Windows код события 4672
Сообщения: 51908
Благодарности: 14931
| Конфигурация компьютера |
| Материнская плата: ASUS P8Z77-V LE PLUS |
| HDD: Samsung SSD 850 PRO 256 Гб, WD Green WD20EZRX 2 Тб |
| Звук: Realtek ALC889 HD Audio |
| CD/DVD: ASUS DRW-24B5ST |
| ОС: Windows 8.1 Pro x64 |
| Прочее: корпус: Fractal Design Define R4 |
| В логе безопасности в то время когда система висит |
Правой кнопкой мыши -> Копировать -> Копировать сведения как текст -> выложите.
Также смотрите в других разделах: Приложение и Система.
«Вход в систему» в вашем случае может означать запуск задачи планировщиком — смотрите в Пуск -> Панель управления -> Администрирование -> Планировщик заданий.
| Имя журнала: Security Источник: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing Дата: 26.03.2013 4:28:44 Код события: 4624 Категория задачи:Вход в систему Уровень: Сведения Ключевые слова:Аудит успеха Пользователь: Н/Д Компьютер: mypc-PC Описание: Вход с учетной записью выполнен успешно. |
Субъект:
ИД безопасности: система
Имя учетной записи: MYPC-PC$
Домен учетной записи: WORKGROUP
Код входа: 0x3e7
Новый вход:
ИД безопасности: система
Имя учетной записи: система
Домен учетной записи: NT AUTHORITY
Код входа: 0x3e7
GUID входа:
Сведения о процессе:
Идентификатор процесса: 0x1d0
Имя процесса: C:\Windows\System32\services.exe
Сведения о сети:
Имя рабочей станции:
Сетевой адрес источника: —
Порт источника: —
Сведения о проверке подлинности:
Процесс входа: Advapi
Пакет проверки подлинности: Negotiate
Промежуточные службы: —
Имя пакета (только NTLM): —
Длина ключа: 0
Данное событие возникает при создании сеанса входа. Оно создается в системе, вход в которую выполнен.
Поля «Субъект» указывают на учетную запись локальной системы, запросившую вход. Обычно это служба, например, служба «Сервер», или локальный процесс, такой как Winlogon.exe или Services.exe.
В поле «Тип входа» указан тип выполненного входа. Самыми распространенными являются типы 2 (интерактивный) и 3 (сетевой).
Поля «Новый вход» указывают на учетную запись, для которой создан новый сеанс входа, то есть на учетную запись, с которой выполнен вход.
В полях, которые относятся к сети, указан источник запроса на удаленный вход. Имя рабочей станции доступно не всегда, и в некоторых случаях это поле может оставаться незаполненным.
Поля сведений о проверке подлинности содержат подробные данные о конкретном запросе на вход.
— GUID входа — это уникальный идентификатор, который позволяет сопоставить данное событие с событием KDC.
— В поле «Промежуточные службы» указано, какие промежуточные службы участвовали в данном запросе на вход.
— Поле «Имя пакета» указывает на подпротокол, использованный с протоколами NTLM.
— Поле «Длина ключа» содержит длину созданного ключа сеанса. Это поле может иметь значение «0», если ключ сеанса не запрашивался.
Xml события:
4624
0
0
12544
0
0x8020000000000000
1120
Security
mypc-PC
S-1-5-18
MYPC-PC$
WORKGROUP
0x3e7
S-1-5-18
система
NT AUTHORITY
0x3e7
5
Advapi
Negotiate
<00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000>
—
—
0
0x1d0
C:\Windows\System32\services.exe
—
—
| Имя журнала: Security Источник: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing Дата: 26.03.2013 4:28:44 Код события: 4672 Категория задачи:Специальный вход Уровень: Сведения Ключевые слова:Аудит успеха Пользователь: Н/Д Компьютер: mypc-PC Описание: Новому сеансу входа назначены специальные привилегии. |
Субъект:
ИД безопасности: система
Имя учетной записи: система
Домен учетной записи: NT AUTHORITY
Код входа: 0x3e7
Привилегии: SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege
SeTcbPrivilege
SeSecurityPrivilege
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
SeLoadDriverPrivilege
SeBackupPrivilege
SeRestorePrivilege
SeDebugPrivilege
SeAuditPrivilege
SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege
SeImpersonatePrivilege
Xml события:
4672
0
0
12548
0
0x8020000000000000
1121
Security
mypc-PC
S-1-5-18
система
NT AUTHORITY
0x3e7
SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege
SeTcbPrivilege
SeSecurityPrivilege
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
SeLoadDriverPrivilege
SeBackupPrivilege
SeRestorePrivilege
SeDebugPrivilege
SeAuditPrivilege
SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege
SeImpersonatePrivilege
В приложениях и системе ничего странного нет, кроме, может быть, кучи вот таких записей в системе:
4672(S): Special privileges assigned to new logon.
