- Enabling the System Event Audit Log
- How to Enable Security Audit Policy
- How to Enable Verbose Logging of Code Integrity Diagnostic Events
- Audit logon events
- Configure this audit setting
- Audit account logon events
- Configure this audit setting
- 1102(S): The audit log was cleared.
- Управление журналом аудита и безопасности Manage auditing and security log
- Справочные материалы Reference
- Возможные значения Possible values
- Рекомендации Best practices
- Location Location
- Значения по умолчанию Default values
- Управление политикой Policy management
- Групповая политика Group Policy
- Вопросы безопасности Security considerations
- Уязвимость Vulnerability
- Противодействие Countermeasure
- Возможное влияние Potential impact
Enabling the System Event Audit Log
This topic includes the following information:
How to Enable Security Audit Policy
To enable security audit policy to capture load failures in the audit logs, follow these steps:
Open an elevated Command Prompt window. To open an elevated Command Prompt window, create a desktop shortcut to Cmd.exe, select and hold (or right-click) the Cmd.exe shortcut, and select Run as administrator.
In the elevated Command Prompt window, run the following command:
Restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
The following screen shot shows an how to use Auditpol to enable security auditing.
How to Enable Verbose Logging of Code Integrity Diagnostic Events
To enable verbose logging, follow these steps:
Open an elevated Command Prompt window.
Run Eventvwr.exe on the command line.
Under the Event Viewer folder in the left pane of the Event Viewer, expand the following sequence of subfolders:
Applications and Services Logs
Microsoft
Windows
Expand the Code Integrity subfolder under the Windows folder to display its context menu.
Select View.
Select Show Analytic and Debug Logs. Event Viewer will then display a subtree that contains an Operational folder and a Verbose folder.
Select and hold (or right-click) Verbose and then select Properties from the pop-up context menu.
Select the General tab on the Properties dialog box, and then select the Enable Logging option near the middle of the property page. This will enable verbose logging.
Restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
Audit logon events
Applies to
Determines whether to audit each instance of a user logging on to or logging off from a device.
Account logon events are generated on domain controllers for domain account activity and on local devices for local account activity. If both account logon and logon audit policy categories are enabled, logons that use a domain account generate a logon or logoff event on the workstation or server, and they generate an account logon event on the domain controller. Additionally, interactive logons to a member server or workstation that use a domain account generate a logon event on the domain controller as the logon scripts and policies are retrieved when a user logs on. For more info about account logon events, see Audit account logon events.
If you define this policy setting, you can specify whether to audit successes, audit failures, or not audit the event type at all. Success audits generate an audit entry when a logon attempt succeeds. Failure audits generate an audit entry when a logon attempt fails.
To set this value to No auditing, in the Properties dialog box for this policy setting, select the Define these policy settings check box and clear the Success and Failure check boxes.
For information about advanced security policy settings for logon events, see the Logon/logoff section in Advanced security audit policy settings.
Configure this audit setting
You can configure this security setting by opening the appropriate policy under Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Audit Policy.
| Logon events | Description |
|---|---|
| 4624 | A user successfully logged on to a computer. For information about the type of logon, see the Logon Types table below. |
| 4625 | Logon failure. A logon attempt was made with an unknown user name or a known user name with a bad password. |
| 4634 | The logoff process was completed for a user. |
| 4647 | A user initiated the logoff process. |
| 4648 | A user successfully logged on to a computer using explicit credentials while already logged on as a different user. |
| 4779 | A user disconnected a terminal server session without logging off. |
When event 528 is logged, a logon type is also listed in the event log. The following table describes each logon type.
Audit account logon events
Applies to
Determines whether to audit each instance of a user logging on to or logging off from another device in which this device is used to validate the account.
This security setting determines whether to audit each instance of a user logging on to or logging off from another computer in which this computer is used to validate the account. Account logon events are generated when a domain user account is authenticated on a domain controller. The event is logged in the domain controller’s security log. Logon events are generated when a local user is authenticated on a local computer. The event is logged in the local security log. Account logoff events are not generated.
If you define this policy setting, you can specify whether to audit successes, audit failures, or not audit the event type at all. Success audits generate an audit entry when an account logon attempt succeeds. Failure audits generate an audit entry when an account logon attempt fails. To set this value to No auditing, in the Properties dialog box for this policy setting, select the Define these policy settings check box and clear the Success and Failure check boxes.
Default: Success
Configure this audit setting
You can configure this security setting by opening the appropriate policy under Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Audit Policy.
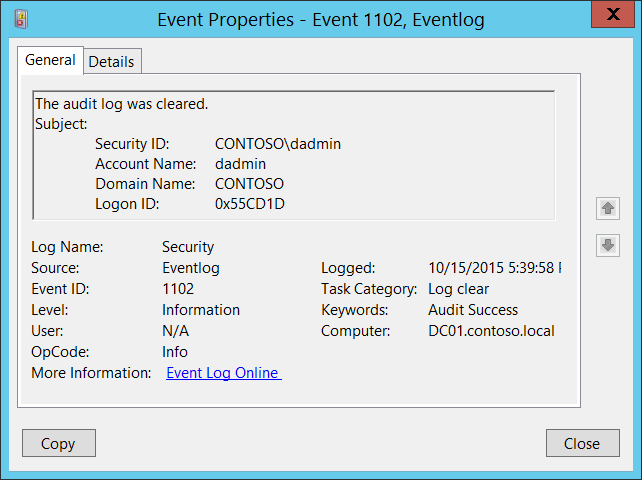
1102(S): The audit log was cleared.
Applies to
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
Event Description:
This event generates every time Windows Security audit log was cleared.
NoteВ В For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Subject:
- Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account that cleared the system security audit log. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
NoteВ В A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that cleared the system security audit log.
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: subject’s domain or computer name. Formats vary, and include the following:
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
For some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is “NT AUTHORITY”.
For local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: “Win81”.
Logon ID [Type = HexInt64]: hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, “4624: An account was successfully logged on.”
Управление журналом аудита и безопасности Manage auditing and security log
Область применения Applies to
В этой статье описываются лучшие методики, расположение, значения, управление политиками и вопросы безопасности для параметра политики безопасности «Управление аудитом и журналом безопасности». Describes the best practices, location, values, policy management, and security considerations for the Manage auditing and security log security policy setting.
Справочные материалы Reference
Этот параметр политики определяет, какие пользователи могут указывать параметры аудита доступа к объектам для отдельных ресурсов, таких как файлы, объекты Active Directory и ключи реестра. This policy setting determines which users can specify object access audit options for individual resources such as files, Active Directory objects, and registry keys. Эти объекты указывают свои системные списки управления доступом (SACL). These objects specify their system access control lists (SACL). Пользователь, которому назначено это право, также может просмотреть и очистить журнал безопасности в окне просмотра событий. A user who is assigned this user right can also view and clear the Security log in Event Viewer. Дополнительные сведения о политике аудита доступа к объектам см. в этой теме. For more info about the Object Access audit policy, see Audit object access.
Константа: SeSecurityPrivilege Constant: SeSecurityPrivilege
Возможные значения Possible values
- Определяемый пользователей список учетных записей User-defined list of accounts
- Администраторы Administrators
- Не определено Not Defined
Рекомендации Best practices
- Перед удалением этого права из группы необходимо выяснить, зависят ли приложения от этого права. Before removing this right from a group, investigate whether applications are dependent on this right.
- Как правило, назначать это право пользователю группам, кроме администраторов, не требуется. Generally, assigning this user right to groups other than Administrators is not necessary.
Location Location
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment
Значения по умолчанию Default values
По умолчанию этот параметр является администратором на контроллерах домена и на автономных серверах. By default this setting is Administrators on domain controllers and on stand-alone servers.
В следующей таблице перечислены фактические и эффективные значения политики по умолчанию для последних поддерживаемых версий Windows. The following table lists the actual and effective default policy values for the most recent supported versions of Windows. Значения по умолчанию также можно найти на странице свойств политики. Default values are also listed on the policy’s property page.
| Тип сервера или объект групповой политики Server type or GPO | Значение по умолчанию Default value |
|---|---|
| Default Domain Policy Default Domain Policy | Не определено Not defined |
| Политика контроллера домена по умолчанию Default Domain Controller Policy | Администраторы Administrators |
| Параметры по умолчанию для автономного сервера Stand-Alone Server Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
| Действующие параметры по умолчанию для контроллера домена Domain Controller Effective Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
| Действующие параметры по умолчанию для рядового сервера Member Server Effective Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
| Действующие параметры по умолчанию для клиентского компьютера Client Computer Effective Default Settings | Администраторы Administrators |
Управление политикой Policy management
В этом разделе описаны компоненты, средства и рекомендации, которые помогут в управлении этой политикой. This section describes features, tools, and guidance to help you manage this policy.
Для активации этого параметра политики не требуется перезагрузка компьютера. A restart of the computer is not required for this policy setting to be effective.
Изменения прав пользователя вступают в силу при его следующем входе в учетную запись. Any change to the user rights assignment for an account becomes effective the next time the owner of the account logs on.
Аудит доступа к объектам не выполняется, если их не включить с помощью редактора локальных групповых политик, консоли управления групповыми политиками (GPMC) или средства командной строки Auditpol. Audits for object access are not performed unless you enable them by using the Local Group Policy Editor, the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), or the Auditpol command-line tool.
Дополнительные сведения о политике аудита доступа к объектам см. в этой теме. For more information about the Object Access audit policy, see Audit object access.
Групповая политика Group Policy
Параметры применяются в следующем порядке с помощью объекта групповой политики (GPO), который будет перезаписывать параметры на локальном компьютере при следующем обновлении групповой политики: Settings are applied in the following order through a Group Policy Object (GPO), which will overwrite settings on the local computer at the next Group Policy update:
- Параметры локальной политики Local policy settings
- Параметры политики сайта Site policy settings
- Параметры политики домена Domain policy settings
- Параметры политики подразделения OU policy settings
Если локальный параметр затеняется, это означает, что в настоящее время этот параметр контролируется GPO. When a local setting is greyed out, it indicates that a GPO currently controls that setting.
Вопросы безопасности Security considerations
В этом разделе описывается, каким образом злоумышленник может использовать компонент или его конфигурацию, как реализовать меры противодействия, а также рассматриваются возможные отрицательные последствия их реализации. This section describes how an attacker might exploit a feature or its configuration, how to implement the countermeasure, and the possible negative consequences of countermeasure implementation.
Уязвимость Vulnerability
Любой пользователь с правом на управление аудитом и журналом безопасности может очистить журнал безопасности, чтобы удалить важные признаки несанкционированной деятельности. Anyone with the Manage auditing and security log user right can clear the Security log to erase important evidence of unauthorized activity.
Противодействие Countermeasure
Убедитесь, что только у локальной группы администраторов есть право на управление аудитом и журналом безопасности. Ensure that only the local Administrators group has the Manage auditing and security log user right.
Возможное влияние Potential impact
Настройка по умолчанию ограничивает права пользователя журнала аудита и безопасности только локальной группой администраторов. Restricting the Manage auditing and security log user right to the local Administrators group is the default configuration.
Предупреждение: Если группе, кроме локальной группы администраторов, назначено это право пользователя, удаление этого права пользователя может привести к проблеме производительности в других приложениях. Warning: If groups other than the local Administrators group have been assigned this user right, removing this user right might cause performance issues with other applications. Перед удалением этого права из группы необходимо выяснить, зависят ли приложения от этого права. Before removing this right from a group, investigate whether applications are dependent on this right.