- How to Block a Program with Windows Firewall in Windows 10 [MiniTool News]
- Summary :
- How to Block a Program with Windows Firewall Windows 10
- How to Temporarily Disable a Program
- Bottom Line
- ABOUT THE AUTHOR
- How to see if Windows Firewall is blocking a port or program
- How do I check if Windows Firewall is blocking a port ?
- 1. Check your firewall settings
- 2. Check for Blocked Port using the Command Prompt
- How to check if Windows Firewall is blocking a program ?
- Best practices for configuring Windows Defender Firewall
- Keep default settings
- Understand rule precedence for inbound rules
- Create rules for new applications before first launch
- Inbound allow rules
- Known issues with automatic rule creation
- Establish local policy merge and application rules
- Know how to use «shields up» mode for active attacks
- Create outbound rules
- Document your changes
How to Block a Program with Windows Firewall in Windows 10 [MiniTool News]
By Alisa | Follow | Last Updated March 22, 2021
Summary :
Sometimes you may want to prevent an application from accessing the Internet. This tutorial gives a step-by-step guide to teach you how to block a program with Windows firewall in Windows 10.
Normally you would want your applications to have free access to the network. However, no matter for what reason, you wish to block a program from accessing the Internet, you can check the step-by-step guide below to block program with Windows firewall in Windows 10.
How to Block a Program with Windows Firewall Windows 10
Step 1. Open Windows Firewall window
You can click Start, and type Windows Defender Firewall. Choose the top result to open Windows Defender Firewall.
Step 2. Click Advanced settings
In the Windows Defender Firewall, you can click Advanced settings to enter into Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security app.
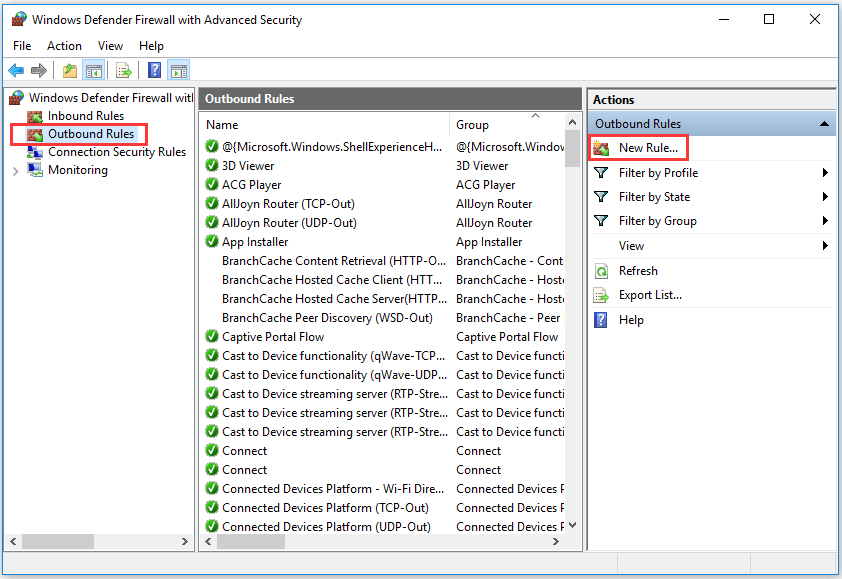
Step 3. Enter into Firewall rule creation window
Next you can click Outbound Rules in the left column and it will display all existing outbound Windows firewall rules in middle window.
In the right Outbound Rules Actions column, you can click New Rule option to open a new window in which you can create a new Firewall rule by your own.
Step 4. Create a new Firewall rule
In the new window, you can choose “What type of rule would you like to create?”
You can click Program to get ready to rule controls connections for a program, and click Next.
Step 5. Select the target program
You can tick This program path and click Browse to find path of the target program you want to block.
You can click This PC in the left column, select the hard drive, and open the program’s folder and select the target program.
If you open the program in Firewall, Windows will restructure the path of the file. You can avoid this problem by manually coping and pasting the file path to the box.
Click the address bar to copy the path of the program, and paste it to the box. Please do contain the app’s name and extension at the end of the path.
Step 6. Name the Firewall rule
You can click Next button three times, and input a name for the new Firewall rule. Then click Finish button to create the new Firewall rule to block the program with Windows Firewall in Windows 10 and prevent the program from accessing the Internet.
How to test internet speed? Here are the top 8 free internet speed test tools for you. Check the internet speed on your Windows 10 PC.
How to Temporarily Disable a Program
Step 1. You can click Start and type Windows Defender Firewall. Choose Windows Defender Firewall to open it.
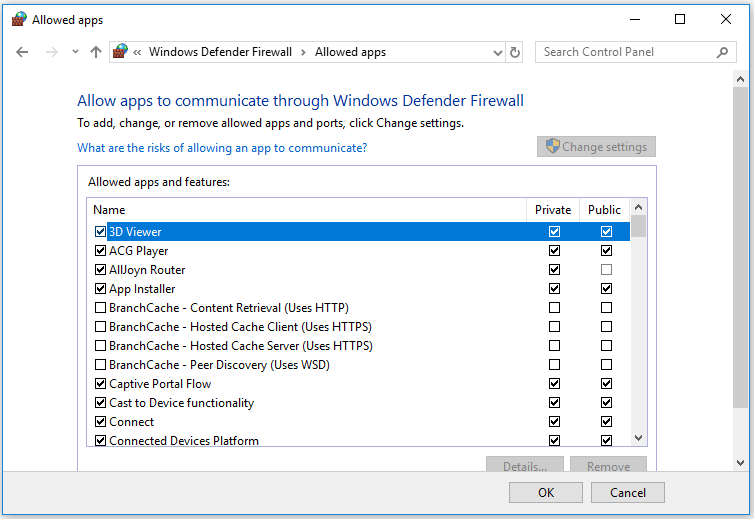
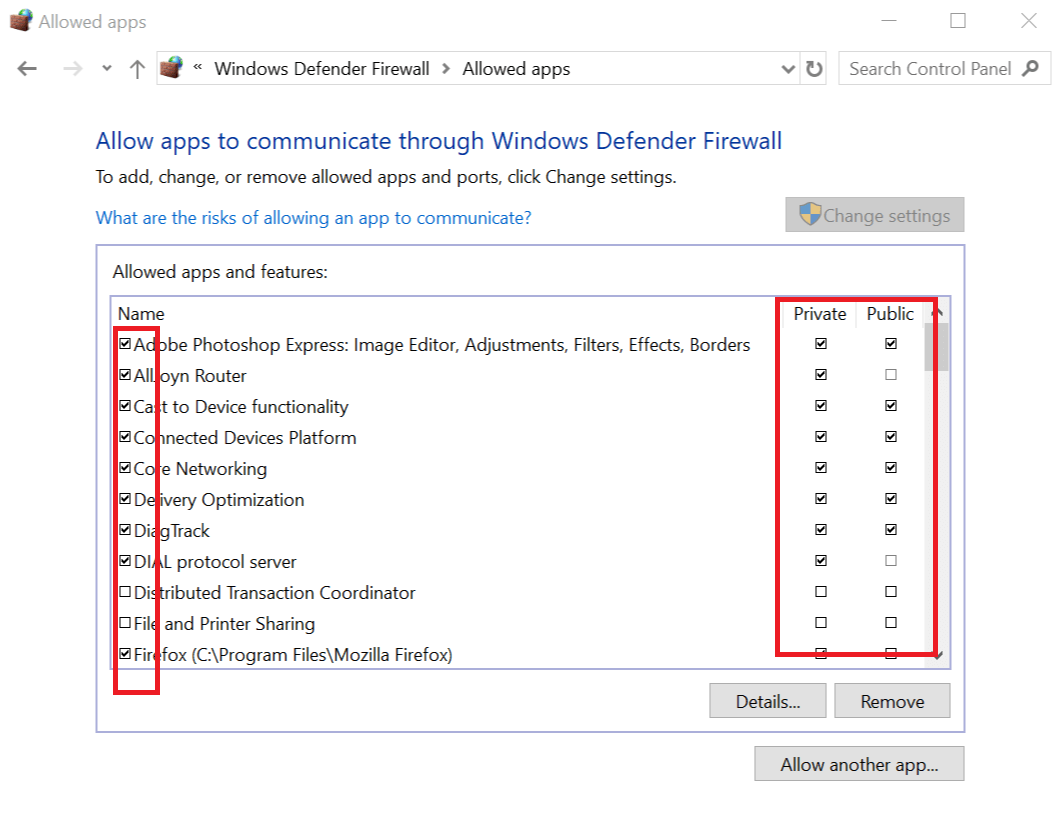
Step 2. Click Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall in the left column. And click Change settings.
Step 3. Find the target program you want to block. If you can’t find the program in the list, you can click Allow another app…-> Browse, locate the program and open it, select the program name and click Add to add it to the list.
Step 4. Make sure the target program is not checked in the left. If a program is not checked, then it means Windows Firewall already blocks the program. Finally, click OK to save the changes and prevent the program from running on your Windows 10 computer.
Bottom Line
With the step-by-step guide above, hope you can easily block a program with Windows Firewall in Windows 10 now.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Position: Columnist
Alisa is a professional English editor with 4-year experience. She loves writing and focuses on sharing detailed solutions and thoughts for computer problems, data recovery & backup, digital gadgets, tech news, etc. Through her articles, users can always easily get related problems solved and find what they want. In spare time, she likes basketball, badminton, tennis, cycling, running, and singing. She is very funny and energetic in life, and always brings friends lots of laughs.
How to see if Windows Firewall is blocking a port or program
- Wondering how you can check if a website is blocked by your Firewall? Check the firewall settings.
- The Windows Firewall settings will give you show you any port is blocked on your PC.
- Easily fix any problem caused by your Firewall blocking the Internet with the solutions below.
- The Windows Firewall also allows you to select which programs can run on your computer.
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
The Windows Firewall is a built-in security application that comes with Windows OS since the beginning. The software is built to filter network data transmission to and from your Windows system.
The Firewall will block any suspicious and harmful connection depending on the threat level.
The users can configure the Windows Firewall settings as per their need to block or open port in Windows 10 and other versions. However, at times the Firewall may block ports or programs accidentally by user’s or administrator’s misconfiguration.
Now, if you want to know if the Windows Firewall is blocking a port or program on your system, you need to check your settings. Here’s how to check firewall settings.
How do I check if Windows Firewall is blocking a port ?
1. Check your firewall settings
- Press Windows Key + R to open Run.
- Type control and press OK to open Control Panel.
- Click on System and Security.
- Scroll down and open Administrative Tools.
- In the Administrative Tools window, open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.
- Click on Actions and select Properties.
- Now select your preferred Profile (Domain, Private, Publick).
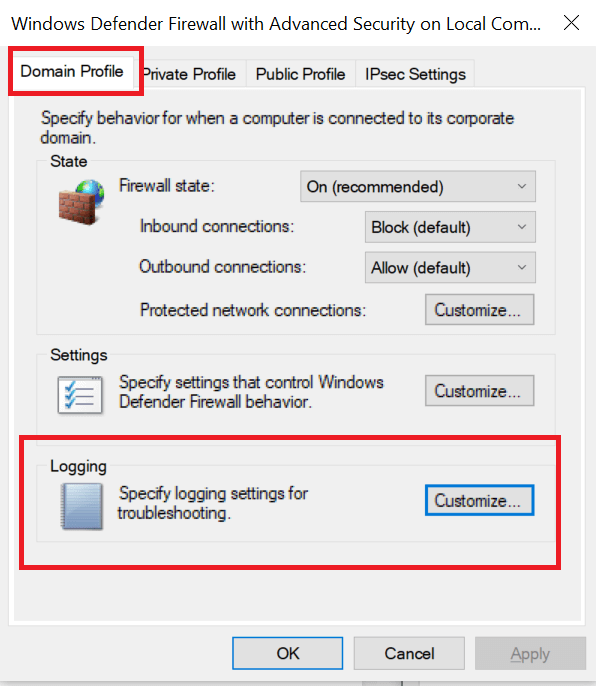
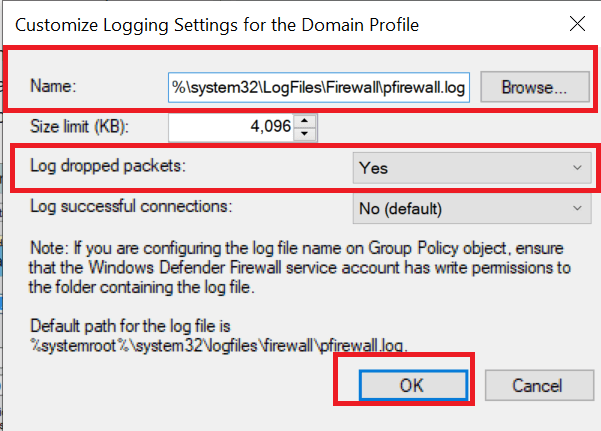
- In the Logging section, click on the Customize button.
- Click on the drop-down menu for Log dropped packets: and select Yes.
- Take note of the pfirewall.log path in the Name section.
- Click OK to save the changes.
- Open File Explorer and go to the path where the log file is saved.
- It should look something like this: %systemroot%system32LogFilesFirewall
- Click on the pfirewall.log file and check for any blocked ports.
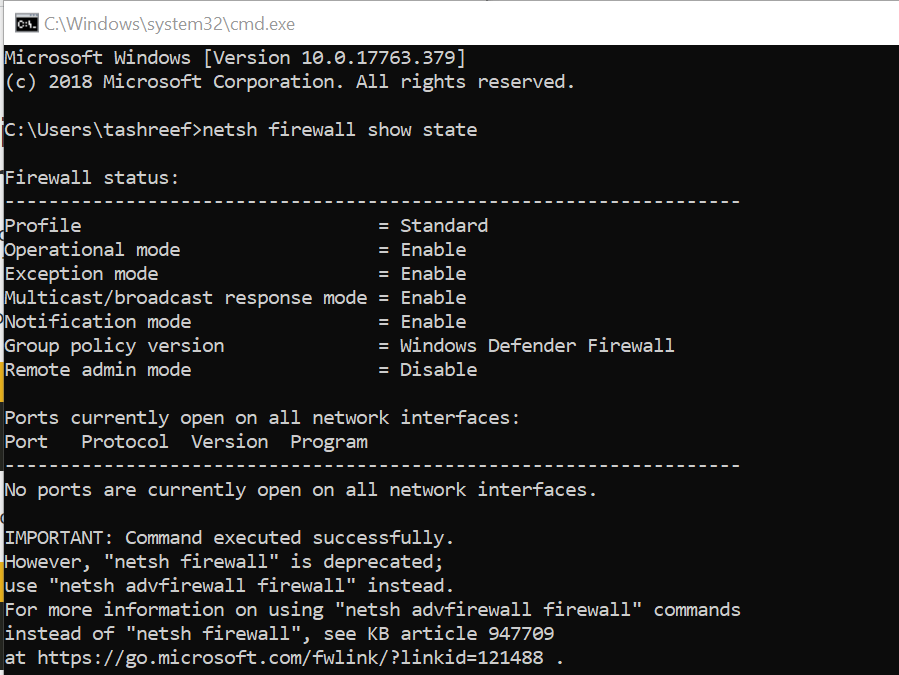
2. Check for Blocked Port using the Command Prompt
- Type cmd in the search bar.
- Right-click on the Command Prompt and select Run as Administrator.
- In the command prompt, type the following command and hit enter.
- netsh firewall show state
- This will display all the blocked and active port configured in the firewall.
How to check if Windows Firewall is blocking a program ?
- Press Windows Key + R to open Run.
- Type control and press OK to open Control Panel.
- Click on System and Security.
- Click on Windows Defender Firewall.
- From the left pane Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall.
- In the allowed app window, scroll through all the apps.
- Locate the app you want to check and see if the app is checked.
- If it is unchecked, the app is blocked on the Firewall.
- If your program is blocked, simply uncheck the app and click OK.
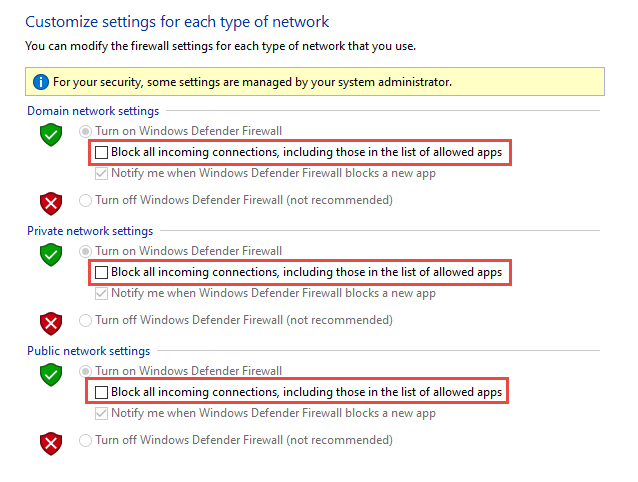
In the Customize Settings window, click the circle(s) next to Turn off Windows Defender Firewall for public networks, private networks, or both.
That’s about it for this article. Make sure you follow the solutions thoroughly and see what works for you. Also, feel free to send us any feedback regarding the subject in the comment section below.
Best practices for configuring Windows Defender Firewall
Applies to
Windows operating systems including WindowsВ 10
Windows Server Operating Systems
Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security provides host-based, two-way network traffic filtering and blocks unauthorized network traffic flowing into or out of the local device. Configuring your Windows Firewall based on the following best practices can help you optimize protection for devices in your network. These recommendations cover a wide range of deployments including home networks and enterprise desktop/server systems.
To open Windows Firewall, go to theВ StartВ menu, selectВ Run, typeВ WF.msc, and then selectВ OK. See also Open Windows Firewall.
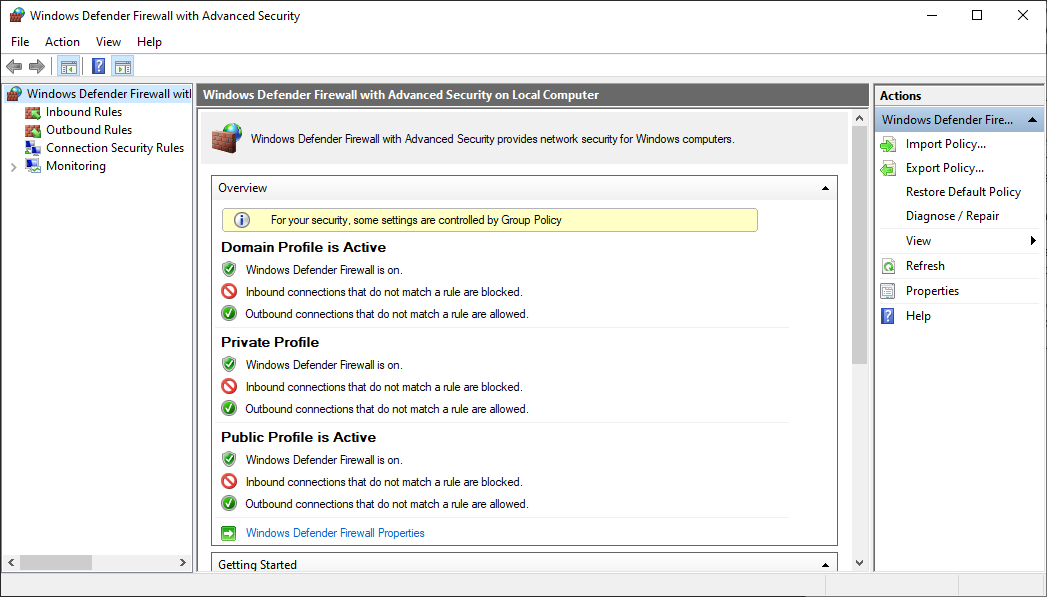
Keep default settings
When you open the Windows Defender Firewall for the first time, you can see the default settings applicable to the local computer. The Overview panel displays security settings for each type of network to which the device can connect.
Figure 1: Windows Defender Firewall
Domain profile: Used for networks where there is a system of account authentication against a domain controller (DC), such as an Azure Active Directory DC
Private profile: Designed for and best used in private networks such as a home network
Public profile: Designed with higher security in mind for public networks like Wi-Fi hotspots, coffee shops, airports, hotels, or stores
View detailed settings for each profile by right-clicking the top-level Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security node in the left pane and then selecting Properties.
Maintain the default settings in Windows Defender Firewall whenever possible. These settings have been designed to secure your device for use in most network scenarios. One key example is the default Block behavior for Inbound connections.
Figure 2: Default inbound/outbound settings
To maintain maximum security, do not change the default Block setting for inbound connections.
Understand rule precedence for inbound rules
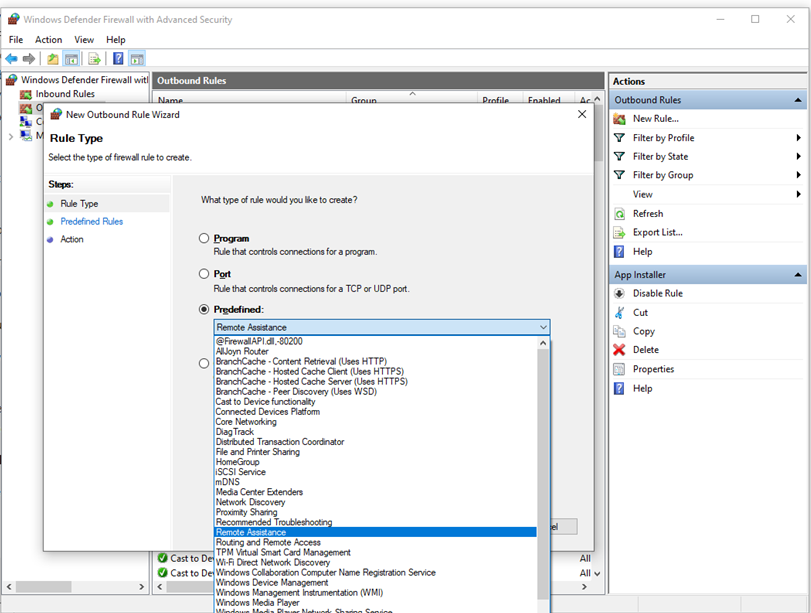
In many cases, a next step for administrators will be to customize these profiles using rules (sometimes called filters) so that they can work with user apps or other types of software. For example, an administrator or user may choose to add a rule to accommodate a program, open a port or protocol, or allow a predefined type of traffic.
This can be accomplished by right-clicking either Inbound Rules or Outbound Rules, and selecting New Rule. The interface for adding a new rule looks like this:
Figure 3: Rule Creation Wizard
This article does not cover step-by-step rule configuration. See the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Deployment Guide for general guidance on policy creation.
In many cases, allowing specific types of inbound traffic will be required for applications to function in the network. Administrators should keep the following rule precedence behaviors in mind when allowing these inbound exceptions.
Explicitly defined allow rules will take precedence over the default block setting.
Explicit block rules will take precedence over any conflicting allow rules.
More specific rules will take precedence over less specific rules, except in the case of explicit block rules as mentioned in 2. (For example, if the parameters of rule 1 includes an IP address range, while the parameters of rule 2 include a single IP host address, rule 2 will take precedence.)
Because of 1 and 2, it is important that, when designing a set of policies, you make sure that there are no other explicit block rules in place that could inadvertently overlap, thus preventing the traffic flow you wish to allow.
A general security best practice when creating inbound rules is to be as specific as possible. However, when new rules must be made that use ports or IP addresses, consider using consecutive ranges or subnets instead of individual addresses or ports where possible. This avoids creation of multiple filters under the hood, reduces complexity, and helps to avoid performance degradation.