Applies to
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
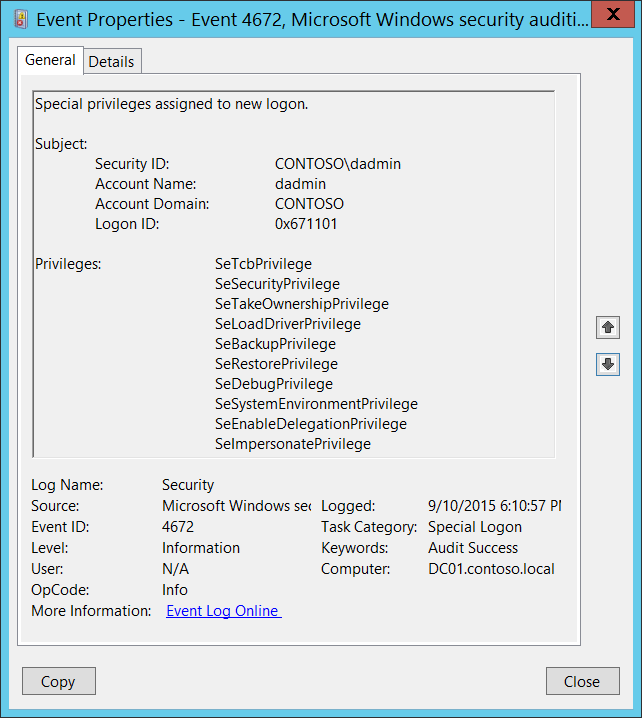
Event Description:
This event generates for new account logons if any of the following sensitive privileges are assigned to the new logon session:
SeTcbPrivilege — Act as part of the operating system
SeBackupPrivilege — Back up files and directories
SeCreateTokenPrivilege — Create a token object
SeDebugPrivilege — Debug programs
SeEnableDelegationPrivilege — Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation
SeAuditPrivilege — Generate security audits
SeImpersonatePrivilege — Impersonate a client after authentication
SeLoadDriverPrivilege — Load and unload device drivers
SeSecurityPrivilege — Manage auditing and security log
SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege — Modify firmware environment values
SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege — Replace a process-level token
SeRestorePrivilege — Restore files and directories,
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege — Take ownership of files or other objects
You typically will see many of these events in the event log, because every logon of SYSTEM (Local System) account triggers this event.
NoteВ В For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Subject:
- Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account to which special privileges were assigned. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
NoteВ В A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account to which special privileges were assigned.
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: subject’s domain or computer name. Formats vary, and include the following:
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
For some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is “NT AUTHORITY”.
For local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: “Win81”.
Logon ID [Type = HexInt64]: hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, “4624: An account was successfully logged on.”
