- Configuring Windows Firewall Settings and Rules with Group Policy
- Group Policy Settings to Manage Windows Defender Firewall Rules
- How to Enable Windows Firewall Using GPO?
- How to Create a Firewall Rule Using GPO?
- Testing Windows Firewall Policies on Clients
- How to Import/Export Windows Firewall Rules to/from GPO?
- Domain and Local Windows Defender Firewall Rules
- Tips: Managing Windows Firewall with GPOs
- Configure Firewall Port Requirements for Group Policy
- Remote Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) Group Policy results: ports that require firewall rules
- Configure firewall rules by creating a GPO from the Group Policy Reporting Firewall Ports Starter GPO and linking to the domain
- To create a GPO from the Group Policy Reporting Firewall Ports Starter GPO and link to the domain
- Remote Group Policy refresh: ports that require firewall rules
- Configure firewall rules by creating a GPO from the Group Policy Remote Update Firewall Ports Starter GPO and linking to the domain
- To create a GPO from the Group Policy Remote Update Firewall Ports Starter GPO and link to the domain
Configuring Windows Firewall Settings and Rules with Group Policy
Windows Firewall allows to restrict inbound/outbound network traffic for a certain application, protocol or a TCP/IP port. This is an easy way to restrict network access to/from user workstations or servers. You can configure Windows Firewall rules individually on each computer or, if a user computer is joined to an Active Directory domain, an administrator can manage Windows Defender Firewall settings and rules using GPO.
In large enterprises, the port filtering rules are usually set at the level of routers, L3 switches or dedicated firewall devices. However, nothing prevents you from deploying your Windows Firewall network access restriction rules to workstations or Windows servers.
Group Policy Settings to Manage Windows Defender Firewall Rules
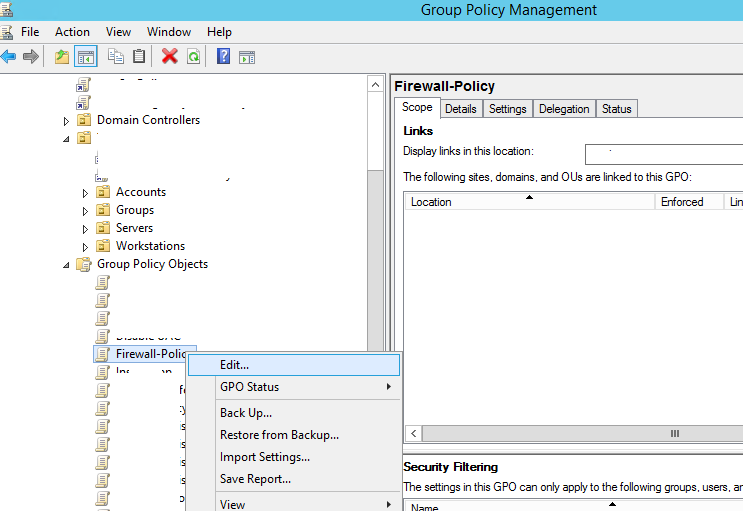
Using the domain group policy editor (Group Policy Management console – gpmc.msc), create a new GPO object (policy) with the name Firewall-Policy and switch to the edit mode.
