- Environment Variables
- Set PATH and other environment variables in Windows 10
- Set environment variables from command prompt
- Set environment variable by Registry edit
- Изучаем переменные среды в Windows 10
- Переменные среды Windows
- Переменные PATH и PATHEXT
- Создание переменных среды
- Заключение
- How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 10
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 8
- Setting the path and variables in Windows Vista and Windows 7
- Setting the path and variables in Windows 2000 and Windows XP
- What is the default Windows %PATH%?
- Setting path in the MS-DOS and Windows command line
Environment Variables
Every process has an environment block that contains a set of environment variables and their values. There are two types of environment variables: user environment variables (set for each user) and system environment variables (set for everyone).
By default, a child process inherits the environment variables of its parent process. Programs started by the command processor inherit the command processor’s environment variables. To specify a different environment for a child process, create a new environment block and pass a pointer to it as a parameter to the CreateProcess function.
The command processor provides the set command to display its environment block or to create new environment variables. You can also view or modify the environment variables by selecting System from the Control Panel, selecting Advanced system settings, and clicking Environment Variables.
Each environment block contains the environment variables in the following format: Var1=Value1\0
Var2=Value2\0
Var3=Value3\0
.
VarN=ValueN\0\0
The name of an environment variable cannot include an equal sign (=).
The GetEnvironmentStrings function returns a pointer to the environment block of the calling process. This should be treated as a read-only block; do not modify it directly. Instead, use the SetEnvironmentVariable function to change an environment variable. When you are finished with the environment block obtained from GetEnvironmentStrings, call the FreeEnvironmentStrings function to free the block.
Calling SetEnvironmentVariable has no effect on the system environment variables. To programmatically add or modify system environment variables, add them to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment registry key, then broadcast a WM_SETTINGCHANGE message with lParam set to the string «Environment». This allows applications, such as the shell, to pick up your updates.
The maximum size of a user-defined environment variable is 32,767 characters. There is no technical limitation on the size of the environment block. However, there are practical limits depending on the mechanism used to access the block. For example, a batch file cannot set a variable that is longer than the maximum command line length.
Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: The maximum size of the environment block for the process is 32,767 characters. Starting with WindowsВ Vista and Windows ServerВ 2008, there is no technical limitation on the size of the environment block.
The GetEnvironmentVariable function determines whether a specified variable is defined in the environment of the calling process, and, if so, what its value is.
To retrieve a copy of the environment block for a given user, use the CreateEnvironmentBlock function.
To expand environment-variable strings, use the ExpandEnvironmentStrings function.
Set PATH and other environment variables in Windows 10
In older windows systems you had to navigate to Advanced System Settings in Control Panel to view, edit or add environmental variables.
- Windows XP — Right-click My Computer, and then click Properties → Advanced → Environment variables → Choose New, Edit or Delete.
- Windows 7 — Click on Start → Computer → Properties → Advanced System Settings → Environment variables → Choose New, Edit or Delete.
In Windows 8 and 10, you can navigate to Advanced System Settings in a similar way.
- Windows 8 — Right click on bottom left corner to get Power User Task Menu → Select System → Advanced System Settings → Environment variables → Choose New, Edit or Delete.
- Windows 10 — Right click on Start Menu to get Power User Task Menu → Select System → Advanced System Settings → Environment variables → Choose New, Edit or Delete.
However, in Windows 10 you can directly get to the Environment Variables window using Search the web and Windows box next to the Start menu. Type environment variables in Windows Search box which gives you two options in search results:
- Edit the system environment variables
- Edit environment variables for your account.
Choose either option and you can add, edit or delete environment variables like PATH.


Set environment variables from command prompt
You can set environment variables from Windows Command Prompt using the set or setx command. The set command only sets the environment variable for the current session. The setx command sets it permanently, but not for the current session. If you want to set it for current as well as future sessions, use both setx and set.
For example, you can set the PATH environment variable permanently (current and future sessions) as below:
To view the current path, run:
- By default setx sets the variable in the local environment (Under HKEY_Current_User Registry key). If you want to set the system variable (Under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE registry key), use the flag /m. Start the command prompt as administrator on Windows 10, right click on Start menu and select Command Prompt(Admin).
