- Introduction to page files
- Functionality
- Physical extension of RAM
- Application requirements
- Support for system crash dumps
- Page files in Windows with large physical memory
- System committed memory
- Создание задачи управления пользовательскими файлами Create a Custom File Management Task
- Создание пользовательской задачи To create a custom task
- File Management Functions
- In this section
Introduction to page files
A page file (also known as a «paging file») is an optional, hidden system file on a hard disk.
Functionality
Page files have the following functionalities.
Physical extension of RAM
Page files enable the system to remove infrequently accessed modified pages from physical memory to let the system use physical memory more efficiently for more frequently accessed pages.
Application requirements
Some products or services require a page file for various reasons. For specific information, check the product documentation.
For example, the following Windows servers requires page files:
- Windows Server domain controllers (DCs)
- DFS Replication (DFS-R) servers
- Certificate servers
- ADAM/LDS servers
This is because the algorithm of the database cache for Extensible Storage Engine (ESENT, or ESE in Microsoft Exchange Server) depends on the «\Memory\Transition Pages RePurposed/sec» performance monitor counter. A page file is required to make sure that the database cache can release memory if other services or applications request memory.
For Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V and Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V, the page file of the management OS (commonly called the host OS) should be left at the default of setting of «System Managed» .
Support for system crash dumps
Page files can be used to «back» (or support) system crash dumps and extend how much system-committed memory (also known as “virtual memory”) a system can support.
For more information about system crash dumps, see system crash dump options.
Page files in Windows with large physical memory
When large physical memory is installed, a page file might not be required to support the system commit charge during peak usage. For example, 64-bit versions of Windows and Windows Server support more physical memory (RAM) than 32-bit versions support. The available physical memory alone might be large enough.
However, the reason to configure the page file size has not changed. It has always been about supporting a system crash dump, if it is necessary, or extending the system commit limit, if it is necessary. For example, when a lot of physical memory is installed, a page file might not be required to back the system commit charge during peak usage. The available physical memory alone might be large enough to do this. However, a page file or a dedicated dump file might still be required to back a system crash dump.
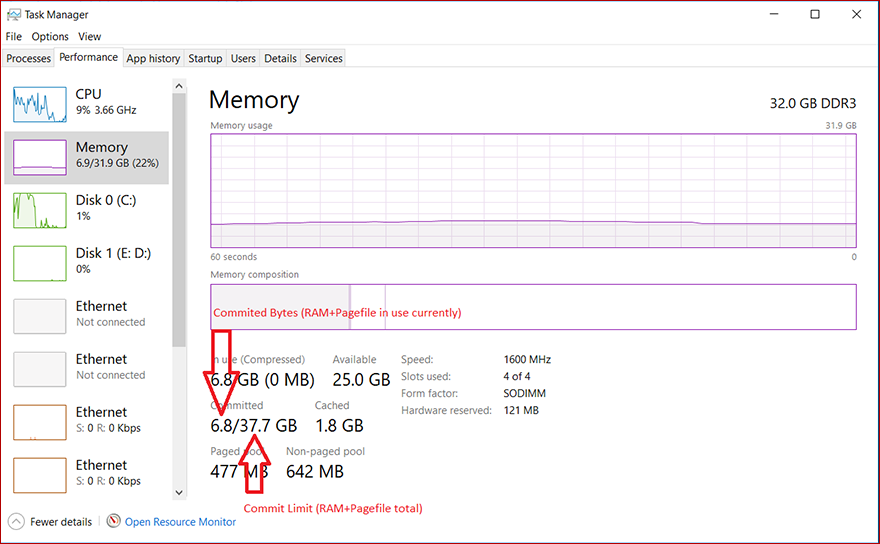
