- Отключение NTLM аутентификации в домене Windows
- Переключаемся на использование NTLMv2
- Аудит событий NTLM аутентификации в домене
- Полное отключение NTLM в домене Active Directory
- Network security: LAN Manager authentication level
- Reference
- Possible values
- Best practices
- Location
- Default values
- Operating system version differences
- Policy management
- Restart requirement
- Group Policy
- Security considerations
- Vulnerability
- Countermeasure
- Potential impact
Отключение NTLM аутентификации в домене Windows
NTLM (NT LAN Manager) – это довольно старый протокол аутентификации Microsoft, который появился еще в Windows NT. Несмотря на то, что еще в Windows 2000 Майкрософт внедрила более безопасный протокол аутентификации Kerberos, NTLM (в основном это NTLMv2) широко используется для аутентификации в Windows сетях до сих пор. В этом статье мы рассмотрим особенности процесс отключения протокола NTLMv1 и NTLMv2, и перехода на Kerberos в домене Active Directory.
Основные проблема NTLMv1 – слабое шифрование, хранение хэша пароля в оперативной памяти в службе LSA, который может извлечь различными утилитами (типа mimikatz) и использовать хэш для дальнейших атак, отсутствие взаимной проверки подлинности клиента и сервера, что делает вполне реальными атаки перехвата данных и неавторизованного доступа к ресурсам сети (утилиты типа Responder могут перехватывать данные NTLM, передаваемые по сети и использовать их для доступа к сетевым ресурсам) и ряд других уязвимостей.
Часть этих недостатков исправлена в более новой версии NTLMv2, который использует более криптостойкие алгоритмы шифрования и позволяет предотвратить популярные атаки на NTLM. Начиная с Windows 7 / Windows Server 2008 R2 использование NTLMv1 и LM для авторизации по умолчанию выключено.
Переключаемся на использование NTLMv2
Если вы задумались полностью отказаться от NTLM в своем домене, сначала нужно убедиться, что у вас не используется его более уязвимая версия- NTLMv1. Вероятно в вашей сети имеется ряд устаревших устройств или служб, которые все еще используют аутентификацию NTLMv1 вместо NTLMv2 (или Kerberos). Поэтому прежде, чем прибегнуть к его полному отключению прочитайте раздел этой статьи по аудиту событий авторизации с помощью NTLM.
В первую очередь администратору домена нужно убедиться, что в его сети запрещено использовать NTLM или LM для авторизации, т.к. в некоторых случаях атакующий может с помощью специальных запросов получить ответ на NTLM/LM запрос.
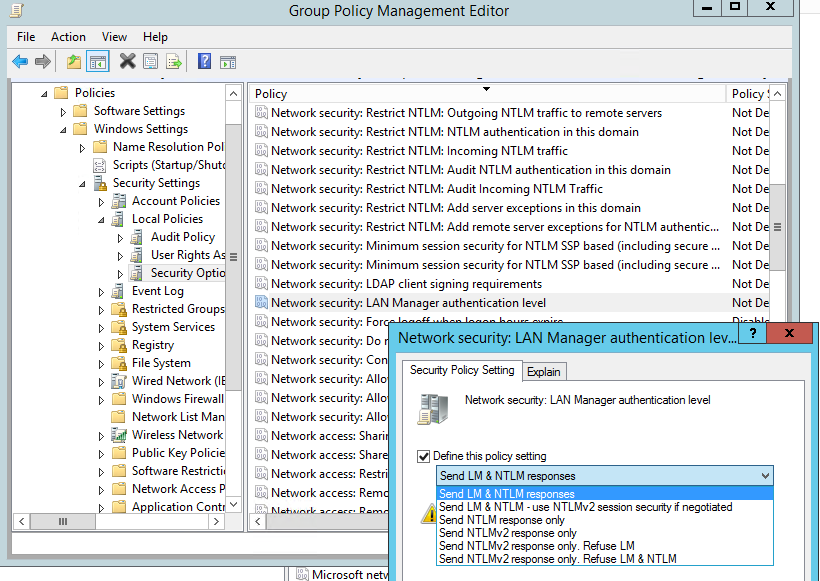
Тип аутентификации можно задать с помощью доменной (или локальной) политики. Откройте консоль управления доменными политиками и отредактируйте Default Domain Policy. Перейдите в раздел Computer Configurations -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options и найдите политику
Network Security: LAN Manager authentication level (Сетевая безопасность: уровень проверки подлинности LAN Manager).
