- Анализ аварийных дампов Windows
- Содержание
- Анализ аварийного дампа утилитой BlueScreenView
- Анализ аварийного дампа отладчиком WinDbg
- Установка Debugging Tools for Windows (WinDbg)
- Настройка отладочных символов
- Анализ аварийного дампа
- Получение информации о проблемном драйвере
- Аппаратные причины возникновения критических ошибок
- Диагностика неисправностей диска
- Диагностика неисправностей памяти
- Настройка параметров сохранения аварийного дампа
- Windows crash dump location (memory.dmp file)
- How to enable or disable kernel memory dump? If dump is enabled, how to choose mini dump or full kernel dump?
- How to change crash dump file location?
- How to enable or disable crash dump file overwrite?
- Modifying Windows dump settings using registry keys
- How to disable crash dump?
- Disable crash dump overwrite
- DumpChk
- Where to get DumpChk
- DumpChk command-line options
- Parameters
- Using DumpChk
- Generate a kernel or complete crash dump
- Set up page files
- Enable memory dump setting
- Tips to generate memory dumps
- Manually generate a memory dump file
- Use the NotMyFault tool
- Use NMI
Анализ аварийных дампов Windows
В случае критической ошибки система останавливает свою работу, отображает синий экран смерти (BSOD), информация об ошибке и содержимое памяти сохраняется в файле подкачки. При последующей загрузке системы, на основе сохраненных данных, создается аварийный дамп c отладочной информацией. В системном журнале событий создается запись о критической ошибке.
Если критическая ошибка возникла на ранней стадии загрузки системы или в результате ошибки произошел отказ дисковой подсистемы, аварийный дамп сохранен не будет.
Аварийный дамп может быть проанализирован с помощью утилиты BlueScreenView или системного отладчика WinDbg (Debugging Tools for Windows).
Содержание
Анализ аварийного дампа утилитой BlueScreenView
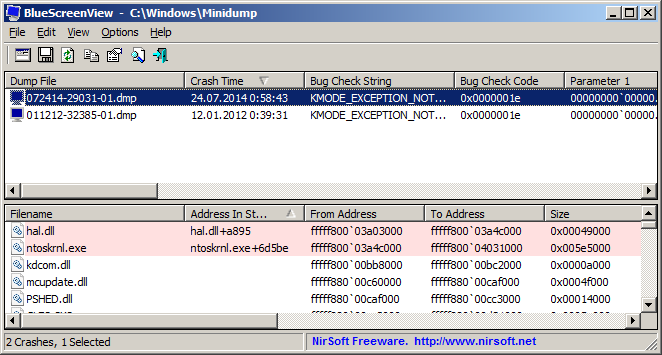
Простейшим инструментом для анализа аварийных дампов является утилита BlueScreenView от NirSoft.
BlueScreenView сканирует папку с минидампами и отображает информацию по найденным отказам.
По каждому отказу отображается дата, данные об ошибке и драйвер, который предположительно вызвал отказ.
В нижней части окна отображается список загруженных в системе драйверов. Модули, к которым выполнялось обращение в момент отказа, выделены цветом, на них следует обратить особое внимание, они могут быть причиной отказа.
По двойному клику отображается дополнительная информация.
Анализ аварийного дампа отладчиком WinDbg
С помощью WinDbg из аварийного дампа можно вытащить более детальную информацию, включая расшифровку стека.
Установка Debugging Tools for Windows (WinDbg)
Microsoft распространяет WinDbg только в составе SDK, загрузить веб-установщик можно на странице загрузки.
Для анализа аварийных дампов установка SDK не требуется. Скачать Debugging Tools for Windows (WinDbg) отдельным пакетом можно здесь.
После установки, корректируем ярлык для запуска WinDbg. В свойствах ярлыка, устанавливаем флажок запуска от имени администратора. Также, в качестве рабочей папки, задаем: %SystemRoot%\Minidump.
Настройка отладочных символов
Отладочные символы содержат символические имена функций из исходного кода. Они необходимы для расшифровки и интерпретации аварийного дампа.
При первом запуске WinDbg, необходимо указать путь к отладочным символам, для этого открываем меню File, Symbol File Path, или используем комбинацию Ctrl+S.