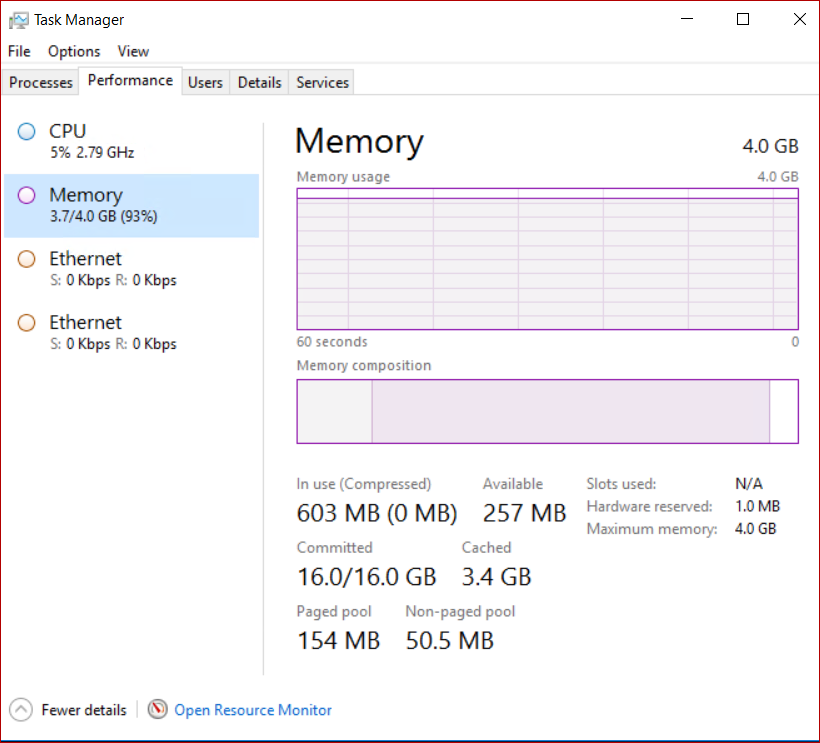
System committed memory
Page files extend how much «committed memory» (also known as «virtual memory») is used to store modified data.
The system commit memory limit is the sum of physical memory and all page files combined. It represents the maximum system-committed memory (also known as the «system commit charge») that the system can support.
The system commit charge is the total committed or «promised» memory of all committed virtual memory in the system. If the system commit charge reaches the system commit limit, the system and processes might not get committed memory. This condition can cause freezing, crashing, and other malfunctions. Therefore, make sure that you set the system commit limit high enough to support the system commit charge during peak usage.
The system committed charge and system committed limit can be measured on the Performance tab in Task Manager or by using the «\Memory\Committed Bytes» and «\Memory\Commit Limit» performance counters. The \Memory% Committed Bytes In Use counter is a ratio of \Memory\Committed Bytes to \Memory\Commit Limit values.
System-managed page files automatically grow up to three times the physical memory or 4 GB (whichever is larger, but no more than one-eighth of the volume size) when the system commit charge reaches 90 percent of the system commit limit. This assumes that enough free disk space is available to accommodate the growth.
Создание задачи управления пользовательскими файлами Create a Custom File Management Task
Область применения: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2 Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2
Истечение срока действия не всегда является необходимым действие, которое требуется применить к файлам. Expiration is not always a desired action to be performed on files. Задачи управления файлами также позволяют выполнять пользовательские команды. File management tasks allow you to run custom commands as well.
В описании этой процедуры предполагается, что вы уже знакомы с принципами работы задач управления файлами и поэтому в нем рассматривается только вкладка Действие, на которой выполняется настройка пользовательских параметров. This procedure assumes that you are familiar with file management tasks, and therefore only covers the Action tab where custom settings are configured.
Создание пользовательской задачи To create a custom task
Щелкните узел Задачи управления файлами. Click the File Management Tasks node.
Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Задачи управления файлами, а затем нажмите кнопку Создать задачу управления файлами (или щелкните Создать задачу управления файлами на панели Действия). Right-click File Management Tasks, and then click Create File Management Task (or click Create File Management Task in the Actions pane). Откроется диалоговое окно Создать задачу управления файлами. This opens the Create File Management Task dialog box.
