- Media Foundation
- Содержание
- Архитектура
- Media Foundation Transforms
- Enhanced Video Renderer
- Преимущества над DirectShow
- Использование в приложениях
- What’s New for Media Foundation
- Better Format Support
- Hardware Device Support
- Simplified Programming Model
- Platform Improvements
- SDK Changes
- New in Windows 8
- Как установить Windows Media Foundation или MFREADWRITE.DLL отсутствует
- Как установить Windows Media Foundation
- About Media Foundation
- Audio and Video Quality
- Content Access
- About Media Foundation
- How to Play Media Files with Media Foundation
- Prerequisites
- Overview
Media Foundation
Media Foundation (сокращается до MF) — мультимедийный фреймворк и интерфейс программирования приложений нового поколения, созданный корпорацией Microsoft для работы с цифровым мультимедиа под операционными системами семейства Windows, начиная с Vista. Согласно планам Microsoft, он заменит DirectShow, Windows Media SDK, DirectX Media Objects (DMOs) и более старые мультимедийные API, такие, как Audio Compression Manager (ACM) и Video for Windows (VfW). При этом в течение некоторого времени предполагается параллельное сосуществование DirectShow и Media Foundation. В Windows XP и более старых операционных системах использование MF не планируется.
В первом релизе Media Foundation, выпущенном с Windows Vista, основное внимание уделено качеству воспроизведения аудио и видео, контенту высокой чёткости (то есть, ТВЧ), защите контента, более унифицированному подходу к контролю доступа к цифровым данным для средств защиты авторских прав (DRM) и их взаимодействию.
Содержание
Архитектура
Архитектура MF подразделяется на слой управления (Control layer), слой ядра (Core layer) и слой платформы (Platform layer). Слой ядра включает большую часть функциональности Media Foundation. Он является мультимедийным конвейером, состоящим из трёх частей: Media Source (объект-«источник» мультимедиа данных), Media Sink (объект-«приёмник» обработанных данных) и Media Foundation Transforms (MFT).
Media Foundation Transforms
Media Foundation Transforms получает от Media Source данные, производит промежуточную обработку и отдаёт объекту Media Sink. Он может состоять из нескольких обрабатывающих фильтров, а может быть и пустым. Эти фильтры могут идти последовательно, образуя мультимедийный конвейер (pipeline), а могут и независимо друг от друга. Примеры фильтров MFT:
- Аудио- и видеокодеки
- Аудио- и видеоэффекты
- Мультиплексоры и демультиплексоры
- Разветвители
- Преобразователи цветового пространства
- Преобразователи частоты
- Преобразователи размера видео
Для Windows Vista Microsoft рекомендует разработчикам писать фильтры MFT вместо DirectShow [1] .
Enhanced Video Renderer
В MF включён новый видео рендерер, Enhanced Video Renderer (EVR), который является следующим поколением рендереров в ряду VMR 7 и 9. В Media Foundation EVR выступает в качестве объекта Media Sink (объекта-приёмника), при этом он может смешивать до 16 параллельных потоков, один из которых является референсным. Все потоки, кроме референсного, могут содержать информацию о прозрачности каждого своего пикселя и информацию о порядке наложения. Референсный поток не имеет прозрачных пикселей и всегда находится в самом низу порядка наложения. Результирующее изображение создаётся путём окраски каждого пикселя согласно цвету и прозрачности соответствующих пикселей всех потоков.
Преимущества над DirectShow
MF обладает следующими преимуществами:
- Масштабируемость для высокоразмерного контента и контента, защищённого DRM.
- Позволяет использовать DirectX-акселерацию видео без использования инфраструктуры DirectShow. DXVA 2.0 может быть доступен для компонент пользователя без использования видео рендерера DirectShow.
- Media Foundation позволяет совместно работать различным системам защиты контента.
- Media Foundation использует Multimedia Class Scheduler Service (MMCSS, англ.), новую службу, которая выставляет воспроизведению мультимедиа приоритет реального времени для резервирования требуемых при воспроизведения ресурсов. MMCSS гарантирует мультимедийным приложениям приоритетный доступ к ресурсам ЦП, который обеспечивает более точное по времени воспроизведение мультимедиа.
Media Foundation сопутствует двум другим технологиям — Direct3D 10 и Windows Presentation Foundation, идя в ногу с эволюцией графики и мультимедийного аппаратного обеспечения и требованиями мультимедийных приложений.
Использование в приложениях
Сейчас Media Foundation используется главным образом в службах и сервисах Windows:
- Windows Protected Media Path (PMP), полностью основан на Media Foundation.
- Windows Media Player в Windows Vista использует Media Foundation для воспроизведения формата ASF (WMA и WMV) и защищённого контента, но вместо этого также может использовать DirectShow или Windows Media Format SDK. В случае воспроизведения WMV9, также используется DXVA 2.0 вместо DXVA 1.0, если поддерживается аппаратное декодирование WMV9/VC-1.
- DirectX Video Acceleration (DXVA) 2.0, конвейер аппаратной акселерации видео в Windows Vista, также основан на Media Foundation.