There are two sections in the Group Policy Management console that allow you to manage firewall settings:
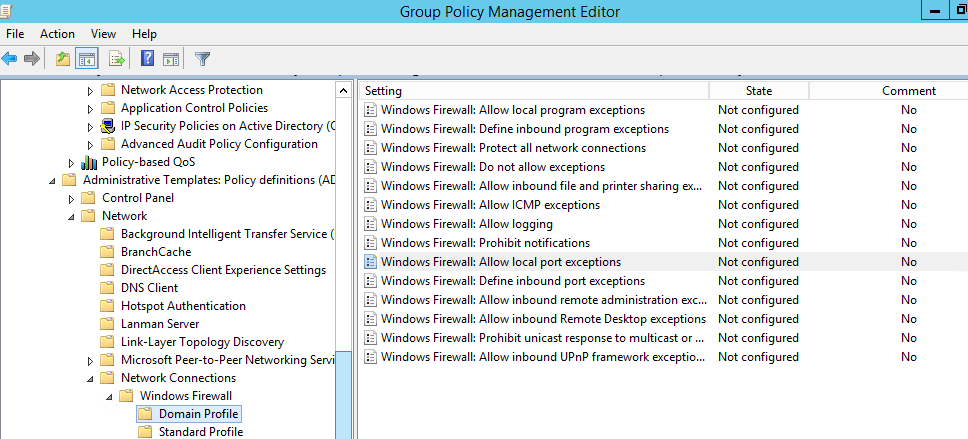
- Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Firewall – this GPO section was used to configure firewall rules in OS Vista/Windows Server 2008 or earlier. If you don’t have any computers with these old OS versions, use the next policy section to configure your firewall;
- Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security – is the actual section to configure Windows Firewall in modern Windows OS versions, and its interface is similar to that of the local Defender Firewall management console.
How to Enable Windows Firewall Using GPO?
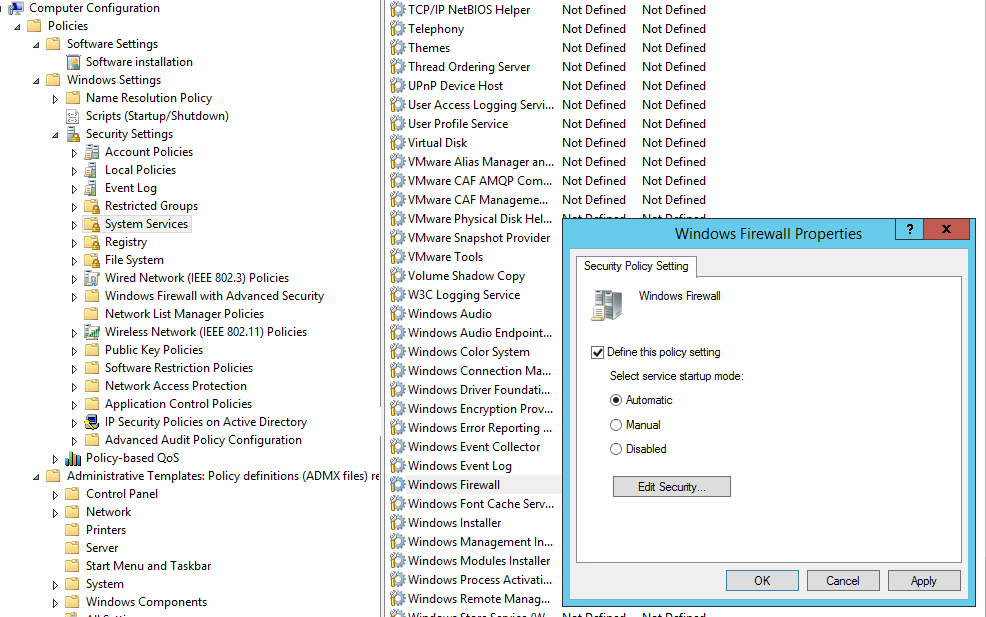
In order users (even having local admin permissions) cannot stop the firewall service, it is recommended to configure the automatic startup of Windows Firewall using GPO. To do it, go to Computer Configuration- > Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services. Find Windows Firewall in the list of services and change the startup mode to automatic (Define this policy setting -> Service startup mode Automatic). Make sure that your users don’t have the permissions to stop the service.
