- The file size exceeds the limit allowed and cannot be saved
- How do I fix the file size exceeds the limit allowed error?
- 1. Use WinZip as a file compression tool
- WinZip
- 2. Modify your registry
- 3. Scan your PC for viruses
- Bitdefender Antivirus Plus
- 4. Configure your SharePoint storage
- 5. Set a file size upload limit
- 6. Change the SharePoint web.config file
- 7. Increase the machine-level request setting
- Anand, the Architect
- ..Solutions..Answers..Ideas..Fixes..Madness..
- WebDAV: Increasing Maximum File Size Limit in Windows Server
- Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
- Memory and Address Space Limits
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Vista
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home Server
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP
- Physical Memory Limits: Windows Embedded
- How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limits
The file size exceeds the limit allowed and cannot be saved
- If you’re getting an ERROR _FILE_TOO_LARGE message, you might need to compress the file.
- In case some settings need changing, we’re showing you exactly how to do it.
- Our Troubleshooting Hub is a resourceful option whenever you need to fix blocker errors like this one.
- If you ever need expert advice on using SharePoint, visit our Teamwork section.
- Unzip all major file formats: ZIP, RAR, 7Z, TGZ, TAR, etc.
- Encrypts the files you zip for maximum protection
- Manage your files easily (PC, Cloud, network)
Open archived files
with ease on your PC
System errors can be a big problem, and many users reported ERROR_FILE_TOO_LARGE error on their PC.
This error usually displays the following message: The file size exceeds the limit allowed and cannot be saved.
Today we’re going to show you how to fix this error on Windows 10.
How do I fix the file size exceeds the limit allowed error?
1. Use WinZip as a file compression tool
Perhaps the easiest, and the first-on-the-list solution, is to try and compress the respective file or files with a dedicated tool.
WinZip is the most popular app in this segment, with more than one billion users.
With WinZip, you can compress most major formats, such as Zip, Zipx, RAR, 7z, TAR, GZIP, VHD, XZ, and more, so you won’t have any trouble to quickly shrink the size of any file to get rid or avoid the above-mentioned error.
In case you need further features, WinZip helps with finding, opening, editing, moving, and sharing the files stored on PCs, networks, or cloud services.
It conveniently comes with Dropbox, G-Suite, or OneDrive integrations.
WinZip
2. Modify your registry
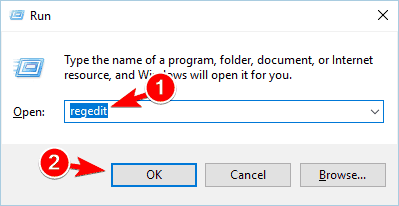
- Press Windows Key + R and enter regedit. Press Enter or click OK.
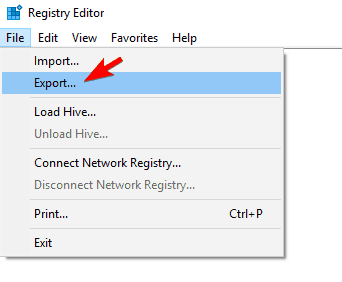
- Optional: Modifying the registry comes with certain risks, and if you don’t modify it properly you can cause system stability issues to occur. To prevent any potential problems, it’s important to backup your registry. To do that, click on File > Export.
Select a safe location for your backup. Enter the desired file name, select All as Export range and click on Save.
After exporting the registry, you can use the exported file to restore everything to the original state if anything goes wrong.
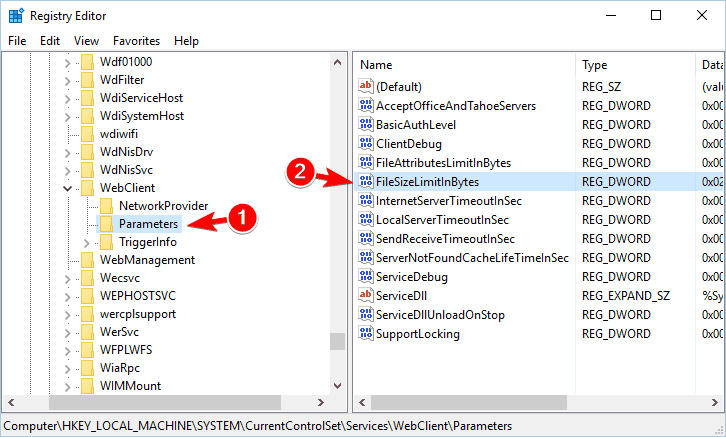
- In the left pane navigate to the following location HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesWebClientParameters
- Locate FileSizeLimitInBytes DWORD in the right pane and double click it.
- In the Value data field enter 4294967295 and click OK to save changes.
- Close Registry Editor.
After doing that, you just need to restart your PC and the issue should be resolved.
By modifying the registry you’ll change the maximum file size to 4GB. Instead of restarting your PC, some users are recommending to restart the WebClient service. To do that, follow these steps:
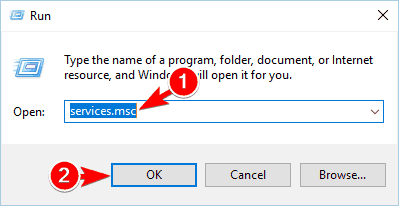
- Press Windows Key + R and enter services.msc.
- Locate the WebClient service and restart it.
- Close the Services window.
After you restart the service, changes will be applied and the file size limit will be removed.
3. Scan your PC for viruses
Several users reported that this error can occur due to malware infection.
That’s why we strongly advise you to perform a detailed scan using a dedicated anti-malware program. We recommend Bitdefender, which is the best tool on the market at the moment.
A deep system scan will surely clean your device from any possible infection. It might take a while, but at least you will eliminate this issue.
And, if you’ve already installed the tool, you’ll also benefit from some very useful features, such as a nti-phishing and anti-fraud shields, advanced network threat protection, VPN, battery saver, or online banking protection.
Bitdefender Antivirus Plus
4. Configure your SharePoint storage
Few users reported that The file size exceeds the limit allowed and cannot be saved message appears with files located in the SharePoint folder.
To fix this issue, users are suggesting to configure your SharePoint storage so it can save larger files.
Apparently, SharePoint has a storage limit, but you can easily change it. After doing that, you should be able to save files without any issues.
5. Set a file size upload limit
- Login to SharePoint’s Central Admin and navigate to Central Administration > Application Management > Manage Web Applications.
- Select the applications you want to change and click on General Settings.
- Once the General Settings opens, you’ll see Maximum upload size value. Change that value to 2047 MB and save changes.
After performing these steps, the error message should be gone.
6. Change the SharePoint web.config file
- Open Internet Information Server console on server desktop.
- Open the Websites tree and select the desired website. Select Open in Explorer View option.
- Locate web.config file in the folder.
- Create a copy of that file and use it as a backup in case anything goes wrong. Open the original web.config file with Notepad (or any other text editor).
- In the Notepad text, locate the line and change it to .
- Repeat these steps for each server in SharePoint.
7. Increase the machine-level request setting
- Open the SharePoint Administrative Command Prompt.
- Enter the following command: %windir%system32inetsrv appcmd set config -section:requestFiltering -requestLimits.maxAllowedContentLength:209715200
- You should receive a confirmation message after applying this command.
As seen, The file size exceeds the limit allowed and cannot be saved error usually affects SharePoint users. We truly hope that using one of our solutions has been helpful.
We’d appreciated it if you’d tell us which solutions you tried or if you have further suggestions on this topic.
Anand, the Architect
..Solutions..Answers..Ideas..Fixes..Madness..
WebDAV: Increasing Maximum File Size Limit in Windows Server
Windows (IIS) server based WebDAV server has “laughable” file size limit for download or uploads to/from the server. It turn out to be the restriction is on the client side (Windows). Microsoft says the reason for this restriction is,
This issue occurs because a security change that was introduced in
Windows XP SP2 affects the Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning
(WebDAV) redirector. This security change makes sure that an
unauthorized server cannot force a client computer into a denial of
service attack. If you try to download a file that is larger than
50000000 bytes, the client computer interprets this download as a denial
of service attack. Therefore, the download process stops.
Also it’s fixable. Too bad we have to fix this for every client machine that needs to use WebDAV with huge files. It is documented at http://support.microsoft.com/kb/900900.
The fix is also described in above KB article. You can also see fix below as per in the KB article.
- Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
- Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
Unfortunately I didn’t find any server side solution, since Windows clients are set to restriction.
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases.
Limits on memory and address space vary by platform, operating system, and by whether the IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE value of the LOADED_IMAGE structure and 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT) are in use. IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE is set or cleared by using the /LARGEADDRESSAWARE linker option.
4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications. Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT.
Limits on physical memory for 32-bit platforms also depend on the Physical Address Extension (PAE), which allows 32-bit Windows systems to use more than 4 GB of physical memory.
Memory and Address Space Limits
The following table specifies the limits on memory and address space for supported releases of Windows. Unless otherwise noted, the limits in this table apply to all supported releases.
| Memory type | Limit on X86 | Limit in 64-bit Windows | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User-mode virtual address space for each 32-bit process | 2 GB Up to 3 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE and 4GT | 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared (default) 4 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| User-mode virtual address space for each 64-bit process | Not applicable | With IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set (default): x64: WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB x64: Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB Intel Itanium-based systems: 7 TB 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kernel-mode virtual address space | 2 GB From 1 GB to a maximum of 2 GB with 4GT | WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2 or later: 128 TB Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paged pool | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with Service PackВ 1 (SP1), the paged pool can also be limited by the PagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server and Windows ServerВ 2003: 530 MB WindowsВ XP: 490 MB | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008 and WindowsВ Vista: 128 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonpaged pool | 75% of RAM or 2 GB, whichever is smaller. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space and physical memory. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, the nonpaged pool can also be limited by the NonPagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 256 MB, or 128 MB with 4GT. | RAM or 128 GB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM) WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, WindowsВ 7 and Windows ServerВ 2008: 75% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB WindowsВ Vista: 40% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System cache virtual address space (physical size limited only by physical memory) | Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space or the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. WindowsВ Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space. Starting with WindowsВ Vista with SP1, system cache virtual address space can also be limited by the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: 860 MB with LargeSystemCache registry key set and without 4GT; up to 448 MB with 4GT. | Always 1 TB regardless of physical RAM WindowsВ 8.1 and Windows ServerВ 2012В R2: 16 TB. Windows ServerВ 2003 and WindowsВ XP: Up to 1 TB depending on configuration and RAM. Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 10.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2016.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 8.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2012. Windows ServerВ 2012 is available only in X64 editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ 7.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 is available only in 64-bit editions.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2008. Limits greater than 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows VistaThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ Vista.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home ServerWindows Home Server is available only in a 32-bit edition. The physical memory limit is 4 GB. Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003В R2. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 2 (SP2). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service PackВ 1 (SP1). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows ServerВ 2003. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows XPThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for WindowsВ XP.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows EmbeddedThe following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Embedded.
How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limitsDevices have to map their memory below 4 GB for compatibility with non-PAE-aware Windows releases. Therefore, if the system has 4GB of RAM, some of it is either disabled or is remapped above 4GB by the BIOS. If the memory is remapped, X64 Windows can use this memory. X86 client versions of Windows don’t support physical memory above the 4GB mark, so they can’t access these remapped regions. Any X64 Windows or X86 Server release can. X86 client versions with PAE enabled do have a usable 37-bit (128 GB) physical address space. The limit that these versions impose is the highest permitted physical RAM address, not the size of the IO space. That means PAE-aware drivers can actually use physical space above 4 GB if they want. For example, drivers could map the «lost» memory regions located above 4 GB and expose this memory as a RAM disk. |


 Select a safe location for your backup. Enter the desired file name, select All as Export range and click on Save.
Select a safe location for your backup. Enter the desired file name, select All as Export range and click on Save. 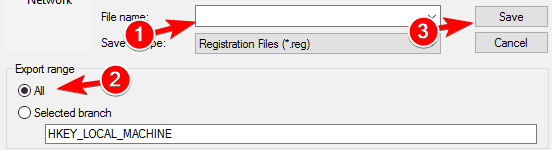 After exporting the registry, you can use the exported file to restore everything to the original state if anything goes wrong.
After exporting the registry, you can use the exported file to restore everything to the original state if anything goes wrong.