- Как узнать характеристики оперативной памяти в командной строке
- Как узнать характеристики оперативной памяти в командной строке
- How to Find the RAM type (DDR2, DDR3, DDR4), Speed, and other Details in Windows
- Find the RAM module type:
- Determine the Memory Module Information Quickly
- Using Task Manager
- Memory Type, part number, speed, etc using WMIC
- MemoryType shows up as 0 (Unknown)?
- Using PowerShell
- One small request: If you liked this post, please share this?
- About the author
- 4 thoughts on “How to Find the RAM type (DDR2, DDR3, DDR4), Speed, and other Details in Windows”
- How to Get Full RAM Specifications in Windows 10
- Introduction
- How to get detailed information on system memory with the command prompt console
- Identify the manufacturer
- Identify the part number
- Check the serial number of your memory module
- Identify RAM capacity
- Discover capacity of each RAM module
- Displaying total amount of RAM
- Check RAM speed
- Check RAM type
- The comprehensive list of supported memory types
- Check RAM form factor
- The comprehensive list of supported memory form factors
- Displaying all RAM details
- Conclusion
Как узнать характеристики оперативной памяти в командной строке
В данной статье показаны действия, с помощью которых можно узнать характеристики оперативной памяти в командной строке.
Чтобы узнать характеристики оперативной памяти установленной в компьютере существуют различные способы, например утилиты сторонних разработчиков. Также некоторая информация представлена в графическом интерфейсе операционной системы Windows, а именно в диспетчере задач на вкладке Производительность.
Ниже будет рассмотрен способ как узнать характеристики оперативной памяти с помощью утилиты командной строки WMIC.exe (Windows Management Instrumentation Command — Инструментарий управления Windows). .
Данная статья носит информационно познавательный характер и будет полезна для всех пользователей компьютеров с установленной операционной системой Windows.
Как узнать характеристики оперативной памяти в командной строке
Чтобы узнать основные характеристики оперативной памяти, запустите командную строку от имени администратора и выполните следующую команду:
wmic memorychip get Manufacturer,Capacity,PartNumber,Speed,DeviceLocator
Теперь разберём результат выполненной команды.
Столбец Capacity (с англ. Capacity — Вместительность, Ёмкость, Объём) показывает нам объём установленных модулей памяти в байтах для каждого отдельно (в данном примере установлено два модуля памяти). Минусом является то, что объём модулей указывается в байтах, однако все же узнать его в привычном виде нетрудно (в гигабайтах нужно брать первую или две первых цифры).
Столбец DeviceLocator показывает список слотов в которые установлены модули памяти. В зависимомти от материнской платы, маркировка слотов может быть разная, например: ( DIMM_A , DIMM_B ), ( DIMM_A1 , DIMM_A2 , DIMM_B1 , DIMM_B2 ), ( DIMM0 , DIMM1 ), ( DIMM0 , DIMM1 , DIMM2 , DIMM3 ).
Столбец Manufacturer отображает производителя модуля памяти. В зависимомти от модели и производителя модуля памяти параметр Manufacturer может быть пустым.
Столбец PartNumber отображает номер детали, присвоенный организацией, ответственной за создание или производство физического элемента.
Параметр PartNumber очень интересный и полезный.
Немного разберём параметр данного примера KHX2400C15D4/8G.
Цифры 2400 говорят о том что частота модуля памяти равна 2400 MHz.
C15 это так называемые тайминги или CAS Latency, если вам будет интересно то можно почитать статью Тайминги_(оперативная_память).
D4 могу предположить что это стандарт (поколение) оперативной памяти DDR4 (в данном примере как раз и есть DDR4, но об этом немного позже).
Ну и осталась маркировка 8G — здесь без комментариев.
Хочу отметить что параметр PartNumber от других производителей может не так наглядно выглядеть.
О интересностях всё, теперь о полезности данного параметра. А полезность заключается в том, что Вы можете скопировать параметр PartNumber вашей планки памяти и загуглить его в интернете, помимо характеристик вашего модуля памяти, Вы можете также узнать и его цену, ну только если память не слишком древняя или планка не от какого-нибудь очень китайского noname производителя.
Теперь рассмотрим ещё несколько примеров интересных команд.
Чтобы узнать общее количество слотов для модулей памяти, выполните следующую команду:
wmic memphysical get MemoryDevices
Чтобы узнать какой максимально возможный объём оперативной памяти можно установить, выполните следующую команду:
wmic memphysical get MaxCapacity
Значение указано в килобайтах.
Полный объем установленной физической памяти в русской версии Windows, можно узнать при помощи следующей команды:
systeminfo | find «Полный объем физической памяти»
Значение указано в мегабайтах.
Полный объем установленной физической памяти для системы с английской локализацией, можно узнать выполнив команду:
systeminfo | find «Total Physical Memory»
Для того чтобы узнать форм-фактор модулей памяти, выполните команду:
wmic memorychip get FormFactor
На скриншоте показан результат выполненной команды, цифра 8 говорит о том что модули памяти соответствуют форм-фактору DIMM , стандартный форм-фактор десктопных компьютеров.
На скриншоте ниже показан результат выполненной команды wmic memorychip get FormFactor, цифра 12 говорит о том что модули памяти соответствуют форм-фактору SODIMM , которые обычно устанавливают в ноутбуки.
Немного информации о форм-факторе модулей оперативной памяти.
Форм-фактор (от англ. form factor) или типоразмер — стандарт, задающий габаритные размеры технического изделия, а также описывающий дополнительные совокупности его технических параметров, например форму.
Существуют следующие конструктивно и электрически несовместимые друг с другом типы DIMM , в том числе SO-DIMM (от англ. Small Outline, компактные модули, используемые, в частности, в ноутбуках):
- 184-pin DIMM — используется для DDR SDRAM
- 200-pin SO-DIMM — используется для DDR SDRAM и DDR2 SDRAM
- 214-pin MicroDIMM — используется для DDR2 SDRAM
- 204-pin SO-DIMM — используется для DDR3 SDRAM
- 240-pin DIMM — используется для DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM и FB-DIMM DRAM
- 260-pin SO-DIMM — используется для DDR4 SDRAM
- 288-pin DIMM — используется для DDR4 SDRAM
Ниже представлены изображения честно позаимствованные с википедии для основных форм-факторов модулей памяти.
Идём далее, при помощи следующей команды, Вы можете узнать тип (поколение) оперативной памяти:
wmic memorychip get MemoryType
В данном примере цифры 24 говорят о том что установлены модули памяти типа DDR3 .
Также параметр MemoryType может отображать нули, как показано на скрине ниже, это говорит о том что утилита wmic.exe не может определить тип памяти (в этом примере тип памяти DDR4), так как в спецификации нет значений для DDR4.
Ниже представлены некоторые значения параметра MemoryType :
- 20 = DDR
- 21 = DDR2
- 22 = DDR2 FB=DIMM
- 24 = DDR3
- 25 = FBD2
И ещё одна команда, с её помощью Вы можете узнать напряжение модуля памяти:
wmic memorychip get ConfiguredVoltage
Значение параметра отображается в милливольтах. Если значение 0 или не отображается, то напряжение неизвестно.
Для справки ниже представлены напряжения для разных типов памяти:
- DDR2.5V2500mV
- DDR21.8V1800mV
- DDR31.5V1500mV
- DDR41.2V1200mV
How to Find the RAM type (DDR2, DDR3, DDR4), Speed, and other Details in Windows
This post explains two different ways to find full information about the Memory module installed in your system, without using 3rd party tools. You may need the existing Memory module information such as the type, part number, number of available slots, capacity, and speed if you plan to upgrade the RAM.
Find the RAM module type:
Determine the Memory Module Information Quickly
Using Task Manager
Start Task Manager, select the Performance tab, and click Memory.
This tab lists the available and used memory along with memory chip information such as the module capacity, speed, type, and the number of available slots.
Memory Type, part number, speed, etc using WMIC
The Windows Management Instrumentation is an extremely useful tool to view hardware information and automate system tasks. You can use WMI’s command-line tool (WMIC) to view memory chip information. Open a Command Prompt window and type:
This copies the memory module information to the clipboard, which you can paste in Notepad or any text editor of choice.
The following properties of your Memory module are shown using the above command. However, the data for some fields/properties show up empty.
- BankLabel
- Capacity
- DataWidth
- Description
- DeviceLocator
- FormFactor
- HotSwappable
- InstallDate
- InterleaveDataDepth
- InterleavePosition
- Manufacturer
- MemoryType
- Model
- Name
- OtherIdentifyingInfo
- PartNumber
- PositionInRow
- PoweredOn
- Removable
- Replaceable
- SKU
- SerialNumber
- Speed
- Status
- Tag
- TotalWidth
- TypeDetail
- Version
If you need only specific data required in order to purchase a new module, you’d run this command:
That shows the Manufacturer Name, Part Number, Memory type, Socket Name, speed of the memory chip.
The most important field is the Memory type. It’s indicated in CIM values. A value of 20 means DDR, 21 is DDR2, 22 is DDR2 FB-DIMM, 24 is DDR3, 26 is DDR4.
For DDR4 and higher, you may have to use the SMBIOSMemoryType field, since the MemoryType column shows 0 .
MemoryType shows up as 0 (Unknown)?
If you have DDR4 (and higher) RAM installed on your system, the WMIC command-line may show the memory type as 0 . However, you can rely on the SMBIOSMemoryType data.
Microsoft documentation says DDR4 is 26 ( 0x1A ).
| Memory Type/SMBIOSMemoryType | RAM Type |
| 20 | DDR |
| 21 | DDR2 |
| 22 | DDR2 FB-DIMM |
| 24 | DDR3 |
| 26 | DDR4 |
In addition, there are other fields such as the part number, speed, etc., that can help you find the RAM module type.
The DeviceLocator field tells you the label of the socket in the System board that holds the memory, such as DIMM1, DIMM2, DIMM 3, and DIMM4.
This MSDN page has all the details about WMI’s physicalmemory class.
Part Number is another useful information that can help when purchasing memory chip online; you can look up the Part Number on the web or on your favorite shopping site.
You don’t always need a module of the exact same Part Number. The memory chip from any manufacturer should work fine, provided the specifications match.
Using PowerShell
The following PowerShell script (via SuperUser) shows the list of available DIMM slots, form factor, type, and speed.
- Using Notepad, copy/save the above lines of code to a file with .ps1 extension — memory.ps1 .
- Right-click memory.ps1 and click Run with PowerShell. You’ll get an output similar to the following:
MemoryType info using PowerShell script
(Another option is to use the VBScript RAM Upgrade.vbs written by someone named “Alex Yancey” and hosted on GitHub. Also, there are some excellent third-party tools such as HWiNFO and Speccy which show a wealth of information about the hardware installed in your computer.)
One small request: If you liked this post, please share this?
About the author
Ramesh Srinivasan founded Winhelponline.com back in 2005. He is passionate about Microsoft technologies and he has been a Microsoft Most Valuable Professional (MVP) for 10 consecutive years from 2003 to 2012.
Microsoft → Windows → How to Find the RAM type (DDR2, DDR3, DDR4), Speed, and other Details in Windows
4 thoughts on “How to Find the RAM type (DDR2, DDR3, DDR4), Speed, and other Details in Windows”
Memory type. It’s indicated in CIM values. A value of 20 means DDR, 21 is DDR2, 22 is DDR2 FB-DIMM, 24 is DDR3.
What Kind of Memory type is DDR4?
@RamBo: The article is updated now. If it shows the MemoryType as 0 , then it’s most likely DDR4. You can use the SMBIOSMemoryType column data instead. Also, you can Google the part number to verify.
Thank you, I used the script and got the info I needed.
How to Get Full RAM Specifications in Windows 10
Read this article to find out how to find specifications for the system memory installed on your computer, including information about its manufacturer, part number, serial number, effective speed, capacity, form factor, type etc.
Introduction
There are many scenarios when the ability of Windows 10 to supply specifications data on installed computer hardware may come in handy. Getting to know the detailed information on system memory (also known as random-access memory, or RAM) can sometimes be very useful in helping you to take the correct decision if any problems arise. For example, if a computer works slowly because it has to run memory-intensive applications or games, then adding more system memory may give it a considerable boost. Knowing certain peculiarities and required standards of the system memory can help you decide on the correct capacity, speed and brand of RAM to buy a piece of compatible hardware for an upgrade.
If you are having issues with system memory, knowing the information on its manufacturer, part number and serial number will help you to contact the tech support and solve the problem. At least, you will be able to find a memory module of the same type which, as you already know, is fully compatible with your PC. Besides, when you are configuring memory settings in the basic input / output system (BIOS) or in the unified extensible firmware interface (UEFI), a chance to have a look at memory information can help you to understand if a particular configuration was applied correctly.
Whatever might be your reasons, Windows 10 can provide you with all the information you may need; what is more, it saves you the trouble of having to open the computer case or install third-party tools, which may trigger a conflict of interest or cause compatibility issues.
In this tutorial, we will try to show you how to find specifications for the system memory installed on your computer, including information about its manufacturer, part number, serial number, effective speed, capacity, form factor, type etc.
A brief note: Despite the fact that Windows 10 lets users see detailed information on the system memory in their devices, some data may be unavailable due to peculiarities of specific hardware.
How to get detailed information on system memory with the command prompt console
If you suspect that Task Manager displays inaccurate or wrong information on your RAM specifications, or if you need to learn more detailed data such as serial number, part number, manufacturer etc on every memory module, Windows 10 is here to help you find all that information by using a certain set of system commands.
To start searching and find specific data on memory modules installed on your desktop PC or laptop, you need to use the functions of the command prompt with administrator rights in Windows 10. There are a few ways to open the Command Prompt application, the rich functionality of which we are going to explore today.
Click the Search button, shaped as a magnifying glass and located on the Taskbar next to the Start button, and open the search panel. There, type command prompt or cmd. The Best match section will show you the app you are looking for. Right-click on it and select Run as administrator from the context menu.
Identify the manufacturer
Here is what you do to identify the manufacturer company (brand or trademark) that produced the RAM modules installed on your PC.
Open the Command Prompt with administrator rights using the way you prefer.
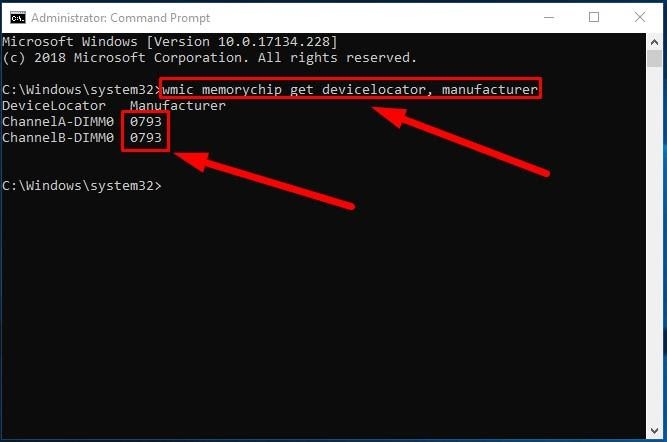
To find out the manufacturer’s name, type the following command and press the Enter key (make sure there are no quotation marks):
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, manufacturer
Read the RAM module manufacturer name under the column Manufacturer.
Identify the part number
To find data on the part number that the manufacturer assigned to a specific RAM module, here’s a simple sequence of steps to take.
Use any method you prefer to open the command prompt console with extended rights.
In the window that appear, type the command to run (without quotation marks) and press the Enter key.
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, partnumber
Under the column PartNumber you will see the product identifier you are looking for.
Note: If the speed of data processing and overall performance of your computer is decreasing, upgrading your RAM modules might be one of the best way to solve the issue. Using modern memory sticks, you can add high-quality components to your machine, with a pleasant bonus of higher bandwidth and advanced settings at an affordable price.
Check the serial number of your memory module
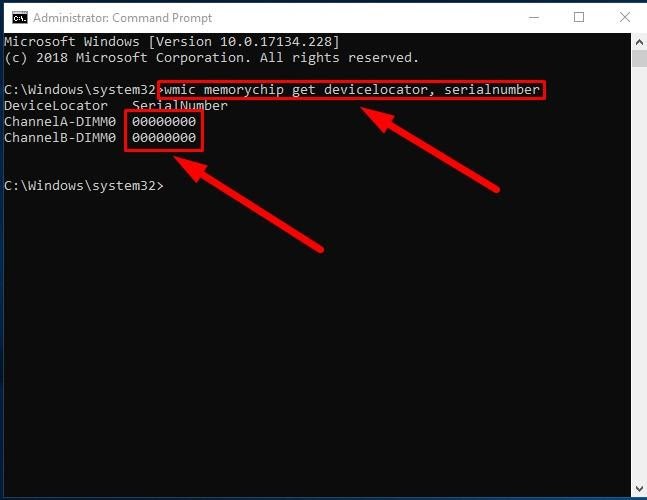
Take these steps to find out the serial numbers for every memory stick currently installed in your computer:
Open Command Prompt with administrator rights using any way you prefer.
In the corresponding line, type the command for identification of RAM serial number (make sure there are no quotation marks) and hit the Enter key to begin.