Следующей строкой включаем загрузку отладочных символов из сети, задаем локальный путь для сохранения файлов и адрес для загрузки из интернета:
Анализ аварийного дампа
В меню выбираем File, Open Crash Dump, или нажимаем Ctrl+D.
Указываем путь к дампу %SystemRoot%\MEMORY.DMP или %SystemRoot%\Minidump\файл.dmp.
Загрузка отладочных символов из интернета может занять некоторое время.
Для получения детальной информации выполняем команду:
Дебаггер сам вам предложит ее выполнить, достаточно навести указатель мыши на ссылку и кликнуть.
В результате получаем следующий вывод:
Получение информации о проблемном драйвере
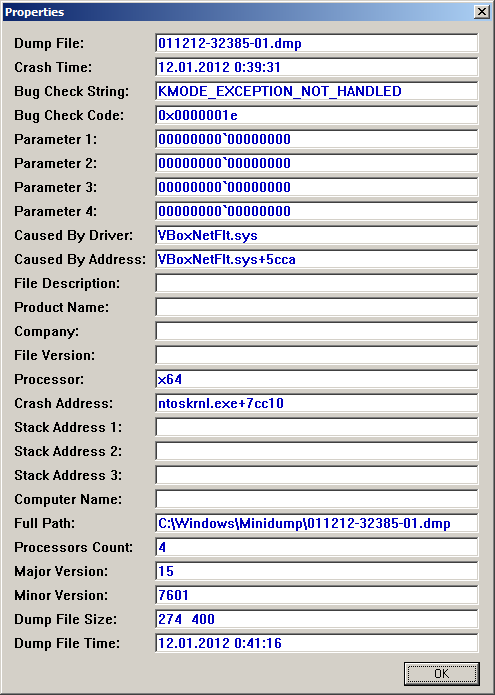
Если удалось обнаружить драйвер, в котором возникла ошибка, имя драйвера будет отображено в полях MODULE_NAME и IMAGE_NAME.
Чтобы получить путь к файлу и прочую информацию, щелкаем по ссылке на модуль:
Если полный путь к драйверу не указан, по умолчанию используется папка %SystemRoot%\system32\drivers.
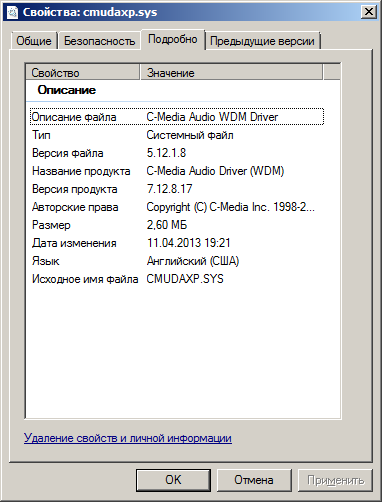
Находим указанный файл, и изучаем его свойства.
Обновляем проблемный драйвер.
Аппаратные причины возникновения критических ошибок
Источником критических ошибок нередко бывают неисправности в дисковой подсистеме, или в подсистеме памяти.
Диагностика неисправностей диска
В случае ошибок дисковой подсистемы, аварийный дамп может не сохраняться.
Чтобы исключить проблемы с диском, проверяем системный журнал событий на наличие ошибок чтения и записи на диск.
Проверяем параметры S.M.A.R.T жесткого диска, получить их можно, например, с помощью программы SpeedFan.
Особое внимание обращаем на параметры: «Current Pending Sector Count» и «Uncorrectable Sector Count», ненулевые значения этих параметров сигнализируют о неисправности диска.
Ненулевое значение параметра: «UltraDMA CRC Error Count», сигнализирует о проблеме с SATA-кабелем.
Подробнее о параметрах S.M.A.R.T. читаем в статье Википедии.
Диагностика неисправностей памяти
Проблемы с памятью нередко могут стать причиной самых разнообразных глюков, включая различные синие экраны, зависания, аварийное завершение программ, повреждение реестра, повреждение файловой системы и данных.
Выявить проблемы с памятью можно с помощью утилиты Memtest86+.