Privileges [Type = UnicodeString]: the list of sensitive privileges, assigned to the new logon. The following table contains the list of possible privileges for this event:
| Privilege Name | User Right Group Policy Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege | Replace a process-level token | Required to assign the primary token of a process. With this privilege, the user can initiate a process to replace the default token associated with a started subprocess. |
| SeAuditPrivilege | Generate security audits | With this privilege, the user can add entries to the security log. |
| SeBackupPrivilege | Back up files and directories | — Required to perform backup operations. With this privilege, the user can bypass file and directory, registry, and other persistent object permissions for the purposes of backing up the system. This privilege causes the system to grant all read access control to any file, regardless of the access control list (ACL) specified for the file. Any access request other than read is still evaluated with the ACL. The following access rights are granted if this privilege is held: READ_CONTROL ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY FILE_GENERIC_READ FILE_TRAVERSE |
| SeCreateTokenPrivilege | Create a token object | Allows a process to create a token which it can then use to get access to any local resources when the process uses NtCreateToken() or other token-creation APIs. When a process requires this privilege, we recommend using the LocalSystem account (which already includes the privilege), rather than creating a separate user account and assigning this privilege to it. |
| SeDebugPrivilege | Debug programs | Required to debug and adjust the memory of a process owned by another account. With this privilege, the user can attach a debugger to any process or to the kernel. We recommend that SeDebugPrivilege always be granted to Administrators, and only to Administrators. Developers who are debugging their own applications do not need this user right. Developers who are debugging new system components need this user right. This user right provides complete access to sensitive and critical operating system components. |
| SeEnableDelegationPrivilege | Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation | Required to mark user and computer accounts as trusted for delegation. With this privilege, the user can set the Trusted for Delegation setting on a user or computer object. The user or object that is granted this privilege must have write access to the account control flags on the user or computer object. A server process running on a computer (or under a user context) that is trusted for delegation can access resources on another computer using the delegated credentials of a client, as long as the account of the client does not have the Account cannot be delegated account control flag set. |
| SeImpersonatePrivilege | Impersonate a client after authentication | With this privilege, the user can impersonate other accounts. |
| SeLoadDriverPrivilege | Load and unload device drivers | Required to load or unload a device driver. With this privilege, the user can dynamically load and unload device drivers or other code in to kernel mode. This user right does not apply to Plug and Play device drivers. |
| SeRestorePrivilege | Restore files and directories | Required to perform restore operations. This privilege causes the system to grant all write access control to any file, regardless of the ACL specified for the file. Any access request other than write is still evaluated with the ACL. Additionally, this privilege enables you to set any valid user or group SID as the owner of a file. The following access rights are granted if this privilege is held: WRITE_DAC WRITE_OWNER ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY FILE_GENERIC_WRITE FILE_ADD_FILE FILE_ADD_SUBDIRECTORY DELETE With this privilege, the user can bypass file, directory, registry, and other persistent objects permissions when restoring backed up files and directories and determines which users can set any valid security principal as the owner of an object. |
| SeSecurityPrivilege | Manage auditing and security log | Required to perform a number of security-related functions, such as controlling and viewing audit events in security event log. With this privilege, the user can specify object access auditing options for individual resources, such as files, Active Directory objects, and registry keys. A user with this privilege can also view and clear the security log. |
| SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege | Modify firmware environment values | Required to modify the nonvolatile RAM of systems that use this type of memory to store configuration information. |
| SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege | Take ownership of files or other objects | Required to take ownership of an object without being granted discretionary access. This privilege allows the owner value to be set only to those values that the holder may legitimately assign as the owner of an object. With this privilege, the user can take ownership of any securable object in the system, including Active Directory objects, files and folders, printers, registry keys, processes, and threads. |
| SeTcbPrivilege | Act as part of the operating system | This privilege identifies its holder as part of the trusted computer base. This user right allows a process to impersonate any user without authentication. The process can therefore gain access to the same local resources as that user. |
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4672(S): Special privileges assigned to new logon.
Monitor for this event where “Subject\Security ID” is not one of these well-known security principals: LOCAL SYSTEM, NETWORK SERVICE, LOCAL SERVICE, and where “Subject\Security ID” is not an administrative account that is expected to have the listed Privileges.
If you have a list of specific privileges which should never be granted, or granted only to a few accounts (for example, SeDebugPrivilege), use this event to monitor for those “Privileges.”
- If you are required to monitor any of the sensitive privileges in the Event Description for this event, search for those specific privileges in the event.
—>