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, serialnumber
Hint: In the command for identification of the serial number, you can replace the part devicelocator by banklabel to see the serial number of the physical label of the bank where the memory is installed on the motherboard.
The result will be displayed in the Command Prompt window under the column SerialNumber.
Identify RAM capacity
In Windows 10 you can use a variable set of commands to find out total capacity for every RAM module, and for the entire system memory.
Discover capacity of each RAM module
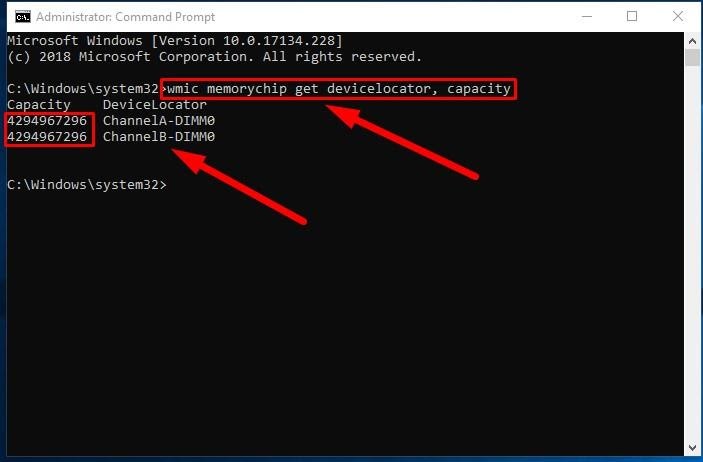
To learn capacity of each memory stick in your configuration, take a few steps.
Open Command Prompt with administrator rights, using any method you prefer.
In the program’s window, type the following command for displaying the memory capacity, and then press the Enter key to run it (make sure the command doesn’t contain any quotation marks).
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, capacity
The total capacity of RAM installed on your computer will be shown under the column Capacity.
Note: The memory module capacity is represented in bytes, so to understand the figure properly you need to convert it into gigabytes (divide the value shown in the Command Prompt window by 1073741824, which is how many bytes are there in one gigabyte).
Displaying total amount of RAM
In addition, you can quickly learn the total size of system memory on your computer by taking another sequence of simple steps.
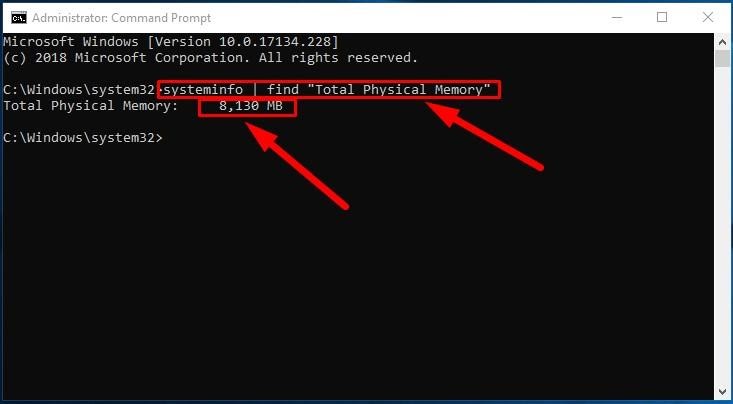
Open Command Prompt with administrator rights.
When the corresponding window opens, type the following command to see the total system memory size installed on your computer with Windows 10, and press the Enter key to run the command (remove any quotation marks).
systeminfo | find “Total Physical Memory”
Note: If the total memory size is not displayed, try a similar command:
systeminfo | findstr /C:”Total Physical Memory”
With every command, make sure there are no quotation marks.
The total size of physical system memory (in megabytes) available on this computer will be shown in the corresponding line.
Check RAM speed
To find out the speed that the memory modules are operating at, here are the steps to use:
Open the Command Prompt console with administrator rights in any way you prefer.
