- Вики IT-KB
- Инструменты пользователя
- Инструменты сайта
- Боковая панель
- Содержание
- Создание учётных записей MSA и gMSA
- Создание Managed Service Account
- Создание Group Managed Service Account
- Замечания
- how to change username on pc located in c:/users in windows 10 pro?
- Replies (1)
- Одна учетная запись для всех служб Microsoft
- Нет учетной записи Microsoft?
- Безопасность
- Конфиденциальность
- Семья
- Платежи и выставление счетов
- Подписки
- Устройства
- Справка
- Войдите в учетную запись и начните работу
- Outlook
- Skype
- Microsoft Edge
- Microsoft Bing
- Microsoft 365
- OneDrive
- Windows
- Microsoft Store
- Кортана
- Naming conventions in Active Directory for computers, domains, sites, and OUs
- Summary
- Computer names
- NetBIOS computer names
- DNS host names
- Domain names
- NetBIOS domain names
- DNS domain names
- Disjointed namespaces
- Other factors
- Site names
Вики IT-KB
Пошаговые руководства, шпаргалки, полезные ссылки.
Инструменты пользователя
Инструменты сайта
Боковая панель
Содержание
Создание учётных записей MSA и gMSA

Создание Managed Service Account
При необходимости создать учётную запись Managed Service Account, которая будет ограничена действием только в рамках одного компьютера, то есть учётную запись типа msDS-ManagedServiceAccount, достаточно выполнить команду типа:
-Name – имя создаваемой учётной записи MSA.
Обратите внимание на то, что имя имеет ограничение в 15 символов.
-RestrictToSingleComputer – наличие этого параметра говорит о том, что нужно создать именно учётную запись MSA (не gMSA) действие которой ограничено одним каким-либо сервером.
После успешного выполнения командлета убедимся в наличии объекта класса msDS-ManagedServiceAccount в указанном OU в домене.
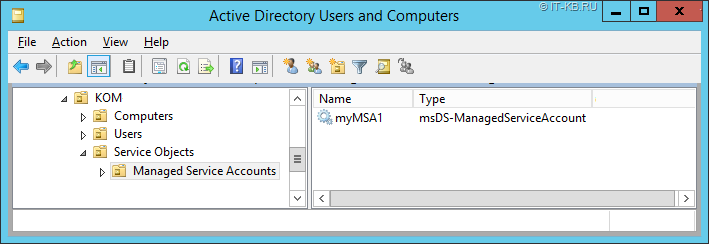
С помощью PowerShell можем запросить информацию о созданной учётной записи MSA командлетом Get-ADServiceAccount.
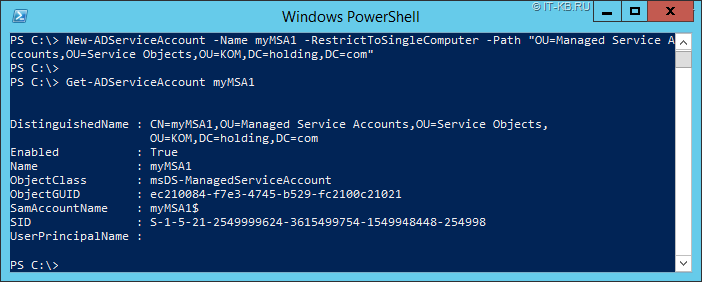
Командлет New-ADServiceAccount имеет ряд других интересных параметров, узнать о которых можно, например, в онлайн справке.
В последствии созданную учётную запись можно будет привязать только к одному серверу.
Создание Group Managed Service Account
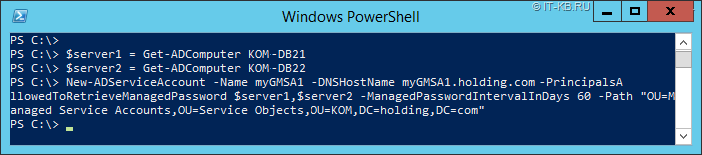
При необходимости создать групповую учётную запись Group Managed Service Account (класса msDS-GroupManagedServiceAccount), которую можно будет использовать в рамках нескольких компьютеров, например, на нескольких узлах какого-либо кластера, выполняем команду типа:
-Name – имя создаваемой учётной записи gMSA
-DNSHostName — FQDN имя, складывающееся из имени учётной записи (sAMAccountName) и доменного суффикса. Хотя есть разные толкования того, что должно быть указано в этом параметре (здесь и здесь.)
-PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword — перечень компьютеров домена, которым можно предоставить доступ к паролю учётной записи gMSA.
Если количество серверов в кластере большое и может со временем меняться, то, возможно имеет смысл создать в домене AD отдельную глобальную группу безопасности, включить в неё учётные записи серверов-узлов кластера, и уже эту группу использовать в качестве значения параметра PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword . Особенностью такого метода является то, что при изменении членства группы для вступления изменений в силу требуется перезагрузка сервера-участника группы.
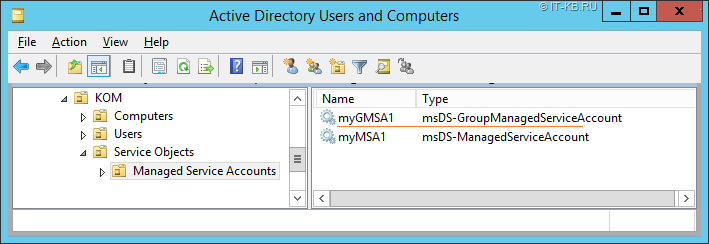
После успешного выполнения командлета убедимся в наличии объекта класса msDS-GroupManagedServiceAccount в указанном OU в домене
Замечания
Создавая учётные записи MSA/gMSA лучше руководствоваться принципом «отдельный сервис – отдельная учётная запись» и не пытаться использовать одну учётную запись MSA/gMSA для разных служб, так как это понижает уровень безопасности всех служб/приложений, совместно использующих одну и туже учётную запись. К тому же даже с точки зрения отладки работы служб и приложений использование разных учётных записей может дать свои преимущества.
Проверено на следующих конфигурациях:
| Версия ОС |
|---|
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard EN (6.3.9600) |

Алексей Максимов
Время публикации: 30.10.2018 17:21
how to change username on pc located in c:/users in windows 10 pro?
I have a problem that my name is «Srijan» but in users folder located in local disk c: is showing first five words .
Help me! I want my full name on that folder.
Replies (1)
I would like to ask if you are using Microsoft account or Local account.
I suggest you to follow the methods below and check if it helps.
Method 1: Please follow the steps to rename the user account.
- In the search box, type user accounts and click on User Accounts.
- Click on “Change your account name”
- If it’s prompting for password please enter and click on Yes. If you do not have password click on Yes.
- Enter the new user name.
- Click on change name.
Method 2:
Note: Before you start, please back up all you data and create a system restore point first.
- Press Windows Key + R combination and then type netplwiz in the Run dialog box. Click OK. If prompted for UAC, click Yes.
- Now in the User Accounts window, check Users must enter a user name and password to enter this computer, if it is unchecked.
- In the User Name section, select the user name to which you want to change the name and click Properties.
- In the Properties window, in the User name field, provide the desired user name. Then click Apply followed by OK.
- Reboot to see the change.
Change User Folder name: Even after you change the username using this method, your personal folder will continue to display the old username. To rename the user folder, do the following.
- Create a system restore point first. Then open Registry Editor and navigate to the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
2. You will find several folders here like S-1-5-. Search through them till you find a ProfileImagePath pointing to your old username. Double-click on it and replace your old username with your new username.
3. Restart your computer to see the change.
Disclaimer:
Important: The System Restore restores the computer back to an earlier point in time, called a restore point. System Restore doesn’t change your personal files, but it might remove recently installed apps and drivers and also reset the recently changed settings on the computer.
Registry disclaimer: Important this section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base: 322756 ( http://support.microsoft.com/kb/322756/ )
How to back up and restore the registry in Windows
Write us back with status of the issue in regards with your account. Your reply is important to assist you further.
Одна учетная запись для всех служб Microsoft
Одна учетная запись. Одна панель управления. Добро пожаловать на страницу учетной записи.