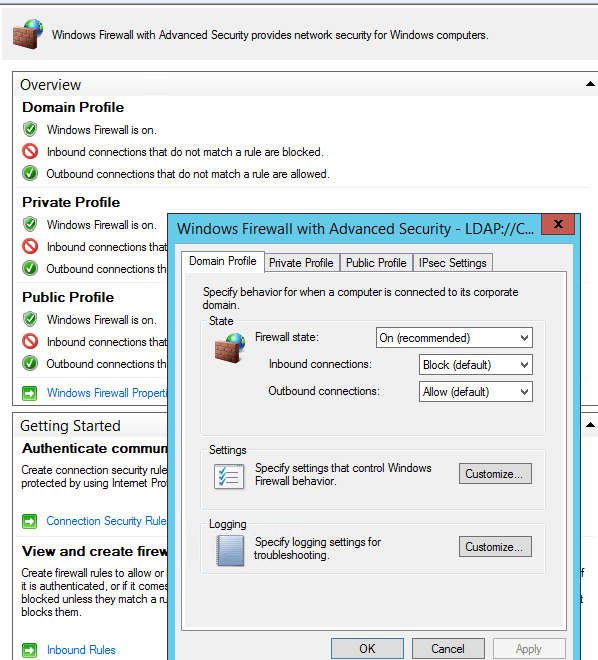
Go to the Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings section in the GPO console. Right-click Windows Firewall with Advanced Security and open the properties.
Change the Firewall state to On (recommended) in all three tabs: Domain Profile, Private Profile and Public Profile (What are network locations in Windows?). Depending on the security policies in your company, you can specify that all inbound connections are blocked by default (Inbound connections -> Block), and outbound connections are allowed (Outbound connections -> Allow). Save the changes.
How to Create a Firewall Rule Using GPO?
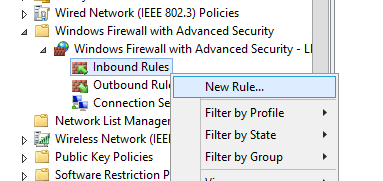
Let’s try to create an allowing inbound Windows Firewall rule. For example, we want to allow the incoming RDP connection to all computers (TCP 3389 port). Right-click the Inbound Rules section and select New Rule.
The firewall rule wizard has an interface similar to that of local Windows Firewall on the user’s desktop computer.
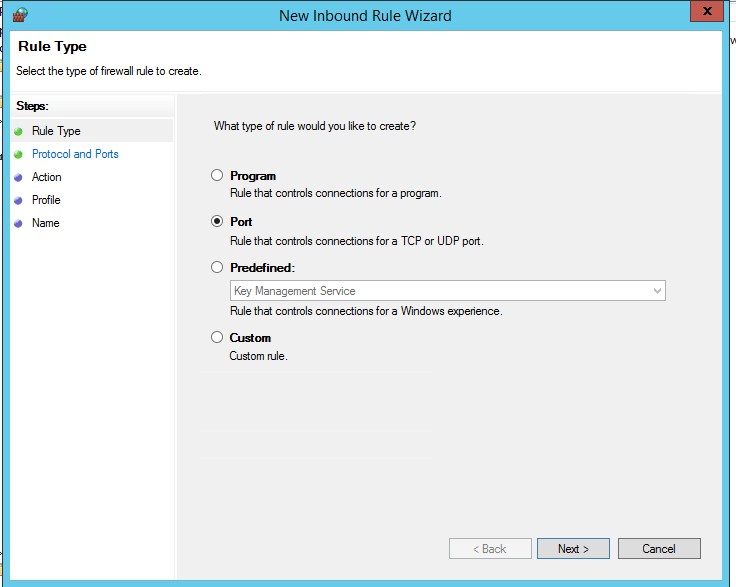
Select the rule type. You can allow access to:
- Program – you can select a program executable (.exe);
- Port – you can select a TCP/UDP port or a port range;
- Predefined – you can select one of the standard Windows rules, which already contain access rules (both executable files and ports are described) to typical services (e. g., AD, HTTP(s), DFS, BranchCache, remote restart, SNMP, KMS, etc.);
- Custom – here you can specify a program, a protocol (protocols other than TCP or UDP, like ICMP, GRE, L2TP, IGMP, etc.), client IP addresses or entire IP subnets.
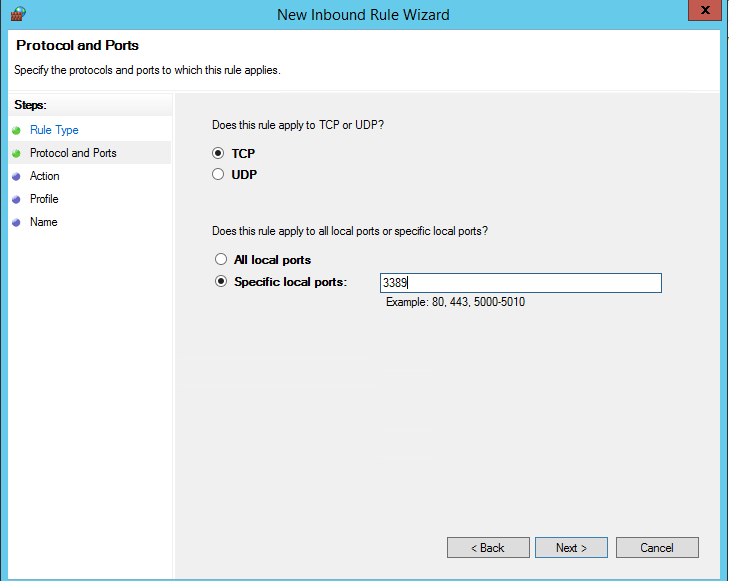
In our case, we’ll select the Port rule. Let’s specify TCP as the protocol, and Port 3389 as the port (it is the default RDP port, but you can change it via the registry).
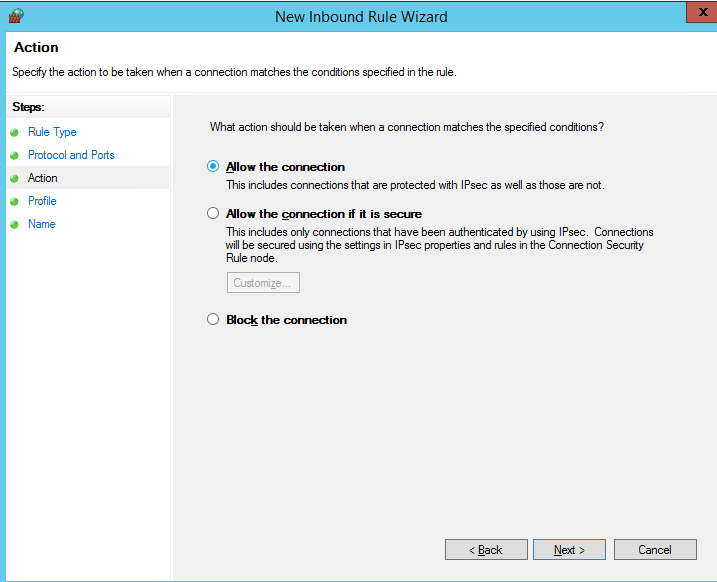
Then you must select what to do with such a network connection: Allow the connection, allow if it is secure or Block the connection.
