- Graphical User Interface
- Using Icons
- Creating an Icon
- Displaying an Icon
- Sharing Icon Resources
- Windows, Icons, Menus And Pointing Device (WIMP)
- What Does Windows, Icons, Menus And Pointing Device (WIMP) Mean?
- Techopedia Explains Windows, Icons, Menus And Pointing Device (WIMP)
- ПАКЕТНАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ И ИНТЕРФЕЙС КОМАНДНОЙ СТРОКИ
- ДИАЛОГОВАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ И ГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС (GUI)
- ГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС WIMP (WINDOW, ICON, MENU, POINTER)
- СТРУКТУРУ ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЯ ДЛЯ ГРАФИЧЕСКОГО ИНТЕРФЕЙСА
- ГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС WIMP ПРЕИМУЩЕСТВА/НЕДОСТАТКИ
- РЕЧЕВАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ
- БИОМЕТРИЧЕСКАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ
- СЕНСОРНЫЙ (ЖЕСТОВЫЙ) ИНТЕРФЕЙС
- ТАКТИЛЬНЫЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС
- НЕЙРОКОМПЬЮТЕРНЫЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС
Graphical User Interface
An operating system is a group of programs that tell a computer how to perform basic functions, e. g. how to respond when a key on the keyboard is pressed, how to display a character on the monitor screen, or how to read and write to a disk. The operating system is started automatically when a computer is switched on. It is then used to start up and control other programs. The operating system determines how the user interacts with the computer. Some operating systems require the user to type commands, but an operating system with a graphical user interface (GUI) makes it easier for the user to control the computer. The most common type of graphical user interface is a WIMP (windows, icons, menus, pointer) system, such as Microsoft Windows or the Apple Mac operating system. It should be noted that the recycle bin icon used in the Microsoft Windows system has the same function as the trashcan icon used in the Apple Mac system, i. e. to access the program that stores deleted files, and allow them to be recovered.
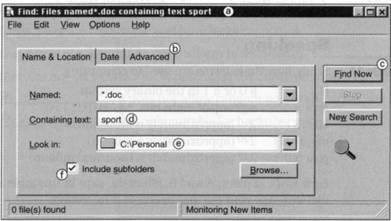
When information has to be given to the user or information has to be input by the user, a window known as a dialog box is often used. Notice that the American spelling of dialog is commonly used in this context, although the British spelling dialogue is also found. Other American spellings such as disk and program are also normally used in computing. Dialog boxes can contain a variety of elements to gather information from the user including: text boxes, drop-down list boxes, checkboxes, and command buttons. A Find dialog box is used to gather information from the user about the files they wish to find. Note that you can search for a piece of text in a file, or search for a file in a folder, but you search for a file on a disk.
9 Graphical User Interface
Task 1 A Graphical User Interface (GUI) makes computers easier to use. A GUI uses icons. Icons are pictures which represent programs, folders, and files. Can you identify any of these icons?
Task 2 Find the icons for the software which controls these items.
1 date and time 3 fonts 5 a modem
2 the mouse 4 the keyboard 6 sounds
Listening: Dialog box
Task 4 Now listen and check your answers.
| Task 5 | Listen again. Match the features of a dialog box (1-4) with the examples from the screen (a-d). | 1 command button 2 dialog box 3 tab 4 drop-down list box | a Find b Advanced с Look in d Stop |
Task 6 Here are the steps for using this dialog box. Put them in the correct order.
a Enter name, location, and text required. с Choose tab.
b Press Find Now command button. d Open dialog box.
Task 7 Study this screen display. Can you find these items?
1 a window 2 an icon 3 a pointer 4 a menu
Task 8 Find definitions in the text of these items.
1 menu 3 window 5 pointer
2 interface 4 active window 6 icon
| Most computers have a Graphical User Interface.The interface is the connection between the user and the computer.The most common type of GUI uses a WIMP system. WIMP stands for Window, Icon, Menu (or Mouse), Pointer (or Pull-down/Pop-up menu). Windows A window is an area of the computer screen where you can see the contents of a folder, a file, or a program. Some systems allow several windows on the screen at the same time and windows can overlap each other.The window on the top is the one which is ‘active’, the one in use. Icons are small pictures on the screen.They represent programs, folders, or files. For example, the Recycle Bin icon represents a program for deleting and restoring files. Most systems have a special area of the screen on which icons appear. Menus give the user a list of choices. You operate the menu by pressing and releasing one or more buttons on the mouse. The pointer is the arrow you use to select icons or to choose options from a menu. You move the pointer across the screen with the mouse.Then you click a button on the mouse to use the object selected by the pointer. |
| Language work: Making definitions |
| Study these descriptions of an icon. An icon is a small picture on a computer screen. An icon represents items such as floppy disks. |
| We can link these sentences to make a definition of an icon. An icon is a small picture on a computer screen which represents items such as floppy disks. |
| Study these other examples of definitions. |
| A mainframe is a very large computer which is used by universities, businesses, and government departments. A palmtop is a very small computer which can be held in one hand. A byte is a small unit of memory which can hold one character of data. |
Task 9 Add to the statements (1-10) using the extra information (a-j).
Example A barcode is a pattern of printed black lines which supermarkets use for pricing.
| 1 A barcode is a pattern of printed black lines 2 A floppy is a disk 3 A motherboard is a printed circuit board 4 A password is a secret set of characters 5 A monitor is an output device 6 A disk drive is a unit 7 An expansion card is an electronic board 8 A CD-ROM drive is a common storage device 9 A notebook is a portable compute 10 The system unit is the main part of the computer | a it contains the main electronic components. b it adds features to a computer. с it is about the size of a piece of paper. d supermarkets use them for pricing. e it reads and writes to disks. f it can hold 1.44Mb of data. g it allows access to a computer system. h it controls all the other boards in a computer. i it displays data on a screen. j it reads data from a CD-ROM disk. |
Task 10 Work with a partner. Ask for and make definitions of these items. Add other examples of your own.
1 PC 4 active window
2 menu 5 pointer
| Aids to communication You can use these phrases when you’re discussing possibilities. I think it’s. It might/could be. Possibly it’s. |
Task 11 Work in pairs. Study these forms the cursor can take on your computer. Try to match each icon to one item from the list below.
| 1 hourglass 2 arrow pointer 3 pointing finger 4 not available | 5 crosshair 6 magnifying glass 7 drag and drop arrow |
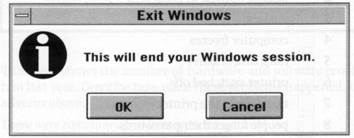
Task 12 Write a description of the Exit Windows dialog box. Your description should answer these questions.
1 What does this computer screen show?
2 What do you use this dialog box for?
3 What features does the dialog box contain?
4 What happens if you click on each button?
| | | следующая лекция ==> | |
| Parts of a computer | | | Происхождение искусства |
Дата добавления: 2016-04-26 ; просмотров: 2238 ; ЗАКАЗАТЬ НАПИСАНИЕ РАБОТЫ
Using Icons
The following topics describe how to perform certain tasks related to icons:
Creating an Icon
To use an icon, your application must get a handle to the icon. The following example shows how to create two different icon handles: one for the standard question icon and one for a custom icon included as a resource in the application’s resource-definition file.
An application should implement custom icons as resources and should use the LoadIcon or LoadImage function, rather than create the icons at run-time. This approach avoids device dependence, simplifies localization, and enables applications to share icon bitmaps. However, the following example uses CreateIcon to create a custom icon at run-time, based on bitmap bitmasks; it is included to illustrate how the system interprets icon bitmap bitmasks.
To create the icon, CreateIcon applies the following truth table to the AND and XOR bitmasks.
| AND bitmask | XOR bitmask | Display |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Black |
| 0 | 1 | White |
| 1 | 0 | Screen |
| 1 | 1 | Reverse screen |
Before closing, your application must use DestroyIcon to destroy any icon it created by using CreateIconIndirect. It is not necessary to destroy icons created by other functions.
Displaying an Icon
Your application can load and create icons to display in the application’s client area or child windows. The following example demonstrates how to draw an icon in the client area of the window whose device context (DC) is identified by the hdc parameter.
The system automatically displays the class icon(s) for a window. Your application can assign class icons while registering a window class. Your application can replace a class icon by using the SetClassLong function. This function changes the default window settings for all windows of a given class. The following example replaces a class icon with the icon whose resource identifier is 480.
For more information about window classes, see Window Classes.
Sharing Icon Resources
The following code uses the functions CreateIconFromResourceEx, DrawIcon, and LookupIconIdFromDirectoryEx, and several of the resource functions, to create an icon handle based on icon data from another executable file. Then, it displays the icon in a window.
Security Warning: Using LoadLibrary incorrectly can compromise the security of your application by loading the wrong DLL. Refer to the LoadLibrary documentation for information on how to correctly load DLLs with different versions of Windows.
Windows, Icons, Menus And Pointing Device (WIMP)
Table of Contents
What Does Windows, Icons, Menus And Pointing Device (WIMP) Mean?
Windows, icons, menus and pointing device (WIMP) denotes a style of computer-human interaction involving the aforementioned elements of the graphical user interface (GUI) which is the most common interaction method being used by desktop computers today. WIMP interaction was developed at Xerox PARC in 1973, and the term coined by Merzouga Wilberts in 1980, with the method popularized by Apple’s Macintosh in 1984.
Techopedia Explains Windows, Icons, Menus And Pointing Device (WIMP)
Windows, icons, menus and pointing device (WIMP) interaction is what the general public is used to in computing, because it is the most common interaction used in popular operating systems such as Windows, Apple’ OS and even in modern Linux and UNIX-like operating systems. But in more development-oriented operating systems such as Linux and UNIX, there is an option to forgo the pointing device altogether and perform all interaction with the OS through the command prompt or shell, but the windows remain.
Characteristics of a WIMP system:
- A window isolates programs from each other, which allows a user to switch between running programs by giving focus to specific windows.
- Icons act as shortcuts to various programs, locations and actions possible in the OS.
- A menu which can be text-based, icon-based or a combination of both can be used as a selection system for various tasks.
- A pointer represents the location of a device movement, typically a mouse used to make selections in the GUI.
Because WIMP is so common, it has been erroneously used as a synonym for the GUI. This is false because even though all WIMP systems are a type of GUI, not all types of GUIs are WIMP, some do not use windows to isolate applications, and mobile operating systems like Android and iOS use icons, widgets and menus, but not windows or pointing devices.
ПАКЕТНАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ И ИНТЕРФЕЙС КОМАНДНОЙ СТРОКИ
Пакетная технология – «черный ящик», в который постоянно подается информация и который также «информирует» мир о своем состоянии. Человек здесь имеет малое влияние на работу машины – он может приостановить работу машины,
сменить программу и вновь запустить.
высокая скорость обработки
эффективность и экономия использования ресурсов системы.
алгоритмическая полнота: в GUI пользователь ограничен теми возможностями, для которых разработчик программы нарисовал иконки или сочинил пункты в меню.
Любопытно, что последнее достижение в области пользовательского интерфейса – распознавание речи и голосовое управление – означает, по существу, возврат к командному языку, с той лишь разницей, что команды произносятся.
ДИАЛОГОВАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ И ГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС (GUI)
1 этап: Простой графический интерфейс
Отличительные особенности этого интерфейса:
1) Выделение областей экрана.
2) Переопределение клавиш клавиатуры в зависимости от контекста.
3) Использование манипуляторов и клавиш клавиатуры для управления курсором.
4) Широкое использование цветных мониторов.
Появление этого типа интерфейса совпадает с широким распространением операционной системы MS-DOS
Примеры: файловая оболочка Nortron Commander и текстовый редактор Multi-Edit,текстовые редакторы Лексикон, текстовый процессор Microsoft Word for Dos
ГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС WIMP (WINDOW, ICON, MENU, POINTER)
1. Вся работа с программами, файлами и документами происходит в окнах – определенных очерченных рамкой частях экрана.
2. Все программы, файлы, документы, устройства и другие объекты представляются в виде значков – иконок. При открытии иконки превращаются в окна.
3. Все действия с объектами осуществляются с помощью меню. Хотя меню появилось
на первом этапе становления графического интерфейса, оно не имело в нем
главенствующего значения, а служило лишь дополнением к командной строке. В WIMP- интерфейсе меню становится основным элементом управления.
4. Широкое использование манипуляторов для указания на объекты. Манипулятор
перестает быть просто игрушкой – дополнением к клавиатуре, а становится основным элементом управления. С помощью манипулятора УКАЗЫВАЮТ на любую область экрана, окна или иконки, ВЫДЕЛЯЮТ ее, а уже потом через меню или с использованием других технологий осуществляют управление ими.
Cейчас WIMP-интерфейс стал стандартом де-факто
Одним из требований к хорошему графическому интерфейсу является концепция «делай то, что я имею в виду» или DWIM (Do What I Mean)
СТРУКТУРУ ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЯ ДЛЯ ГРАФИЧЕСКОГО ИНТЕРФЕЙСА
Структуру взаимодействия для графического интерфейса пользователя можно разделить на:
Множественные окна. Оконная технология. Суть “оконной технологии” заключается в том, что для каждой программы на экране отводится прямоугольный сектор – окно, причем все операции с данной программой пользователь выполняет именно в нем.
MDI (многодокументный интерфейс) — способ организации графического интерфейса пользователя, предполагающий использование оконного интерфейса, в котором большинство окон (исключая, как правило, только модальные окна) расположены внутри одного общего окна.
Множественные фреймы – множественные окна, позволяющие выводить в
одном окне браузера, несколько страниц одновременно.
Неструктурированное взаимодействие: экраны с гиперссылками (гиперссылки – это подход для обращения с текстовой и графической информацией, который позволяет пользователям перескакивать от данной темы, когда они захотят, к относящимся к ней идеям. Гипертекст позволяет пользователям осуществлять доступ к информации нелинейно, следуя мысленному ряду, управлять уровнем детализации и выбирать тип отображаемой информации, позволяет осуществлять быстрый поиск в
соответствии с интересом пользователя).
ГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС WIMP ПРЕИМУЩЕСТВА/НЕДОСТАТКИ
чем более сложным является приложение, тем труднее осваивать интерфейс, причем эти трудности возрастают нелинейно
пользователи часто бывают раздражены слишком большим количеством слоев, возникающих в процессе point and click
(принцип Point and Click (указать и щелкнуть)
Если же приложение является по своей сути трехмерным, то
работа с ним с помощью 2D элементов управления становится
не слишком естественной
не все пользователи способны эффективно использовать
мышь и клавиатуру (никак не используют такие каналы взаимодействия, как речь и слух)
Билл Бакстон (Bill Buxton) из Aliias/Wavefront: WIMP- интерфейсы являются совершенным инструментом только для существ с одним глазом, одним пальцем, лишенных всяких иных органов чувств.
РЕЧЕВАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ
SILK-интерфейс (Speech – речь, Image – образ,
Language – язык, Knowledge – знание).
I. Первая задача состоит в том, чтобы компьютер мог «понять» то, что ему говорит человек, то есть он доложен уметь извлекать из речи человека полезную информацию.
II. Вторая задача состоит в том, чтобы компьютер воспринял смысл сказанного.
III. Третья задача состоит в том, чтобы компьютер мог преобразовать информацию, с которой он оперирует, в речевое сообщение, понятное человеку.
БИОМЕТРИЧЕСКАЯ ТЕХНОЛОГИЯ
Для управления компьютером используется выражение лица человека, направление его взгляда, размер зрачка и другие признаки. Для идентификации пользователя используется рисунок радужной оболочки его глаз, отпечатки пальцев и другая уникальная информация. Изображения считываются с цифровой видеокамеры, а затем с помощью специальных программ распознавания образов из этого изображения выделяются команды.
СЕМАНТИЧЕСКИЙ (ОБЩЕСТВЕННЫЙ) ИНТЕРФЕЙС
Его трудно назвать самостоятельным видом интерфейса – он включает в себя и интерфейс командной строки, и графический, и речевой, и мимический интерфейс. Основная его отличительная черта – это отсутствие команд при общении с компьютером. Запрос формируется на естественном языке, в виде связанного текста и образов. По своей сути это трудно называть интерфейсом – это уже моделирование «общения» человека с компьютером.
СЕНСОРНЫЙ (ЖЕСТОВЫЙ) ИНТЕРФЕЙС
Сенсорный интерфейс, который состоит из сенсорной панели и контроллера. Сенсорная панель накладывается на поверхность внешнего экрана монитора и улавливает нажатия на нее. Сенсорный контроллер – это устройство, которое преобразовывает данные с сенсорной панели в понятный для компьютера формат. В основе проектирования – точность управления.
На сегодняшний день все лидеры игрового рынка представили свои
решения в сфере жестовых интерфейсов. Первой на рынок вышла Nintendo с Wii, следом за ней с небольшим отставанием последовали Microsoft с Kinect и Sonu с Move.
ТАКТИЛЬНЫЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС
Тактильный интерфейс – это интерфейс с обратной связью (сопротивление
усилиям пользователя в соответствии с происходящими на экране событиями).
Объектами интерфейса можно не только управлять, их можно чувствовать.
Тактильные устройства, в отличие от других интерактивных устройств, способны как «чувствовать», так и передавать информацию. Таким образом, дизайнеры тактильных интерфейсов рассматривают две равно важные стороны: тактильные ощущения (чувство касания) и «кинестетическое» (kinesthetic) чувство (ощущение, где находится тело).
НЕЙРОКОМПЬЮТЕРНЫЙ ИНТЕРФЕЙС
Первый в мире коммерчески доступный нейрокомпьютерный интерфейс привезла компания Guger Technologies на выставку CeBIT 2010.
Устройство Intendix предназначено в первую очередь для парализованных пациентов больниц. Интерфейс готов к использованию через 10 минут настройки. После тренировки можно набирать тексты с экранной клавиатуры на скорости до 1,25 символа в секунду путём концентрации внимания на строках
и столбцах, мерцающих
снимает сигнал с коры головного мозга. Такая скорость является рекордной для прототипов подобных устройств.