What’s New for Media Foundation
Microsoft Media Foundation was introduced in WindowsВ Vista as the replacement for DirectShow. Of course, DirectShow is still supported in WindowsВ 7, but developers are encouraged to use Media Foundation in their new digital media applications.
The improvements to Media Foundation can be summarized as follows:
- Better format support, including MPEG-4
- Support for capture devices and hardware codecs
- A simplified programming model
- Improvements to the platform
Better Format Support
The Media Foundation audio/video pipeline was implemented in WindowsВ Vista, but it supported a limited set of formats and file containers, which meant that some applications needed to fall back on older technologies such as DirectShow. In WindowsВ 7, Media Foundation includes the following new codecs, media sources, and media sinks:
- AAC decoder
- AAC encoder
- AVI/WAVE file source
- DV video decoder
- H.264 video decoder
- H.264 video encoder
- MJPEG decoder
- MP3 file sink*
- MP4/3GP file source
- MP4/3GP file sink
The MP3 file sink does not include an MP3 audio encoder.
Hardware Device Support
Media Foundation now supports the following types of hardware devices in the audio/video pipeline:
- UVC 1.1 video capture devices, such as webcams
- Audio capture devices
- Hardware encoders and decoders
- Hardware video processors, such as color-space converters
Hardware codecs can perform very fast video transcoding. For example, an application might transfer Windows Media Video (WMV) files to a cell phone that supports only 3GP files. Using a hardware encoder, the application can transcode the file in the backgound, just before transferring it to the device.
Hardware devices are represented in Media Foundation by a proxy object, and are used in the pipeline just like software-based components.
Simplified Programming Model
In WindowsВ Vista, Media Foundation exposed a relatively low-level set of APIs. These APIs are flexible, but too complex for simple tasks. WindowsВ 7 adds new high-level APIs that make it simpler to write media applications in C++. These new high-level APIs include the following.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Reader | The source reader pulls raw or decoded data from a media file. For example, you can use the source reader to get thumbnail bitmaps from a video file, or to analyze the waveform data in an audio file. You can also use the source reader to get live data from an audio or video capture device. |
| Sink Writer | The sink writer enables you to author media files by passing in uncompressed or encoded data. For example, you can use it to re-encode a video file, or to capture live video from a webcam to a file. |
| Transcode API | This feature supports the most common audio/video encoding scenarios. |
You can still use the low-level APIs in Media Foundation. You might do so if you need more control over the audio/video pipeline.
Platform Improvements
WindowsВ 7 includes numerous enhancements to the underlying Media Foundation platform APIs. Advanced applications can use these APIs directly; other applications will get the benefits indirectly. The improvements include:
- Changes in the video pipeline to reduce power consumption and video memory usage.
- DXVA-HD: Microsoft DirectX Video Acceleration High Definition (DXVA-HD) is a new API for hardware-accelerated video processing. DXVA-HD offers a more flexible compositing model than the previous DXVA video processing API, and is better suited for high-definition video formats..
- A new mechanism for enumerating sources and decoders, which includes merit values and a preferred/blocked list. This feature improves the overall reliability of the system. For more information, see the following topics:
- MFTEnumEx
- IMFPluginControl
- Codec Merit
SDK Changes
- New headers and library files: Media Foundation Headers and Libraries
- DLL and .lib changes: Library Changes in WindowsВ 7
- New SDK Samples:
- Audio Clip Sample
- DXVA-HD Sample
- MFCaptureD3D Sample
- MFCaptureToFile Sample
- Transcode Sample
- VideoThumbnail Sample
- Improvements to TopoEdit:
- Support for transcoding. See Building a Transcode Topology with TopoEdit.
- Support for audio and video capture. See Topology Menu.
New in Windows 8
Some of the new updates to Media Foundation with WindowsВ 8 are:
Как установить Windows Media Foundation или MFREADWRITE.DLL отсутствует
Как установить Windows Media Foundation
После выхода второго патча весрии (1.0.335.1) для GTA 5 на PC, для игры теперь не обязательно требуется устанавливать Windows Media Player, но Windows Media Foundation должен быть установлен.
У большей части пользователей Windows Media Foundation уже установлен по умолчанию, но в случае если у вас появляется ошибка “Файл MFREADWRITE.DLL отсутствует. Переустановите игру.“.
Вопрос: Мне все время выдает ошибку «Подключение MFREADWRITE.DLL отсутствует, необходимо переустановить игру» (Dependency MFREADWRITE.DLL is missing. Please reinstall the game) при запуске GTAV для ПК, даже если я недавно уже переустановливал игру. Как я могу исправить эту проблему?
Ответ: Эта ошибка обычно появляется, когда вы используете операционную систему Windows 8 N или Windows 8 KN. Они не включают некоторые мультимедийные функции, необходимые для запуска игры. Для установки необходимых мультимедийных функций, пройдите по ссылке ниже и выберете файлы для конкретной операционной системы. После завершения установки ошибка больше не будет появляться.
Чтобы исправить эту ошибку, перейдите по ссылкам на официальный сайт Microsoft, и скачайте Media Feature Pack и данная ошибка исчезнет:
- Для Windows 8 N/KN
- Для Windows 8.1 N/KN
- Для Windows 8.1 Update N/KN
About Media Foundation
Microsoft Media Foundation is the next generation multimedia platform for Windows that enables developers, consumers, and content providers to embrace the new wave of premium content with enhanced robustness, unparalleled quality, and seamless interoperability.
Media Foundation requires Windows Vista or later. It uses the component object model (COM) and requires C/C++. Microsoft does not provide a managed API for Media Foundation.
The Media Foundation APIs are part of the Windows SDK. To develop a Media Foundation application, install the latest version of the Windows SDK.
Audio and Video Quality
Media Foundation has been designed to meet the challenges posed by high-definition content. Audio and video quality enhancements made throughout the platform now make it possible to deliver a great experience for next generation high-definition content.
DirectX Video Acceleration (DXVA) 2.0 offers more efficient video acceleration, compared with DXVA 1.0, with more robust and streamlined video decoding and extended use of hardware in video processing. With DXVA 2.0, Windows can handle some of the most demanding high-definition content with high quality and improved glitch-resilience.
Color-space information is preserved throughout the video pipeline. Users can enjoy video content with full fidelity. Color information and interlaced images are now passed to hardware for single-pass compositions. Preserving color-space information also reduces unnecessary color space conversions, which frees more cycles to process demanding HD content.
The enhanced video renderer (EVR) offers better timing support, enhanced video processing, and improved glitch-resilience. Full-screen playback support has been enhanced, and video tearing in windowed mode has been minimized.
Media Foundation uses the Multimedia Class Scheduler Service (MMCSS), a new system service in Windows Vista. MMCSS enables multimedia applications to ensure that their time-sensitive processing receives prioritized access to CPU resources.
Content Access
As digital entertainment moves into the high-definition era and content becomes more portable and ubiquitous, content protection will become an integral part of digital media products. The extensibility of Media Foundation ensures that it can support these trends.
In addition, Media Foundation extensibility enables different content protection systems to operate together.
About Media Foundation
This section contains general information about the Media Foundation APIs. Detailed programming information can be found in the Media Foundation Programming Guide.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| What’s New for Media Foundation | Describes new features in Media Foundation. |
| Media Foundation Headers and Libraries | Lists the header and library files that define the Media Foundation APIs. |
| Media Foundation Tools | Describes the development tools that are available for Media Foundation. |
Media Foundation is not included with the N and KN editions of WindowsВ 8. For more information, see Microsoft Windows Media Feature Pack for N and KN Versions of all Windows 8 Editions.
How to Play Media Files with Media Foundation
This tutorial shows how to play media files using the Media Session object.
Prerequisites
Before reading this topic, you should be familiar with the following Media Foundation concepts:
This topic does not describe how to play files that are protected by digital rights management (DRM). For information about DRM in Microsoft Media Foundation, see How to Play Protected Media Files.
Overview
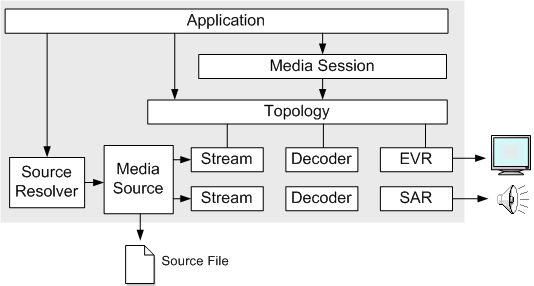
The following objects are used to play a media file with the Media Session:
- A media source is an object that parses a media file or other source of media data. The media source creates stream objects for each audio or video stream in the file. Decoders convert encoded media data into uncompressed video and audio.
- The Source Resolver creates a media source from a URL.
- The Enhanced Video Renderer (EVR) renders video to the screen.
- The Streaming Audio Renderer (SAR) renders audio to a speaker or other audio output device.
- A topology defines the flow of data from the media source to the EVR and SAR.
- The Media Session controls the data flow and sends status events to the application. The following diagram illustrates this process.
The following is a general outline of the steps needed to play a media file using the Media Session:
Call the MFStartup function to initialize the Media Foundation platform.
Call MFCreateMediaSession to create a new instance of the Media Session.
Use the source resolver to create a media source. For more information, see Using the Source Resolver.
Create a topology that connects the media source to the EVR and SAR. In this step, the application creates a partial topology that does not include the decoders. For more information, see Creating Playback Topologies.
Call IMFMediaSession::SetTopology to set the topology on the Media Session.
Use the IMFMediaEventGenerator interface to get events from the Media Session.
When the application exits, release resources:
- Call IMFMediaSession::Close to close the Media Session. This method is asynchronous. When it completes, the Media Session sends an MESessionClosed event. Then it is safe to perform the remaining steps.
- Call IMFMediaSource::Shutdown to shut down the media source.
- Call IMFMediaSession::Shutdown to shut down the Media Session.
- Call MFShutdown to shut down the Media Foundation platform.
The following sections show a complete code example: