- Настройка правил брандмауэра Windows групповыми политиками
- Групповые политики, использующиеся для управления настройками Брандмауэра Защитника Windows
- Включаем Windows Firewall с помощью GPO
- Создаем правило файервола с помощью групповой политики
- Проверка политик брандмаэера Windows на клиентах
- Импорт / экспорт правил Брандмауэра Windows в GPO
- Доменные и локальные правила брандмауэра
- Несколько советов об управлении брандмауэром Windows через GPO
- Configuring Windows Firewall Settings and Rules with Group Policy
- Group Policy Settings to Manage Windows Defender Firewall Rules
- How to Enable Windows Firewall Using GPO?
- How to Create a Firewall Rule Using GPO?
- Testing Windows Firewall Policies on Clients
- How to Import/Export Windows Firewall Rules to/from GPO?
- Domain and Local Windows Defender Firewall Rules
- Tips: Managing Windows Firewall with GPOs
Настройка правил брандмауэра Windows групповыми политиками
Брандмауэр Windows позволяет ограничить исходящий / входящий сетевой трафик для определенного приложения или TCP/IP порта, и является популярным средством ограничения сетевого доступа к (от) рабочим станциям пользователей или серверам. Правила Windows Firewall можно настроить индивидуально на каждом компьютере, или, если компьютер пользователя включен в домен Windows, администратор может управлять настройками и правилами брандмауэра Windows с помощью групповых политик.
В крупных организация правила фильтрации портов обычно выносятся на уровень маршрутизатором, L3 коммутаторов или выделенных межсетевых экранах. Однако ничего не мешает вам распространить ваши правила ограничения сетевого доступа Windows Firewall к рабочим станциям или серверам Windows.
Групповые политики, использующиеся для управления настройками Брандмауэра Защитника Windows
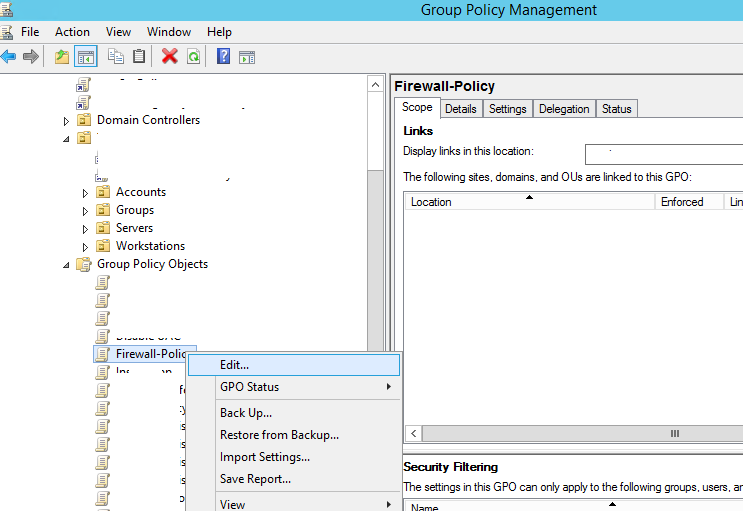
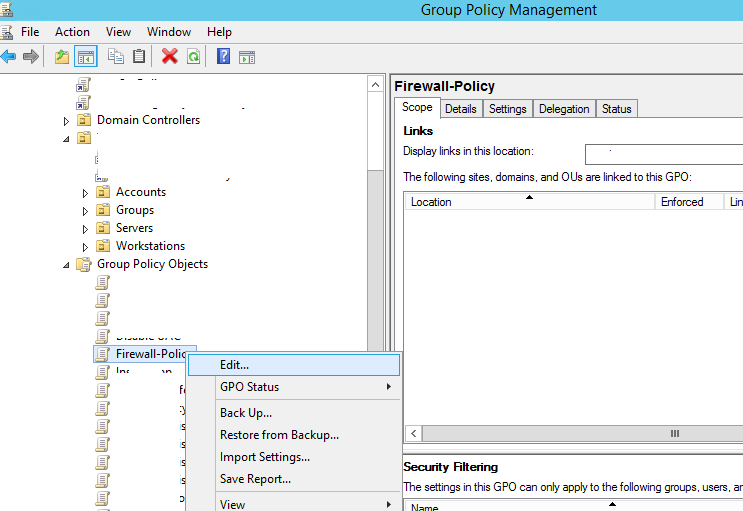
С помощью редактора доменной групповой политики (group Policy Management Console – gpmc.msc) создайте новую политику с именем Firewall-Policy и перейдите в режим редактирования (Edit).
В консоли групповой политики есть две секции, в которых можно управлять настройками брандмауэра:
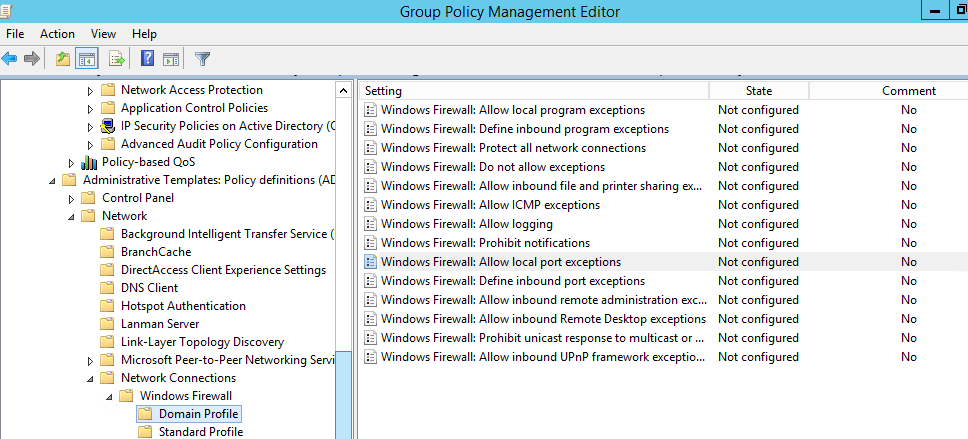
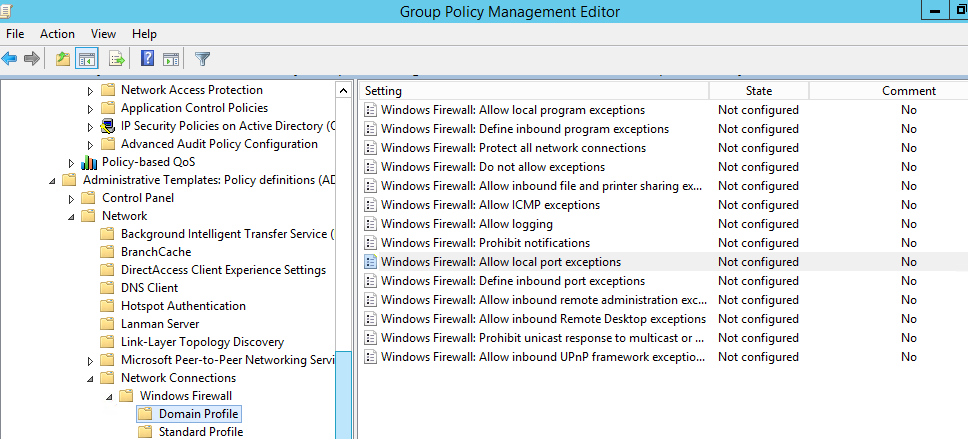
- Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Firewall – эта секция GPO использовалась для настройки правил брандмауэра для ОС Vista / Windows Server 2008 и ниже. Если у вас в домене нет компьютеров со старыми ОС, для настройки файервола используется следующая секция.
Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Firewall » width=»609″ height=»276″ srcset=»https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con.png 968w, https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con-300×136.png 300w, https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con-768×348.png 768w» sizes=»(max-width: 609px) 100vw, 609px»/>
- Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security – это актуальный раздел для настройки Брандмауэра Windows в современных версиях ОС и по интерфейсу он напоминает интерфейс локальной консоли управления Брандмауэра.
Включаем Windows Firewall с помощью GPO
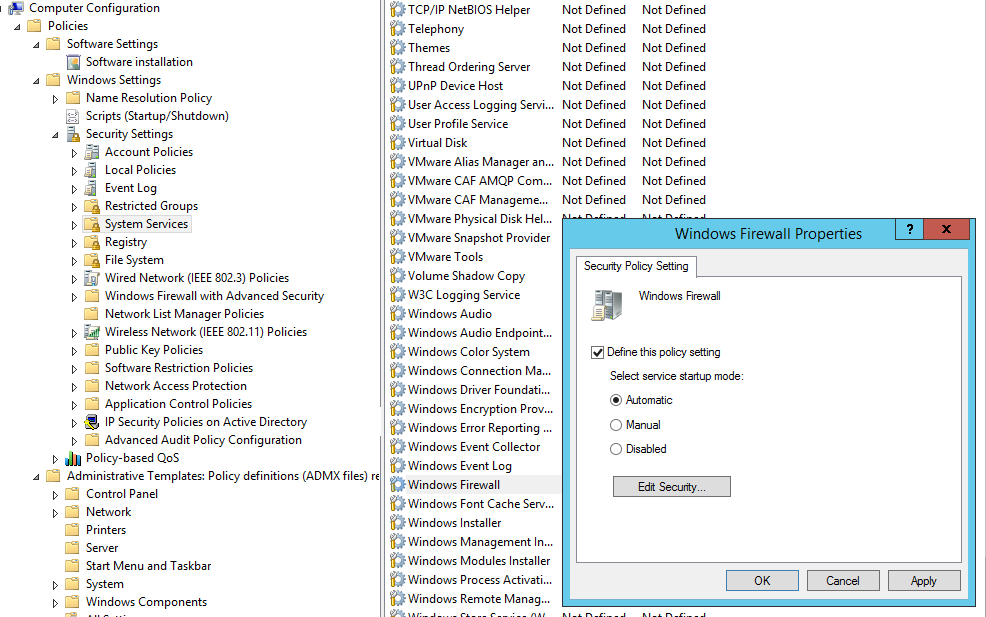
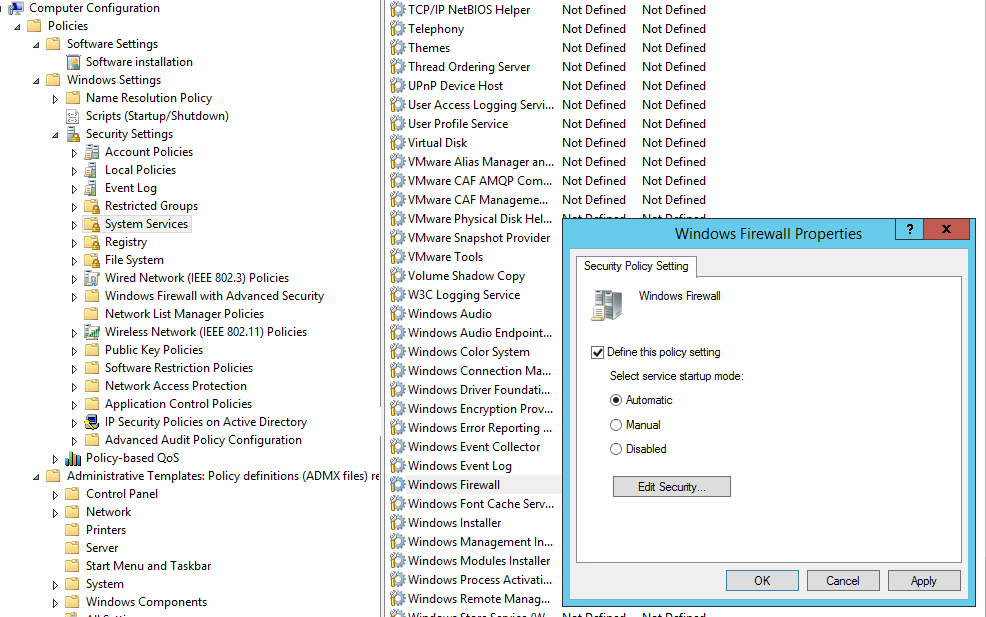
Чтобы пользователи (даже с правами локального админа) не могли выключить службу брандмауэра, желательно настроить автоматический запуск службы Windows Firewall через GPO. Для этого перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration- > Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services. Найдите в списке служб Windows Firewall и измените тип запуск службы на автоматический (Define this policy setting -> Service startup mode Automatic). Убедитесь, что у пользователей нет прав на остановку службы.