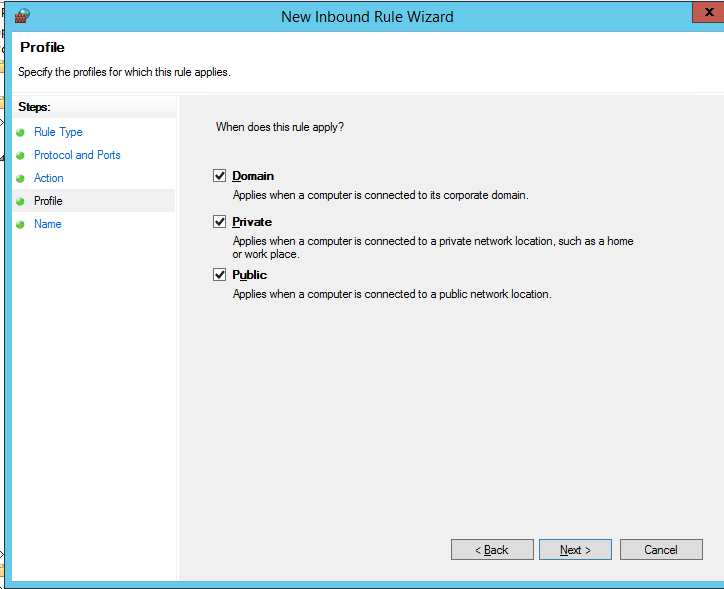
Then select the firewall profiles to apply the rule to. You can leave all profiles enabled (Domain, Private and Public).
On the last step, specify the name and description of the rule. Click Finish, and it will appear in the list of firewall rules.
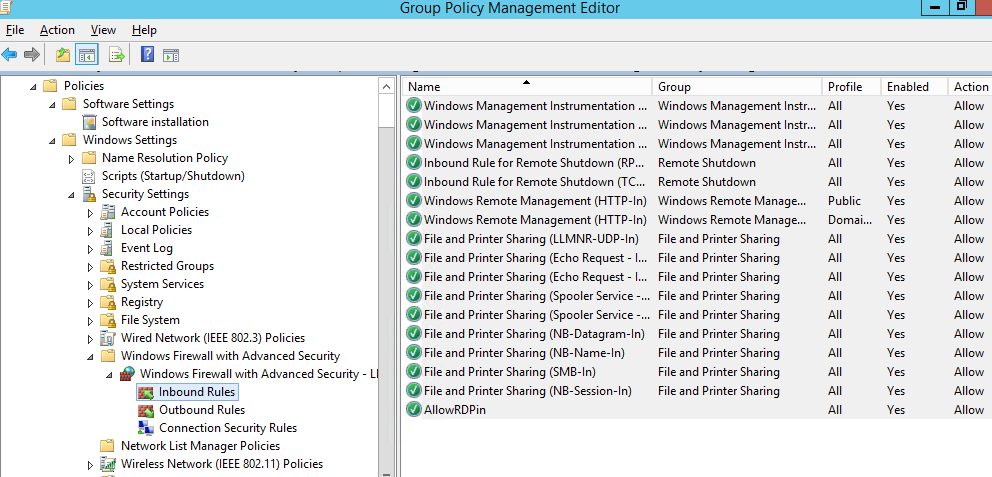
In the same way you can configure other rules for the inbound traffic to be applied to your Windows clients.Don’t forget to create rules for the inbound and outbound traffic.
Now just assign the Firewall Policy to the OU with user computers.
Testing Windows Firewall Policies on Clients
Update the group policy settings on your clients (gpupdate /force). Make sure that the ports you have specified are available on user computers (you can use Test-NetConnection cmdlet or Portqry tool).
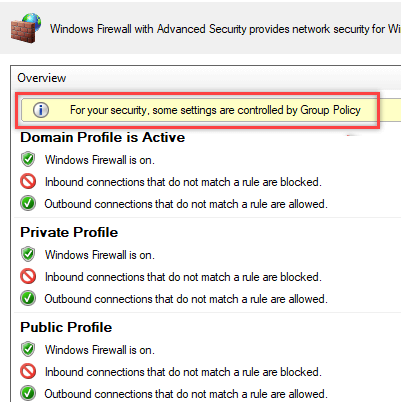
On a user PC, open the Control Panel -> System&Security -> Windows Defender Firewall and make sure that there is the message For your security, some settings are controlled by Group Policy and your firewall settings are used.