Загружаем образ по ссылке, записываем на диск, загружаемся с диска, запускается тест.
Начиная с Windows Vista, в системе имеется свой тест памяти. Для его запуска нажимаем «Пуск», в строке поиска набираем «памяти«, выбираем «Средство диагностики памяти Windows».
Проблемы с памятью в некоторых случаях могут быть устранены обновлением BIOS.
Настройка параметров сохранения аварийного дампа
Для изменения параметров сохранения аварийного дампа нажимаем кнопку «Пуск», щелкаем на «Компьютер» правой кнопкой мыши, в контекстном меню выбираем «Свойства». В окне «Система» слева выбираем «Дополнительные параметры системы», в группе «Загрузка и восстановление» нажимаем кнопку «Параметры».
Windows crash dump location (memory.dmp file)
When Windows OS crashes (Blue Screen of Death or BSOD) it dumps all the memory information into a file on disk. This dump file can help the developers to debug the cause for the crash. The default location of the dump file is %SystemRoot%memory.dmp i.e C:\Windows\memory.dmp if C: is the system drive. Windows can also capture small memory dumps which occupy less space. These dumps are created at %SystemRoot%Minidump.dmp (C:\Window\Minidump.dump if C: is the system drive). Below you can find details on crash dump settings. This article is applicable for XP, Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 10.
How to enable or disable kernel memory dump? If dump is enabled, how to choose mini dump or full kernel dump?
We can configure the dump settings through system properties. Detailed steps are given below.
- Open System properties(Execute sysdm.cpl from Run window)
- Click on Advanced tab
- Click on the Settings button under Startup and Recovery
- In this window, click on the drop down list under ‘Write Debugging information’
- This list would show 6 options – None, Small memory dump(64 KB), Kernel memory dump, Complete memory dump, Automatic memory dump and Active memory dump. If you want to disable memory dump then select none from these options. Otherwise select your required option from the other three. After this click on OK and close the windows.
How to change crash dump file location?
You can set the dump file location in the same Startup and recovery window mentioned above. In the ‘Dump File’ text field you can enter the location of the file.
You can also change mini dump file location – Select ‘small memory dump‘ from the drop down box and then give the location of the file in the bottom text box.
How to enable or disable crash dump file overwrite?
In the Startup and recovery window(which can be opened from System properties window) unselect the check button ‘Overwrite any existing file‘ to disable crash dump overwrite.
Modifying Windows dump settings using registry keys
Registry values related to Windows crash dump settings are stored under the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl.
We can configure crash dump by modifying these registry values also(listed below).
-
- AutoReboot
- CrashDumpEnabled
- DumpFile
- LogEvent
- MinidumpDir
- Overwrite
- SendAlert
How to disable crash dump?
Open registry editor and navigate to the path HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl . Set the registry value CrashDumpEnabled to 0. Or you can simply run the below command which does the same.
Disable crash dump overwrite
Set the value of the registry key ‘Overwrite’ to 0. This key can be found in the registry path mentioned above. If you want to overwrite existing crash dump file, then set its value to 1. Below command would disable crash dump overwrite.
DumpChk
DumpChk (the Microsoft Crash Dump File Checker tool) is a program that performs a quick analysis of a crash dump file. This enables you to see summary information about what the dump file contains. If the dump file is corrupt in such a way that it cannot be opened by a debugger, DumpChk reveals this fact.
Where to get DumpChk
DumpChk command-line options
Parameters
-y SymbolPath
SymbolPath specifies where DumpChk is to search for symbols. Symbol information may be necessary for some dump files. It can also help to improve the information shown in the dump file by allowing symbol names to be resolved.DumpFile
DumpFile specifies the crash dump file that is to be analyzed. This may include an absolute or relative directory path or universal naming convention (UNC) path. If DumpFile contains spaces, it must be enclosed in quotation marks.Using DumpChk
Here is an example in which the dump file is corrupt. The error shown at the end, DebugClient cannot open DumpFile , indicates that some kind of corruption must have occurred:
Because this display does not end with the words Finished dump check , the dump file is corrupt. The error message at the end explains that the dump file could not be opened.
