- How to configure a firewall for Active Directory domains and trusts
- More information
- Windows Server 2008 and later versions
- Active Directory
- Reference
- How to open ports in Windows Firewall
- How to open a port for incoming traffic in Windows Firewall
- How to open a port for outgoing traffic in Windows Firewall
- How to close a port in Windows Firewall
- More resources
- Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
- Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
- Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
- These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
- How to open firewall ports in Windows 10 [Step-by-step guide]
- How do I open a port on my firewall?
- Why should I use a Firewall on my PC?
How to configure a firewall for Active Directory domains and trusts
This article describes how to configure a firewall for Active Directory domains and trusts.
Original product version: В Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard, Windows Server 2012 Standard
Original KB number: В 179442
Not all the ports that are listed in the tables here are required in all scenarios. For example, if the firewall separates members and DCs, you don’t have to open the FRS or DFSR ports. Also, if you know that no clients use LDAP with SSL/TLS, you don’t have to open ports 636 and 3269.
More information
The two domain controllers are both in the same forest, or the two domain controllers are both in a separate forest. Also, the trusts in the forest are Windows Server 2003 trusts or later version trusts.
| Client Port(s) | Server Port | Service |
|---|---|---|
| 1024-65535/TCP | 135/TCP | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| 1024-65535/TCP | 1024-65535/TCP | RPC for LSA, SAM, NetLogon (*) |
| 1024-65535/TCP/UDP | 389/TCP/UDP | LDAP |
| 1024-65535/TCP | 636/TCP | LDAP SSL |
| 1024-65535/TCP | 3268/TCP | LDAP GC |
| 1024-65535/TCP | 3269/TCP | LDAP GC SSL |
| 53,1024-65535/TCP/UDP | 53/TCP/UDP | DNS |
| 1024-65535/TCP/UDP | 88/TCP/UDP | Kerberos |
| 1024-65535/TCP | 445/TCP | SMB |
| 1024-65535/TCP | 1024-65535/TCP | FRS RPC (*) |
NETBIOS ports as listed for Windows NT are also required for Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 when trusts to domains are configured that support only NETBIOS-based communication. Examples are Windows NT-based operating systems or third-party Domain Controllers that are based on Samba.
For more information about how to define RPC server ports that are used by the LSA RPC services, see:
Windows Server 2008 and later versions
Windows Server 2008 newer versions of Windows Server have increased the dynamic client port range for outgoing connections. The new default start port is 49152, and the default end port is 65535. Therefore, you must increase the RPC port range in your firewalls. This change was made to comply with Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) recommendations. This differs from a mixed-mode domain that consists of Windows Server 2003 domain controllers, Windows 2000 server-based domain controllers, or legacy clients, where the default dynamic port range is 1025 through 5000.
For more information about the dynamic port range change in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2, see:
- The default dynamic port range for TCP/IP has changed.
- Dynamic Ports in Windows Server.
| Client Port(s) | Server Port | Service |
|---|---|---|
| 49152 -65535/UDP | 123/UDP | W32Time |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 135/TCP | RPC Endpoint Mapper |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 464/TCP/UDP | Kerberos password change |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 49152-65535/TCP | RPC for LSA, SAM, NetLogon (*) |
| 49152 -65535/TCP/UDP | 389/TCP/UDP | LDAP |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 636/TCP | LDAP SSL |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 3268/TCP | LDAP GC |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 3269/TCP | LDAP GC SSL |
| 53, 49152 -65535/TCP/UDP | 53/TCP/UDP | DNS |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 49152 -65535/TCP | FRS RPC (*) |
| 49152 -65535/TCP/UDP | 88/TCP/UDP | Kerberos |
| 49152 -65535/TCP/UDP | 445/TCP | SMB (**) |
| 49152 -65535/TCP | 49152-65535/TCP | DFSR RPC (*) |
NETBIOS ports as listed for Windows NT are also required for Windows 2000 and Server 2003 when trusts to domains are configured that support only NETBIOS-based communication. Examples are Windows NT-based operating systems or third-party Domain Controllers that are based on Samba.
(*) For information about how to define RPC server ports that are used by the LSA RPC services, see:
(**) For the operation of the trust this port is not required, it is used for trust creation only.