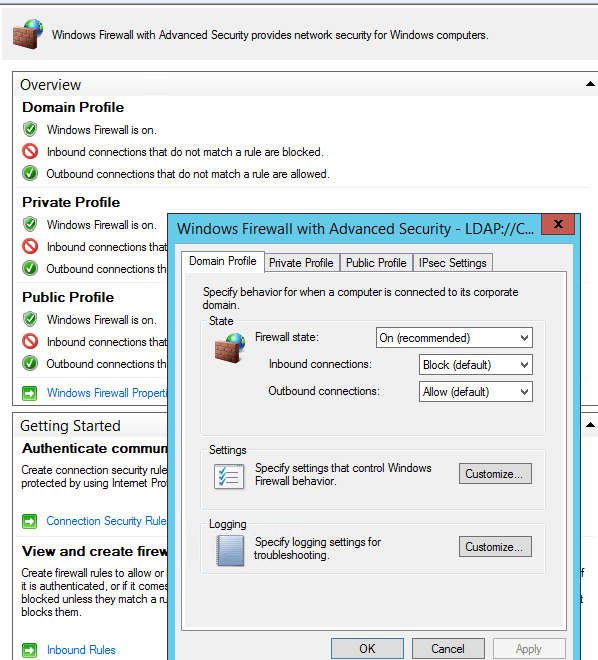
Перейдите в раздел консоли GPO Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings. Щелкните ПКМ по Windows Firewall with Advanced Security и откройте свойства.
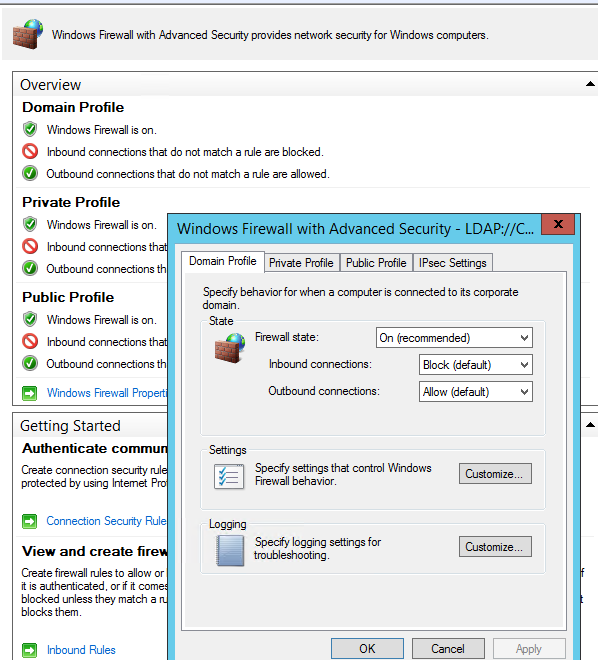
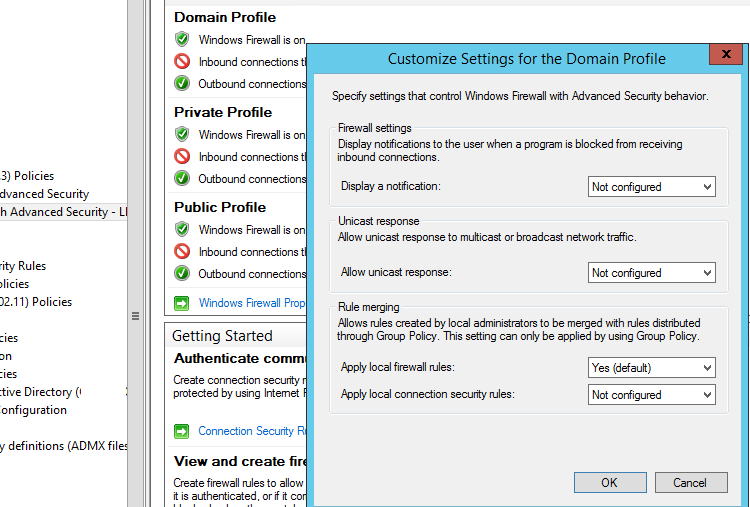
На всех трех вкладках Domain Profile, Private Profile и Public Profile (что такое профиль сети) измените состояние Firewall state на On (recommended). В зависимости от политик безопасности в вашей организации вы можете указать, что все входящие подключения по умолчанию запрещены(Inbound connections -> Block), а исходящие разрешены (Outbound connections -> Allow) и сохраните изменения.
Создаем правило файервола с помощью групповой политики
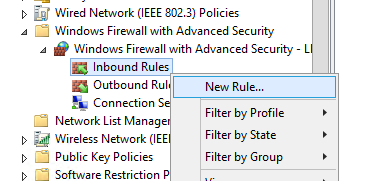
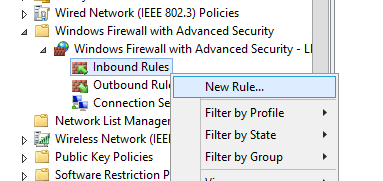
Теперь попробуем создать разрешающее входящее правило файервола для всех. Например, мы хотим разрешить подключение к компьютерам по RDP (порт TCP 3389). Щелкните ПКМ по разделу Inbound Rules и выберите пункт меню New Rule.
Мастер создания правила брандмауэра очень похож на интерфейс локального Windows Firewall на обычном компьютере.