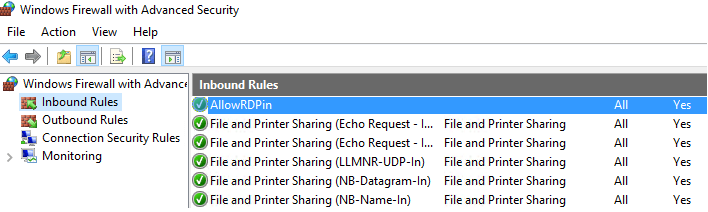
Now a user cannot change firewall settings, and all rules that you have created must appear in the Inbound Rules list.
You can also display the firewall settings using this command:
netsh firewall show state
How to Import/Export Windows Firewall Rules to/from GPO?
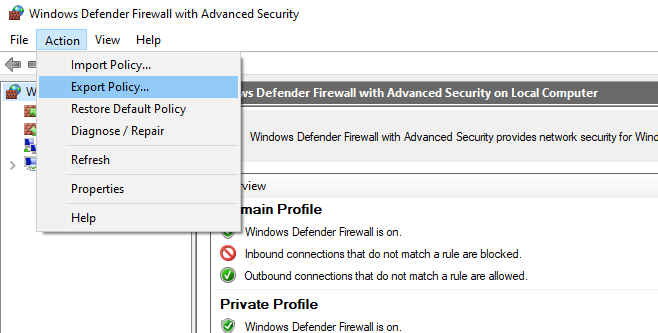
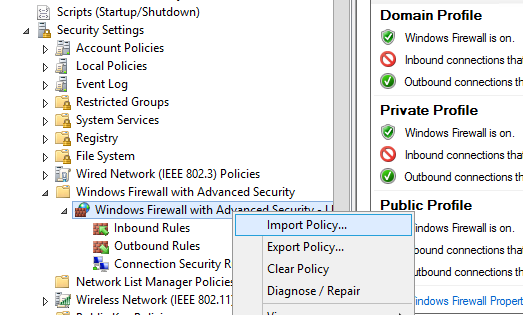
Of course, the process of creating Windows Firewall rules is a painstaking and time consuming task (however, it is worth the effort). To make it easier, you can import/export Windows Firewall settings. To do it, it’s enough to configure local firewall settings on a reference workstation as you need. Then go to the root of Windows Firewall snap-in (Windows Firewall with Advanced Security) and select Action -> Export Policy.
The policy will be exported into a WFW file, which can be imported to the Group Policy Management Editor by selecting Import Policy option and specifying the path to the .wfw file (the current policy settings will be overwritten).
Domain and Local Windows Defender Firewall Rules
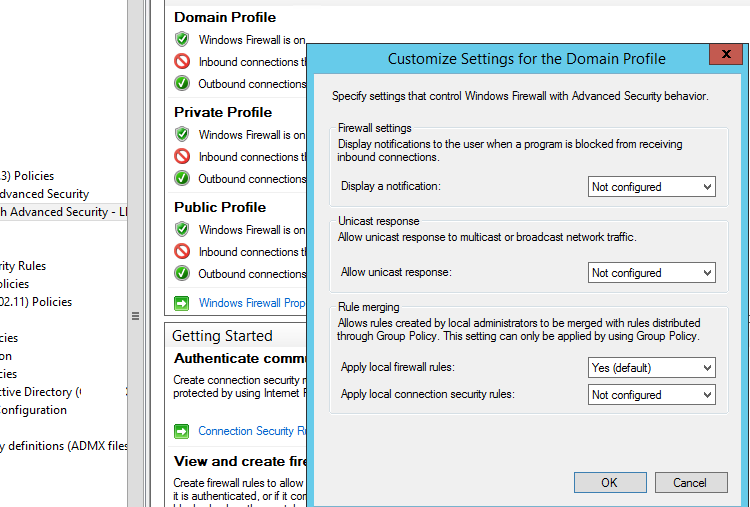
Depending on whether you want that local administrators can create their own firewall rules on their computers to be combined with the rules obtained from the group policy, you can select the rule merging option. Open the policy properties and view the settings in the Rule merging section. By default rule merging is enabled. You can force that a local administrator can create their own firewall rules: select Yes (default) in the Apply local firewall rules option.