Type the command to determine the RAM speed and press Enter on your keyboard (make sure there are no quotation marks):
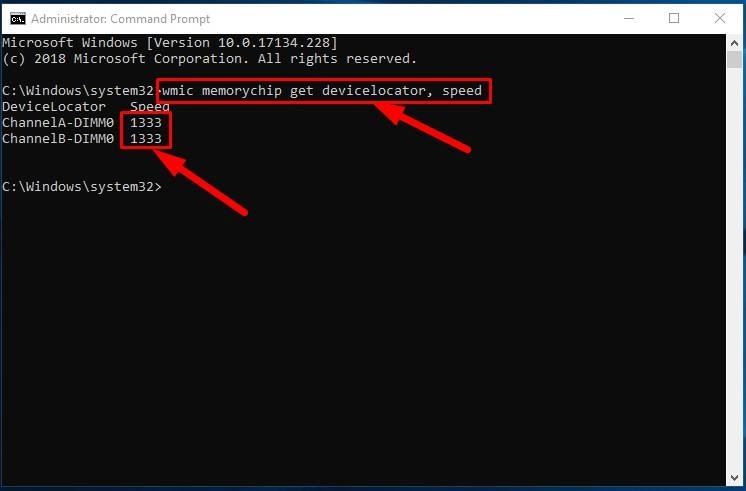
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, speed
In the corresponding Speed column, the program will display the speed of your memory modules (in MHz).
Check RAM type
To check the system memory type (generation) in Windows 10, take these steps:
Open Command Prompt with administrator rights, using any method you prefer.
In the corresponding line, type the following command to determine the memory type and press Enter on your keyboard (make sure there are no quotation marks):
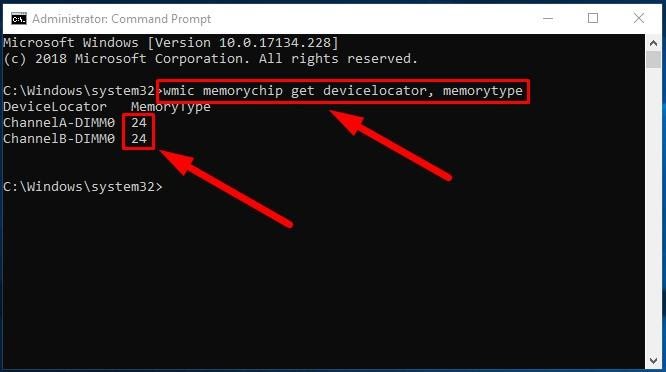
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, memorytype
The MemoryType column will contain a digit from zero to twenty-five that denotes a certain memory type. For example, if you see 24 in the column, it means this computer is using DDR3memory modules.
Also, you may see zeroes in the MemoryType column: it means the Windows system tool wmic.exe cannot identify the memory generation properly (it may happen if you’re using DDR4 modules), as such values are not provided in the specifications.
The comprehensive list of supported memory types
Below, find the comprehensive list of file types that can be identified by this command:
- 0: Unknown.
- 1: Other.
- 2: DRAM.
- 3: Synchronous DRAM
- 4: Cache DRAM.
- 5: EDO.
- 6: EDRAM.
- 7: VRAM.
- 8: SRAM.
- 9: RAM.
- 10: ROM.
- 11: Flash.
- 12: EEPROM.
- 13: FEPROM.
- 14: EPROM.
- 15: CDRAM.
- 16: 3DRAM.
- 17: SDRAM.
- 18: SGRAM.
- 19: RDRAM.
- 20: DDR.
- 21: DDR2.
- 22: DDR2 FB-DIMM.
- 24: DDR3.
- 25: FBD2.
Check RAM form factor
The word “form factor” (standard size) suggests certain standard dimensions of a memory module which also includes additional characteristics such as the module shape. By form factor, there are twenty-five types of system memory. However, the two most widespread categories are DIMM and SODIMM.
To find out if your RAM sticks are DIMM or SODIMM, follow these steps:
Use your preferred method to open Command Prompt with administrator rights.
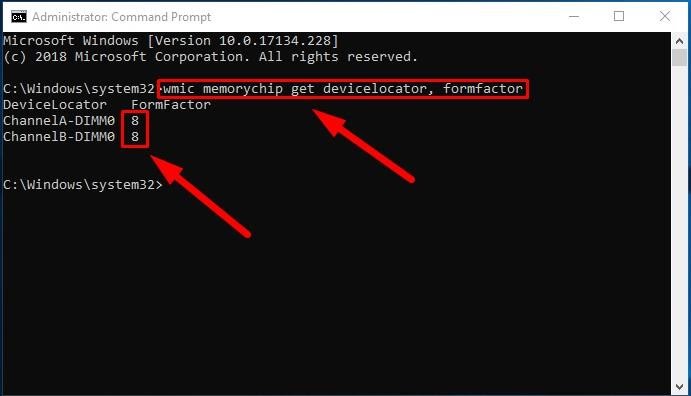
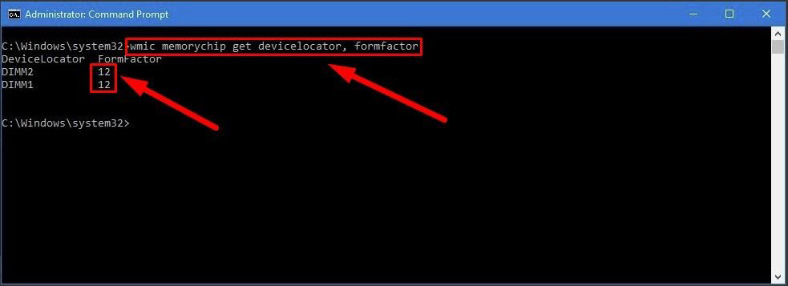
In the window Administrator: Command Prompt, type the following command to identify the memory form factor and press the Enter key (make sure there are no quotation marks):
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, formfactor
If the result in the FormFactor column is 8, then your computer is using DIMM modules (the default option for desktop computers). Otherwise, if the command displays the number 12, then your computer is using SODIMM modules (the typical choice for laptops).
The comprehensive list of supported memory form factors
Here is the list of form factors that this command can identify:
- 0: Unknown.
- 1: Other.
- 2: SIP.
- 3: DIP.
- 4: ZIP.
- 5: SOJ
- 6: Proprietary.
- 7: SIMM.
- 8: DIMM.
- 9: TSOP.
- 10: PGA.
- 11: RIMM.
- 12: SODIMM.
- 13: SRIMM.
- 14: SMD.
- 15: SSMP.
- 16: QFP.
- 17: TQFP.
- 18: SOIC.
- 19: LCC.
- 20: PLCC.
- 21: BGA.
- 22: FPBGA.
- 23: LGA.
- 24: FB-DIMM.
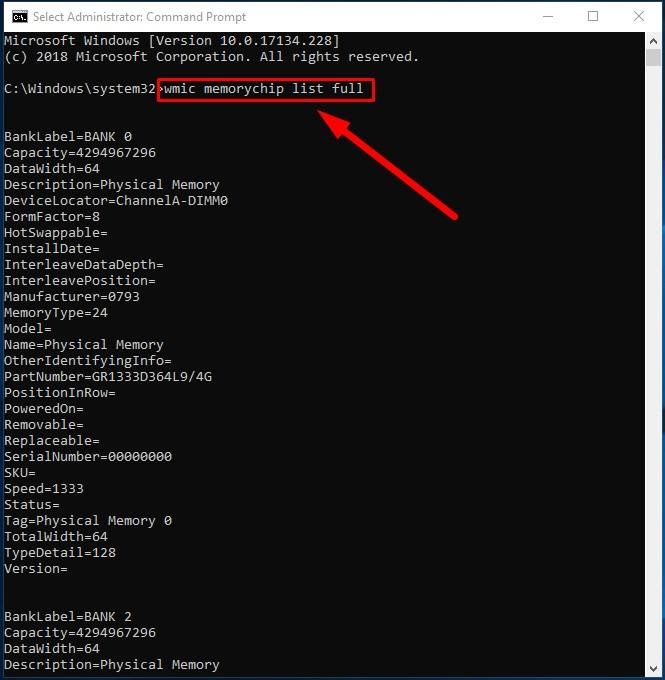
Displaying all RAM details
The commands described above allow you to identify the most important data about memory modules. However, if you want to find all the information, here’s what you do:
Open Command Prompt with administrator rights in any way you prefer.
In the corresponding line, type the following command to display all memory details and press Enter to run it (don’t forget to remove any quotation marks):
wmic memorychip list full
View all the available information for each RAM module installed on your computer.
(Optional) if the list of data is too big and you don’t actually need all that stuff, type the following command to view only the necessary things and press Enter (everything should be typed into one line; remember to remove the quotation marks):
wmic memorychip get devicelocator, manufacturer, partnumber, serialnumber, capacity, speed, memorytype, formfactor
Now you can view the memory information you prefer.
Conclusion
Using the steps described in this article, you’ll get an impressive amount of data on the RAM modules installed on your computer. These hints will come in handy when troubleshooting PC issues, tweaking configuration (e.g. when overclocking), or when you’re planning to upgrade your system memory to improve overall computer performance.
See the full article with all additional video tutorials