Windows Defender Firewall does not support traditional weighted, administrator-assigned rule ordering. An effective policy set with expected behaviors can be created by keeping in mind the few, consistent, and logical rule behaviors described above.
Create rules for new applications before first launch
Inbound allow rules
When first installed, networked applications and services issue a listen call specifying the protocol/port information required for them to function properly. As there is a default block action in Windows Defender Firewall, it is necessary to create inbound exception rules to allow this traffic. It is common for the app or the app installer itself to add this firewall rule. Otherwise, the user (or firewall admin on behalf of the user) needs to manually create a rule.
If there are no active application or administrator-defined allow rule(s), a dialog box will prompt the user to either allow or block an application’s packets the first time the app is launched or tries to communicate in the network.
If the user has admin permissions, they will be prompted. If they respond No or cancel the prompt, block rules will be created. Two rules are typically created, one each for TCP and UDP traffic.
If the user is not a local admin, they will not be prompted. In most cases, block rules will be created.
In either of the scenarios above, once these rules are added they must be deleted in order to generate the prompt again. If not, the traffic will continue to be blocked.
The firewall’s default settings are designed for security. Allowing all inbound connections by default introduces the network to various threats. Therefore, creating exceptions for inbound connections from third-party software should be determined by trusted app developers, the user, or the admin on behalf of the user.
Known issues with automatic rule creation
When designing a set of firewall policies for your network, it is a best practice to configure allow rules for any networked applications deployed on the host. Having these rules in place before the user first launches the application will help ensure a seamless experience.
The absence of these staged rules does not necessarily mean that in the end an application will be unable to communicate on the network. However, the behaviors involved in the automatic creation of application rules at runtime requires user interaction.
To determine why some applications are blocked from communicating in the network, check for the following:
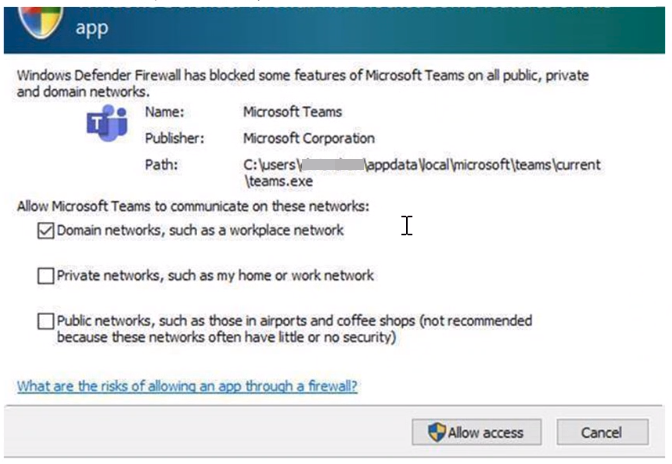
A user with sufficient privileges receives a query notification advising them that the application needs to make a change to the firewall policy. Not fully understanding the prompt, the user cancels or dismisses the prompt.
A user lacks sufficient privileges and is therefore not prompted to allow the application to make the appropriate policy changes.
Local Policy Merge is disabled, preventing the application or network service from creating local rules.
Figure 4: Dialog box to allow access
Establish local policy merge and application rules
Firewall rules can be deployed:
- Locally using the Firewall snap-in (WF.msc)
- Locally using PowerShell
- Remotely using Group Policy if the device is a member of an Active Directory Name, System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), or Intune (using workplace join)
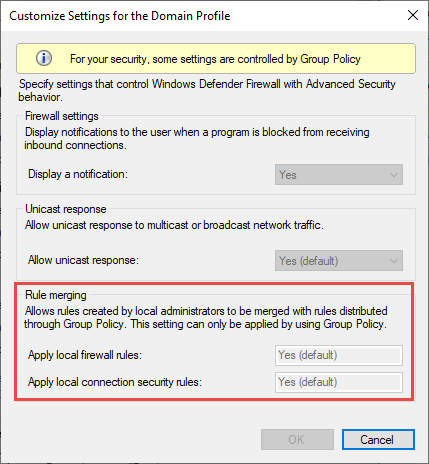
Rule merging settings control how rules from different policy sources can be combined. Administrators can configure different merge behaviors for Domain, Private, and Public profiles.
The rule merging settings either allow or prevent local admins from creating their own firewall rules in addition to those obtained from Group Policy.
Figure 5: Rule merging setting
In the firewall configuration service provider, the equivalent setting is AllowLocalPolicyMerge. This setting can be found under each respective profile node, DomainProfile, PrivateProfile, and PublicProfile.
If merging of local policies is disabled, centralized deployment of rules is required for any app that needs inbound connectivity.
Admins may disable LocalPolicyMerge in high security environments to maintain tighter control over endpoints. This can impact some apps and services that automatically generate a local firewall policy upon installation as discussed above. For these types of apps and services to work, admins should push rules centrally via group policy (GP), Mobile Device Management (MDM), or both (for hybrid or co-management environments).
Firewall CSP and Policy CSP also have settings that can affect rule merging.
As a best practice, it is important to list and log such apps, including the network ports used for communications. Typically, you can find what ports must be open for a given service on the app’s website. For more complex or customer application deployments, a more thorough analysis may be needed using network packet capture tools.
In general, to maintain maximum security, admins should only push firewall exceptions for apps and services determined to serve legitimate purposes.
The use of wildcard patterns, such as C:*\teams.exe is not supported in application rules. We currently only support rules created using the full path to the application(s).
Know how to use «shields up» mode for active attacks
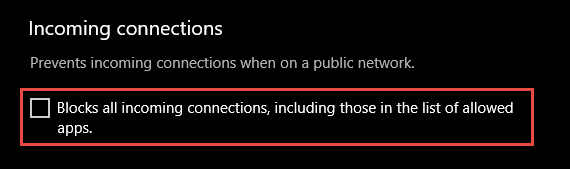
An important firewall feature you can use to mitigate damage during an active attack is the «shields up» mode. It is an informal term referring to an easy method a firewall administrator can use to temporarily increase security in the face of an active attack.
Shields up can be achieved by checking Block all incoming connections, including those in the list of allowed apps setting found in either the Windows Settings app or the legacy file firewall.cpl.
Figure 6: Windows settings App/Windows Security/Firewall Protection/Network Type
Figure 7: Legacy firewall.cpl
By default, the Windows Defender Firewall will block everything unless there is an exception rule created. This setting overrides the exceptions.
For example, the Remote Desktop feature automatically creates firewall rules when enabled. However, if there is an active exploit using multiple ports and services on a host, you can, instead of disabling individual rules, use the shields up mode to block all inbound connections, overriding previous exceptions, including the rules for Remote Desktop. The Remote Desktop rules remain intact but remote access will not work as long as shields up is activated.
Once the emergency is over, uncheck the setting to restore regular network traffic.
Create outbound rules
What follows are a few general guidelines for configuring outbound rules.
The default configuration of Blocked for Outbound rules can be considered for certain highly secure environments. However, the Inbound rule configuration should never be changed in a way that Allows traffic by default.
It is recommended to Allow Outbound by default for most deployments for the sake of simplification around app deployments, unless the enterprise prefers tight security controls over ease-of-use.
In high security environments, an inventory of all enterprise-spanning apps must be taken and logged by the administrator or administrators. Records must include whether an app used requires network connectivity. Administrators will need to create new rules specific to each app that needs network connectivity and push those rules centrally, via group policy (GP), Mobile Device Management (MDM), or both (for hybrid or co-management environments).
For tasks related to creating outbound rules, see Checklist: Creating Outbound Firewall Rules.
Document your changes
When creating an inbound or outbound rule, you should specify details about the app itself, the port range used, and important notes like creation date. Rules must be well-documented for ease of review both by you and other admins. We highly encourage taking the time to make the work of reviewing your firewall rules at a later date easier. AndВ neverВ create unnecessary holes in your firewall.