Нет учетной записи Microsoft?
Узнайте, как начать работу с продуктами Microsoft.
Безопасность
Изменяйте пароль, обновляйте секретные вопросы и поддерживайте актуальность важных сведений учетной записи.
Конфиденциальность
Просматривайте историю поиска, посещений веб-страниц, местоположений и многое другое.
Семья
Обезопасьте свою семью в Интернете и оставайтесь на связи, даже когда находитесь вдали друг от друга.
Платежи и выставление счетов
Обновляйте платежную информацию, просматривайте историю заказов, используйте подарочные карты и получайте помощь с оплатой.
Подписки
Быстро продлевайте подписки и управляйте службами Microsoft из единой панели.
Устройства
Найдите и заблокируйте утерянное или украденное устройство Windows 10, сотрите с него данные или запланируйте ремонт и получите помощь.
Справка
Получите помощь и советы экспертов по продуктам и службам Microsoft.
Войдите в учетную запись и начните работу
Пользуйтесь всеми любимыми продуктами и службами Microsoft с помощью единого входа. От Office и Windows до Xbox и Skype – одно имя пользователя и один пароль объединяют вас с самыми важными файлами, фотографиями, людьми и контентом.
Outlook
Почта и календарь в одном. Все, что нужно для эффективной работы и общения дома и в дороге.
Skype
Оставайтесь на связи с близкими на всех устройствах с помощью текстовых сообщений, голосовых и видеозвонков Skype.
Microsoft Edge
Быстрый браузер для эффективной работы в сети: с ним удобно искать информацию, узнавать новое и систематизировать закладки.
Microsoft Bing
Интеллектуальные функции поиска помогают быстро и удобно находить все необходимое — ответы, новости, развлечения и многое другое.
Играйте в любимые игры где угодно. Играйте, общайтесь с друзьями и заходите в сообщества на Xbox One, компьютерах с Windows 10 и мобильных устройствах.
Microsoft 365
Выполняйте важные задачи с Word, Excel, PowerPoint и не только. Каким будет ваш следующий успех с Office 365?
OneDrive
Бесплатно сохраняйте и просматривайте файлы и фотографии на своих устройствах. В учетной записи Microsoft доступно 5 ГБ хранилища, и вы сможете добавить больше при необходимости.
Windows
Найдите и заблокируйте утерянное или украденное устройство Windows 10, сотрите с него данные или запланируйте ремонт и получите помощь.
Microsoft Store
Воспользуйтесь лучшими предложениями Microsoft — от приложений для работы и творчества до игр и развлечений.
Кортана
Экономьте время и будьте организованными — Кортана помогает решать повседневные задачи, чтобы вы не отвлекались на мелочи.
Благодаря MSN полезная информация доступна в любое время.
Naming conventions in Active Directory for computers, domains, sites, and OUs
This article describes the naming conventions for computer accounts in Windows, NetBIOS domain names, DNS domain names, Active Directory sites, and organizational units (OUs) that are defined in the Active Directory directory service.
Original product version: В Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: В 909264
Summary
This article discusses the following topics:
- The valid characters for names
- The minimum and maximum name lengths
- Reserved names
- Names that we don’t recommend
- General recommendations that are based on supporting Active Directory in small, medium, and large deployments
All objects that are named within Active Directory, or within AD/AM and LDS, are subject to name matching based on the algorithm described in the following article:
In that article, this naming convention applies to computer, OU, and site names.
Computer names
NetBIOS computer names
NetBIOS computer names can contain all alphanumeric characters except for the extended characters that are listed in Disallowed characters. Names can contain a period, but names can’t start with a period.
NetBIOS computer names can’t contain the following characters:
Names can contain a period (.). But the name can’t start with a period. The use of non-DNS names with periods is allowed in Microsoft Windows NT. Periods should not be used in Microsoft Windows 2000 or later versions of Windows. If you’re upgrading a computer whose NetBIOS name contains a period, change the machine name. For more information, see Special characters.
In Windows 2000 and later versions of Windows, computers that are members of an Active Directory domain can’t have names that are composed completely of numbers. This restriction is because of DNS restrictions.
For more information about the NetBIOS name syntax, see NetBIOS name syntax.
Minimum name length: 1 character
Maximum name length: 15 characters
The 16th character is reserved to identify the functionality that is installed on the registered network device.
Special characters: Period (.)
A period character separates the name into a NetBIOS scope identifier and the computer name. The NetBIOS scope identifier is an optional string of characters that identify logical NetBIOS networks that run on the same physical TCP/IP network. For NetBIOS to work between computers, the computers must have the same NetBIOS scope identifier and unique computer names.
The use of NetBIOS scopes in names is a legacy configuration. It shouldn’t be used with Active Directory forests. For more information about NetBIOS scopes, see the following web sites:
DNS host names
DNS names can contain only alphabetical characters (A-Z), numeric characters (0-9), the minus sign (-), and the period (.). Period characters are allowed only when they are used to delimit the components of domain style names.
In the Windows 2000 domain name system (DNS) and the Windows Server 2003 DNS, Unicode characters are supported. Other implementations of DNS don’t support Unicode characters. Avoid Unicode characters if queries will be passed to the servers that use non-Microsoft implementations of DNS.
For more information, see the following websites:
DNS host names can’t contain the following characters:
white space (blank)
The underscore has a special role. It is permitted for the first character in SRV records by RFC definition. But newer DNS servers may also allow it anywhere in a name. For more information, see Complying with Name Restrictions for Hosts and Domains.
All characters preserve their case formatting except for American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) characters.
The first character must be alphabetical or numeric.
The last character must not be a minus sign or a period.
Two-character SDDL user strings that are listed in well-known SIDs list can’t be used. Otherwise, import, export, and take control operations fail.
In Windows 2000 and later versions of Windows, computers that are members of an Active Directory domain can’t have names that are composed completely of numbers. This restriction is because of DNS restrictions.
DNS Host Name Registration substitutes a hyphen (-) character for invalid characters.
Minimum name length: 2 characters
Maximum name length: 63 characters
The maximum length of the host name and of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is 63 bytes per label and 255 bytes per FQDN.
Windows doesn’t permit computer names that exceed 15 characters, and you can’t specify a DNS host name that differs from the NETBIOS host name. You might however create host headers for a web site hosted on a computer and that is then subject to this recommendation.
In Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003, the maximum host name and the FQDN use the standard length limitations that are mentioned earlier, with the addition of UTF-8 (Unicode) support. Because some UTF-8 characters exceed one octet in length, you can’t determine the size by counting the characters.
Domain controllers must have an FQDN of less than 155 bytes.
Reserved names per RFC 952
For more information, see rfc952.
Reserved names in Windows
When you create names for the DNS computers in a new Windows Server 2003 DNS infrastructure, use the following guidelines:
- Choose computer names that are easy for users to remember.
- Identify the owner of the computer in the computer name.
- Choose a name that describes the purpose of the computer.
- For ASCII characters, don’t use character case to indicate the owner or the purpose of a computer. For ASCII characters, DNS is not case-sensitive, Windows and Windows applications are not case-preserving in all places.
- Match the Active Directory domain name to the primary DNS suffix of the computer name. For more information, see the Disjointed namespaces section below.
- Use a unique name for every computer in your organization. Avoid the same computer name for computers in different DNS domains.
- Use ASCII characters. This guarantees interoperability with computers that are running versions of Windows that are earlier than Windows 2000.
- In DNS computer names, use only the characters that are listed in RFC 1123. These characters include A-Z, a-z, 0-9, and the hyphen (-). In Windows Server 2003, DNS allows most UTF-8 characters in names. Don’t use extended ASCII or UTF-8 characters unless all the DNS servers in your environment support them.
Domain names
Here are details for NetBIOS domain names and DNS domain names.
NetBIOS domain names
NetBIOS domain names can contain all alphanumeric characters except for the extended characters that are listed in Disallowed characters. Names can contain a period, but names can’t start with a period.
NetBIOS computer names can’t contain the following characters:
Names can contain a period (.). But the name can’t start with a period. The use of non-DNS names with periods is allowed in Microsoft Windows NT. Periods shouldn’t be used in Active Directory domains. If you are upgrading a domain whose NetBIOS name contains a period, change the name by migrating the domain to a new domain structure. Do not use periods in new NetBIOS domain names.
In Windows 2000 and later versions of Windows, computers that are members of an Active Directory domain can’t have names that are composed completely of numbers. This restriction is because of DNS restrictions.
Minimum name length: 1 character
Maximum name length: 15 characters.
The 16th character is reserved to identify the functionality that is installed on the registered network device.
Reserved names in Windows
The names of an upgraded domain can include a reserved word. However, trust relationships with other domains fail in this situation.
Special characters: Period (.).
A period character separates the name into a NetBIOS scope identifier and the computer name. The NetBIOS scope identifier is an optional string of characters that identify logical NetBIOS networks that run on the same physical TCP/IP network. For NetBIOS to work between computers, the computers must have the same NetBIOS scope identifier and unique computer names.
The use of NetBIOS scopes in names is a legacy configuration. It shouldn’t be used with Active Directory forests. There is no inherent problem with this, but there may be applications that filter the name and assume a DNS name when a period is found.
DNS domain names
DNS names can contain only alphabetical characters (A-Z), numeric characters (0-9), the minus sign (-), and the period (.). Period characters are allowed only when they are used to delimit the components of domain style names.
In the Windows 2000 domain name system (DNS) and the Windows Server 2003 DNS, Unicode characters are supported. Other implementations of DNS don’t support Unicode characters. Avoid Unicode characters if queries will be passed to the servers that use non-Microsoft implementations of DNS.
For more information, visit the following web sites:
DNS domain names can’t contain the following characters:
white space (blank)
The underscore has a special role. It’s permitted for the first character in SRV records by RFC definition. But newer DNS servers may also allow it anywhere in a name. For more information, see Complying with Name Restrictions for Hosts and Domains.
When promoting a new domain, you get a warning that an underscore character might cause problems with some DNS servers. But it still lets you create the domain.
All characters preserve their case formatting except for ASCII characters.
The first character must be alphabetical or numeric.
The last character must not be a minus sign or a period.
Minimum name length: 2 characters
Maximum name length: 255 characters
The maximum length of the host name and of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is 63 bytes per label and 255 characters per FQDN. The latter is based on the maximum path length possible with an Active Directory Domain name with the paths needed in SYSVOL , and it needs to obey to the 260 character MAX_PATH limitation.
An example path in SYSVOL contains:
The might contain user input such as the logon script file name, thus it can also reach a significant length.
The AD FQDN domain name appears in the path twice, due to that the length of an AD FQDN domain name is restricted to 64 characters.
In Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003, the maximum host name and the FQDN use the standard length limitations that are mentioned earlier, with the addition of UTF-8 (Unicode) support. Because some UTF-8 characters exceed one octet in length, you can’t determine the size by counting the characters.
Single-label domain namespaces
Single-label DNS names are names that don’t contain a suffix, such as .com , .corp , .net , .org , or companyname . For example, host is a single-label DNS name. Most Internet registrars don’t allow the registration of single-label DNS names.
Generally, we recommend that you register DNS names for internal and external namespaces with an Internet registrar. This includes the DNS names of Active Directory domains, unless such names are subdomains of DNS names that are registered by your organization name. For example, corp.example.com is a subdomain of example.com . Registering your DNS name with an Internet registrar may help prevent a name collision. A name collision may occur if another organization tries to register the same DNS name, or if your organization merges with another organization that uses the same DNS name.
Problems that are associated with single-label namespaces include:
Single-label DNS names can’t be registered by using an Internet registrar.
Domains that have single-label DNS names require additional configuration.
The DNS Server service may not be used to locate domain controllers in domains that have single-label DNS names.
By default, Windows Server 2003-based domain members, Windows XP-based domain members, and Windows 2000-based domain members don’t perform dynamic updates to single-label DNS zones.
Don’t use top-level Internet domain names on the intranet, such as .com , .net , and .org . If you use top-level Internet domain names on the intranet, computers on the intranet that are also connected to the Internet may experience resolution errors.
Disjointed namespaces
A disjointed namespace occurs when a computer’s primary DNS suffix doesn’t match the DNS domain of which it is a member. For example, a disjointed namespace occurs when a machine that has the DNS name of dc1.contosocorp.com is in a domain that has the DNS name of contoso.com .
How disjointed namespaces occur:
A Windows NT 4.0 primary domain controller is upgraded to a Windows 2000 domain controller by using the original release version of Windows 2000. In the Networking item in Control Panel, multiple DNS suffixes are defined.
The domain is renamed when the forest is at the Windows Server 2003 forest functional level. And the primary DNS suffix isn’t changed to reflect the new DNS domain name.
Effects of a disjointed namespace:
Suppose a domain controller named DC1 resides in a Windows NT 4.0 domain whose NetBIOS domain name is contoso. This domain controller is upgraded to Windows 2000. When this upgrade occurs, the DNS domain is renamed contoso.com . In the original release version of Windows 2000, the upgrade routine clears the check box that links the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller to its DNS domain name. So, the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller is the Windows NT 4.0 DNS suffix that was defined in the Windows NT 4.0 suffix search list. In this example, the DNS name is DC1.northamerica.contoso.com .
The domain controller dynamically registers its service location (SRV) records in the DNS zone that corresponds to its DNS domain name. However, the domain controller registers its host records in the DNS zone that corresponds to its primary DNS suffix.
For more information about a disjoint namespace, see the following articles:
Other factors
Forests that are connected to the Internet
A DNS namespace that is connected to the Internet must be a subdomain of a top-level or second-level domain of the Internet DNS namespace.
Maximum number of domains in a forest
In Windows 2000, the maximum number of domains in a forest is 800. In Windows Server 2003 and later versions, the maximum number of domains at Forest Functional Level 2 is 1200. This restriction is a limitation of multivalued non-linked attributes in Windows Server 2003.
The DNS names of all the nodes that require name resolution include the Internet DNS domain name for the organization. So, choose an Internet DNS domain name that is short and easy to remember. Because DNS is hierarchical, DNS domain names grow when you add subdomains to your organization. Short domain names make the computer names easy to remember.
If the organization has an Internet presence, use names that are relative to the registered Internet DNS domain name. For example, if you have registered the Internet DNS domain name contoso.com , use a DNS domain name such as corp.contoso.com for the intranet domain name.
Don’t use the name of an existing corporation or product as your domain name. You can run into a name collision later on.
Avoid a generic name like maybe domain.localhost. Another company you merge with in a few years might follow the same thinking.
Don’t use an acronym or an abbreviation as a domain name. Users may have difficulty recognizing the business unit that an acronym represents.
Avoid the use of underscores (_) in domain names. Applications might be very RFC obedient and reject the name, and will not install or work in your domain. And you might experience problems with older DNS servers.
Don’t use the name of a business unit or of a division as a domain name. Business units and other divisions will change, and these domain names can be misleading or become obsolete.
Don’t use geographic names that are difficult to spell and remember.
Avoid extending the DNS domain name hierarchy more than five levels from the root domain. You can reduce administrative costs by limiting the extent of the domain name hierarchy.
If you are deploying DNS in a private network, and you don’t plan to create an external namespace, register the DNS domain name that you create for the internal domain. Otherwise, you may find that the name is unavailable if you try to use it on the Internet, or if you connect to a network that is connected to the Internet.
Site names
We recommend that you use a valid DNS name when you create a new site name. Otherwise, your site will be available only where a Microsoft DNS server is used. For more information about valid DNS names, see the DNS host names section.
DNS names can contain only alphabetical characters (A-Z), numeric characters (0-9), the minus sign (-), and the period (.). Period characters are allowed only when they are used to delimit the components of domain style names.
In the Windows 2000 domain name system (DNS) and the Windows Server 2003 DNS, Unicode characters are supported. Other implementations of DNS don’t support Unicode characters. Avoid Unicode characters if queries will be passed to the servers that use non-Microsoft implementations of DNS.
For more information, visit the following web sites:
DNS names can’t contain the following characters:






