy Text or Error Messages from Windows
- Session host virtual machine configuration
- Provide feedback
- VMs are not joined to the domain
- Error: Incorrect credentials
- Error: Timeout waiting for user input
- Error: The account used during provisioning doesn’t have permissions to complete the operation
- Error: Domain name doesn’t resolve
- Windows Virtual Desktop Agent and Windows Virtual Desktop Boot Loader are not installed
- Error: Windows Virtual Desktop Agent and Windows Virtual Desktop Agent Boot Loader are missing. C:\Windows\Temp\ScriptLog.log is also missing
- Error: Authentication failed, error in C:\Windows\Temp\ScriptLog.log
- Windows Virtual Desktop Agent is not registering with the Windows Virtual Desktop service
- Error: The status filed in Get-AzWvdSessionHost cmdlet shows status as Unavailable
- Error: Windows Virtual Desktop Agent registry entry IsRegistered shows a value of 0
- Error: Windows Virtual Desktop agent isn’t reporting a heartbeat when running Get-AzWvdSessionHost
- Troubleshooting issues with the Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack
- Error: O_REVERSE_CONNECT_STACK_FAILURE
- How to fix a Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack that malfunctions
- Remote Desktop licensing mode isn’t configured
- Disable the Remote Desktop licensing mode group policy setting
- Identify which version of Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session you’re using
- Version 1809
- Version 1903
- We couldn’t connect to the remote PC because of a security error
Windows Errors, System Error Messages and Codes: Complete List and Meaning
There used to be a nice resource – Microsoft Support ErrorFlow Website which had a wizard that took you through 3 key steps in finding the meaning of any error message and code. But unfortunately, that resource no longer exists.
Windows Error Codes
Searching for such a similar resource, I stumbled upon this 533-page document and some links from Microsoft that will help you find out the meaning of any error code.
The Windows Error Codes document lists the common usage details for those Win32 error codes, HRESULT values, and NTSTATUS values that are referenced by specifications in the protocol documentation set. You can download the PDF from Microsoft by visiting here.
In a lighter vein, it may amuse you to learn that Microsoft appears to have an error code even if the operation completes successfully! Check what it says for 0x00000000: The operation completed successfully! 🙂
System Error Codes
When using an application on your computer, if it is well-written, it will include an error-handling code that allows them to recover from unexpected errors. When such a system error occurs, the application may request user intervention, or it may be able to recover on its own, or it may require a system reboot. This page lists the system error codes and their meanings.
Events and Errors Message Center
At times you may want to search for help, support, detailed message explanations, recommended user actions and links to additional support and resources, to events & error messages which your Windows Operating System or any other Microsoft product may throw up. The Microsoft Events and Errors Message Center is a great place to start a search for these!
Events and Errors Message Center lets you search for and find detailed message explanations, recommended user actions, and offers links to additional support and resources. To perform a search, you will need details like Event ID, Event Source, Message Text, File Name. These values can be found in the Event Viewer logs. The Event Viewer can be accessed from the Administrative Tools section of the Control Panel. You can locate the Error Source and the ID in the list of events there.
Visit Microsoft Events and Errors Message Center for drtails.
TIP: These free Windows Error Code Lookup Tools may also help you.
7 Ways to Copy Text or Error Messages from Windows
If you are having problems with Windows itself or any other software, one of the things you might be asked to do is supply the information in any errors or messages that are being displayed to help with troubleshooting. Some error messages are quite short and not difficult to type in, and others can be long and a real pain to repeat accurately with combinations of numbers, letters and special characters all being used.
It’s often better to also enter an exact error code or phrase into a search engine such as Google to get more precise results for the problem. Of course, taking a screenshot can be used to send an error message to someone else, but this isn’t always that helpful because they might have to re-type the message data in at the other end, and it also won’t help if you want to search the internet.
Windows error dialog boxes and general information windows don’t have a nice and easy button for you to copy all the error messages, and they won’t let you highlight the the text so it can be copied. There are ways for you to do it though and copying information from Windows message boxes, 3rd party software dialogs or the Command Prompt can be made easier when you know how. Here are 7 solutions to try.
Actually there is a very easy way you can copy Windows dialog box and error messages. When the box appears, simply make sure it’s the active window and press the standard Windows copy shortcut combination of Ctrl+C. Now the data is in the clipboard, paste the contents into notepad or webpage etc.