External trust 123/UDP is only needed if you have manually configured the Windows Time Service to Sync with a server across the external trust.
Active Directory
In Windows 2000 and Windows XP, the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) must be allowed through the firewall from the clients to the domain controllers so that the Active Directory Group Policy client can function correctly through a firewall. ICMP is used to determine whether the link is a slow link or a fast link.
In Windows Server 2008 and later versions, the Network Location Awareness Service provides the bandwidth estimate based on traffic with other stations on the network. There is no traffic generated for the estimate.
The Windows Redirector also uses ICMP Ping messages to verify that a server IP is resolved by the DNS service before a connection is made, and when a server is located by using DFS. If you want to minimize ICMP traffic, you can use the following sample firewall rule:
Unlike the TCP protocol layer and the UDP protocol layer, ICMP does not have a port number. This is because ICMP is directly hosted by the IP layer.
By default, Windows Server 2003 and Windows 2000 Server DNS servers use ephemeral client-side ports when they query other DNS servers. However, this behavior may be changed by a specific registry setting. Or, you can establish a trust through the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) compulsory tunnel. This limits the number of ports that the firewall has to open. For PPTP, the following ports must be enabled.
| Client Ports | Server Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| 1024-65535/TCP | 1723/TCP | PPTP |
In addition, you would have to enable IP PROTOCOL 47 (GRE).
When you add permissions to a resource on a trusting domain for users in a trusted domain, there are some differences between the Windows 2000 and Windows NT 4.0 behavior. If the computer cannot display a list of the remote domain’s users, consider the following behavior:
- Windows NT 4.0 tries to resolve manually typed names by contacting the PDC for the remote user’s domain (UDP 138). If that communication fails, a Windows NT 4.0-based computer contacts its own PDC, and then asks for resolution of the name.
- Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 also try to contact the remote user’s PDC for resolution over UDP 138. However, they do not rely on using their own PDC. Make sure that all Windows 2000-based member servers and Windows Server 2003-based member servers that will be granting access to resources have UDP 138 connectivity to the remote PDC.
Reference
Service overview and network port requirements for Windows is a valuable resource outlining the required network ports, protocols, and services that are used by Microsoft client and server operating systems, server-based programs, and their subcomponents in the Microsoft Windows Server system. Administrators and support professionals may use the article as a roadmap to determine which ports and protocols Microsoft operating systems and programs require for network connectivity in a segmented network.
You should not use the port information in Service overview and network port requirements for Windows to configure Windows Firewall. For information about how to configure Windows Firewall, see Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
How to open ports in Windows Firewall
When dealing with certain apps and processes on your Windows 10 PC, you might run issues if you aren’t connecting properly to the internet. If you’ve come across a potential fix that involves opening a certain port in your firewall, you might be wondering what exactly that process entails. This is a problem that can arise in plenty of situations, but especially when attempting to set up a VPN. If you suspect Windows Firewall is part of your connectivity issue, here’s how to open ports.
How to open a port for incoming traffic in Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall is designed as a security measure for your PC. To put it simply, a firewall analyzes incoming and outgoing connections to determine whether or not they’re threats. If you suspect that your Windows Firewall is causing connectivity issues, you can open a port for incoming traffic. Here’s how:
- Right-click the Start button.
- Click Search.
Type Windows Firewall.
Click Advanced settings.
Click New Rule… in the right frame of the window.
Click Next.
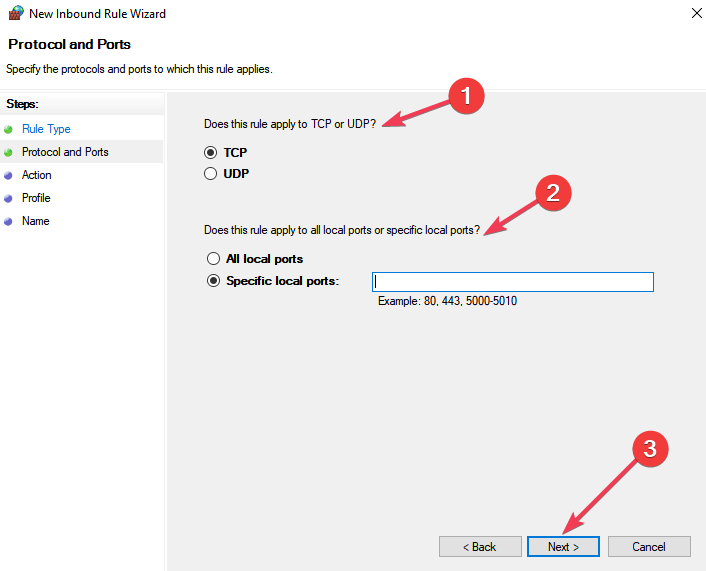
Click Specific local ports.