Tips: Managing Windows Firewall with GPOs
Of course, you should create separate policies to manage Windows Firewall rules for servers and workstations (you may have to create separate policies for each group of similar servers depending on their role). It means that firewall rules for the domain controller, an Exchange mail server and an SQL server will differ.
You can find what ports must be opened for each service on the vendor’s website. The process is quite painstaking and complicated at the first glance. However, you can finally get a working Windows Firewall configuration that allows only approved network connections and blocks other ones. From my experience, I’d like to note that you can quickly find the list of used TCP/UDP ports for Microsoft software.
Configure Firewall Port Requirements for Group Policy
Applies To: Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8
You can use the information in this topic to configure the firewall port requirements for Group Policy. Group Policy requires that firewall ports are opened on client computers for an administrator to perform these two remote operations:
By default, Windows Firewall enables all outbound network traffic,and it allows only inbound traffic that is enabled by firewall rules. This topic identifies the TCP and UDP ports for which you must have active firewall rules to allow the inbound traffic. This allows Group Policy to perform remote Group Policy Results reporting from client computers and to perform remote Group Policy refresh to client-based computers. You can use the information in this topic to configure non-Microsoft firewall products and to create a GPO to configure a client computer with the required firewall rules. This topic also presents two new starter Group Policy Objects (GPOs) that configure the proper firewall rules on client computers.
If you have configured client computers by using Group Policy, the Group Policy settings override any manual configuration of client computers to which the policies are applied. If you want to review these rules, from the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), you can run a Group Policy Results report or Group Policy Planning report. Or from a client computer, open the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in and click Inbound Rules . Membership in the Administrators group or equivalent is the minimum permissions required to make these configuration changes.
If you use a non-Microsoft firewall product, check your firewall product documentation for instructions about how to open these ports to allow network traffic as required by Group Policy.
Remote Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) Group Policy results: ports that require firewall rules
You can use the RSoP feature of the GPMC to create detailed reports about the policy settings that are applied to computers or users who have signed in. When RSoP reporting targets remote computers, all connections are direct to each remote client from the computer running the GPMC (that is, not transitively through a domain controller).
To use RSoP reporting for remotely targeted computers through the firewall, you must have firewall rules that allow inbound network traffic on the ports listed in the following table. This allows remote WMI and event log traffic to flow between the computer running the GPMC and the remotely targeted computer.
Type of network traffic
TCP SMB 445, all services and programs
Remote Event Log Management (NP-in)
TCP RPC dynamic ports, EventLog (Windows Event Log service)
Remote Event Log Management (RPC)
TCP port 135, RPCSS (Remote Procedure Call service)
Remote Event Log Management (RPC-EPMAP)
TCP all ports, Winmgmt (Windows Management Instrumentation service)
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-in)
Configure firewall rules by creating a GPO from the Group Policy Reporting Firewall Ports Starter GPO and linking to the domain
In Windows Server 2012, Group Policy adds a new Starter GPO called, Group Policy Reporting Firewall Ports. This Starter GPO includes policy settings to configure the firewall rules that are specified in the previous table. This enables inbound network traffic on the ports, which is necessary to allow the GPMC to gather the Group Policy results RSoP information from a remote computer. It is a best practice to create a new GPO from this Starter GPO, and then link the new GPO to your domain with a higher precedence than the Default Domain GPO, so that you can configure all computers in the domain for remote Group Policy results reporting.
To create a GPO from the Group Policy Reporting Firewall Ports Starter GPO and link to the domain
In the GPMC console tree, right-click the domain for which you want to configure all computers to enable a remote Group Policy refresh, and then click Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…В
In the New GPO dialog box, type the name of the new Group Policy Object in the Name box.