For example, if you type raymond.exe into a Run box (Win key+R), Windows will show a not found error:
Press Ctrl+C, open Notepad and then press Ctrl+V to produce the following:
[Content]
Windows cannot find ‘raymond.exe’. Make sure you typed the name correctly, and then try again.
You will get not just the text content but also the window’s title and the name of any buttons. This is very useful but unfortunately only works on dialog boxes created by Windows. If the window message is custom and created by third party software, this method won’t work. For that, you will need to use one of the other tools below.
2. GetWindowText
GetWindowText is a free and portable tool by the same developer of the popular Q-Dir file manager. To use it to copy the text from control boxes, left click on the question mark icon in the top left and drag the mouse cursor to the box that you want it to read the data from. It can read almost all text from edit, static, sysTreeView, sysListView, combobox and groupbox controls etc. Simply highlight and copy the text from the box in the GetWindowText program.
3. ShoWin
ShoWin is actually a small tool from McAfee and in addition to finding text in a window or dialog, it can also be used to display the password in a dialog hidden behind asterisks. Simply drag the cross hair over the control to get information about it and the included text, the copy button will copy all details, not just the text. Additional features include the ability to enable disabled windows, unhide hidden windows and force windows to stay on top or be placed below others.
4. SysExporter
SysExporter is another small and portable utility from Nirsoft and allows you to grab the data stored in list-views, tree-views, list boxes, combo boxes, text-boxes, and controls from most applications. It also has a drag and drop target icon to catch specific window contents from error message boxes etc, and can be used to capture a folder tree or list of files from an Explorer or application window. Any data can be copied or exported to a text, html or xml file.
5. WinScraper
WinScraper is able to scrape the text from a dialog box control or message box by dragging the target icon over the text or window. The result will show in the “Window Text:” box and can be copied out and pasted as text into an email or forum post etc. It can capture images of controls or windows from applications such as icons, and also can resize application or web browser windows to a specific size for testing alternate screen resolutions.
6. Textractor
Textractor is a text monitoring tool that captures and logs all text a program writes to the screen. The tool works by you supplying the program to monitor and then it captures and records any output from the application to its window. Each line can be right clicked on and copied / removed or the whole text can be saved to a file. This obviously won’t record general Windows errors but can get error dialogs or window text from specific software.
7. Copy Text from Command Prompt
Although not a dialog window, copying text out from the Command Prompt is quite useful if you want to copy the results or errors of a command. It’s very easy when you know how and doesn’t require the use of software, but still many people don’t know you can. There are 2 ways to do it.
1. While you’re in Command Prompt, right click at anywhere inside the window and select Mark.
2. Now use your left mouse button to drag a box over the area of text that you want to copy, scroll can also be used to capture multiple lines. Once you have the text, click the right mouse button or press Enter to copy the selected text to the clipboard. Then you can right click and select Paste to paste into Notepad or a webpage etc.
1. Right click on Command Prompt’s title bar and select Properties. On the options tab, tick to enable QuickEdit Mode and click OK.
Now your left mouse button will permanently be used to mark text and the right mouse will copy it to the clipboard. If there is no highlighted text, the right mouse button will paste any clipboard contents to the window, useful for copying commands off a webpage etc.
Session host virtual machine configuration
This content applies to Windows Virtual Desktop with Azure Resource Manager Windows Virtual Desktop objects. If you’re using Windows Virtual Desktop (classic) without Azure Resource Manager objects, see this article.
Use this article to troubleshoot issues you’re having when configuring the Windows Virtual Desktop session host virtual machines (VMs).
Provide feedback
Visit the Windows Virtual Desktop Tech Community to discuss the Windows Virtual Desktop service with the product team and active community members.
VMs are not joined to the domain
Follow these instructions if you’re having issues joining virtual machines (VMs) to the domain.
- Join the VM manually using the process in Join a Windows Server virtual machine to a managed domain or using the domain join template.
- Try pinging the domain name from a command line on the VM.
- Review the list of domain join error messages in Troubleshooting Domain Join Error Messages.
Error: Incorrect credentials
Cause: There was a typo made when the credentials were entered in the Azure Resource Manager template interface fixes.
Fix: Take one of the following actions to resolve.
- Manually add the VMs to a domain.
- Redeploy the template once credentials have been confirmed. See Create a host pool with PowerShell.
- Join VMs to a domain using a template with Joins an existing Windows VM to AD Domain.
Error: Timeout waiting for user input
Cause: The account used to complete the domain join may have multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Fix: Take one of the following actions to resolve.
- Temporarily remove MFA for the account.
- Use a service account.
Error: The account used during provisioning doesn’t have permissions to complete the operation
Cause: The account being used doesn’t have permissions to join VMs to the domain due to compliance and regulations.
Fix: Take one of the following actions to resolve.
- Use an account that is a member of the Administrator group.
- Grant the necessary permissions to the account being used.
Error: Domain name doesn’t resolve
Cause 1: VMs are on a virtual network that’s not associated with the virtual network (VNET) where the domain is located.
Fix 1: Create VNET peering between the VNET where VMs were provisioned and the VNET where the domain controller (DC) is running. See Create a virtual network peering — Resource Manager, different subscriptions.
Cause 2: When using Azure Active Directory Domain Services (Azure AD DS), the virtual network doesn’t have its DNS server settings updated to point to the managed domain controllers.
Fix 2: To update the DNS settings for the virtual network containing Azure AD DS, see Update DNS settings for the Azure virtual network.
Cause 3: The network interface’s DNS server settings do not point to the appropriate DNS server on the virtual network.
Fix 3: Take one of the following actions to resolve, following the steps in [Change DNS servers].
- Change the network interface’s DNS server settings to Custom with the steps from Change DNS servers and specify the private IP addresses of the DNS servers on the virtual network.
- Change the network interface’s DNS server settings to Inherit from virtual network with the steps from Change DNS servers, then change the virtual network’s DNS server settings with the steps from Change DNS servers.
Windows Virtual Desktop Agent and Windows Virtual Desktop Boot Loader are not installed
The recommended way to provision VMs is using the Azure portal creation template. The template automatically installs the Windows Virtual Desktop Agent and Windows Virtual Desktop Agent Boot Loader.
Follow these instructions to confirm the components are installed and to check for error messages.
- Confirm that the two components are installed by checking in Control Panel >Programs >Programs and Features. If Windows Virtual Desktop Agent and Windows Virtual Desktop Agent Boot Loader are not visible, they aren’t installed on the VM.
- Open File Explorer and navigate to C:\Windows\Temp\ScriptLog.log. If the file is missing, it indicates that the PowerShell DSC that installed the two components was not able to run in the security context provided.
- If the file C:\Windows\Temp\ScriptLog.log is present, open it and check for error messages.
Error: Windows Virtual Desktop Agent and Windows Virtual Desktop Agent Boot Loader are missing. C:\Windows\Temp\ScriptLog.log is also missing
Cause 1: Credentials provided during input for the Azure Resource Manager template were incorrect or permissions were insufficient.
Fix 1: Manually add the missing components to the VMs using Create a host pool with PowerShell.
Cause 2: PowerShell DSC was able to start and execute but failed to complete as it can’t sign in to Windows Virtual Desktop and obtain needed information.
Fix 2: Confirm the items in the following list.
- Make sure the account doesn’t have MFA.
- Confirm the host pool’s name is accurate and the host pool exists in Windows Virtual Desktop.
- Confirm the account has at least Contributor permissions on the Azure subscription or resource group.
Error: Authentication failed, error in C:\Windows\Temp\ScriptLog.log
Cause: PowerShell DSC was able to execute but couldn’t connect to Windows Virtual Desktop.
Fix: Confirm the items in the following list.
- Manually register the VMs with the Windows Virtual Desktop service.
- Confirm account used for connecting to Windows Virtual Desktop has permissions on the Azure subscription or resource group to create host pools.
- Confirm account doesn’t have MFA.
Windows Virtual Desktop Agent is not registering with the Windows Virtual Desktop service
When the Windows Virtual Desktop Agent is first installed on session host VMs (either manually or through the Azure Resource Manager template and PowerShell DSC), it provides a registration token. The following section covers troubleshooting issues that apply to the Windows Virtual Desktop Agent and the token.
Error: The status filed in Get-AzWvdSessionHost cmdlet shows status as Unavailable
Cause: The agent isn’t able to update itself to a new version.
Fix: Follow these instructions to manually update the agent.
- Download a new version of the agent on the session host VM.
- Launch Task Manager and, in the Service Tab, stop the RDAgentBootLoader service.
- Run the installer for the new version of the Windows Virtual Desktop Agent.
- When prompted for the registration token, remove the entry INVALID_TOKEN and press next (a new token isn’t required).
- Complete the installation Wizard.
- Open Task Manager and start the RDAgentBootLoader service.
Error: Windows Virtual Desktop Agent registry entry IsRegistered shows a value of 0
Cause: Registration token has expired.
Fix: Follow these instructions to fix the agent registry error.
- If there’s already a registration token, remove it with Remove-AzWvdRegistrationInfo.
- Run the New-AzWvdRegistrationInfo cmdlet to generate a new token.
- Confirm that the -ExpriationTime parameter is set to 3 days.
Error: Windows Virtual Desktop agent isn’t reporting a heartbeat when running Get-AzWvdSessionHost
Cause 1: RDAgentBootLoader service has been stopped.
Fix 1: Launch Task Manager and, if the Service Tab reports a stopped status for RDAgentBootLoader service, start the service.
Cause 2: Port 443 may be closed.
Fix 2: Follow these instructions to open port 443.
Confirm port 443 is open by downloading the PSPing tool from Sysinternal tools.
Install PSPing on the session host VM where the agent is running.
Open the command prompt as an administrator and issue the command below:
Confirm that PSPing received information back from the RDBroker:
Troubleshooting issues with the Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack
The Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack is automatically installed with Windows Server 2019. Use Microsoft Installer (MSI) to install the side-by-side stack on Microsoft Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2012 R2. For Microsoft Windows 10, the Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack is enabled with enablesxstackrs.ps1.
There are three main ways the side-by-side stack gets installed or enabled on session host pool VMs:
- With the Azure portal creation template
- By being included and enabled on the master image
- Installed or enabled manually on each VM (or with extensions/PowerShell)
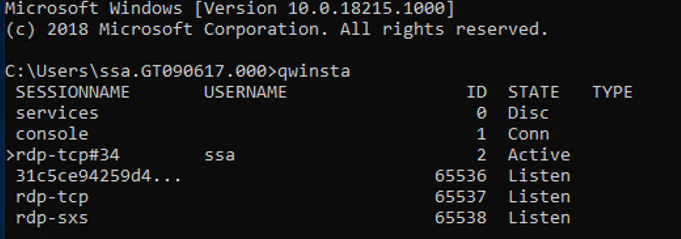
If you’re having issues with the Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack, type the qwinsta command from the command prompt to confirm that the side-by-side stack is installed or enabled.
The output of qwinsta will list rdp-sxs in the output if the side-by-side stack is installed and enabled.
Examine the registry entries listed below and confirm that their values match. If registry keys are missing or values are mismatched, make sure you’re running a supported operating system. If you are, follow the instructions in Create a host pool with PowerShell on how to reinstall the side-by-side stack.
Error: O_REVERSE_CONNECT_STACK_FAILURE
Cause: The side-by-side stack isn’t installed on the session host VM.
Fix: Follow these instructions to install the side-by-side stack on the session host VM.
- Use Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to get directly into the session host VM as local administrator.
- Install the side-by-side stack using Create a host pool with PowerShell.
How to fix a Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack that malfunctions
There are known circumstances that can cause the side-by-side stack to malfunction:
- Not following the correct order of the steps to enable the side-by-side stack
- Auto update to Windows 10 Enhanced Versatile Disc (EVD)
- Missing the Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) role
- Running enablesxsstackrc.ps1 multiple times
- Running enablesxsstackrc.ps1 in an account that doesn’t have local admin privileges
The instructions in this section can help you uninstall the Windows Virtual Desktop side-by-side stack. Once you uninstall the side-by-side stack, go to «Register the VM with the Windows Virtual Desktop host pool» in Create a host pool with PowerShell to reinstall the side-by-side stack.
The VM used to run remediation must be on the same subnet and domain as the VM with the malfunctioning side-by-side stack.
Follow these instructions to run remediation from the same subnet and domain:
Connect with standard Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to the VM from where fix will be applied.
Unzip the downloaded file.
Start command prompt as local administrator.
Navigate to folder where PsExec was unzipped.