В настройках политики есть 6 опций:
- Send LM & NTLM responses;
- Send LM & NTLM responses – use NTLMv2 session security if negotiated;
- Send NTLM response only;
- Send NTLMv2 response only;
- Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM;
- Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM& NTLM.
Политики использования NTLM аутентификации расположены в порядке возрастания их безопасности. По умолчанию в Windows 7 и выше используется настройка Send NTLMv2 response only (Отправлять только NTLMv2-ответ). При этой настройке клиентские компьютеры используют NTLMv2 аутентификацию, но контролеры домены принимают LM, NTLM, и NTLMv2 запросы.
Вы можете изменить значение политики на более безопасную 6 опцию — “Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM & NTLM”. При этой политике контролеры домена также будут отвергать запросы LM и NTLM.
Также вы можете отключить NTLMv1 через реестр. Для этого в ветке
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Lsa нужно создать параметр DWORD с именем LmCompatibilityLevel и значением от 0 до 5. Значение 5 соответствует значению политики «Отправлять только NTLMv2-ответ. Отказывать LM и NTLM».
Не забудьте применить эту политику для контроллеров домена.
Если вы убедились, что у вас не используется NTLMv1, вы можете пойти дальше и попытаться отказаться от NTLMv2. NTLMv2 хотя и более защищенный протокол аутентификации, но все равно существенно проигрывает Kerberos в плане безопасности (хотя уязвимостей в NTLMv2 намного меньше, чем в первой версии протокола, все-таки существуют возможности перехвата и повторного использования данных, и отсутствует взаимная аутентификации).
Главная риск отключения NTLM – возможное использование в домене устаревших или некорректно настроенных приложений, которые все еще могут использовать проверку подлинности NTLM, и для перехода на Kerberos их придется обновлять или настраивать особым образом.
Аудит событий NTLM аутентификации в домене
Перед полным отключением NTLM в домене и переходе на Kerberos желательно убедиться, что в домене не осталось приложений, которые требуют и используют NTLM авторизацию.
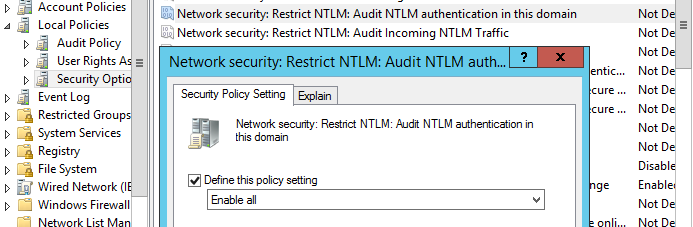
Для отслеживания учетных записей и приложение, которые используют NTLM аутентификацию, вы можете включить политики аудита на всех компьютерах с помощью GPO. В разделе Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options найдите и включите политику Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Audit NTLM authentication in this domain, установив ее значение на Enable all.