Note that other errors may be listed, some of which are actually benign. For example, the following error message does not represent a problem:
Here is an example of DumpChk run on a healthy user-mode minidump. The display begins with an overall summary of the dump file, and then gives detailed information about what data is contained in the dump file:
The output begins by identifying the characteristics of the dump file — in this case, a user-mode minidump with full memory information, including application data but not operating-system data. This is followed by the symbol path being used by DumpChk, and then a summary of the dump file contents.
Because this display ends with the words Finished dump check , the dump file is probably not corrupt, and can be opened by a debugger. However, more subtle forms of corrruption might still be present in the file.
Generate a kernel or complete crash dump
A system crash (also known as a “bug check” or a «Stop error») occurs when Windows can’t run correctly. The dump file that is produced from this event is called a system crash dump.
A manual kernel or complete memory dump file is useful when you troubleshoot several issues because the process captures a record of system memory at the time of a crash.
Set up page files
See Support for system crash dumps for the page file size requirement for system crash dump.
Enable memory dump setting
You must be logged on as an administrator or a member of the Administrators group to complete this procedure. If your computer is connected to a network, network policy settings may prevent you from completing this procedure.
To enable memory dump setting, follow these steps:
In Control Panel, select System and Security > System.
Select Advanced system settings, and then select the Advanced tab.
In the Startup and Recovery area, select Settings.
Make sure that Kernel memory dump or Complete memory dump is selected under Writing Debugging Information.
Restart the computer.
You can change the dump file path by edit the Dump file field. In other words, you can change the path from %SystemRoot%\Memory.dmp to point to a local drive that has enough disk space, such as E:\Memory.dmp.
Tips to generate memory dumps
When the computer crashes and restarts, the contents of physical RAM are written to the paging file that is located on the partition on which the operating system is installed.
Depending on the speed of the hard disk on which Windows is installed, dumping more than 2 gigabytes (GB) of memory may take a long time. Even in a best case scenario, if the dump file is configured to reside on another local hard drive, a significant amount of data will be read and written to the hard disks. This can cause a prolonged server outage.
Use this method to generate complete memory dump files with caution. Ideally, you should do this only when you are explicitly requested to by the Microsoft Support engineer. Any kernel or complete memory dump file debugging should be the last resort after all standard troubleshooting methods have been completely exhausted.
Manually generate a memory dump file
Use the NotMyFault tool
If you can log on while the problem is occurring, you can use the Microsoft Sysinternals NotMyFault tool. To do this, follow these steps:
Download the NotMyFault tool.
Select Start, and then select Command Prompt.
At the command line, run the following command:
This operation generates a memory dump file and a D1 Stop error.
Use NMI
On some computers, you cannot use keyboard to generate a crash dump file. For example, Hewlett-Packard (HP) BladeSystem servers from the Hewlett-Packard Development Company are managed through a browser-based graphical user interface (GUI). A keyboard is not attached to the HP BladeSystem server.
In these cases, you must generate a complete crash dump file or a kernel crash dump file by using the Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) switch that causes an NMI on the system processor.
To do this, follow these steps:
Follow the steps in this section carefully. Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Before you modify it, back up the registry for restoration in case problems occur.
In Registry Editor, locate the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl
Right-click CrashControl, point to New, and then click DWORD Value.
Type NMICrashDump, and then press Enter.
Right-click NMICrashDump, and then select Modify.
In the Value data box, type 1, and then select OK.
Restart the computer.
Hardware vendors, such as HP, IBM, and Dell, may provide an Automatic System Recovery (ASR) feature. You should disable this feature during troubleshooting. For example, if the HP and Compaq ASR feature is enabled in the BIOS, disable this feature while you troubleshoot to generate a complete Memory.dmp file. For the exact steps, contact your hardware vendor.
Enable the NMI switch in the BIOS or by using the Integrated Lights Out (iLO) Web interface.
For the exact steps, see the BIOS reference manual or contact your hardware vendor.
Test this method on the server by using the NMI switch to generate a dump file. You will see a STOP 0x00000080 hardware malfunction.
If you want to run NMI in Microsoft Azure using Serial Console, see Use Serial Console for SysRq and NMI calls.