На вкладке Действие введите следующие данные: On the Action tab, enter the following information:
- Type. Type. В раскрывающемся списке выберите Пользовательская. Select Custom from the drop-down menu.
- Исполняемый файл. Executable. Введите или выберите команду, которая будет выполняться при обработке файлов задачей управления файлами. Type or browse to a command to run when the file management task processes files. Для этого исполняемого файла необходимо настроить права редактирования только для администраторов и системы. This executable must be set to be writable by Administrators and System only. Если у других пользователей есть доступ к записи в исполняемом файле, оно будет работать правильно. If any other users have write access to the executable, it will not run correctly.
- Параметры команд. Command settings. Чтобы настроить аргументы, передаваемые исполняемому файлу при обработке файлов задачей управления файлами, измените текстовое поле с меткой Аргументы. To configure the arguments passed to the executable when a file management job processes files, edit the text box labeled Arguments. Чтобы добавить дополнительные переменные в текст, поместите курсор в место в текстовом поле, в котором необходимо вставить переменную, выберите переменную, которую необходимо вставить, и нажмите кнопку Вставить переменную. To insert additional variables in the text, place the cursor in the location in the text box where you want to insert the variable, select the variable that you want to insert, and then click Insert Variable. Текст в квадратных скобках вставляет сведения о переменных, получаемые исполняемым файлом. The text that is in brackets inserts variable information that the executable can receive. Например, [ Переменная пути к исходному файлу ] вставляет имя файла, который должен быть обработан исполняемым файлом. For example, the [Source File Path] variable inserts the name of the file that should be processed by the executable. При необходимости нажмите кнопку Рабочий каталог, чтобы указать расположение настраиваемого исполняемого файла. Optionally, click the Working directory button to specify the location of the custom executable.
- Безопасность команд. Command Security. Настройте параметры безопасности для этого исполняемого файла. Configure the security settings for this executable. По умолчанию команда выполняется как локальная служба, которая представляет собой учетную запись с наиболее строгими ограничениями. By default, the command is run as Local Service, which is the most restrictive account available.
Нажмите кнопку ОК. Click OK.
File Management Functions
The following functions are used to manage files.
In this section
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| AddUsersToEncryptedFile | Adds user keys to the specified encrypted file. |
| AreFileApisANSI | Determines whether the file I/O functions are using the ANSI or OEM character set code page. |
| CancelIo | Cancels all pending input and output (I/O) operations that are issued by the calling thread for the specified file. |
| CancelIoEx | Marks any outstanding I/O operations for the specified file handle. The function only cancels I/O operations in the current process, regardless of which thread created the I/O operation. |
| CancelSynchronousIo | Marks pending synchronous I/O operations that are issued by the specified thread as canceled. |
| CheckNameLegalDOS8Dot3 | Determines whether the specified name can be used to create a file on a FAT file system. |
| CloseEncryptedFileRaw | Closes an encrypted file after a backup or restore operation, and frees associated system resources. |
| CopyFile | Copies an existing file to a new file. |
| CopyFile2 | Copies an existing file to a new file, notifying the application of its progress through a callback function. |
| PCOPYFILE2_PROGRESS_ROUTINE | An application-defined callback function used with the CopyFile2 function. |
| CopyFileEx | Copies an existing file to a new file, notifying the application of its progress through a callback function. |
| CopyFileTransacted | Copies an existing file to a new file as a transacted operation, notifying the application of its progress through a callback function. |
| CopyProgressRoutine | An application-defined callback function used with the CopyFileEx, MoveFileTransacted, and MoveFileWithProgress functions. |
| CreateFile | Creates or opens a file or I/O device. The most commonly used I/O devices are as follows: file, file stream, directory, physical disk, volume, console buffer, tape drive, communications resource, mailslot, and pipe. |
| CreateFile2 | Creates or opens a file. |
| CreateFileTransacted | Creates or opens a file, file stream, or directory as a transacted operation. |
| CreateHardLink | Establishes a hard link between an existing file and a new file. |
| CreateHardLinkTransacted | Establishes a hard link between an existing file and a new file as a transacted operation. |
| CreateIoCompletionPort | Creates an input/output (I/O) completion port and associates it with a specified file handle, or creates an I/O completion port that is not yet associated with a file handle, allowing association at a later time. |
| CreateSymbolicLink | Creates a symbolic link. |
| CreateSymbolicLinkTransacted | Creates a symbolic link as a transacted operation. |
| DecryptFile | Decrypts an encrypted file or directory. |
| DeleteFile | Deletes an existing file. |
| DeleteFileTransacted | Deletes an existing file as a transacted operation. |
| DuplicateEncryptionInfoFile | Copies the EFS metadata from one file or directory to another. |
| EncryptFile | Encrypts a file or directory. |
| EncryptionDisable | Disables or enables encryption of the specified directory and the files in it. |
| ExportCallback | An application-defined callback function used with ReadEncryptedFileRaw. |
| FileEncryptionStatus | Retrieves the encryption status of the specified file. |
| FileIOCompletionRoutine | An application-defined callback function used with the ReadFileEx and WriteFileEx functions. It is called when the asynchronous input and output (I/O) operation is completed or canceled and the calling thread is in an alertable state. |
| FindClose | Closes a file search handle opened by the FindFirstFile, FindFirstFileEx, FindFirstFileNameW, FindFirstFileNameTransactedW, FindFirstFileTransacted, FindFirstStreamTransactedW, or FindFirstStreamW functions. |
| FindFirstFile | Searches a directory for a file or subdirectory with a name that matches a specific name (or partial name if wildcards are used). |
| FindFirstFileEx | Searches a directory for a file or subdirectory with a name and attributes that match those specified. |
| FindFirstFileNameTransactedW | Creates an enumeration of all the hard links to the specified file as a transacted operation. The function returns a handle to the enumeration that can be used on subsequent calls to the FindNextFileNameW function. |
| FindFirstFileNameW | Creates an enumeration of all the hard links to the specified file. The FindFirstFileNameW function returns a handle to the enumeration that can be used on subsequent calls to the FindNextFileNameW function. |
| FindFirstFileTransacted | Searches a directory for a file or subdirectory with a name that matches a specific name as a transacted operation. |
| FindFirstStreamTransactedW | Enumerates the first stream in the specified file or directory as a transacted operation. |
| FindFirstStreamW | Enumerates the first stream with a ::$DATA stream type in the specified file or directory. |
| FindNextFile | Continues a file search from a previous call to the FindFirstFile, FindFirstFileEx, or FindFirstFileTransacted functions. |
| FindNextFileNameW | Continues enumerating the hard links to a file using the handle returned by a successful call to the FindFirstFileNameW function. |
| FindNextStreamW | Continues a stream search started by a previous call to the FindFirstStreamW function. |
| FlushFileBuffers | Flushes the buffers of a specified file and causes all buffered data to be written to a file. |
| FreeEncryptionCertificateHashList | Frees a certificate hash list. |
| GetBinaryType | Determines whether a file is an executable (.exe) file, and if so, which subsystem runs the executable file. |
| GetCompressedFileSize | Retrieves the actual number of bytes of disk storage used to store a specified file. |
| GetCompressedFileSizeTransacted | Retrieves the actual number of bytes of disk storage used to store a specified file as a transacted operation. |
| GetExpandedName | Retrieves the original name of a compressed file, if the file was compressed by the Lempel-Ziv algorithm. |
| GetFileAttributes | Retrieves file system attributes for a specified file or directory. |
| GetFileAttributesEx | Retrieves attributes for a specified file or directory. |
| GetFileAttributesTransacted | Retrieves file system attributes for a specified file or directory as a transacted operation. |
| GetFileBandwidthReservation | Retrieves the bandwidth reservation properties of the volume on which the specified file resides. |
| GetFileInformationByHandle | Retrieves file information for the specified file. |
| GetFileInformationByHandleEx | Retrieves file information for the specified file. |
| GetFileSize | Retrieves the size of the specified file, in bytes. |
| GetFileSizeEx | Retrieves the size of the specified file. |
| GetFileType | Retrieves the file type of the specified file. |
| GetFinalPathNameByHandle | Retrieves the final path for the specified file. |
| GetFullPathName | Retrieves the full path and file name of the specified file. |
| GetFullPathNameTransacted | Retrieves the full path and file name of the specified file as a transacted operation. |
| GetLongPathName | Converts the specified path to its long form. |
| GetLongPathNameTransacted | Converts the specified path to its long form as a transacted operation. |
| GetQueuedCompletionStatus | Attempts to dequeue an I/O completion packet from the specified I/O completion port. |
| GetQueuedCompletionStatusEx | Retrieves multiple completion port entries simultaneously. |
| GetShortPathName | Retrieves the short path form of the specified path. |
| GetTempFileName | Creates a name for a temporary file. If a unique file name is generated, an empty file is created and the handle to it is released; otherwise, only a file name is generated. |
| GetTempPath | Retrieves the path of the directory designated for temporary files. |
| ImportCallback | An application-defined callback function used with WriteEncryptedFileRaw. The system calls ImportCallback one or more times, each time to retrieve a portion of a backup file’s data. |
| LockFile | Locks the specified file for exclusive access by the calling process. |
| LockFileEx | Locks the specified file for exclusive access by the calling process. This function can operate either synchronously or asynchronously and can request either an exclusive or a shared lock. |
| LZClose | Closes a file that was opened by using the LZOpenFile function. |
| LZCopy | Copies a source file to a destination file. |
| LZInit | Allocates memory for the internal data structures required to decompress files, and then creates and initializes them. |
| LZOpenFile | Creates, opens, reopens, or deletes the specified file. |
| LZRead | Reads (at most) the specified number of bytes from a file and copies them into a buffer. |
| LZSeek | Moves a file pointer the specified number of bytes from a starting position. |
| MoveFile | Moves an existing file or a directory, including its children. |
| MoveFileEx | Moves an existing file or directory, including its children, with various move options. |
| MoveFileTransacted | Moves an existing file or a directory, including its children, as a transacted operation. |
| MoveFileWithProgress | Moves a file or directory, including its children. You can provide a callback function that receives progress notifications. |
| OpenEncryptedFileRaw | Opens an encrypted file in order to backup (export) or restore (import) the file. |
| OpenFile | Creates, opens, reopens, or deletes a file. |
| OpenFileById | Opens the file that matches the specified identifier. |
| PostQueuedCompletionStatus | Posts an I/O completion packet to an I/O completion port. |
| QueryRecoveryAgentsOnEncryptedFile | Retrieves a list of recovery agents for the specified file. |
| QueryUsersOnEncryptedFile | Retrieves a list of users for the specified file. |
| ReadEncryptedFileRaw | Backs up (export) encrypted files. |
| ReadFile | Reads data from the specified file or input/output (I/O) device. Reads occur at the position specified by the file pointer if supported by the device. |
| ReadFileEx | Reads data from the specified file or input/output (I/O) device. It reports its completion status asynchronously, calling the specified completion routine when reading is completed or canceled and the calling thread is in an alertable wait state. |
| ReadFileScatter | Reads data from a file and stores it in an array of buffers. |
| RemoveUsersFromEncryptedFile | Removes specified certificate hashes from a specified file. |
| ReOpenFile | Reopens the specified file system object with different access rights, sharing mode, and flags. |
| ReplaceFile | Replaces one file with another file, with the option of creating a backup copy of the original file. |
| SearchPath | Searches for a specified file in a specified path. |
| SetEndOfFile | Sets the physical file size for the specified file to the current position of the file pointer. |
| SetFileApisToANSI | Causes the file I/O functions to use the ANSI character set code page for the current process. |
| SetFileApisToOEM | Causes the file I/O functions for the process to use the OEM character set code page. |
| SetFileAttributes | Sets the attributes for a file or directory. |
| SetFileAttributesTransacted | Sets the attributes for a file or directory as a transacted operation. |
| SetFileBandwidthReservation | Requests that bandwidth for the specified file stream be reserved. The reservation is specified as a number of bytes in a period of milliseconds for I/O requests on the specified file handle. |
| SetFileCompletionNotificationModes | Sets the notification modes for a file handle, allowing you to specify how completion notifications work for the specified file. |
| SetFileInformationByHandle | Sets the file information for the specified file. |
| SetFileIoOverlappedRange | Associates a virtual address range with the specified file handle. |
| SetFilePointer | Moves the file pointer of the specified file. |
| SetFilePointerEx | Moves the file pointer of the specified file. |
| SetFileShortName | Sets the short name for the specified file. |
| SetFileValidData | Sets the valid data length of the specified file. This function is useful in very limited scenarios. For more information, see the Remarks section. |
| SetSearchPathMode | Sets the per-process mode that the SearchPath function uses when locating files. |
| SetUserFileEncryptionKey | Sets the user’s current key to the specified certificate. |
| UnlockFile | Unlocks a region in an open file. |
| UnlockFileEx | Unlocks a region in the specified file. This function can operate either synchronously or asynchronously. |
| WofEnumEntries | Enumerates all the data sources from a specified provider for a specified volume. |
| WofEnumEntryProc | Callback function that gets called for each data source in response to a call to WofEnumEntries. |
| WofEnumFilesProc | Callback function that gets called for each file backed by an external data source, such as a WIM file. |
| WofFileEnumFiles | Enumerates all of the files which are compressed with a specified compression algorithm on a specified volume. |
| WofGetDriverVersion | Used to query the version of the driver used to support a particular provider. |
| WofIsExternalFile | Used to determine if a file is being backed by a physical file or is backed by a system data provider, and optionally indicates which provider or additional data about the file. |
| WofSetFileDataLocation | Used to change a file from being backed by a physical file to one backed by a system data provider. |
| WofShouldCompressBinaries | Indicates whether compression should be used on a particular volume, and if so, which compression algorithm should be used. |
| WofWimAddEntry | Adds a single WIM data source to a volume such that files can be created on the volume which are stored within the WIM. |
| WofWimEnumFiles | Enumerates all of the files which are being backed by a specified WIM data source on a specified volume. |
| WofWimRemoveEntry | Removes a single WIM data source from backing files on a volume. |
| WofWimSuspendEntry | Temporarily removes a WIM data source from backing files on a volume until the volume is remounted or the data source is updated with WofWimUpdateEntry. |
| WofWimUpdateEntry | Updates a WIM entry to point to a different WIM file location. |
| Wow64DisableWow64FsRedirection | Disables file system redirection for the calling thread. File system redirection is enabled by default. |
| Wow64EnableWow64FsRedirection | Enables or disables file system redirection for the calling thread. |
| Wow64RevertWow64FsRedirection | Restores file system redirection for the calling thread. |
| WriteEncryptedFileRaw | Restores (import) encrypted files. |
| WriteFile | Writes data to the specified file or input/output (I/O) device. |
| WriteFileEx | Writes data to the specified file or input/output (I/O) device. It reports its completion status asynchronously, calling the specified completion routine when writing is completed or canceled and the calling thread is in an alertable wait state. |
| WriteFileGather | Retrieves data from an array of buffers and writes the data to a file. |
The following functions are used with file I/O.
The following functions are used with the encrypted file system.
The following functions are used with the file system redirector.