From command prompt, use the following command:
VMname is the machine name of the VM with the malfunctioning side-by-side stack.
Accept the PsExec License Agreement by clicking Agree.
This dialog will show up only the first time PsExec is run.
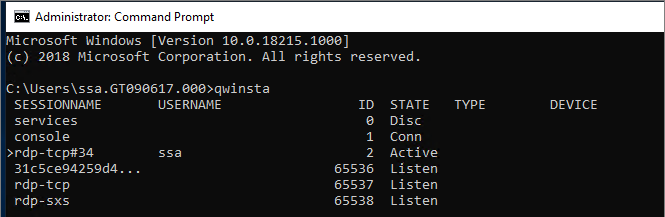
After the command prompt session opens on the VM with the malfunctioning side-by-side stack, run qwinsta and confirm that an entry named rdp-sxs is available. If not, a side-by-side stack isn’t present on the VM so the issue isn’t tied to the side-by-side stack.
Run the following command, which will list Microsoft components installed on the VM with the malfunctioning side-by-side stack.
Run the command below with product names from step above.
Uninstall all products that start with «Remote Desktop.»
After all Windows Virtual Desktop components have been uninstalled, follow the instructions for your operating system:
If your operating system is Windows Server, restart the VM that had the malfunctioning side-by-side stack (either with Azure portal or from the PsExec tool).
If your operating system is Microsoft Windows 10, continue with the instructions below:
From the VM running PsExec, open File Explorer and copy disablesxsstackrc.ps1 to the system drive of the VM with the malfunctioned side-by-side stack.
VMname is the machine name of the VM with the malfunctioning side-by-side stack.
The recommended process: from the PsExec tool, start PowerShell and navigate to the folder from the previous step and run disablesxsstackrc.ps1. Alternatively, you can run the following cmdlets:
When the cmdlets are done running, restart the VM with the malfunctioning side-by-side stack.
Remote Desktop licensing mode isn’t configured
If you sign in to Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session using an administrative account, you might receive a notification that says, «Remote Desktop licensing mode is not configured, Remote Desktop Services will stop working in X days. On the Connection Broker server, use Server Manager to specify the Remote Desktop licensing mode.»
If the time limit expires, an error message will appear that says, «The remote session was disconnected because there are no Remote Desktop client access licenses available for this computer.»
If you see either of these messages, this means the image doesn’t have the latest Windows updates installed or that you are setting the Remote Desktop licensing mode through group policy. Follow the steps in the next sections to check the group policy setting, identify the version of Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session, and install the corresponding update.
Windows Virtual Desktop only requires an RDS client access license (CAL) when your host pool contains Windows Server session hosts. To learn how to configure an RDS CAL, see License your RDS deployment with client access licenses.
Disable the Remote Desktop licensing mode group policy setting
Check the group policy setting by opening the Group Policy Editor in the VM and navigating to Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Licensing > Set the Remote Desktop licensing mode. If the group policy setting is Enabled, change it to Disabled. If it’s already disabled, then leave it as-is.
If you set group policy through your domain, disable this setting on policies that target these Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session VMs.
Identify which version of Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session you’re using
To check which version of Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session you have:
Sign in with your admin account.
Enter «About» into the search bar next to the Start menu.
Select About your PC.
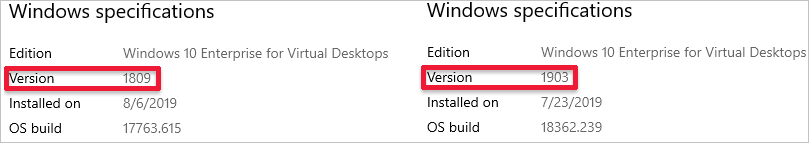
Check the number next to «Version.» The number should be either «1809» or «1903,» as shown in the following image.
Now that you know your version number, skip ahead to the relevant section.
Version 1809
If your version number says «1809,» install the KB4516077 update.
Version 1903
Redeploy the host operating system with the latest version of the Windows 10, version 1903 image from the Azure Gallery.
We couldn’t connect to the remote PC because of a security error
If your users see an error that says, “We couldn’t connect to the remote PC because of a security error. If this keeps happening, ask your admin or tech support for help,” validate any existing policies that change default RDP permissions. One policy that might cause this error to appear is “Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services security policy.»