Click Next.
Click Next.
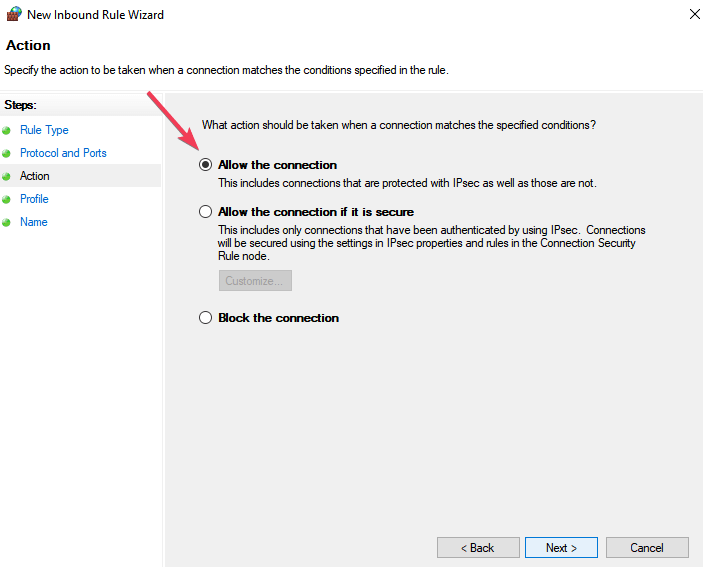
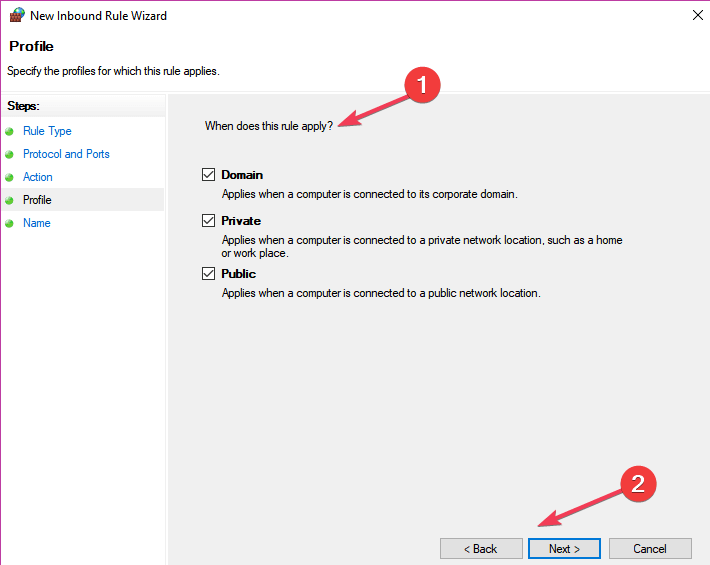
Click Next.
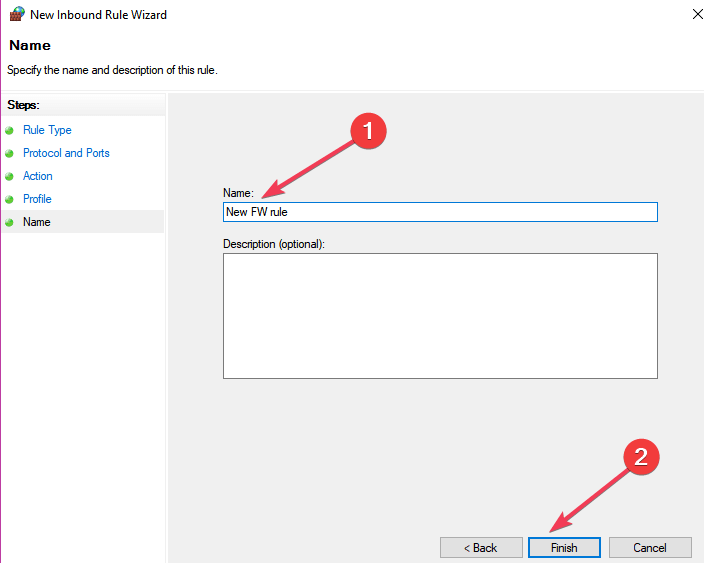
Click Finish.