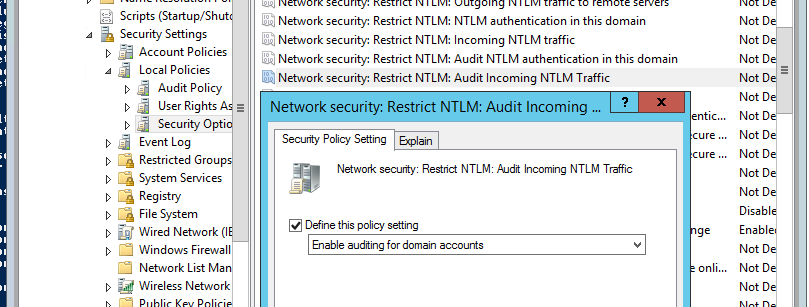
Аналогичным образом включите политику Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Audit Incoming NTLM Traffic, установив ее значение на Enable auditing for domain accounts.
После включения данных политик события использования NTLM аутентификации записываться в журнал событий Event Viewer в секцию Application and Services Logs-> Microsoft -> Windows -> NTLM.
Можно проанализировать события на каждом сервере, или собрать все события в центральный Event Log.
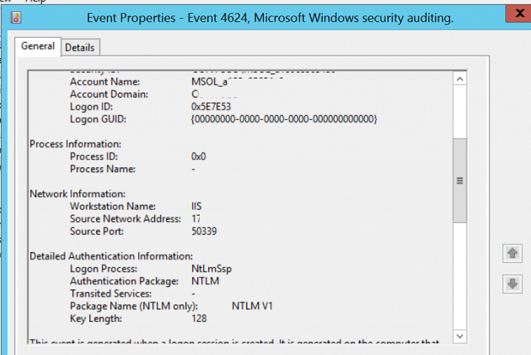
Вам нужно собрать события от Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing c Event ID 4624 – An Account was successfully logged on. Обратите внимание на информацию в секции “Detailed Authentication Information”. Если в строке Authentication Package указано NTLM, значит для аутентификации этого пользователя использовался протокол NTLM.
Теперь обратите внимание на значение Package Name (NTLM only). Здесь должно быть указано какой протокол (LM, NTLMv1 или NTLMv2) использовался для аутентификации. Таким образом вам нужно идентифицировать все сервера/приложения, которые используют устаревший протокол.
Например, для поиска всех событий аутентификации по NTLMv1 по всем контроллерам домена можно использовать такой PowerShell скрипт:
$ADDCs = Get-ADDomainController -filter * -Server winitpro.ru
$Now = Get-Date
$Yesterday = $Now.AddDays(-1)
$NewOutputFile = «c:\ps\Events\$($Yesterday.ToString(‘yyyyMMdd’))_AD_NTLMv1_events.log»
function GetEvents($DC)<
Write-Host «Searching log on » $DC.HostName
$Events = Get-EventLog «Security» -After $Yesterday.Date -Before $Now.Date -ComputerName $DC.HostName -Message «*V1*» -instanceid 4624
foreach($Event in $Events)<
Write-Host $DC.HostName $Event.EventID $Event.TimeGenerated
Out-File -FilePath $NewOutputFile -InputObject «$($Event.EventID), $($Event.MachineName), $($Event.TimeGenerated), $($Event.ReplacementStrings),($Event.message)» -Append
>
>
foreach($DC in $ADDCs)
После того, как вы нашли пользователей и приложения, использующие NTLM в вашем домене, попробуйте перевести их на использование Kerberos (возможно с использованием SPN). Некоторые приложения достаточно донастроить для работы Kerberos авторизации (см. статьи Kerberos авторизация в IIS, использование Kerberos авторизация в браузерах). Из личного опыта: даже действительно большие коммерческие продукты иногда еще не перешли с использования NTLM на Kerberos, некоторые продукты требуют обновления или изменений конфигурации. Все сводится к определению того, какие приложения используют проверку подлинности NTLM, и теперь у вас есть способ для выяснения этого софта и устройств.