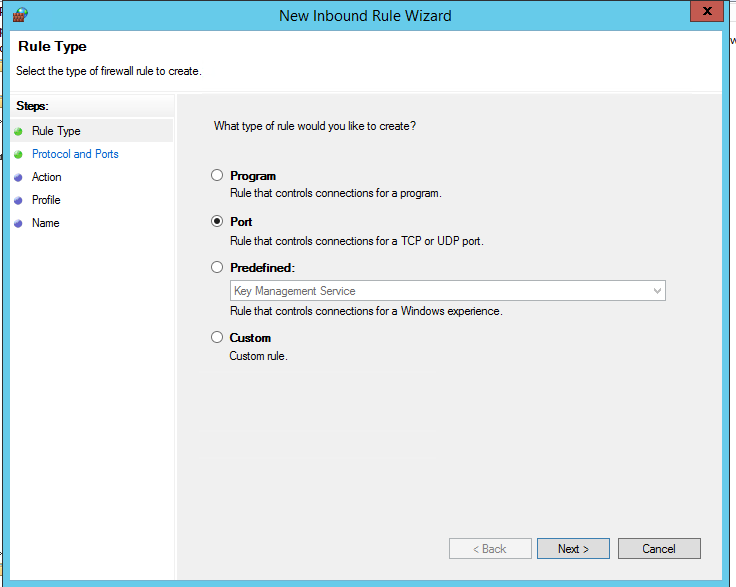
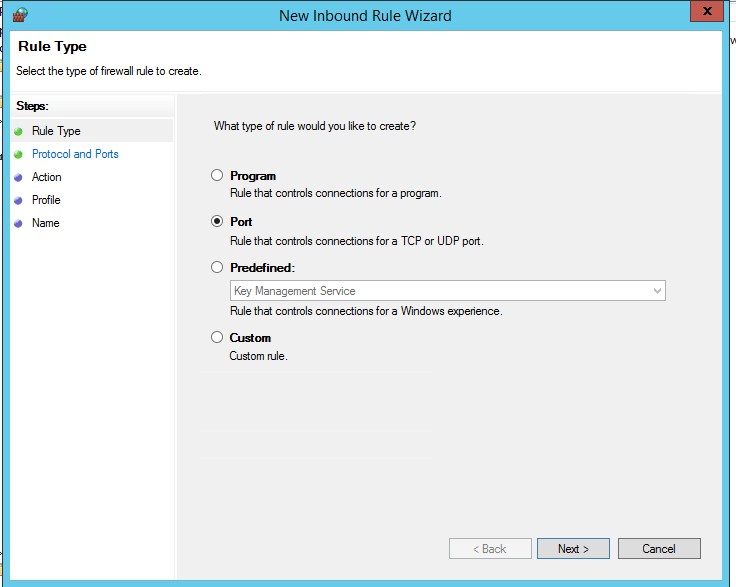
Выберите тип правила. Можно разрешить доступ для:
- Программы (Program) – можно выбрать исполняемый exe программы;
- Порта (Port) – выбрать TCP/UDP порт или диапазон портов;
- Преднастроенное правило (Predefined) – выбрать одно из стандартных правил Windows, в которых уже имеются правила доступа (описаны как исполняемые файлы, так и порты) к типовым службам (например, AD, Http, DFS, BranchCache, удаленная перезагрузка, SNMP, KMS и т.д.);
- Собственное правило (Custom) – здесь можно указать программу, протокол (другие протоколы помимо TCP и UDP, например, ICMP, GRE, L2TP, IGMP и т.д.), IP адреса клиентов или целые IP подсети.
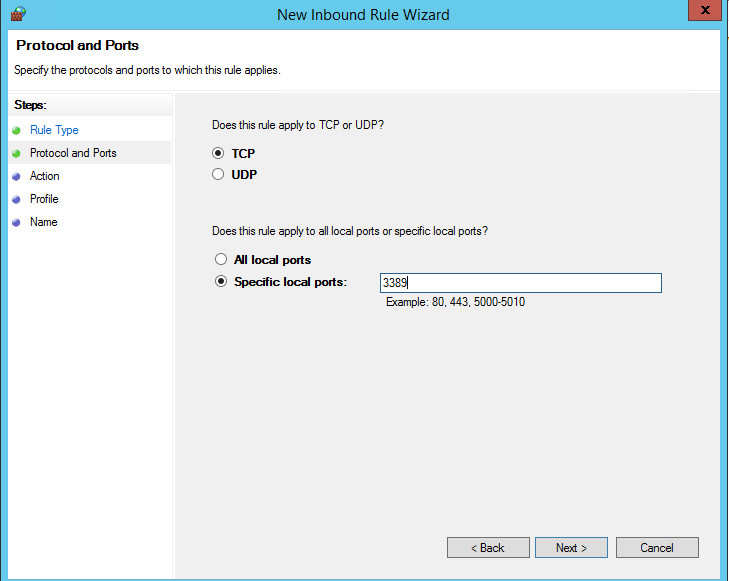
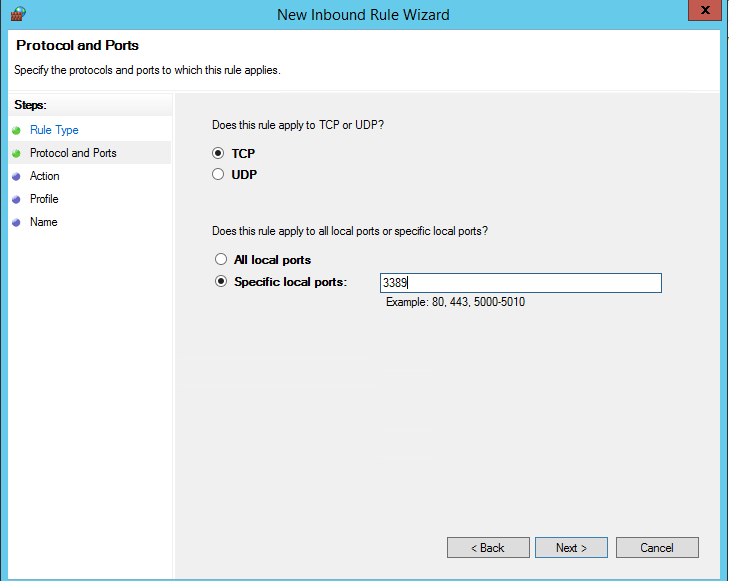
В нашем случае мы выберем правило Port. В качестве протокола укажем TCP, в качестве порта – порт 3389 (RDP порт по-умолчанию, можно изменить).
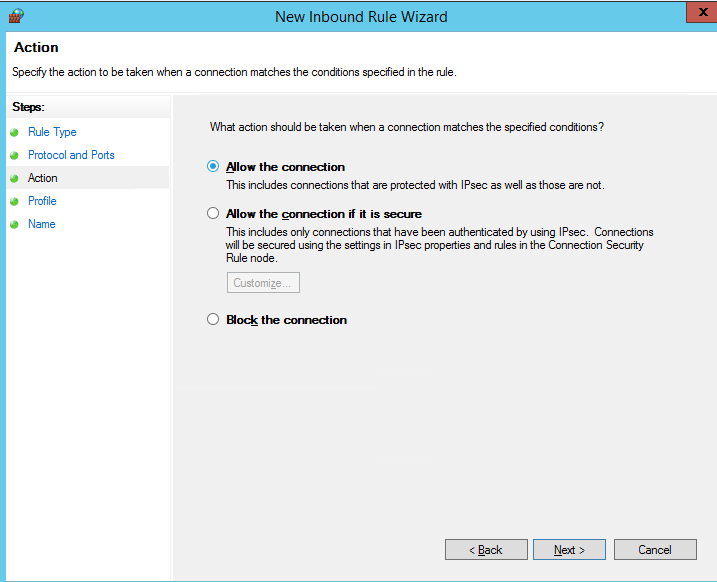
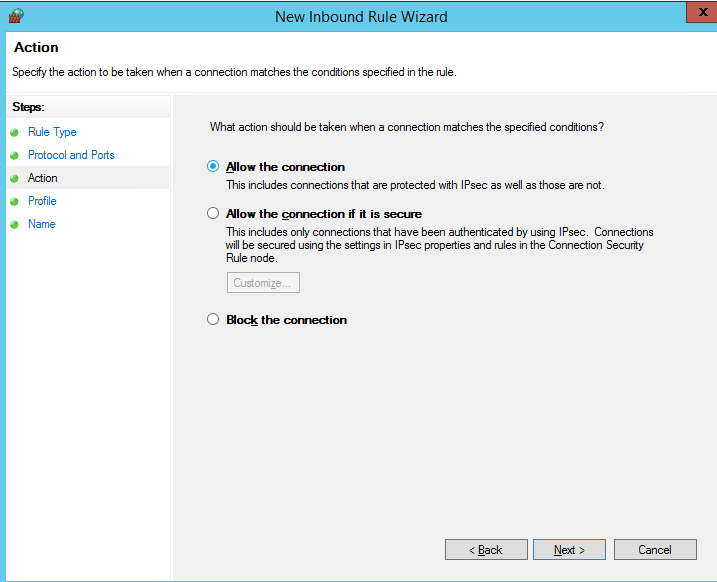
Далее нужно выбрать что нужно сделать с таким сетевым соединением: разрешить (Allow the connection), разрешить если оно безопасное или заблокировать (Block the connection).
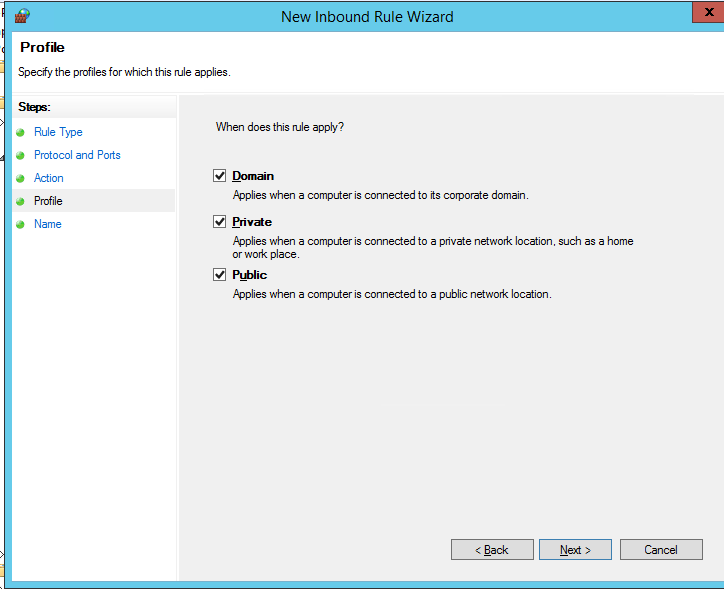
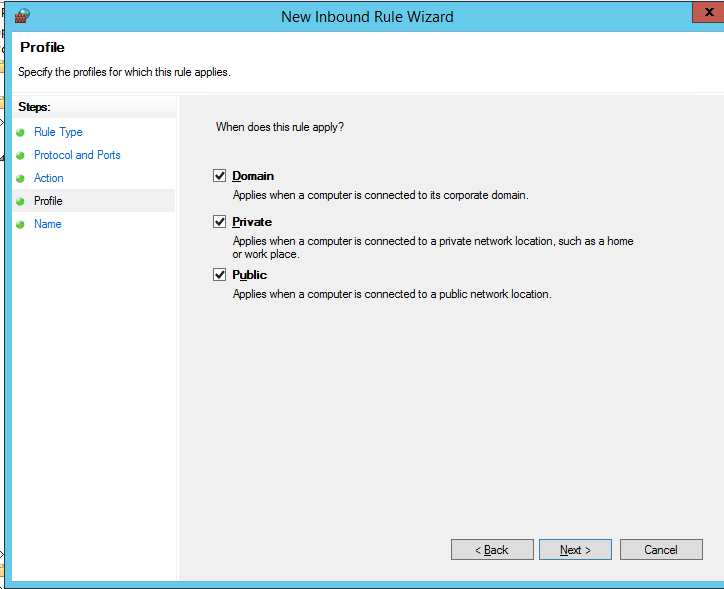
Осталось выбрать профили файервола, которым нужно применить правило. Можно оставить все профили (Domain, Private и Public).
На последнем шаге нужно указать имя правило и его описание. Нажмите кнопку Finish и оно появится в списке правил брандмауэра.
Аналогичным образом вы можете настроить другие правила для входящего трафика, которые должны применятся к вашим клиентам Windows.
Не забываете, что нужно создать правила для входящего и исходящего трафика.
Теперь осталось назначить политику Firewall-Policy на OU с компьютерами пользователей
Проверка политик брандмаэера Windows на клиентах
Обновите политики на клиентах (gpupdate /force). Проверьте, что указанные вами порты доступны на компьютерах пользователей (можно использовать командлет Test-NetConnection или утилиту Portqry).
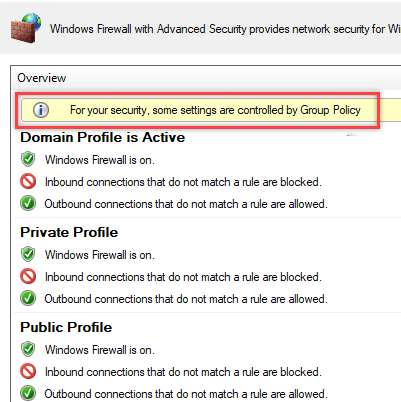
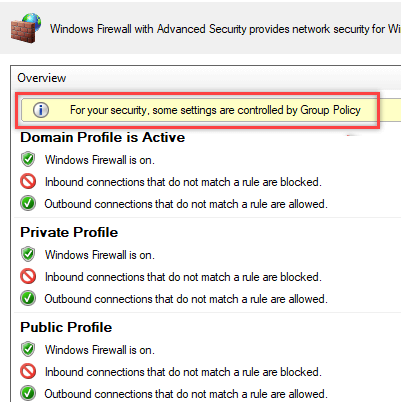
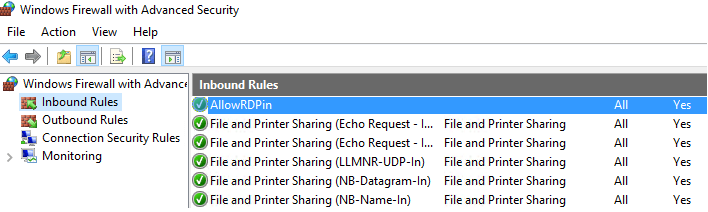
На ПК пользователя откройте Панель управления\Система и безопасность\Брандмауэр Защитника Windows и убедитесь, что появилась надпись: Для обеспечения безопасности, некоторые параметры управляются групповой политикой (For your security, some settings are controlled by Group Policy), и используются заданные вами настройки брандмаэера.
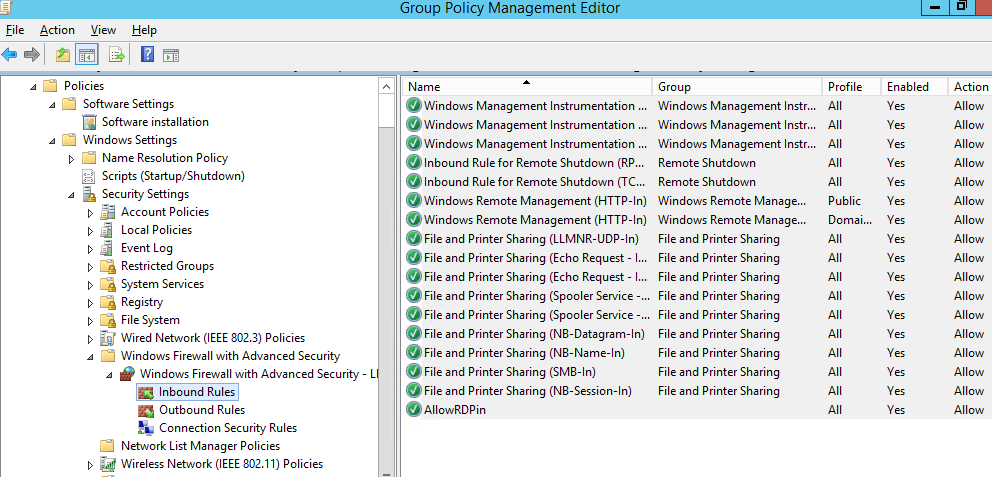
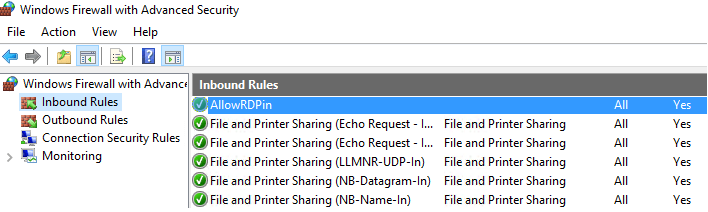
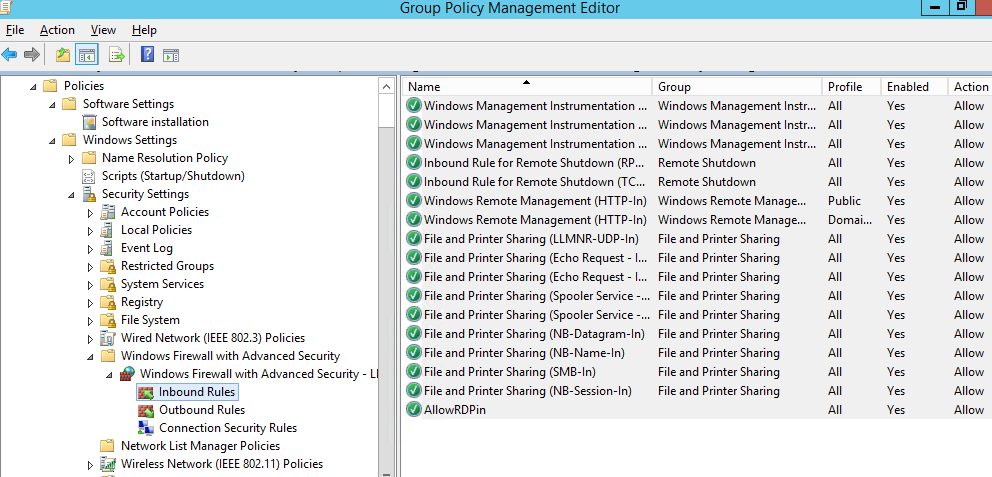
Пользователь теперь не может изменить настройки брандмауэра, а в списке Inbound Rules должны быть указаны все созданные вами правила.
Также вы можете вывести настройки файервола с помощью команды:
netsh firewall show state
Импорт / экспорт правил Брандмауэра Windows в GPO
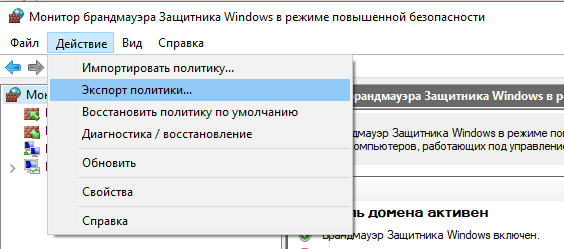
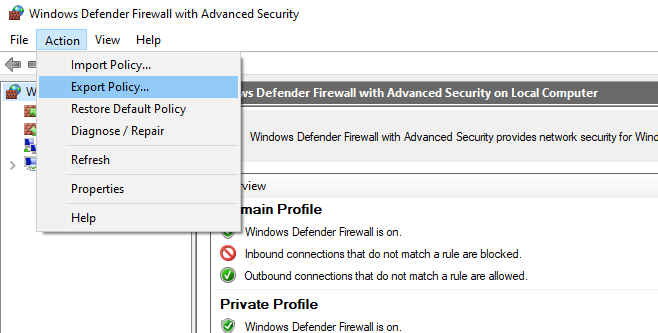
Конечно, процесс создания правил для брандмауэра Windows – очень кропотливое и долгое занятие (но результате того стоит). Для упрощения свое задачи можно воспользоваться возможностью импорт и экспорта настроек брандмауэра Windows. Для этого вам достаточно нужным образом настроить локальные правила брандмауэра на обычном рабочей станции. Затем встаньте на корень оснастки брандмауэра (Монитор Брандмауэра Защитника Windows в режиме повышенной безопасности) и выберите пункт Действие -> Экспорт политики.
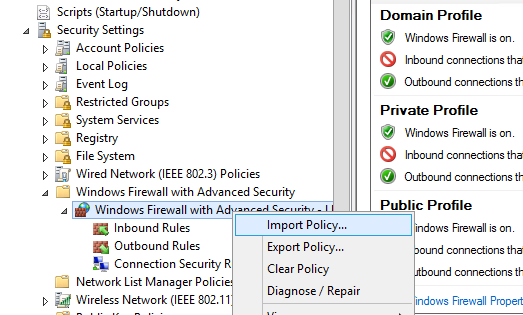
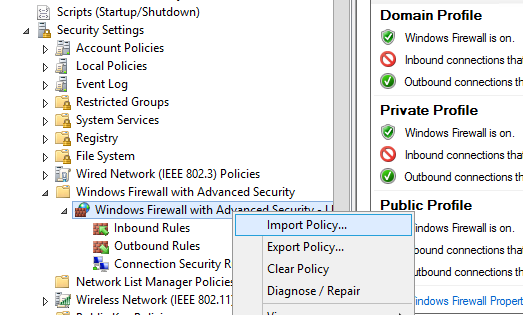
Политика выгружается в WFW файл, который можно импортировать в редакторе Group Policy Management Editor, выбрав пункт Import Policy и указав путь к файлу wfw (текущие настройки будут перезаписаны).
Доменные и локальные правила брандмауэра
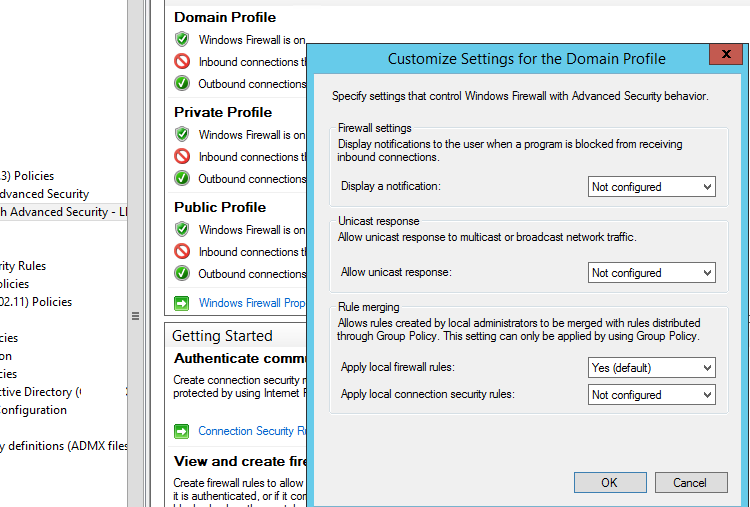
В зависимости от того, хотите ли вы, чтобы локальные администраторы могли создавать на своих компьютерах собственные правила брандмауэра и эти должны быть объединены с правилами, полученными с помощью групповой политики. в групповой политике вы можете выбрать режим объединения правил. Откройте свойства политики и обратите внимание на настройки в разделе Rule merging. По умолчанию режим объединения правил включен. Вы можете принудительно указать, что локальный администратор может создавать собственные правила брандмауэра: в параметре Apply local firewall rules выберите Yes (default).
Несколько советов об управлении брандмауэром Windows через GPO
Конечно, для серверов и рабочих станций нужно создавать отдельные политики управления правилами брандмауэра (для каждой группы одинаковых серверов возможно придется создать собственные политики в зависимости от их роли). Т.е. правила файервола для контроллера домена, почтового Exchange сервера и сервера SQL будут отличаться.
Какие порты нужно открыть для той или иной службы нужно искать в документации на сайте разработчика. Процесс довольно кропотливый и на первый взгляд сложный. Но постепенно вполне реальной придти к работоспособной конфигурации Windows файервола, который разрешает только одобренные подключения и блокирует все остальное. По опыту хочу отметить, что на ПО Microsoft можно довольно быстро найти список используемых TCP/UDP портов.
Configuring Windows Firewall Settings and Rules with Group Policy
Windows Firewall allows to restrict inbound/outbound network traffic for a certain application, protocol or a TCP/IP port. This is an easy way to restrict network access to/from user workstations or servers. You can configure Windows Firewall rules individually on each computer or, if a user computer is joined to an Active Directory domain, an administrator can manage Windows Defender Firewall settings and rules using GPO.
In large enterprises, the port filtering rules are usually set at the level of routers, L3 switches or dedicated firewall devices. However, nothing prevents you from deploying your Windows Firewall network access restriction rules to workstations or Windows servers.
Group Policy Settings to Manage Windows Defender Firewall Rules
Using the domain group policy editor (Group Policy Management console – gpmc.msc), create a new GPO object (policy) with the name Firewall-Policy and switch to the edit mode.
There are two sections in the Group Policy Management console that allow you to manage firewall settings:
- Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Firewall – this GPO section was used to configure firewall rules in OS Vista/Windows Server 2008 or earlier. If you don’t have any computers with these old OS versions, use the next policy section to configure your firewall;
- Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security – is the actual section to configure Windows Firewall in modern Windows OS versions, and its interface is similar to that of the local Defender Firewall management console.
How to Enable Windows Firewall Using GPO?
In order users (even having local admin permissions) cannot stop the firewall service, it is recommended to configure the automatic startup of Windows Firewall using GPO. To do it, go to Computer Configuration- > Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services. Find Windows Firewall in the list of services and change the startup mode to automatic (Define this policy setting -> Service startup mode Automatic). Make sure that your users don’t have the permissions to stop the service.
Go to the Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings section in the GPO console. Right-click Windows Firewall with Advanced Security and open the properties.
Change the Firewall state to On (recommended) in all three tabs: Domain Profile, Private Profile and Public Profile (What are network locations in Windows?). Depending on the security policies in your company, you can specify that all inbound connections are blocked by default (Inbound connections -> Block), and outbound connections are allowed (Outbound connections -> Allow). Save the changes.
How to Create a Firewall Rule Using GPO?
Let’s try to create an allowing inbound Windows Firewall rule. For example, we want to allow the incoming RDP connection to all computers (TCP 3389 port). Right-click the Inbound Rules section and select New Rule.
The firewall rule wizard has an interface similar to that of local Windows Firewall on the user’s desktop computer.
Select the rule type. You can allow access to:
- Program – you can select a program executable (.exe);
- Port – you can select a TCP/UDP port or a port range;
- Predefined – you can select one of the standard Windows rules, which already contain access rules (both executable files and ports are described) to typical services (e. g., AD, HTTP(s), DFS, BranchCache, remote restart, SNMP, KMS, etc.);
- Custom – here you can specify a program, a protocol (protocols other than TCP or UDP, like ICMP, GRE, L2TP, IGMP, etc.), client IP addresses or entire IP subnets.
In our case, we’ll select the Port rule. Let’s specify TCP as the protocol, and Port 3389 as the port (it is the default RDP port, but you can change it via the registry).
Then you must select what to do with such a network connection: Allow the connection, allow if it is secure or Block the connection.
Then select the firewall profiles to apply the rule to. You can leave all profiles enabled (Domain, Private and Public).
On the last step, specify the name and description of the rule. Click Finish, and it will appear in the list of firewall rules.
In the same way you can configure other rules for the inbound traffic to be applied to your Windows clients.Don’t forget to create rules for the inbound and outbound traffic.
Now just assign the Firewall Policy to the OU with user computers.
Testing Windows Firewall Policies on Clients
Update the group policy settings on your clients (gpupdate /force). Make sure that the ports you have specified are available on user computers (you can use Test-NetConnection cmdlet or Portqry tool).
On a user PC, open the Control Panel -> System&Security -> Windows Defender Firewall and make sure that there is the message For your security, some settings are controlled by Group Policy and your firewall settings are used.
Now a user cannot change firewall settings, and all rules that you have created must appear in the Inbound Rules list.
You can also display the firewall settings using this command:
netsh firewall show state
How to Import/Export Windows Firewall Rules to/from GPO?
Of course, the process of creating Windows Firewall rules is a painstaking and time consuming task (however, it is worth the effort). To make it easier, you can import/export Windows Firewall settings. To do it, it’s enough to configure local firewall settings on a reference workstation as you need. Then go to the root of Windows Firewall snap-in (Windows Firewall with Advanced Security) and select Action -> Export Policy.
The policy will be exported into a WFW file, which can be imported to the Group Policy Management Editor by selecting Import Policy option and specifying the path to the .wfw file (the current policy settings will be overwritten).
Domain and Local Windows Defender Firewall Rules
Depending on whether you want that local administrators can create their own firewall rules on their computers to be combined with the rules obtained from the group policy, you can select the rule merging option. Open the policy properties and view the settings in the Rule merging section. By default rule merging is enabled. You can force that a local administrator can create their own firewall rules: select Yes (default) in the Apply local firewall rules option.
Tips: Managing Windows Firewall with GPOs
Of course, you should create separate policies to manage Windows Firewall rules for servers and workstations (you may have to create separate policies for each group of similar servers depending on their role). It means that firewall rules for the domain controller, an Exchange mail server and an SQL server will differ.
You can find what ports must be opened for each service on the vendor’s website. The process is quite painstaking and complicated at the first glance. However, you can finally get a working Windows Firewall configuration that allows only approved network connections and blocks other ones. From my experience, I’d like to note that you can quickly find the list of used TCP/UDP ports for Microsoft software.
 Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Firewall » width=»609″ height=»276″ srcset=»https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con.png 968w, https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con-300×136.png 300w, https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con-768×348.png 768w» sizes=»(max-width: 609px) 100vw, 609px»/>
Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Firewall » width=»609″ height=»276″ srcset=»https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con.png 968w, https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con-300×136.png 300w, https://winitpro.ru/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/administrative-templates-greater-network-greater-network-con-768×348.png 768w» sizes=»(max-width: 609px) 100vw, 609px»/>