How to open a port for outgoing traffic in Windows Firewall
The same set of steps listed above can be used to create a rule for outgoing traffic. In step No. 6, instead of clicking Inbound Rules, you’ll want to click Outgoing Rules. The rest of the steps are the same, and you can disable the rule in the same manner by using the steps in the next section.
How to close a port in Windows Firewall
Want to disable the rule you created to open a port in the Windows Firewall? Here’s how:
- Right-click the Start button.
Click Search.
Click Windows Firewall.
Click Inbound Rules or Outbound Rules in the left frame of the window, depending on what type of rule you created.
Click the name of the rule in the right frame of the window.
Click Delete if you want to completely delete the rule.
More resources
Need a bit more help with Windows Firewall and Windows 10? We have plenty of resources covering a wide range of topics.
Halo: MCC’s live service elements make it better, not worse
Halo: The Master Chief Collection is more popular than ever, but some fans don’t agree with the live service approach 343 Industries has taken with it. Here’s why those elements are, at the end of the day, great for the game and for Halo overall.
Microsoft’s Surface Duo is not ‘failing up’
Microsoft announced this week that it was expanding Surface Duo availability to nine new commercial markets. While Surface Duo is undoubtedly a work in progress, this is not a sign of a disaster. It’s also doesn’t mean that Surface Duo is selling a ton either. Instead, the reason for the expansion is a lot more straightforward.
Here’s what you can do if Windows 10 update KB5001330 is causing issues
In this guide, we’ll show you the steps to get rid of the update KB5001330 to fix profile, gaming, and BSoD problems with the Windows 10 October 2020 Update and May 2020 Update.
These are the best PC sticks when you’re on the move
Instant computer — just add a screen. That’s the general idea behind the ultra-portable PC, but it can be hard to know which one you want. Relax, we have you covered!
How to open firewall ports in Windows 10 [Step-by-step guide]
If you’re looking for a simple solution for opening firewall ports in Windows 10, you’ll find all the necessary details in this article.
Opening Firewall ports allows apps and programs to communicate with the network. So, if some of your apps and programs fail to launch, opening firewall ports is one of the first troubleshooting solutions that you can use.
How do I open a port on my firewall?
Users can manually allow a program to get access to the Internet by opening a firewall port. All you need to know is what port it uses and the protocol to make this function.
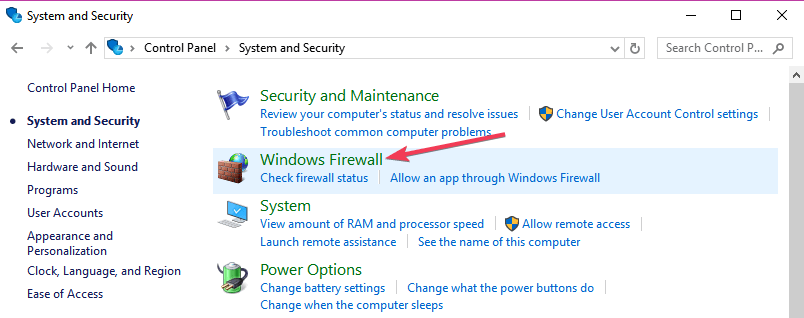
- Go to Control Panel> System and Security > Windows Firewall.
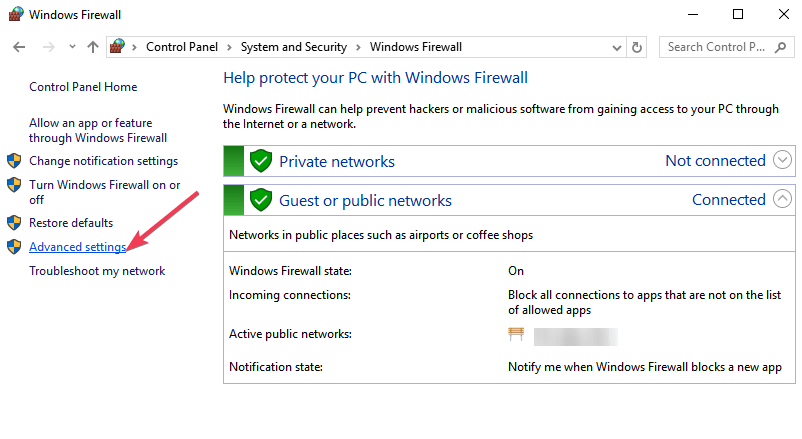
- Go to Advanced settings
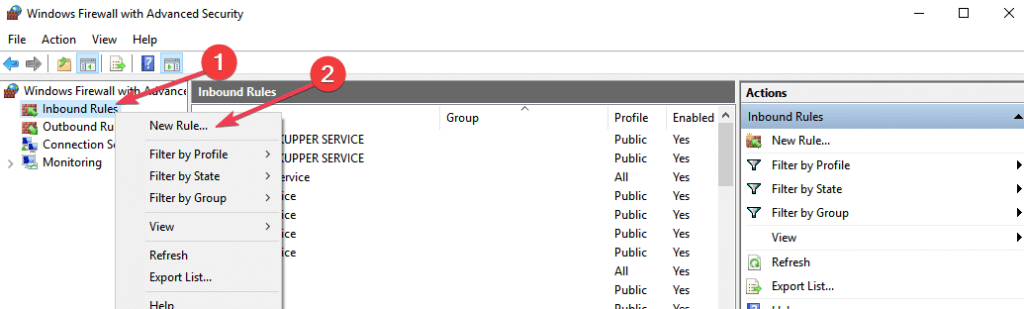
- Right-click Inbound Rules > select New Rule.
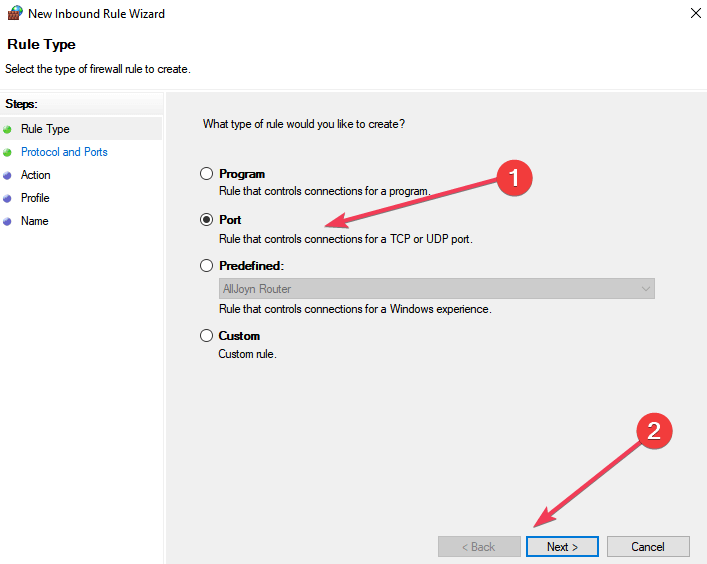
- Add the port you want to open > click Next.
- Add the TCP or UDP protocol and the port number into the next window > click Next.
- Select Allow the connection > hit Next.
- Select the network type > click Next.
- Name the rule > click Finish.
These are all the necessary steps for opening a port in Windows 10. Remember that you can also use this method for blocking programs or ports.
Why should I use a Firewall on my PC?
Firewalls are targeted at protecting your network from various threats coming from outside and trying to get in or threats coming from inside trying to get out. A threat does this by blocking network-enabled ports.
Every time a program tries to communicate through this port, the firewall verifies its database rules to check if it is allowed or not. If it doesn’t know, it will ask the user and that’s why you sometimes see a prompt asking you if a certain program is allowed or not to access the Internet.
A firewall is an essential issue regarding computing and every PC must have one installed. This is the reason for which Windows has a firewall bundled and active as standard.
Windows firewall must occasionally be told to allow a program communicate with the network and this is the point where opening ports step into the picture.
RELATED STORIES TO CHECK OUT: