- Windows linux and unix are different computer operating system ответы
- Windows VS Linux: 8 ключевых отличий операционных систем
- 1. Дистрибутивы
- Что такое дистрибутив Linux?
- 2. Исходный код
- 3. Интерфейсы рабочего стола
- 4. Приложения
- 5. Файловая система
- Файловая система
- 6. Реестр
- 7. Драйверы
- А как насчет видеокарт?
- 8. Команды и инструменты разработки
- Linux vs Windows: What’s the Difference?
- Windows Vs. Linux File System
- KEY DIFFERENCE
- Types of Files
- General Files
- Directory Files
- Device Files:
- Windows Vs. Linux: Users
- Regular User
- Root User
- Service user
- Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
- Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
- Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
Windows linux and unix are different computer operating system ответы
1. UNIX :
UNIX is a powerful, multi-user and multitasking operating system originally developed at AT & T Bell Laboratories. This operating system is very popular among the scientific, engineering and academic due to its most appreciating features like flexibility, portability, network capabilities etc.
2. Windows :
Microsoft window is a most demanding Graphical user Interface (GUI) based operating system that replaces all the command line based functions to the user friendly screens. Microsoft introduced a series of versions with the latest functions.
Difference between UNIX and Windows Operating System :
| Sr. No. | Basis | UNIX | Windows |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Open Source Code | It is an open source code. | It is not an open source code. |
| 2. | Stability | It is more stable. | As, multiple programs are running. So it is unstable. |
| 3. | Case-sensitivity | It is case sensitive. | It is not a case sensitive. |
| 4. | File-extension | In this, extensions have not affect on the type of file. | In this, certain file extensions are used to identify the type of file. |
| 5. | Device drive | In this, several ways are used to manage the device drivers. | After the installation of Windows, the various device-drivers packages provide interactive GUI for the configuration of devices. |
| 6. | Recovery | We cannot recover our data. | In this, we can recover our data from the recycle-bin, because in this after the deletion of data it will store in the recycle-bin. |
| 7. | Processing Power | It has greater processing power. | It has less processing power. |
| 8. | Security | It has greater in-built security. | It has less in-built security. |
| 9. | Virus Attacks | It has interface between user and kernel known as shell, so it does not face any virus attack. | In this, we don’t have shell interface. User direct interact with hardware and it enhances the attack of virus. |
| 10. | File-system | In this, file system is represented as a hierarchical tree under the same root. There is no drive system like drive C, drive D etc. | In this, file system can have many hierarchies; for example, different file system for each partitions and these partitions are represented as drive alphabet letters like as C: D: etc. |
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready.
Windows VS Linux: 8 ключевых отличий операционных систем
Linux появился как страстный проект по созданию операционной системы, которую каждый мог использовать или переделывать по своему усмотрению. Сегодня миллионы людей считают Linux удобной и мощной альтернативой Windows.
Не определились между Linux и Windows? Давайте посмотрим на различия между ними и поможем вам определить, готовы ли вы к новым ощущениям.
1. Дистрибутивы
Существует одна текущая версия Windows, которая поставляется в нескольких разных редакциях. Различия между этими выпусками в основном связаны с дополнительными функциями для использования в корпоративной или образовательной среде.
Не существует единой установленной версии Linux. Вместо этого есть много разных версий, известных как «дистрибутивы» Linux. Существуют сотни различных вариантов, хотя вы можете сузить список выдающихся дистрибутивов, которыми пользуется большинство людей, до менее десятка.
Что касается стоимости операционной системы Linux? Практически все дистрибутивы Linux бесплатны, а некоторые корпоративные варианты требуют контракта на поддержку.
Что такое дистрибутив Linux?
Linux не является единой операционной системой. Название на самом деле относится только к ядру, относительно невидимой части функционирования вашей операционной системы. Интерфейс, который вы видите на своем экране, сервере дисплея, звуковой системе и в приложении — все это из разных источников.
Дистрибуция — это способ объединения всего этого программного обеспечения, чтобы предоставить вам работающий компьютер.
Поскольку существует множество способов соединить эти компоненты в соответствии с желаниями или потребностями человека, существует множество дистрибутивов.
2. Исходный код
Windows является проприетарной операционной системой. Исходный код закрыт, что означает, что вам нужно работать в Microsoft или получить разрешение от Microsoft, чтобы увидеть код, который используется в вашей операционной системе. Если вы попытаетесь получить доступ или распространить этот код без разрешения, вы можете столкнуться с юридической проблемой.
Linux — бесплатная операционная система с открытым исходным кодом. Вы можете свободно просматривать код, учиться на нем, вносить любые изменения и делиться им с другими. Вы по-прежнему должны соблюдать лицензию с открытым исходным кодом, но это обычно означает, что вы не вправе брать код и перепаковывать его в проприетарное программное обеспечение.
3. Интерфейсы рабочего стола
До Windows 8 интерфейс Windows долгое время не испытывал особых инноваций. Меню «Пуск», панель задач, системный трей, проводник Windows — все это было в основном одно и то же, и все это было восстановлено с помощью Windows 10.
В Linux интерфейс не является частью базовой системы. Вы можете переключить свой интерфейс без перебора с переустановками. Есть такие гиганты, как GNOME и KDE, которые поставляются с полным набором интегрированных приложений.
Мало того, у вас больше свободы для их настройки. Вы можете настроить свой рабочий стол так, как нравится вам.
4. Приложения
Чтобы установить программное обеспечение в Windows, вы посещаете какой-либо веб-сайт, переходите в раздел загрузки и нажимаете на ссылку, которая отправляет вам файл EXE. Вы запускаете его, программа делает свое дело, и именно тогда вы считаете, что он «установлен». Когда вы хотите удалить программы, вы должны возиться с панелью управления. Конечно, Microsoft представила магазин приложений с Windows 8, но многое из того, что вы хотите, просто отсутствует.
В большинстве систем Linux вам не придется выискивать исполняемые файлы. Вместо этого у вас будет нечто, называемое менеджером пакетов. Традиционные менеджеры пакетов предоставляют детальный контроль для просмотра, установки и удаления пакетов программ. Новые варианты больше похожи на магазины мобильных приложений.
Минус в том, когда нужного вам приложения нет в диспетчере пакетов. Поскольку не существует одной версии Linux, не существует одного формата пакета, который работает во всех различных дистрибутивах.
5. Файловая система
Фундаментальная структура Linux полностью отличается от Windows — как и должно быть, учитывая, что она была разработана на отдельной базе кода с отдельными разработчиками. Вы не найдете папки Мои документы в Ubuntu, или Программные файлы в Fedora. Дисков C: или D: нет.
Вместо этого существует одно дерево файлов, и ваши диски монтируются в это дерево. Ваши «домашние» и «настольные» каталоги являются частью этого единого файлового дерева. Технически вам нужно изучить совершенно новую файловую систему и ее архитектуру. Делать это не очень сложно, но разница все же есть.
Файловая система
Windows использует файловую систему NTFS. В отличие от Linux поддерживает множество различных вариантов. Если вы устанавливаете Linux на свой ноутбук, скорее всего, вы будете использовать EXT4. Но если вы хотите запустить Linux на сервере, вы можете попробовать BTRFS или ZFS.
Эти файловые системы имеют функции, которые не обязательно подойдут пользователям настольных компьютеров, но отлично подходят для компаний, предоставляющих облачные сервисы, или для людей, обслуживающих свои собственные серверы.
6. Реестр
Реестр Windows — это основная база данных всех настроек вашего компьютера. Он содержит информацию о приложении, пароли пользователей, информацию об устройстве и тому подобное. Если информация не хранится в виде файла, она, вероятно, хранится в реестре Windows.
У Linux нет единого монолитного реестра. Как правило, приложения хранят свои настройки по программам в скрытых папках в домашнем каталоге пользователя. Есть некоторые исключения, такие как среда рабочего стола GNOME, в которой есть GSettings и инструмент настройки dconf.
7. Драйверы
Поскольку Windows широко распространена на рынке ПК, производители устройств стремятся сосредоточить свои усилия на одной операционной системе. Это означает, что компании отдают предпочтение Windows.
Иногда они не предоставляют драйверы Linux, которые взаимодействуют с их устройствами. В других случаях они могут предоставлять драйверы, но не учитывать некоторые функции. Это означает, что вам нужно быть более осторожным при покупке различных периферийных устройств или умных гаджетов.
Это не значит, что ситуация с драйверами в Linux более сложная. В Linux большинство драйверов входят в состав ядра. Когда вы подключаете принтер, есть большая вероятность, что он просто будет работать. Вам не нужно использовать установочный компакт-диск или загружать драйвер из Интернета.
А как насчет видеокарт?
Это проблема, связанная с драйверами, которая возникает больше всего. Хотя есть драйверы с открытым исходным кодом для карт Nvidia и AMD, если вы хотите максимальной производительности, вам нужны проприетарные драйверы. Они доступны, но иногда создают проблемы с другими аспектами рабочего стола Linux, поскольку разработчики не имеют доступа к исходному коду.
8. Команды и инструменты разработки
И в Windows, и в Linux есть возможность открыть маленькое черное окно и ввести команды. Версия для Windows известна как Windows PowerShell и предназначена в основном для разработчиков. Это не основной способ взаимодействия с ПК с Windows.
На Linux это окно больше известно как Терминал. Если вам нравится вводить команды, вы можете полностью отказаться от графического интерфейса. Именно так большинство системных администраторов управляют серверами (большинство из которых работает под управлением Linux).
Linux хорошо известен как дружественная среда для разработчиков. Терминал является большой частью этого. Так же как и природа открытого кода операционной системы. Вы просто уполномочены делать со своей машиной все, что хотите, при условии, что у вас есть знания или вы хотите их получить.
Linux vs Windows: What’s the Difference?
It’s time to make the big switch from your Windows or Mac OS operating system.
Mac OS uses a UNIX core. Your switch from Mac OS to Linux will be relatively smooth.
It’s the Windows users who will need some adjusting. In this tutorial will introduce the Linux OS and compare it with Windows. 
Click here if the video is not accessible
Windows Vs. Linux File System
In Microsoft Windows, files are stored in folders on different data drives like C: D: E:
But, in Linux, files are ordered in a tree structure starting with the root directory.
This root directory can be considered as the start of the file system, and it further branches out various other subdirectories. The root is denoted with a forward slash ‘/’.
A general tree file system on your UNIX may look like this.
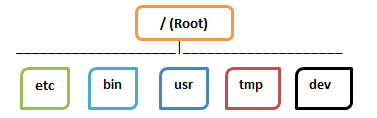
KEY DIFFERENCE
- Linux is an open source operating system so user can change source code as per requirement whereas Windows OS is a commercial operating system so user doesn’t have access to source code.
- Linux is very well secure as it is easy to detect bugs and fix whereas Windows has a huge user base, so it becomes a target of hackers to attack windows system.
- Linux runs faster even with older hardware whereas windows are slower compared to Linux.
- Linux peripherals like hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered files whereas Windows, hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered as devices
- Linux files are ordered in a tree structure starting with the root directory whereas in Windows, files are stored in folders on different data drives like C: D: E:
- In Linux you can have 2 files with the same name in the same directory while in Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder.
- In Linux you would find the system and program files in different directories whereas in Windows, system and program files are usually saved in C: drive.
Types of Files
In Linux and UNIX, everything is a file. Directories are files, files are files, and devices like Printer, mouse, keyboard etc.are files.
Let’s look into the File types in more detail.
General Files
General Files also called as Ordinary files. They can contain image, video, program or simply text. They can be in ASCII or a Binary format. These are the most commonly used files by Linux Users.
Directory Files
These files are a warehouse for other file types. You can have a directory file within a directory (sub-directory).You can take them as ‘Folders’ found in Windows operating system.
Device Files:
In MS Windows, devices like Printers, CD-ROM, and hard drives are represented as drive letters like G: H:. In Linux, there are represented as files.For example, if the first SATA hard drive had three primary partitions, they would be named and numbered as /dev/sda1, /dev/sda2 and /dev/sda3.
Note: All device files reside in the directory /dev/
All the above file types (including devices) have permissions, which allow a user to read, edit or execute (run) them. This is a powerful Linux/Unix feature. Access restrictions can be applied for different kinds of users, by changing permissions.
Windows Vs. Linux: Users
There are 3 types of users in Linux.
- Regular
- Administrative(root)
- Service
Regular User
A regular user account is created for you when you install Ubuntu on your system. All your files and folders are stored in /home/ which is your home directory. As a regular user, you do not have access to directories of other users.
Root User
Other than your regular account another user account called root is created at the time of installation. The root account is a superuser who can access restricted files, install software and has administrative privileges. Whenever you want to install software, make changes to system files or perform any administrative task on Linux; you need to log in as a root user. Otherwise, for general tasks like playing music and browsing the internet, you can use your regular account.
Service user
Linux is widely used as a Server Operating System. Services such as Apache, Squid, email, etc. have their own individual service accounts. Having service accounts increases the security of your computer. Linux can allow or deny access to various resources depending on the service.
Note:
- You will not see service accounts in Ubuntu Desktop version.
- Regular accounts are called standard accounts in Ubuntu Desktop
In Windows, there are 4 types of user account types.
- Administrator
- Standard
- Child
- Guest
Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder. See below —
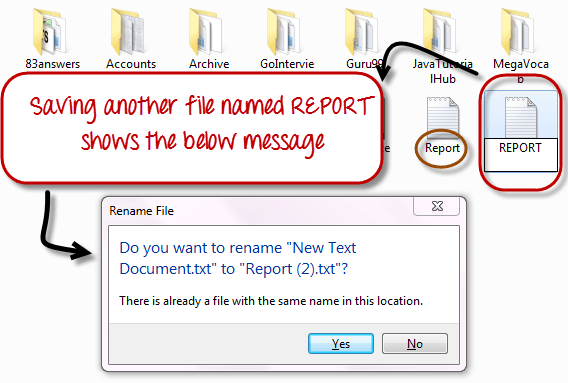
While in Linux, you can have 2 files with the same name in the same directory, provided they use different cases.
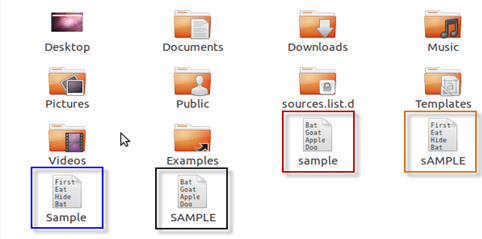
Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
For every user in Linux, a directory is created as /home/
Consider, a regular user account «Tom». He can store his personal files and directories in the directory «/home/tom». He can’t save files outside his user directory and does not have access to directories of other users. For instance, he cannot access directory «/home/jerry» of another user account»Jerry».
The concept is similar to C:\Documents and Settings in Windows.
When you boot the Linux operating system, your user directory (from the above example /home/tom) is the default working directory. Hence the directory «/home/tom is also called the Home directory which is a misnomer.
The working directory can be changed using some commands which we will learn later.
Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
In Windows, System and Program files are usually saved in C: drive. But, in Linux, you would find the system and program files in different directories. For example, the boot files are stored in the /boot directory, and program and software files can be found under /bin, device files in /dev. Below are important Linux Directories and a short description of what they contain.
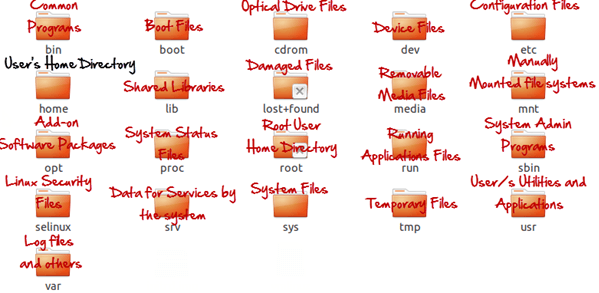
These are most striking differences between Linux and other Operating Systems. There are more variations you will observe when switching to Linux and we will discuss them as we move along in our tutorials.