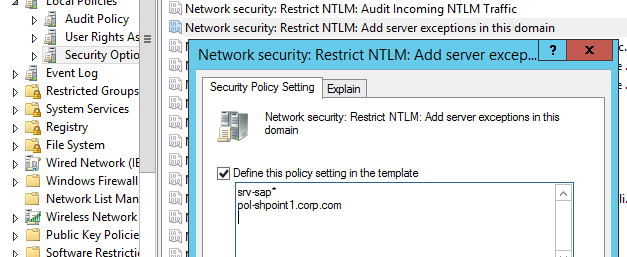
Те приложений, которые нельзя переключить на использование NTLM можно добавить в исключения, разрешив им использовать NTLM аутентификацию, даже если она отключена на уровне домена. Для этого используется политика Network security: Restrict NTLM: Add server exceptions for NTLM authentication in this domain. В список исключений нужно добавить имена серверов, для аутентификации на которых можно использовать NTLM (конечно, в идеале этот список исключений должен быть пустым). Можно использовать знак подстановки *.
Полное отключение NTLM в домене Active Directory
Чтобы проверить, как будет работать аутентификация в различных приложениях в домене без использования NTLM, вы можете добавить учетные записи необходимых пользователей в доменную группу
Protected Users (группа доступна, начиная с Windows Server 2012 R2), членам которой можно аутентифицироваться только по протоколу Kerberos (нельзя использовать NTLM, Digest Authentication или CredSSP). Так вы можете проверить корректность Kerberos аутентификации пользователя в различных приложениях.
Теперь вы можете полностью отключить NTLM в домене с помощью групповой политики Network Security: Restrict NTLM: NTLM authentication in this domain.
В этой политике доступно 5 опций:
- Disable: политика отключена (NTLM аутентификация в домене разрешена);
- Deny for domain accounts to domain servers: контролеры домена запрещают попытки аутентификации NTLM для всех серверов под доменными аккаунтами, возвращается ошибка «NTLM заблокирован»;
- Deny for domain accounts: контролеры домена запрещают попытки NTLM аутентификации для всех учетных записей домена, возвращается ошибка «NTLM заблокирован»;
- Deny for domain servers: запрещены запросы NTLM аутентификации для всех серверов;
- Deny all: контроллеры домена блокируют все запросы NTLM для всех серверов и учетных записей.
Network security: LAN Manager authentication level
Applies To: Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8
This security policy reference topic for the IT professional describes the best practices, location, values, policy management and security considerations for this policy setting. This information applies to computers running at least the Windows Server 2008 operating system.
Reference
This policy setting determines which challenge or response authentication protocol is used for network logons. LAN Manager (LM) includes client computer and server software from Microsoft that allows users to link personal computers together on a single network. Network capabilities include transparent file and print sharing, user security features, and network administration tools. In Active Directory domains, the Kerberos protocol is the default authentication protocol. However, if the Kerberos protocol is not negotiated for some reason, Active Directory uses LM, NTLM, or NTLM version 2 (NTLMv2).
LAN Manager authentication includes the LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 variants, and it is the protocol that is used to authenticate all client computers running the Windows operating system when they perform the following operations:
Authenticate between Active Directory forests
Authenticate to domains based on earlier versions of the Windows operating system
Authenticate to computers that do not run WindowsВ operating systems, beginning with WindowsВ 2000
Authenticate to computers that are not in the domain
Possible values
Send LM & NTLM responses
Send LM & NTLM — use NTLMv2 session security if negotiated
Send NTLM responses only
Send NTLMv2 responses only
Send NTLMv2 responses only. Refuse LM
Send NTLMv2 responses only. Refuse LM & NTLM
The Network security: LAN Manager authentication level setting determines which challenge/response authentication protocol is used for network logons. This choice affects the authentication protocol level that clients use, the session security level that the computers negotiate, and the authentication level that servers accept. The following table identifies the policy settings, describes the setting, and identifies the security level used in the corresponding registry setting if you choose to use the registry to control this setting instead of the policy setting.
Registry security level
Send LM & NTLM responses
Client computers use LM and NTLM authentication, and they never use NTLMv2 session security. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication.
Send LM & NTLM – use NTLMv2 session security if negotiated
Client computers use LM and NTLM authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication.
Send NTLM response only
Client computers use NTLMv1 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication.
Send NTLMv2 response only
Client computers use NTLMv2 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers accept LM, NTLM, and NTLMv2 authentication.
Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM
Client computers use NTLMv2 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers refuse to accept LM authentication, and they will accept only NTLM and NTLMv2 authentication.
Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM & NTLM
Client computers use NTLMv2 authentication, and they use NTLMv2 session security if the server supports it. Domain controllers refuse to accept LM and NTLM authentication, and they will accept only NTLMv2 authentication.
Best practices
- Best practices are dependent on your specific security and authentication requirements.
Location
GPO_name\Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options
Default values
The following table lists the actual and effective default values for this policy. Default values are also listed on the policy’s property page.
Server type or GPO
Default Domain Policy
Default Domain Controller Policy
Stand-Alone Server Default Settings
Send NTLMv2 response only
DC Effective Default Settings
Send NTLMv2 response only
Member Server Effective Default Settings
Send NTLMv2 response only
Client Computer Effective Default Settings
Operating system version differences
In Windows ServerВ 2003, the Default Domain Controllers Policy was Send NTLM response only, which changed to Not defined in later versions.
In WindowsВ Vista, Windows ServerВ 2008, WindowsВ 7, and Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, the default is Send NTLMv2 response only.
Policy management
This section describes features and tools that are available to help you manage this policy.
Restart requirement
None. Changes to this policy become effective without a computer restart when they are saved locally or distributed through Group Policy.
Group Policy
Modifying this setting may affect compatibility with client computers, services, and applications.
Security considerations
This section describes how an attacker might exploit a feature or its configuration, how to implement the countermeasure, and the possible negative consequences of countermeasure implementation.
Vulnerability
In WindowsВ 7 and WindowsВ Vista, this setting is undefined. In WindowsВ ServerВ 2008В R2 and Windows ServerВ 2008 this setting is configured to Send NTLMv2 responses only. In WindowsВ 2000, Windows ServerВ 2003, and WindowsВ XP, client computers are configured by default to send LM and NTLM authentication responses (WindowsВ 95-based and WindowsВ 98-based client computers only send LM). The default setting on servers allows all client computers to authenticate with servers and use their resources. However, this means that LM responses—the weakest form of authentication response—are sent over the network, and it is potentially possible for attackers to intercept that traffic to reproduce the user’s password more easily.
The WindowsВ 95, WindowsВ 98, and WindowsВ NT operating systems cannot use Kerberos protocol version 5 for authentication. For this reason, in a Windows ServerВ 2003 domain, these computers authenticate by default with both the LM and NTLM protocols for network authentication. You can enforce a more secure authentication protocol for WindowsВ 95, WindowsВ 98, and WindowsВ NT by using NTLMv2. For the logon process, NTLMv2 uses a secure channel to protect the authentication process. Even if you use NTLMv2 for client computers and servers running these early versions of the Windows operating system, Windows-based client computers and servers that are members of the domain use the Kerberos protocol to authenticate with Windows ServerВ 2003 domain controllers.
Countermeasure
Configure the Network security: LAN Manager Authentication Level setting to Send NTLMv2 responses only. Microsoft and a number of independent organizations strongly recommend this level of authentication when all client computers support NTLMv2.
For more information about how to enable NTLMv2 on older versions of the Windows operating system, see article 239869 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base. WindowsВ NTВ 4.0 requires Service PackВ 4 (SP4) to support NTLMv2, and WindowsВ 95 and WindowsВ 98 need the directory service client installed to support NTLMv2.
Potential impact
Client computers that do not support NTLMv2 authentication cannot authenticate in the domain and access domain resources by using LM and NTLM.
For information about a hotfix to ensure that this setting works in networks that include Windows NT 4.0-based computers along with Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003-based computers, see article 305379 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base.