- Попробовал Files — файловый менеджер для Windows. Подходит тем, кому надоел стандартный «Проводник»
- Попробовал Files — файловый менеджер для Windows. Подходит тем, кому надоел стандартный «Проводник»
- Что понравилось в файловом менеджере Files
- Best Free File Manager software for Windows 10
- Free File Manager software for Windows 10
- Диспетчер файлов (Windows) — File Manager (Windows)
- Содержание
- Обзор
- Версии
- 16-битная OS / 2 и Windows 3.x
- Windows NT
- Windows 10
- File Caching
Попробовал Files — файловый менеджер для Windows. Подходит тем, кому надоел стандартный «Проводник»
Попробовал Files — файловый менеджер для Windows. Подходит тем, кому надоел стандартный «Проводник»
Мне кажется, что «Проводник» сильно отстал от жизни и в плане дизайна, и с точки зрения функциональности. Я пытался выбрать другой файловый менеджер для Windows, но так и не нашёл подходящий вариант. Либо слишком много функций, как в Total Commander, либо отвратительный внешний вид.
А потом я нашёл Files и понял, что это отличная замена стандартному «Проводнику». Для работы с ним не нужно перестраиваться, есть кастомизация и несколько интересных фишек.
По умолчанию Files открывается на стартовой странице, но можно выбрать любую папку
Files — файловый менеджер с открытым исходным кодом, который использует последние возможности Windows, включая Fluent Design. По функциональности он не сравнится с Total Commander и другими файловыми менеджерами. Но Files неплохо закрывает потребности обычных пользователей.
Что понравилось в файловом менеджере Files
- Есть вкладки, которые обещают добавить в «Проводник» уже больше 3 лет. QTTabBar и Clover всегда казались мне плохой альтернативой.
- Внешний вид — наконец-то Fluent Design.
- Изменение светлой/тёмной темы. Отдельная настройка, только для файлового менеджера, а не для всей Windows.
- Настройки запуска — можно сразу начинать с новой вкладки, открывать определённую папку или продолжить с места, на котором закрыл менеджер.
- Двойная панель — можно открывать все новые вкладки в ней по умолчанию или выбирать этот режим вручную.
- Опция «Открыть в терминале» — можно выбрать CMD или PowerShell.
Классический вид файлового менеджера для удобной работы с файлами
Какие-то функции мигрировали из стандартного «Проводника» и просто стали чуть более удобными — например, управление сортировкой и отображением. Больше нет страшной верхней панели со всеми этими настройками. Все параметры кастомизации находятся на отдельной странице.
Настроек не очень много, но все полезные
В итоге я убрал стандартный «Проводник» с таскбара и прикрепил Files. Можно также перенастроить сочетание Win + E, чтобы оно запускало новый файловый менеджер для Windows. В документации Files предлагают два способа:
- скрипт, добавленный через программу AutoHotKey;
- редактирование реестра.
Первый способ безопаснее и проще. Если выберете редактирование реестра, не забудьте сначала сделать его резервную копию.
Best Free File Manager software for Windows 10
File Manager software offers an easy and convenient way to modify file attributes. Windows has its own file manager – File Explorer. It is designed to simplify file management activities in Windows. Although fine, Windows Explorer doesn’t offer tabs, a dual-pane interface, batch file renaming tools, and other advanced features. This necessitates the use of File Explorer alternatives for your computer-based life. Fortunately, there’s no shortage of File Explorer replacements that do the same job much better than Explorer itself. Below, you can find the list of free File Manager software for Windows 10/8/7 which include Shallot, Tablacus, XYplorer, FreeCommander, Unreal Commander, Multi-commander, Konverter, and FileVoyager.
Free File Manager software for Windows 10
If you aren’t quite sure about which program is best for you, we’ll help you make the right choice with these alternatives and features they support. Today, we take a look at:
- FileVoyager
- Konvertor
- Multi-Commander
- Unreal Commander
- FreeCommander
- XYplorer
- Tablacus
- Shallot
- One Commander.
Let us take a look at them.
Apart from allowing usual file operations like renaming, copying, moving, linking, deleting and recycling files, the tool features a dual pane layout. It makes the transfer operations of files or folders between sources and destinations easier and hassles free.
The portable version of File Voyager supports numerous shortcuts to default folders, such as Documents, Libraries, and Desktop. Moreover, you can easily access the file compressing tool or fax or email the selected document by creating shortcuts. You can also view the file/folder size near each entry and edit the items in notepad.
FileVoyager enables browsing in various modes like report or thumbnail modes and has an extensive collection of tools.
The freeware ships with an impressive set of features and has been designed to co-exist with Windows Explorer/ File Explorer. This means it does not interfere with the default file manager in any way. Similar to FileVoyager, Konverter displays data in two panels. A built-in file conversion tool supports many file formats. For instance, there’s support for 2,034 image file types, 795 audi, 230 video, 102 3D files. Besides, there’s a vast number of extras that make the tool a very capable program.
In all, Konverter is a fast and reliable program with a shallow learning curve. This ability of the program gives its users all levels of expertise required to process and alter files quickly and efficiently.
Multi-Commander comes across as one of the best alternatives to the standard File Explorer. It features an extensive number of tools and plug-ins to help users manage their files and folders.
The program houses a number of buttons, all of which are highly customizable. Plus, there are drive shortcuts for opening specific types of files and accessing the HKEY_CURRENT_USER branch of the Registry.
It is a dual-pane file manager designed to overcome shortfalls of the traditional Windows File Explorer and offer a more convenient way to have control over files and folders. the program comes pre-loaded with a set of useful features and options, like:
- Directory synchronization – Offers the capability to open archives with popular formats (ZIP, RAR, ACE, TAR and CAB)
- Multi-rename tool – Allows renaming multiple files simultaneously, once the naming pattern with rules has been defined
- FTP connection – Allows rapid uploading of files to an FTP server.
The tool advertises itself as an easy-to-use alternative to the standard Windows file manager. Similar to other programs mentioned above, Free Commander helps you undertake all of your daily activities in Windows with convenience.
It has a built-in file viewer to view files in hex, binary, text or image format. With this tool, you can set your own keyboard shortcuts and menu buttons for easier navigation. A simple right click on a folder or file displays the traditional Windows Context Menu.
XYplorer takes basic and familiar features of File Explorer a notch higher. It has multilingual support. The program avoids any entry in the Registry or system folders, allowing you to use it as portable application alongside Explorer. Another unique feature of the tool – it allows users to color-code their tabs for easier identification.
Apart from the above, XYplorer runs powerful file search, multi-level undo or redo, branch view, folder view settings, batch
- Powerful file search
- Multi-level undo or redo
- Branch view
- Folder view settings
- Batch rename
- Color filters
- Directory Print
- File tags.
This tool does not require any installation as it is available in a portable version. Tablacus, basically adds new features to the layout of File Explorer so that you find it easier to search files.
Its design is heavily inspired by File Explorer but makes some necessary changes needed in the file manager. The most obvious being tabs so that a user does not require dozen explorer windows to be opened at once.
Shallot makes possible to customize the interface and configure behavior and options of a file manager as per your liking. This flexible manager comes with a plugin interface that adds a wealth of convenient features and versatility. The freeware program supports built-in plugins as long as they are written in Python. As such, you can create your own plugins to automate a few file management tasks.
For a free and easy way to manage the files on your system, give Shallot, a try!
Instead of just being a dual window file manager, One Commander offers both double window view, and multi-column view. You can choose that when you launch it for the first time. Along with this, you can choose between white, dark and light theme.
Диспетчер файлов (Windows) — File Manager (Windows)
Диспетчер файлов — это программа файлового менеджера , входящая в состав выпусков OS / 2 и Microsoft Windows с 1990 по 1999 год и доступная с 6 апреля. 2018 в качестве дополнительной загрузки для всех современных выпусков Windows, включая Windows 10 .
. Это графический интерфейс с одним экземпляром, заменяющий интерфейс командной строки MS-DOS , для управления файлы (копирование, перемещение, открытие, удаление, поиск и т. Д.) И файловый менеджер MS-DOS Executive из предыдущих версий Windows. Хотя файловый менеджер был включен в Windows 95 и Windows NT 4.0 и некоторые более поздние версии, Windows Explorer был представлен и использовался в качестве основного файлового менеджера с управлением файлами. через представление с двумя панелями, отличное от представления Диспетчера файлов, и представление с одной панелью, получаемое при нажатии значка «Мой компьютер».
Содержание
Обзор
Интерфейс программы показал список каталогов на левой панели и список содержимого текущего каталога на правой. панель. Диспетчер файлов позволял пользователю создавать, переименовывать, перемещать, печатать , копировать, искать и удалять файлы и каталоги, а также устанавливать разрешения (атрибуты ), например архивный, доступный только для чтения, скрытый или системный, и для связывания типов файлов с программами. Также были доступны инструменты для маркировки и форматирования дисков , управления папками для совместного использования файлов, а также для подключения и отключения от сетевого диска . В системах Windows NT также можно было установить списки управления доступом для файлов и папок на разделах NTFS через диалоговое окно настройки безопасности shell32 (также используемое Проводником и другими Windows файловые менеджеры). На дисках NTFS отдельные файлы или целые папки могут быть сжаты или расширены.
Версия диспетчера файлов для Windows NT позволяет пользователям изменять права доступа к каталогам, файлам, локальные, сетевые и пользовательские.
Начиная с Windows 95 и Windows NT 4.0, Диспетчер файлов был заменен Проводником Windows. Однако программный файл WINFILE.EXE все еще был включен в Windows 95, Windows 98 и Windows Me (16-разрядный исполняемый файл) и Windows NT 4.0 ( 32-битный исполняемый файл). Последняя 32-битная сборка WINFILE.EXE (4.0.1381.318) распространялась как часть Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 6a (SP6a). Последняя 16-битная сборка WINFILE.EXE (4.90.3000) распространялась как часть операционной системы Windows Me.
Крис Гузак был разработчиком оболочки в команде Windows 3.1, ответственной за файловый менеджер.
Источник был выпущен на GitHub в 2018 году с Лицензия MIT от Microsoft.
Версии
16-битная OS / 2 и Windows 3.x
Диспетчер файлов был включен в версии OS / 2 1.1, 1.2 и 1.3. Имя исполняемого файла было PMFILE.EXE .
Исходная версия диспетчера файлов была 16-разрядной программой, которая поддерживала имена файлов формата 8.3, которые использовались в то время.
Он не поддерживал расширенные имена файлов, которые стали доступны в Windows 95, включая длинные имена файлов и имена файлов, содержащие пробелы. Вместо этого он будет отображать только первые шесть символов, за которыми следует символ тильды («
«) и число, обычно 1. Дополнительные числа (2, 3 и т. Д.) Добавляются после тильды, если более одного имени файла с такие же начальные символы существовали в том же каталоге.
16-разрядная версия, распространяемая с установками Windows 3.1x и Windows for Workgroups 3.1x , имела проблему 2000 года из-за лексикографической корреляции между представление даты и набор символов ASCII ; двоеточия и точки с запятой заменяли то, что должно было быть «2000». Microsoft выпустила исправленные двоичные файлы для всех сред Windows 3.1x.
Windows NT
Диспетчер файлов был переписан как 32-разрядная программа для Windows NT. Эта новая версия корректно обрабатывала длинные имена файлов в дополнение к файловым системам NTFS . Он был включен в Windows NT 3.1 , 3.5 , 3.51 и 4.0 .
Windows 10
6 апреля 2018 Microsoft выпустила двоичные файлы и исходный код , лицензированный по лицензии MIT , для улучшенной версии диспетчера файлов, которую можно запускать в Windows 10. Это версия включала такие изменения, как возможность компиляции в современных версиях Visual Studio, возможность компиляции как 64-разрядного приложения и многочисленные улучшения удобства использования. Microsoft также выпустила это приложение в Microsoft Store бесплатно в конце января 2019 года.
File Caching
By default, Windows caches file data that is read from disks and written to disks. This implies that read operations read file data from an area in system memory known as the system file cache, rather than from the physical disk. Correspondingly, write operations write file data to the system file cache rather than to the disk, and this type of cache is referred to as a write-back cache. Caching is managed per file object.
Caching occurs under the direction of the cache manager, which operates continuously while Windows is running. File data in the system file cache is written to the disk at intervals determined by the operating system, and the memory previously used by that file data is freed—this is referred to as flushing the cache. The policy of delaying the writing of the data to the file and holding it in the cache until the cache is flushed is called lazy writing, and it is triggered by the cache manager at a determinate time interval. The time at which a block of file data is flushed is partially based on the amount of time it has been stored in the cache and the amount of time since the data was last accessed in a read operation. This ensures that file data that is frequently read will stay accessible in the system file cache for the maximum amount of time.
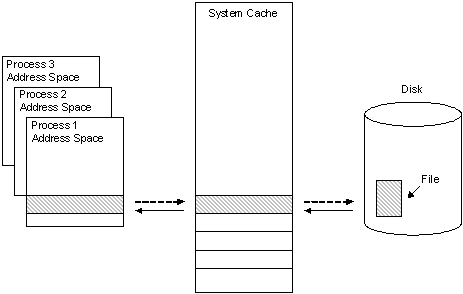
This file data caching process is illustrated in the following figure.
As depicted by the solid arrows in the previous figure, a 256 KB region of data is read into a 256 KB cache «slot» in system address space when it is first requested by the cache manager during a file read operation. A user-mode process then copies the data in this slot to its own address space. When the process has completed its data access, it writes the altered data back to the same slot in the system cache, as shown by the dotted arrow between the process address space and the system cache. When the cache manager has determined that the data will no longer be needed for a certain amount of time, it writes the altered data back to the file on the disk, as shown by the dotted arrow between the system cache and the disk.
The amount of I/O performance improvement that file data caching offers depends on the size of the file data block being read or written. When large blocks of file data are read and written, it is more likely that disk reads and writes will be necessary to finish the I/O operation. I/O performance will be increasingly impaired as more of this kind of I/O operation occurs.
In these situations, caching can be turned off. This is done at the time the file is opened by passing FILE_FLAG_NO_BUFFERING as a value for the dwFlagsAndAttributes parameter of CreateFile. When caching is disabled, all read and write operations directly access the physical disk. However, the file metadata may still be cached. To flush the metadata to disk, use the FlushFileBuffers function.
The frequency at which flushing occurs is an important consideration that balances system performance with system reliability. If the system flushes the cache too often, the number of large write operations flushing incurs will degrade system performance significantly. If the system is not flushed often enough, then the likelihood is greater that either system memory will be depleted by the cache, or a sudden system failure (such as a loss of power to the computer) will happen before the flush. In the latter instance, the cached data will be lost.
To ensure that the right amount of flushing occurs, the cache manager spawns a process every second called a lazy writer. The lazy writer process queues one-eighth of the pages that have not been flushed recently to be written to disk. It constantly reevaluates the amount of data being flushed for optimal system performance, and if more data needs to be written it queues more data. Lazy writers do not flush temporary files, because the assumption is that they will be deleted by the application or system.
Some applications, such as virus-checking software, require that their write operations be flushed to disk immediately; Windows provides this ability through write-through caching. A process enables write-through caching for a specific I/O operation by passing the FILE_FLAG_WRITE_THROUGH flag into its call to CreateFile. With write-through caching enabled, data is still written into the cache, but the cache manager writes the data immediately to disk rather than incurring a delay by using the lazy writer. A process can also force a flush of a file it has opened by calling the FlushFileBuffers function.
File system metadata is always cached. Therefore, to store any metadata changes to disk, the file must either be flushed or be opened with FILE_FLAG_WRITE_THROUGH.