- The maximum value allowed for a enviroment variable is 1024 characters. So if your variable is long and you try to append to it with setx, you may get a truncated result.
Set environment variable by Registry edit
If your PATH variable is too long, then the best method would be to edit the registry.
For user environment variables, change the key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment . For System Environment variables change
Add, Edit or Delete the environment variable you want to change, then reboot to activate the changes.
Изучаем переменные среды в Windows 10
Переменные среды Windows
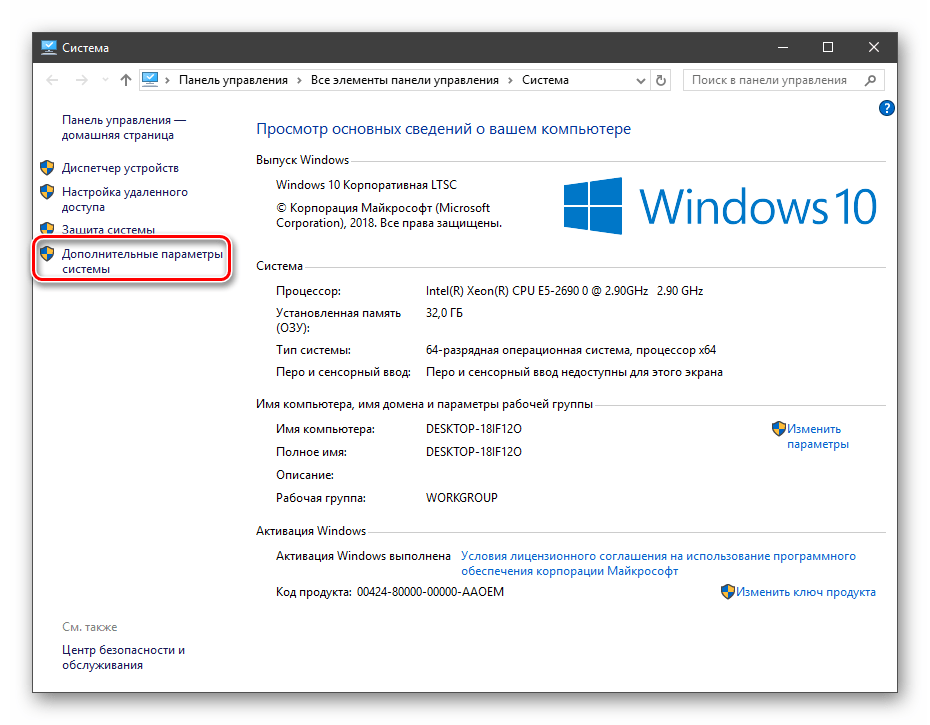
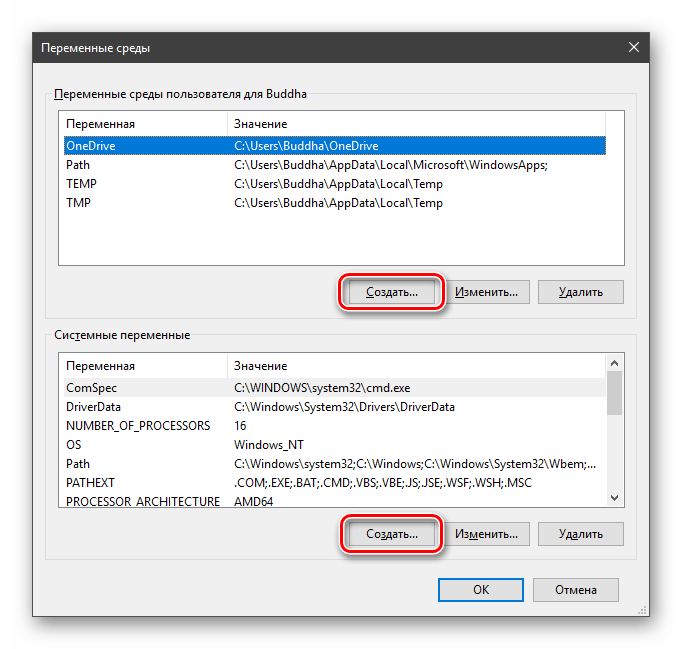
Получить информацию о существующих переменных можно в свойствах системы. Для этого кликаем по ярлыку Компьютера на рабочем столе правой кнопкой мыши и выбираем соответствующий пункт.
Переходим в «Дополнительные параметры».
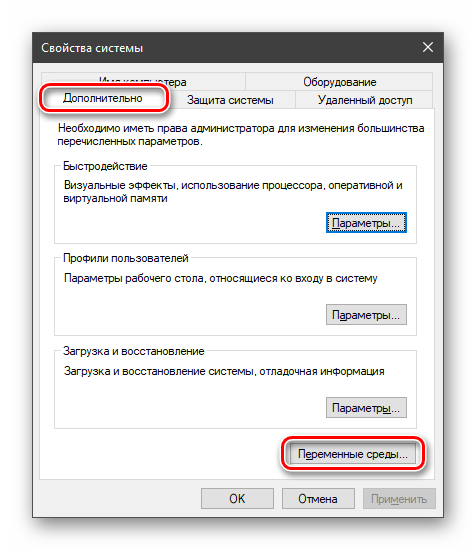
В открывшемся окне с вкладкой «Дополнительно» нажимаем кнопку, указанную на скриншоте ниже.
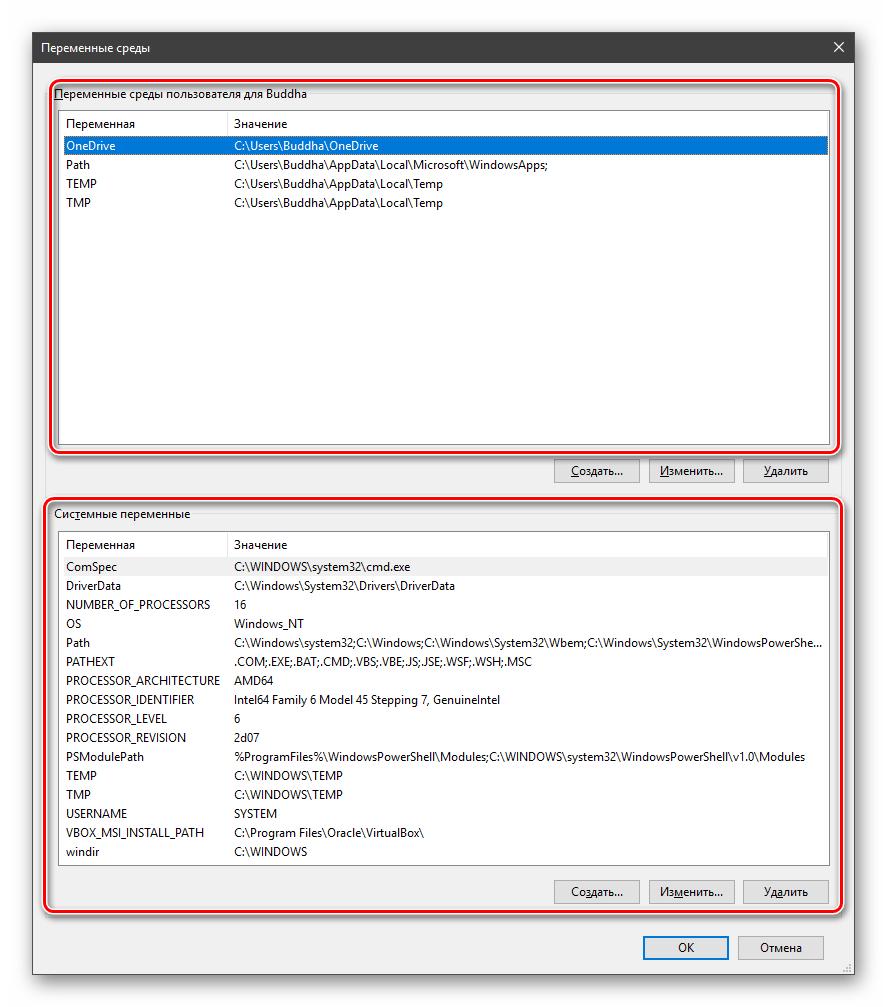
Здесь мы видим два блока. Первый содержит пользовательские переменные, а второй системные.
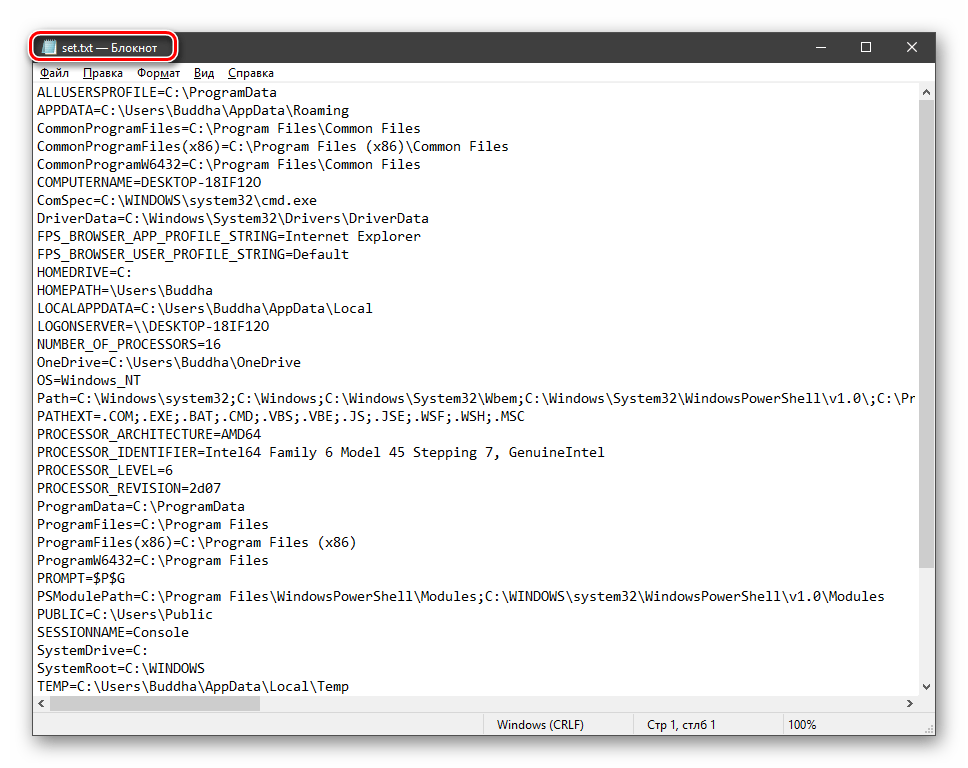
Если требуется просмотреть весь перечень, запускаем «Командную строку» от имени администратора и выполняем команду (вводим и нажимаем ENTER).
На рабочем столе появится файл с названием «set.txt», в котором будут указаны все переменные окружения, имеющиеся в системе.
Все их можно использовать в консоли или скриптах для запуска программ или поиска объектов, заключив имя в знаки процента. Например, в команде выше вместо пути
Примечание: регистр при написании переменных не важен. Path=path=PATH
Переменные PATH и PATHEXT
Если с обычными переменными все понятно (одна ссылка – одно значение), то эти две стоят особняком. При детальном рассмотрении видно, что они ссылаются сразу на несколько объектов. Давайте разберемся, как это работает.
«PATH» позволяет запускать исполняемые файлы и скрипты, «лежащие» в определенных каталогах, без указания их точного местоположения. Например, если ввести в «Командную строку»
система осуществит поиск по папкам, указанным в значении переменной, найдет и запустит соответствующую программу. Этим можно воспользоваться в своих целях двумя способами:
- Поместить необходимый файл в одну из указанных директорий. Полный список можно получить, выделив переменную и нажав «Изменить».
Создать свою папку в любом месте и прописать путь к ней. Для этого (после создания директории на диске) жмем «Создать», вводим адрес и ОК.
%SYSTEMROOT% определяет путь до папки «Windows» независимо от буквы диска.
Затем нажимаем ОК в окнах «Переменные среды» и «Свойства системы».
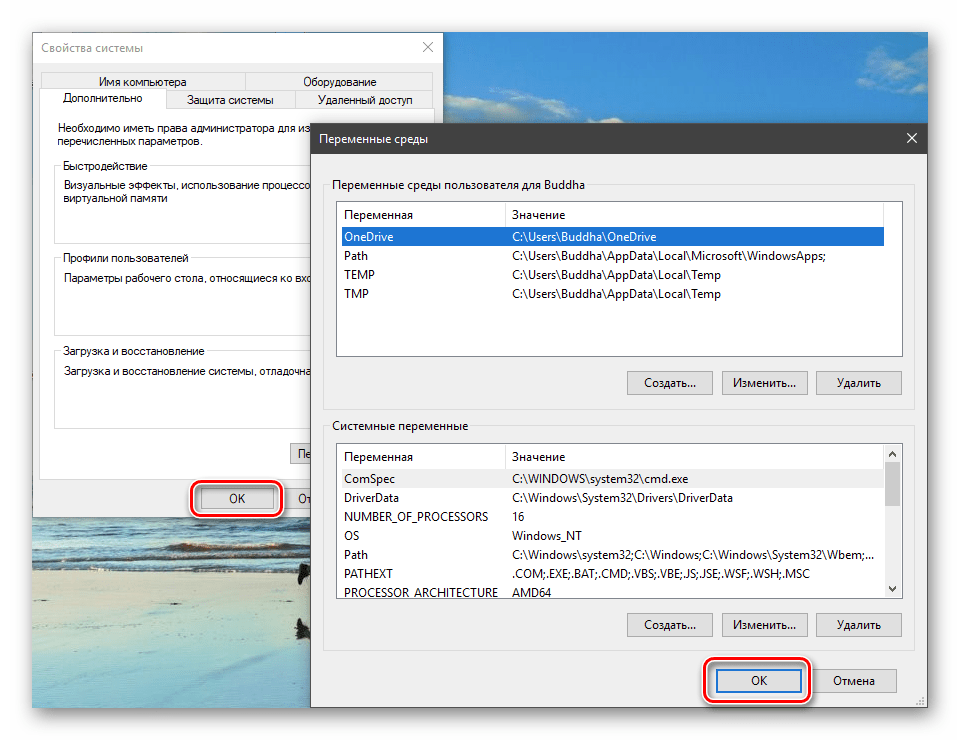
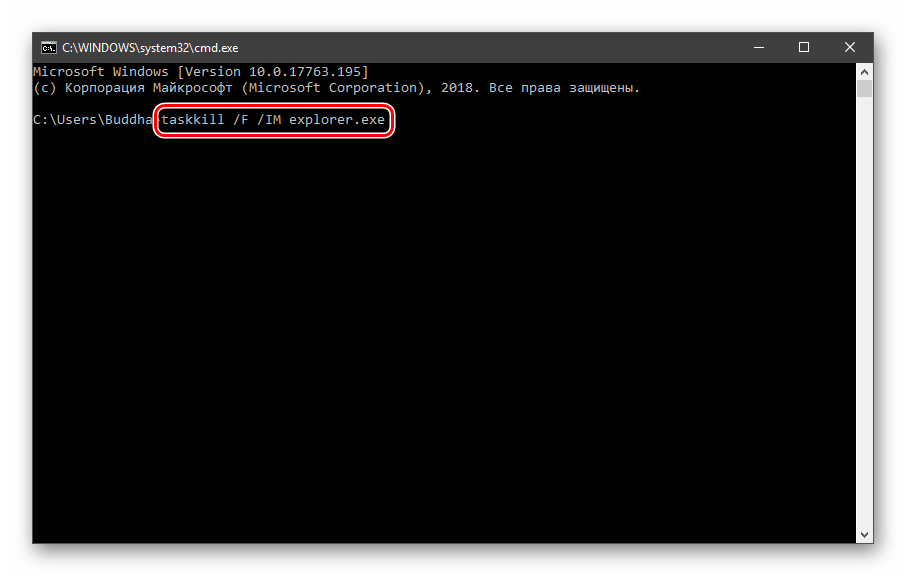
Для применения настроек, возможно, придется перезапустить «Проводник». Сделать это быстро можно так:
Открываем «Командную строку» и пишем команду
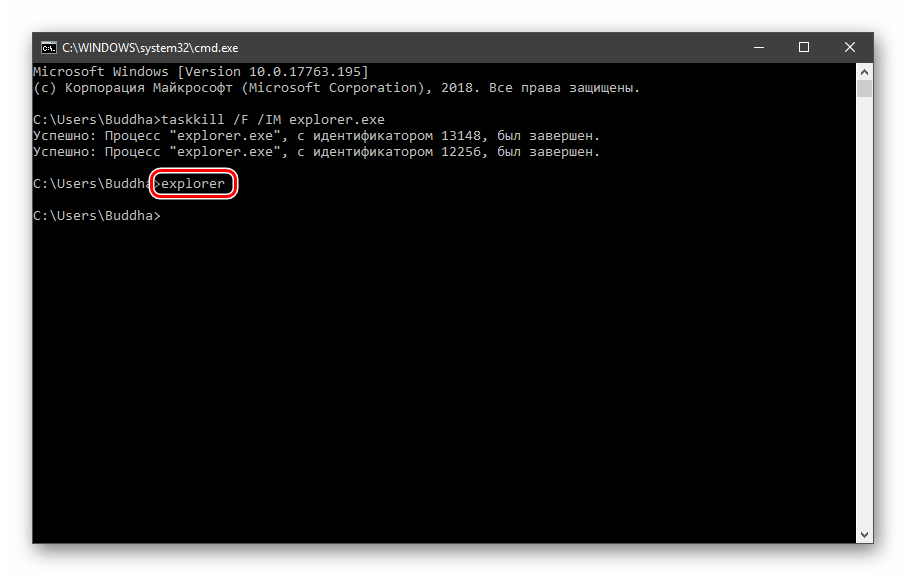
taskkill /F /IM explorer.exe
Все папки и «Панель задач» исчезнут. Далее снова запускаем «Проводник».
Еще один момент: если вы работали с «Командной строкой», ее также следует перезапустить, то есть консоль не будет «знать», что настройки изменились. Это же касается и фреймворков, в которых вы отлаживаете свой код. Также можно перезагрузить компьютер или выйти и снова зайти в систему.
Теперь все файлы, помещенные в «C:\Script» можно будет открывать (запускать), введя только их название.
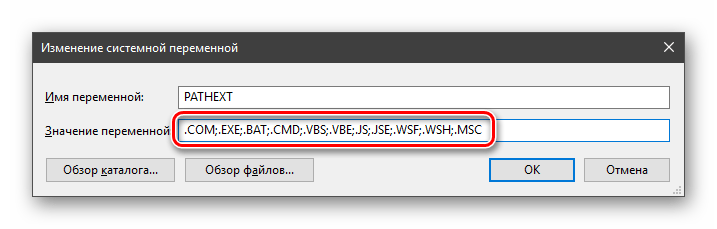
«PATHEXT», в свою очередь, дает возможность не указывать даже расширение файла, если оно прописано в ее значениях.
Принцип работы следующий: система перебирает расширения по очереди, пока не будет найден соответствующий объект, причем делает это в директориях, указанных в «PATH».
Создание переменных среды
Создаются переменные просто:
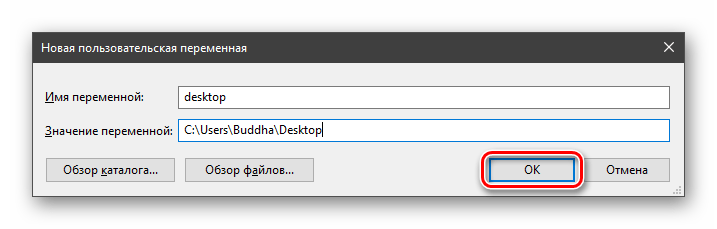
- Нажимаем кнопку «Создать». Сделать это можно как в пользовательском разделе, так и в системном.
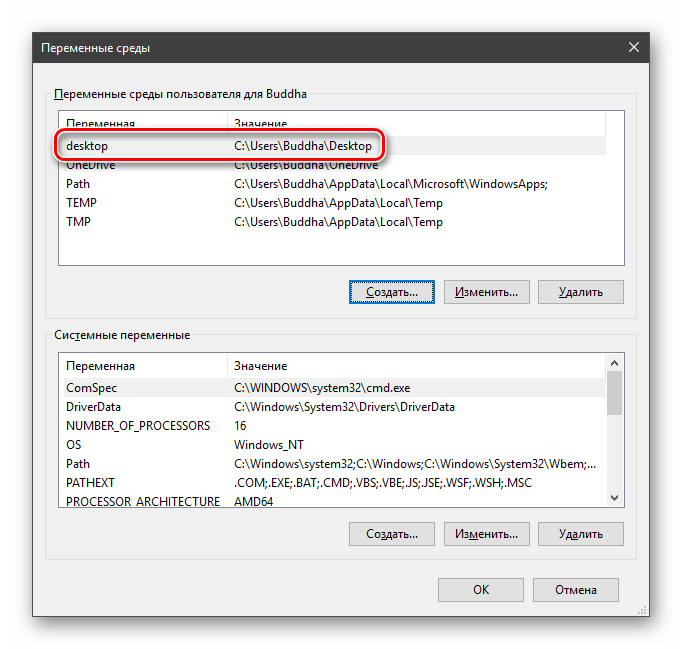
Вводим имя, например, «desktop». Обратите внимание на то, чтобы такое название еще не было использовано (просмотрите списки).
В поле «Значение» указываем путь до папки «Рабочий стол».
Нажимаем ОК. Повторяем это действие во всех открытых окнах (см. выше).
Для примера переделаем команду, которую мы использовали для получения списка (самая первая в статье). Теперь нам вместо
потребуется ввести только
Заключение
Использование переменных окружения позволяет значительно сэкономить время при написании скриптов или взаимодействии с системной консолью. Еще одним плюсом является оптимизация создаваемого кода. Имейте в виду, что созданные вами переменные отсутствуют на других компьютерах, и сценарии (скрипты, приложения) с их использованием работать не будут, поэтому перед тем, как передавать файлы другому пользователю, необходимо уведомить его об этом и предложить создать соответствующий элемент в своей системе.
How to set the path and environment variables in Windows
Setting the path and environment variables will differ depending on the version of Windows you have on your computer. Choose a link below for your version of Windows.
Administrator privileges are usually required to modify the path and environment variables.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 10
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- In the Settings window, scroll down to the Related settings section and click the System info link.
- In the System window, click the Advanced system settings link in the left navigation pane.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the variable name and variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 8
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the variable name and variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows Vista and Windows 7
- From the desktop, right-click the Computer icon and select Properties. If you don’t have a Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variablesbutton near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the Variable name and Variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 2000 and Windows XP
The path is now managed by Windows 2000 and Windows XP and not the autoexec.bat or autoexec.nt files, as was done with earlier versions of Windows. To change the system environment variables, follow the steps below.
- From the desktop, right-click My Computer and click Properties. If you don’t have a My Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the My Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- In the System Propertieswindow, click the Advancedtab.
- In the Advanced section, click the Environment Variablesbutton.
- In the Environment Variables window (as shown below), highlight the Path variable in the System Variable section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New and enter the Variable name and Variable value.
To view and set the path in the Windows command line, use the path command.
What is the default Windows %PATH%?
The path is based on programs installed on the computer, so there is no «default path.» However, the Windows minimum path is often the path below.
Keep in mind that as you install programs, the path is updated with the paths for the newly installed programs. So, if you have erased your path after installing other programs, those programs may be affected.
Setting path in the MS-DOS and Windows command line
To view and set the path in MS-DOS and in the Windows command line, use the path command.