- How to get the file size in bytes with C++17
- Methods from other (old QA’s) on .sx
- 2 Answers 2
- Get File size and directory size from command line
- How to get the file size in bytes with C++17
- Methods from other (old QA’s) on .sx
- 2 Answers 2
- File Size
- Free File Size Calculator & Converter
- What Are File Sizes? How To Convert File Size Units?
- File Sizes Explained
- How to Convert File Sizes
- Why 1 Megabyte is 1024 Kilobytes Instead of 1000 Kilobytes?
- File Size Metric and IEC binary prefixes
- File Size Limits — File Systems
- View File Sizes in Windows File Explorer
- File Size Basics — Common File Sizes
- Common Media and Storage Sizes
- Size-related Questions
- What is the largest file that I can send in email?
- Can I send a video file via email?
- Can I reduce file sizes?
How to get the file size in bytes with C++17
Are there pitfalls for specific operating systems, I should know of?
There are many duplicates (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) of this question but they were answered decades ago. The very high voted answers in many of these questions are wrong today.
Methods from other (old QA’s) on .sx
tellg(), returns per definition a position but not necessarily bytes. The return type is not int .
2 Answers 2
As noted in comments, if you’re planning to use this function to decide how many bytes to read from the file, keep in mind that.
. unless the file is exclusively opened by you, its size can be changed between the time you ask for it and the time you try to read data from it.
– Nicol Bolas
C++17 brings std::filesystem which streamlines a lot of tasks on files and directories. Not only you can quickly get file size, its attributes, but also create new directories, iterate through files, work with path objects.
The new library gives us two functions that we can use:
The first function is a free function in std::filesystem , the second one is a method in directory_entry .
Each method also has an overload, as it can throw an exception or return an error code (through an output parameter). Below is the detail code explaining all the possible cases.
Get File size and directory size from command line
How to find the size of a file
In Windows, we can use dir command to get the file size.
But there is no option/switch to print only the file size.
Get size for all the files in a directory
Dir command accepts wild cards. We can use ‘*” to get the file sizes for all the files in a directory.
We can also get size for files of certain type. For example, to get file size for mp3 files, we can run the command ‘dir *.mp3‘.
The above command prints file modified time also. To print only the file name and size we can run the below command from a batch file.
Save the above commands to a text file, say filesize.bat, and run it from command prompt.
Get directory size
There’s no Windows built in command to find directory size.В But there is a tool called diruse.exe which can be used to get folder size. This tool is part of XP support tools.В This command can be used to get directory size. This command’s syntax is given below.
As you can see in the above example, diruse prints the directory size in bytes and it also prints the number of files in the directory(it counts the number of files in the sub folders also)
To get the directory size in mega bytes we can add /M switch.
Though the tool is intended for XP and Server 2003, I have observed that it works on Windows 7 also.В The above examples were indeed from a Windows 7 computer.
Jan-18-2012
I validated/downloaded/started to install.
The setup software said, “This program has known compatibility issues.”
(I will probably continue anyway, in hopes that SOME of the software may work.)
I’m guessing that the problem is that I am running Windows 7 64-Bit.
Am I correct, that YOU are using Windows 7 32Bit ?
Jan-18-2012—followup
The attempt to instal; anyway, (in spite of compatibility problem) aborted,
It said, approximately, “can only be installed on WinXP”.
Try extracting the files instead of installing them. Command for this is something like this.
installer.exe /x
My machine is also 64 bit and is running on 64-bit OS.
In Windows7, right-click on the installer, select Troubleshoot compatibility, select Troubleshoot program, select first option “This program worked in earlier versions of Windows but won’t install or run now”, select Windows XP (Service Pack 2), select Start the program, ignore the compatibility issue warning by clicking Run program
please suggest how to get size in GB.MB useing DOS
get a calculator divide by 1024
You can get the list of the directories and their size using the following command:
The following command should do and output the file as csv
Dir/s |Find /V “/”> Folder_info.csv
To get the file use
then save as and save where you want.
The ‘for’ command can return the size of a file using %
zI.
Type ‘for /?’ at a command prompt for the details.
How to get the file size in bytes with C++17
Are there pitfalls for specific operating systems, I should know of?
There are many duplicates (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) of this question but they were answered decades ago. The very high voted answers in many of these questions are wrong today.
Methods from other (old QA’s) on .sx
tellg(), returns per definition a position but not necessarily bytes. The return type is not int .
2 Answers 2
As noted in comments, if you’re planning to use this function to decide how many bytes to read from the file, keep in mind that.
. unless the file is exclusively opened by you, its size can be changed between the time you ask for it and the time you try to read data from it.
– Nicol Bolas
C++17 brings std::filesystem which streamlines a lot of tasks on files and directories. Not only you can quickly get file size, its attributes, but also create new directories, iterate through files, work with path objects.
The new library gives us two functions that we can use:
The first function is a free function in std::filesystem , the second one is a method in directory_entry .
Each method also has an overload, as it can throw an exception or return an error code (through an output parameter). Below is the detail code explaining all the possible cases.
File Size
Free File Size Calculator & Converter
What Are File Sizes? How To Convert File Size Units?
This tool will convert file size from one unit of measure to another.
Enter the file size in the field below and specify the measure units in the drop box.
Copy Link to Share File Size Results
File Sizes Explained
File size measures the size of a computer file and is typically measured in bytes with a prefix. The smallest unit in computers is bit and comes from b inary dig it . A bit has only two digits — zero and one. The zero is also known as false (off) state and the one is known as true (on).
The bits are combined in groups in order to form larger units. The next unit larger than the bit is the byte which is formed by the combination of eight bits and can represent a value from 0 to 255 which is 2 to the power of 8 — all the possible combinations of the 8 bits that it includes.
The next larger units after the byte are named kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte, terabyte and so on which lead to great deal of confusion. Though the kilo prefix in the metric system means 1000 (e.g. grams) in computers it means 1024 (e.g. bytes). In order to correct this mess the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) approved a new IEC International Standard in December 1998. You can find the list of IEC metric and binary names in the table at the end of this article.
How to Convert File Sizes
As already described the smallest unit in computers is the bit. Converting file sizes is similar to converting other units with some small differences.
To convert bits to bytes you have to divide the count of bits to eight as one byte contains 8 bits. To further convert the bytes to kilobytes you have to divide the value by 1024. To convert from kilobytes to megabytes you have to divide the kilobytes to 1024 again and so on. This is a bit different than in metric system where values are divided by 1000 to convert them to the next larger unit. For example 1 km is 1000 meters.
Why 1 Megabyte is 1024 Kilobytes Instead of 1000 Kilobytes?
Where does the 1024 number come from? Well most numbers in computers are 2 to the power of X, and 1024 is 2 to the power of 10. That is because computers use the binary system — not the decimal. Of course you can represent the decimal or any other system on a computer, but at its core hardware level the computer uses the binary system. In 1998 IEC introduced new naming convention for the file sizes which now creates even more confusion. If you were using computers for a long time you may think that a megabyte is still 1024 kilobytes, but that is no longer the case. Megabyte is now 1000 kilobytes which on the other hand is one thousand bytes. The old multiples of 1024 units are now with new prefixes and mebibyte is 1024 kibibytes and a kibibyte is 1024 bytes. Changing something existing and well established and known by billions of people in my opinion is not a good idea, but it is my own personal position. It would be much less confusing to use new unit names, but that would not correspond to the metric system naming convention. There was no perfect solution so we have to get used to it.
If you are purchasing a storage device you can see that a 2TB hard drives displays as 1.82 TB which is much smaller in Windows. Windows still uses the old unit naming convention which causes the discrepancy. Of course the new naming convention is very welcome for the storage manufacturers as they now provide 10% less storage while using the same naming convention. So bear in ming that when purchasing a new hard drive or memory card.
File Size Metric and IEC binary prefixes
Here is a list of some of the commonly used units in the metric and their corresponding IEC binary prefixes:
| Name | Size | Name | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| kilobyte (kB) | 10 3 | kibibyte (KiB) | 2 10 |
| megabyte (MB) | 10 6 | mebibyte(MiB) | 2 20 |
| gigabyte (GB) | 10 9 | gibibyte (GiB) | 2 30 |
| terabyte (TB) | 10 12 | tebibyte (TiB) | 2 40 |
| petabyte (PB) | 10 15 | pebibyte (PiB) | 2 50 |
| exabyte (EB) | 10 18 | exbibyte (EiB) | 2 60 |
| zettabyte (ZB) | 10 21 | zebibyte (ZiB) | 2 70 |
| yottabyte (YB) | 10 24 | yobibyte (YiB) | 2 80 |
File Size Limits — File Systems
File sizes are limited by the file system that is used and its implementation. Here are details on the common file systems:
| FAT16 | FAT32 | NTFS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum File Size | 2 32 — 1 bytes | 2 32 — 1 bytes | 2 64 — 1 KB |
| Maximum Volume Size | 4 GB | 32 GB | 2 64 clusters |
| Files Per Volume | 2 16 | 2 22 | 2 32 — 1 |
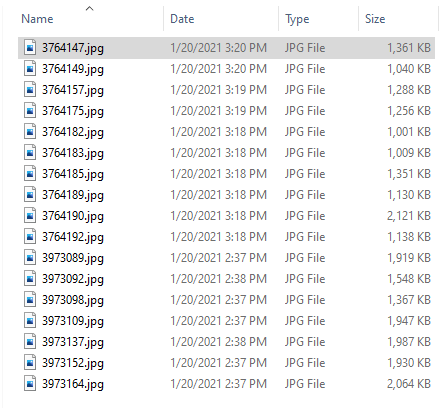
View File Sizes in Windows File Explorer
The core file management application in Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP is the Windows File Explorer. You can use it to manage files and view file sizes. As you can see on the screenshot below we have a list of some image files. The rightmost «Size» column displays the size of the files. To view the sizes of the files you have to switch the view to «Details». To do that click the «More options» button at the top-right corner of Windows Explorer and select «Details».
The size is automatically displayed in the most appropriate units — in this case KB. Clicking the column title the files will be sorted by size. Unfortunately the folder sizes are not listed in the «Size» column. To view those you can use our free Folder Size Explorer application which will reveal all folder sizes and all missing disk space.
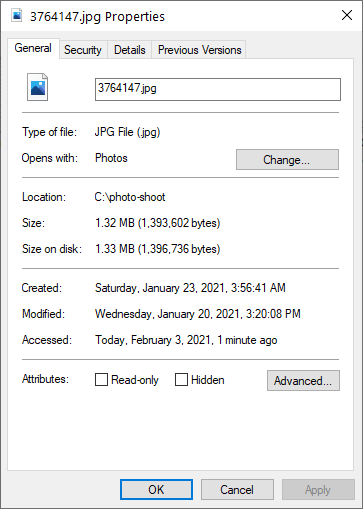
If you want more precise information you can right-click a file and select ‘Properties’. The following file properties panel will be displayed:
Here you can find the exact file size and also the other file properties like created, modified, and accessed times. Some of the file attributes are also listed and can be toggled. These are the read-only and hidden flags. You can also right-click a folder and select «Properties» from the popup menu. That will display the information about the folder and will also calculate its size. Note that this may take some time for large folders. You have to wait until the size property stops changing. There is no indication when the calculation is complete and the size property may stay for several seconds without a change and then continue to grow. Make sure to wait at least ten seconds after the last change to be sure that the calculation is complete.
File Size Basics — Common File Sizes
If you are new to computers and files here are several samples of common file formats (types) and their average sizes:
- Text File (TXT) — Text files are one of the smallest file types. Their sizes are equal to the count of characters they contain. A few pages text file is typically 1-2 KB. These are considered «TINY» files.
- Word documents (DOC, DOCX) — These files contain styling and formatting and are quite larger. A few pages DOC file without images is about 50-300KB. these are considered «SMALL» files.
- A photo (JPG) from a common 12 MPX camera is about 3-5 MB. These are considered «MEDIUM» size.
- MP3 Audio File — a full length song is between 3 and 10 MB depending on its duration and quality (compression). The other compressed audio files are also in this range — MP4, FLAC, OGG etc. Uncompressed WAV files used in CDs are very large. They are about 10 MB per minute — e.g. about 70 MB for a 7 minutes song.
- A 10 second low resolution 640X480 AVI video is about 15 MB — This size leans towards «LARGE».
- A 1-1.5 hour video with a lower SD resolution is about 700-1000MB This is considered a «LARGE» file.
- A 1-1.5 hour video with FULL HD quality is about 7-10GB depending on the codec (compression) that is used to store it.
If you are new to files and computers, the above sample file sizes will give you a rough idea about file types and their common file sizes. Of course those are approximate sizes and may vary, but the files of those types are approximately in those size ranges.
Common Media and Storage Sizes
Size-related Questions
What is the largest file that I can send in email?
This depends both on the sender’s and receiver’s email service provider, but a files size of 5 to 10 MB is considered safe. This is about 2 to 5 photos depending on their size. Large files can not be sent via email and usually are shared using a file hosting service like Google Drive, Dropbox, or Microsoft OneDrive. You upload the file to one of those services and share the link with your partner via email or a messaging application.
Can I send a video file via email?
Video files are usually larger than 10MB and you will not be able to send them as an attachment in an email You have to use a file sharing service to upload the video to the Internet and share a link to it with your friends. File sharing services provide option to password-protect your files and share them only with the users that you give access to.
Can I reduce file sizes?
Yes you can using a file compression tool like WinZip, 7Zip, WinRAR and others. Using those tools you can archive files to compress them. In order to modify or view the files they have to be extracted — decompressed. Please note that image, audio and video files can not be compressed as those formats already use internal compression. Compressing such files will either have nearly no effect or can even make the compressed version larger than the original.