Select the Group Policy Reporting Firewall Ports Starter GPO from the Source Starter GPO list that you want to use to create a new Group Policy Object.
If you do not see any Starter GPOs listed, cancel creating a GPO and do the following before you return to Step 1: Navigate to Starter GPOs . In the results pane, click Create Starter GPOs Folder .
Click OK.
In the results pane, click the Linked Group Policy Objects tab.
Select the GPO that you just created. Click the Up arrow until the GPO you just created is located above the Default Domain Policy. The new GPO will then have a smaller link-order value than the Default Domain Policy.
.jpeg)
The following Windows PowerShell cmdlet or cmdlets perform the same function as the preceding procedure. Enter each cmdlet on a single line, even though they may appear word-wrapped across several lines here because of formatting constraints.
You can use the New-GPO cmdlet with the –StarterGpoName parameter to create a new GPO. You can then pipe the output from the New-GPO cmdlet to the New-GPLink cmdlet.
For example, to create a new GPO, called Configure firewall rules for remote reporting, based on the Group Policy Reporting Firewall Ports Starter GPO, and link the GPO to the Contoso.com domain, type the following:
For more information about the New-GPO cmdlet and the New-GPLink cmdlet, see:
Remote Group Policy refresh: ports that require firewall rules
To schedule a remote Group Policy refresh for domain-joined computers you must have firewall rules that enable inbound network traffic on the ports listed in the following table.
Type of network traffic
TCP RPC dynamic ports, Schedule (Task Scheduler service)
Remote Scheduled Tasks Management (RPC)
TCP port 135, RPCSS (Remote Procedure Call service)
Remote Scheduled Tasks Management (RPC-EPMAP)
TCP all ports, Winmgmt (Windows Management Instrumentation service)
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-in)
Configure firewall rules by creating a GPO from the Group Policy Remote Update Firewall Ports Starter GPO and linking to the domain
In Windows Server 2012, Group Policy adds a new Starter GPO called Group Policy Remote Update Firewall Ports. This Starter GPO includes policy settings to configure the firewall rules that are specified in the previous table. This enables inbound network traffic on the ports, which is necessary to allow the remote Group Policy refresh to run. It is a best practice to create a new GPO from this Starter GPO, and then link the new GPO to your domain with a higher precedence than the Default Domain GPO, so that you can configure all computers in the domain to enable a remote Group Policy refresh.
To create a GPO from the Group Policy Remote Update Firewall Ports Starter GPO and link to the domain
In the GPMC console tree, right-click the domain for which you want to configure all computers to enable a remote Group Policy refresh, and then click Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…В
In the New GPO dialog box, type the name of the new Group Policy Object in the Name box.
Select the Group Policy Remote Update Firewall Ports Starter GPO from the Source Starter GPO list.
If you do not see any Starter GPOs listed, cancel creating a GPO and do the following before you return to the Step 1: Navigate to Starter GPOs In the results pane, click Create Starter GPOs Folder
Click OK.
In the results pane, click the Linked Group Policy Objects tab.
Select the GPO that you just created. Click the up arrow until the GPO you just created is above the Default Domain Policy in link order. The new GPO will then have a smaller link order value than the Default Domain Policy.
.jpeg)
The following Windows PowerShell cmdlet or cmdlets perform the same function as the preceding procedure. Enter each cmdlet on a single line, even though they may appear word-wrapped across several lines here because of formatting constraints.
You can use the New-GPO cmdlet with the –StarterGpoName parameter to create a new GPO. You can then pipe the output from the New-GPO cmdlet to the New-GPLink cmdlet.
For example, to create a new GPO, called Configure firewall rules for remote gpupdate, which is based on the Group Policy Remote Update Firewall Ports Starter GPO, and link the GPO to the Contoso.com domain, type the following:
For more information about the New-GPO cmdlet and the New-GPLink cmdlet, see: