- 990x.top
- Простой компьютерный блог для души)
- find.exe загружает процессор — что делать?
- find.exe — что это за процесс?
- find.exe загружает процессор
- find.exe — вирус?
- How To Know Which Process is Using a File or Folder in Windows
- Resource Monitor
- Process Explorer
- My Take
- How to Identify the Process that has Locked a File in Windows
- Find which process has locked a file using:
- 1. Resource Monitor
- 2. Process Explorer
- 3. Handle from Windows Sysinternals
- Sysinternals Handle: Command-line arguments
- Add Sysinternals Handle to right-click menu
- 4. OpenFiles.exe — a built-in console tool
- Enable “Maintain Objects List” global flag for the First time
- View open files and the corresponding process names
- Disconnect files opened remotely from shared folder.
- 5. OpenedFilesView
990x.top
Простой компьютерный блог для души)
find.exe загружает процессор — что делать?
Приветствую друзья. Данный материал расскажет о процессе find.exe, а также что делать, когда сильно загружает процессор, использует много оперативной памяти.
find.exe — что это за процесс?
Системный компонент, используется для поиска файлов через командную строку. Данный компонент также могут использовать в своих целях сторонние программы, например Malwarebytes.
Важно: была найдена информация, что постоянную нагрузку процесс вызывает из-за установленной антивирусной утилиты Malwarebytes, которая также ставит свою службу Malwarebytes Service.
find.exe загружает процессор
После включения ПК данный процесс может начать грузить процессор (CPU) на 100%.
Кроме процесса find.exe может появляться также другой — Flock.exe, также способен грузить ПК. Предположительная папка запуска Flock.exe:
Оказывается find.exe — не вредоносный процесс, а системный консольный компонент поиска, который запускается из командной строки (Win + R > cmd), имеет параметры запуска. Flock.exe — неизвестен, возможно вирус. Под названием Flock существовал ранее браузер, а также существует мессенджер.

Как решить нагрузку? Точного способа нет. Причина — find.exe является системным компонентом, грузит ПК потому что запущен поиск, который могла запустить стороннее ПО. Необходимо проверить автозагрузку:
- Зажмите Win + R, вставьте команду msconfog, кликните ОК.
- Откроется окошко Конфигурация системы > активируйте вкладку Автозагрузку.
- Отключите временно все подозрительные элементы, программы, выполните перезагрузку.
Также виной может быть служба. Проанализируйте какой софт недавно устанавливали. После — отключите службы, связанные с этим софтом. Способ запуска окна служб:
- Зажмите клавиши Win + R, вставьте команду services.msc, кликните ОК.
- Откроется список служб.
- Найдите подозрительные, связанные с недавно установленными программами. Отключите их автозапуск — два раза нажмите по службе > в меню Тип запуска укажите Отключена, далее нажмите кнопку Остановить.

Важно понимать: универсального рецепта избавления от загрузки — нет. find.exe сам по себе не грузит ПК, это системный компонент поиска файлов/папок, присутствует в OS Windows изначально. Необходимо выяснить приложение, которое запускает данный процесс.
find.exe — вирус?
Выяснили — нет. Однако вирус спокойно может маскироваться под данный процесс.
Найдите процесс find.exe в диспетчере задач, проверьте папку запуска, если это не SysWOW64 или System32 — вероятно вирус. Просканируйте ПК на наличие опасных угроз, рекламных модулей:
- Dr.Web CureIT — утилита против опасных вирусов, например трояны, ботнеты, майнеры, руткиты и прочее. Загружается уже с антивирусными базами, весить может около 100 мб.
- AdwCleaner, HitmanPro — утилиты против рекламных вирусов, показывающие рекламу на рабочем столе, в браузере, устанавливающие левые расширения, тулбары и прочее. Работают быстро. Утилиты похожи, но используют немного разный алгоритм работы, поэтому рекомендуется проверить обоими.
Идеально всего проверить всеми тремя утилитами.
How To Know Which Process is Using a File or Folder in Windows
Ever wondered which program has a particular file or directory open? Quite often, when trying to delete a folder, Windows reports this:
This error also happens with a file, when we tried to move a file, or delete those file. How we can find out which program or application is currently using it and preventing us to delete/move it? To get the process holding those folder or file, we can use these two utilities:
Resource Monitor
For Windows 7 and above, you can use the built-in Resource Monitor.
Open Resource Monitor, which can be found
- By searching for resmon.exe in the start menu, or
- As a button on the Performance tab in your Task Manager
Resource Monitor from Task Manager’s Performance Tab
From CPU tab, use the search field in the Associated Handles section
When you’ve found the handle, you can identify the process by looking at the Image and/or PID column. You can then close the application if you are able to do that, or just right-click the row and you’ll get the option of killing the process (End Process) right there.
Process Explorer
Process Explorer shows you information about which handles and DLLs processes have opened or loaded.
- Open Process Explorer (running as «administrator») by running procexp.exe or procexp64.exe.
- Enter the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+F. Alternatively, click the “Find” menu and select “Find a Handle or DLL”.
Process Explorer — Find Handle or DLL
- Type in the name of the locked file or other file of interest in the Search dialog box, then click «Search». Partial names are usually sufficient.
- A list will be generated. There may be a number of entries. Click one of the entry, it’ll «Refreshing handles».
Process Explorer — Search
Same as Resource Monitor, an individual handle in the list can be killed by selecting it and pressing the delete key (or Close Handle). However, please be careful when deleting handles, as system instabilities may occur. Rebooting your system maybe will free the locked file/folder.
Process Explorer — Close Handle
Handle is a command line version of Process Explorer.
My Take
I prefer to use Resource Monitor compare to Process Explorer since Process Explorer is slower (especially during «Refreshing handles» process). If I can’t find the handle in Resource Monitor, then I use Process Explorer.
Liked this Tutorial? Share it on Social media!
How to Identify the Process that has Locked a File in Windows
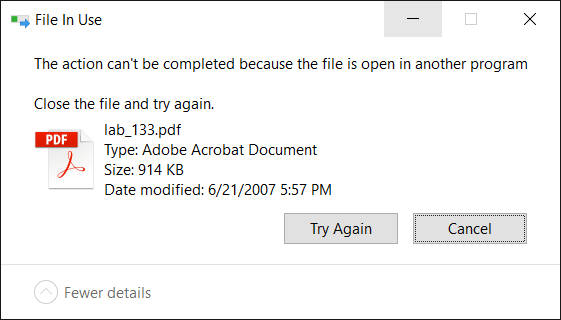
When you attempt to delete a file or folder which is in use by a process, the File In Use dialog appears showing the name of the program that has locked the file.
However, there are cases where the “File In Use” dialog doesn’t show the name of the process that has a lock on the file you’re trying to delete. In some cases, the dialog will show “the action can’t be completed because the file is open in another process“.
For investigating processes and locked files, Windows Sysinternals Process Explorer is probably the first option that comes to mind for most users. However, there are two built-in solutions to display the current open files list along with corresponding process names.
Find which process has locked a file using:
1. Resource Monitor
Resource Monitor (resmon.exe) is a built-in tool that has many useful features. With Resource Monitor, you can track current network and internet usage, view associated handles for locked files, as well as manage processes just as you’d using the Task Manager.
To find the process name that has a file locked, click the CPU tab, type the file name or part of it in the Associated Handles text box.
2. Process Explorer
Process Explorer needs no introduction. In Process Explorer, all you need to do is use the Find feature and type in the file name. This shows the process that’s accessing the file.
From the lower pane view, you can close the file handle if necessary.
You must run Process Explorer as administrator in order to manage processes which are running elevated. To elevate Process Explorer, click the File menu → Show Details for All Processes.
3. Handle from Windows Sysinternals
Handle is a utility from Microsoft Sysinternals that displays information about open handles for any process in the system. You can use it to see the programs that have a file open, or to see the object types and names of all the handles of a program. Handle is like a command-line version of Process Explorer.
Note: Handle v4.21 has a small bug where it always reports “No matching handles found” if the drive-letter is in uppercase. Hope Microsoft fixes it in the next update.
From an admin Command Prompt window, use the command-line syntax to find the process which is having the file open:
If the file name contains spaces, enclose it within double quotes.
Example:
(Mentioning the filename without the path may not necessarily work in every situation. It’s advisable to include the full path always.)
The output shows the process name, the process identifier, user name, the locked (target) file name with path.
Sysinternals Handle: Command-line arguments
| -a | Dump all handle information. |
| -l | Just show pagefile-backed section handles. |
| -c | Closes the specified handle (interpreted as a hexadecimal number). You must specify the process by its PID.WARNING: Closing handles can cause application or system instability. |
| -y | Don’t prompt for close handle confirmation. |
| -s | Print count of each type of handle open. |
| -u | Show the owning user name when searching for handles. |
| -p | Dump handles belonging to process (partial name accepted). |
| name | Search for handles to objects with (fragment accepted). |
| -nobanner | Do not display the startup banner and copyright message. |
No arguments will dump all file references.
Add Sysinternals Handle to right-click menu
You can add Sysinternals Handle to the right-click menu for files to quickly find the program that has locked the file. To add it to the context menu, follow these steps:
- Download Handle from Microsoft Sysinternals site.
- Copy the files handle.exe & handle64.exe to a folder – e.g., d:\tools
- Copy the following lines of code to Notepad, and save the file as find_handle.vbs to a permanent location.
Note: The Sysinternals Handle.exe path is hard-coded as d:\tools\handle.exe in the above script. If the program is located on a different path, modify the path in the script accordingly. For 64-bit Windows, you can use either handle.exe or handle64.exe
To remove the Find Handle context menu entry, start the Registry Editor ( regedit.exe ) and delete the following key:
4. OpenFiles.exe — a built-in console tool
Another built-in tool we’re going to use is Openfiles.exe, a console tool that’s not new to Windows. It was originally introduced in 2000 as part of the Windows Resource Kit 2000/2003 tools. This utility was then included by default in Windows Vista and higher (including Windows 10). Openfiles displays the currently open files list from local or shared folders, along with the Handle ID and Process executable name. This tool also allows you to disconnect one or more files that are opened remotely from a shared folder.
Enable “Maintain Objects List” global flag for the First time
First, to enable tracking of local file handles, you need to turn on ‘maintain objects list’ flag by running the following command from admin Command Prompt.
You’ll see the following message:
INFO: The system global flag ‘maintain objects list’ is currently enabled.
You’ll need to run this command for the first time only. Then restart Windows for the change to take effect.
View open files and the corresponding process names
After restarting Windows, from an admin Command Prompt window, type:
This lists the File/Handle ID, Process Name and the list of files opened locally or opened remotely via local share points, in a table format.
To view the output in List or CSV formats, use the /query parameter.
To copy the output to clipboard, pipe the output to Clip.exe as below. Then paste the output in Notepad or any other editor of your choice.
For more information on copying Command Prompt output to clipboard or save the output to a file, check out the article How to Copy Command Prompt Output Text to Clipboard or Save to File?
To find if a particular file is being in use by a program (and to know which program), you may use the following command-line.
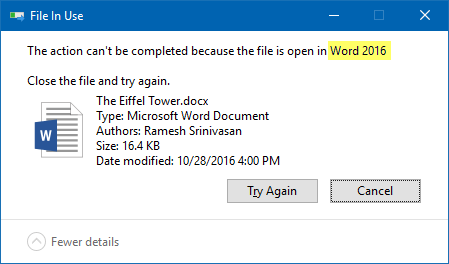
The above command lists all open files that contain the word “eiffel” in the file name. In this example, Word 2016 is currently having the lock over the file “The Eiffel Tower.docx” (ID 4576).
And “File In Use” dialog tells me the same thing.
Disconnect files opened remotely from shared folder.
To disconnect files opened from shared folder so that you can delete, rename the file or modify the contents, use the /disconnect parameter to cut connections to that file. Here are the command-line options.
Openfiles.exe perfectly does the job of listing all open files along with the process names, but it can’t forcibly kill processes. However, this excellent (but overlooked) built-in console tool can come in handy when you want to quickly find a process name that’s using a file, or to disconnect a file that’s being accessed through a shared folder by a network user — without depending on a third-party solution.
5. OpenedFilesView
OpenedFilesView from Nirsoft displays the list of all opened files on your system. For each opened file, additional information is displayed: handle value, read/write/delete access, file position, the process that opened the file, and more… Optionally, you can also close one or more opened files, or close the process that opened these files.