- MODE – настройка параметров системных устройств в командной строке Windows .
- Команда MODE для последовательного порта COM:
- Команда MODE для консоли CON (дисплея и клавиатуры):
- Windows mode serial port
- Serial Port
- Принцип работы
- Какое значение выбрать?
- Win32_SerialPort class
- Syntax
- Members
- Methods
- Properties
- Remarks
- Examples
MODE – настройка параметров системных устройств в командной строке Windows .
Команда MODE используется для изменения параметров последовательного порта, консоли и параллельного порта в командной строке Windows. В основном, использовалась для управления системными устройствами в DOS. С некоторыми ограничениями, может использоваться в среде эмуляции DOS.
Команда MODE без параметров выводит на экран текущие настройки всех системных устройств, доступных в данной системе.
Формат командной строки для каждого устройства зависит от его типа:
Команда MODE для последовательного порта COM:
MODE COMm[:] [BAUD=b] [PARITY=p] [DATA=d] [STOP=s] [to=on|off] [xon=on|off] [odsr=on|off] [octs=on|off] [dtr=on|off|hs] [rts=on|off|hs|tg] [idsr=on|off]
Параметры командной строки:
BAUD — скорость передачи данных.
PARITY — вид контроля четности. Возможные значения: n (none) – без бита четности, o (odd) – нечетный, e (even)-четный
DATA — число бит данных в посылке. Возможные значения: 5-8, по умолчанию – 7 бит.
STOP — число стоповых бит. Возможные значения: 1, 1.5, 2)
to — режим таймаута. Возможные значения: on (включено), off (отключено)
xon — режим программного управления потоком передачи данных XON/XOFF. Возможные значения: on (включено), off (отключено)
odsr — режим управления потоком с синхронизацией по сигналу Data Set Ready (DSR). Возможные значения: on (включено), off (отключено)
octs — режим управления потоком с синхронизацией по сигналу Clear To Send (CTS). Возможные значения: on (включено), off (отключено)
dtr — режим использования сигнала готовности терминала данных Data Terminal Ready (DTR). Возможные значения: on (включено), off (отключено), handshake (согласование).
rts — режим использования сигнала Request To Send (RTS). Возможные значения: on (включено), off (отключено), handshake (согласование) и toggle (переключение).
idsr — режим использования сигнала Data Set Ready (DSR). Возможные значения: on (включено), off (отключено)
Двоеточие после имени устройства не обязательно.
mode com1 — отобразить параметры последовательного порта COM1
mode com1 /STATUS — аналогично предыдущему примеру, отобразить состояние устройства.
mode com1 baud=38400 to=off — установить скорость передачи данных 38400 бит/сек. и отключить режим таймаута.
Пример отображаемой информации:
Состояние устройства COM1:
—————————
| Скорость: Четность: Биты данных: Стоповые биты: Таймаут: XON/XOFF: Синхронизация CTS: Синхронизация DSR: Чувствительность DSR: Цепь DTR: Цепь RTS: | 38400 Even 7 1 ON OFF ON OFF OFF HANDSHAKE HANDSHAKE |
| Строки: Столбцы: Скорость клавиатуры: Задержка клавиатуры: Кодовая страница: | 300 80 31 1 866 |
mode con cp /status или mode con codepage /status — отобразить кодовую страницу.
Пример отображаемой информации:
Состояние устройства CON:
—————————
| Кодовая страница: | 866 |
MODE CON[:] CP SELECT=yyy — установить новую кодовую страницу.
mode con cp select=1251 — установить кодовую страницу номер 1251 (Windows-кодировка)
mode con cp select=866 — установить кодовую страницу номер 866 (DOS-кодировка)
MODE CON[:] [COLS=c] [LINES=n] — изменить режим экрана. COLS – число столбцов (символов в строке), LINES-число строк.
mode con cols=120 lines=400 — установить число столбцов равным 120, строк — 400
mode con cols=150 — изменить только число столбцов, количество строк не изменится.
MODE CON[:] [RATE=r DELAY=d] — изменить параметры ввода с клавиатуры. RATE -определяет частоту повторений вывода знака на экран при нажатии и удержании клавиши. Возможные значения — 1-31. DELAY – задержка времени, после которого начинается повторение ввода удерживаемой клавиши. Возможные значения — 1, 2, 3 и 4 (0,25 секунды, 0,50 секунды, 0,75 секунды и 1 секунда соответственно.
mode con rate=1 delay=1 — установить минимальную задержку и минимальную скорость повтора ввода нажатой клавиши.
mode con rate=32 delay=4 — установить максимальную задержку и максимальную скорость повтора ввода нажатой клавиши. При попытке указать значение RATE более 31, ошибка не выдается, но значение RATE будет установлено равным 31.
Параметры клавиатуры, установленные для консоли, действуют и для графических приложений Windows, а также сохраняются в реестре и не сбрасываются при перезагрузке системы.
Windows mode serial port
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7
Всем привет сегодня расскажу как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7. Windows запоминает устройства, с которыми вы работали ранее. Некоторые программы некорректно работают с COM портами с номерами 10 и выше. Что же делать в случае, если ваша плата получила такой номер? Как задать COM порт для устройства? Как удалить зарезервированные COM порты? Все это и многое другое, вас ожидает в описании данной статьи, все вопросы по данной теме я жду в комментариях, в конце статьи, я постараюсь дать на них развернутый ответ.
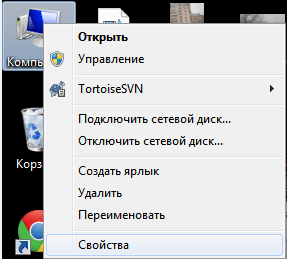
Открываем Мой Компьютер > Свойства
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-01
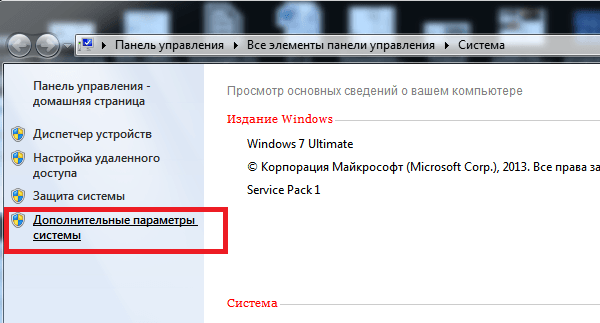
Выбираем «Дополнительные параметры системы».
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-02
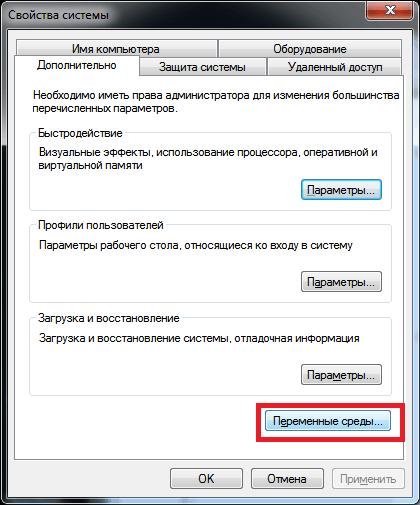
Открываем настройки переменных среды.
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-03
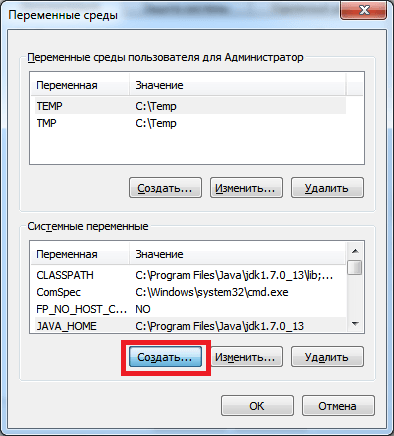
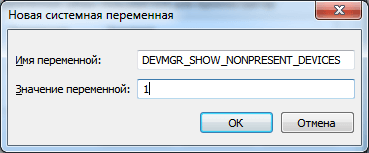
Создаем новую переменную.
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-04
Добавляем переменную DEVMGR_SHOW_NONPRESENT_DEVICES. Устанавливаем для неё значение в 1.
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-05
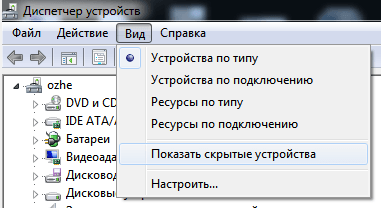
Нажимаем везде «ОК» и выходим. Далее идём в Диспетчер устройств (Мой Компьютер > Свойства > Диспетчер устройств). В пункте меню «Вид» включаем отображение скрытых устройств.
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-06
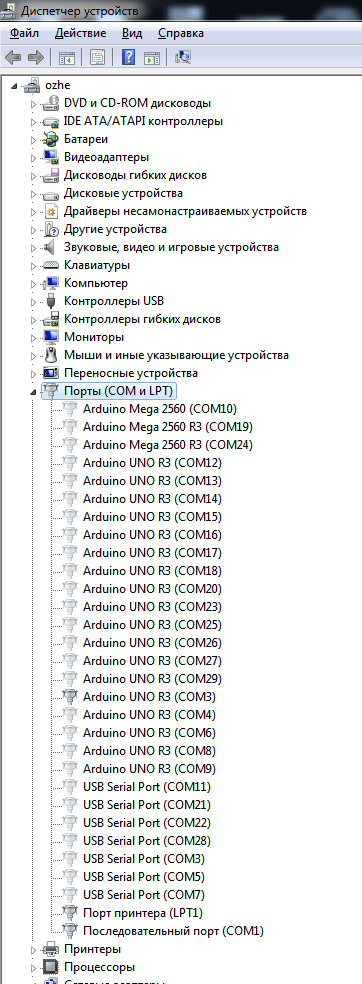
Теперь нам стали видны наши неиспользуемые устройства, занимающие COM порты и мы можем удалить их.
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-07
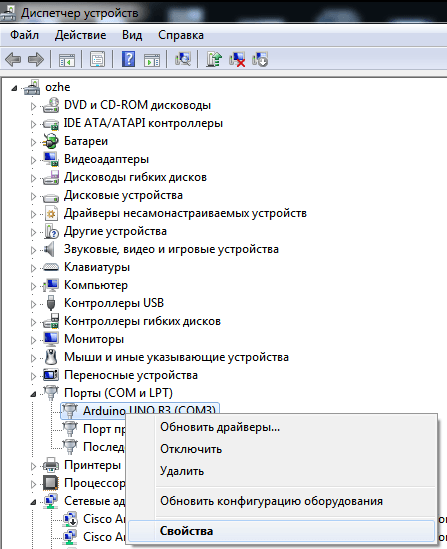
В Диспетчере устройств (Мой Компьютер > Свойства > Диспетчер устройств) выбираем устройство, которому мы хотим изменить COM порт.
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-08
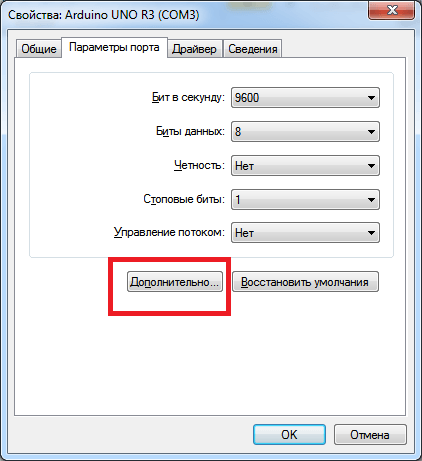
На вкладке «Параметры порта» нажимаем «Дополнительно».
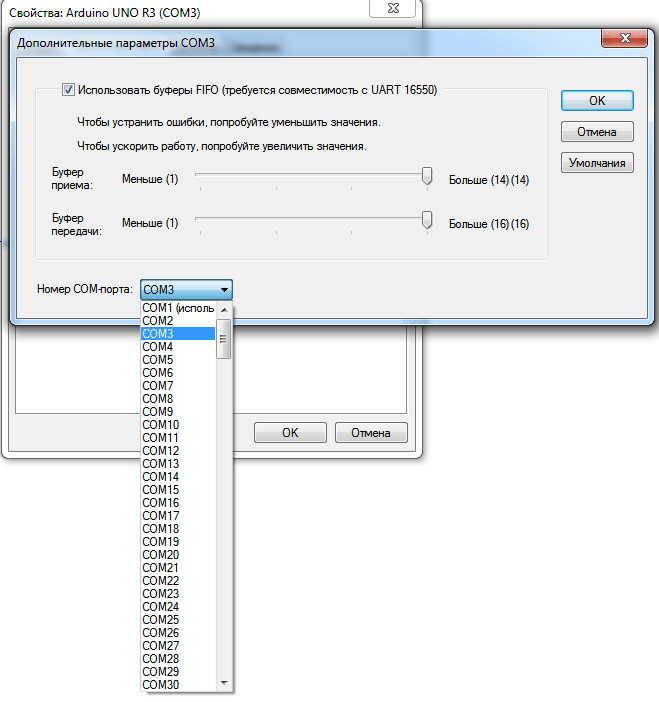
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-09
Назначаем желаемый номер для COM порта и нажимаем «ОК».
Как переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7-10
Вот так вот просто переназначить COM порт для устройства в Windows 7.
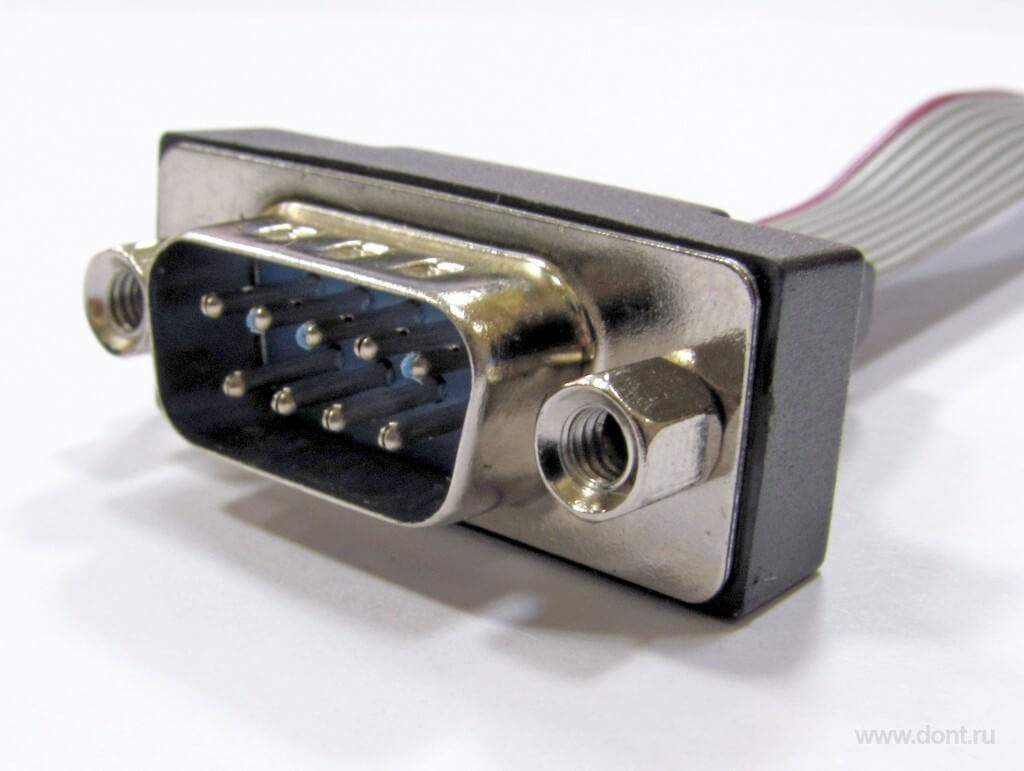
Serial Port
Ряд опций BIOS предназначен для настройки работы портов ввода-вывода компьютера. К подобной категории относится и опция Serial Port(Последовательный порт). Она позволяет настроить основные параметры работы последовательного порта, такие, как номера прерываний IRQ и адреса ввода-вывода.
Принцип работы
Последовательный порт компьютера является одним из самых старых и давно используемых портов ввода-вывода. В современных компьютерах последовательный порт можно встретить далеко не всегда, но и сейчас он имеет применение в определенных сферах. Также последовательный порт часто называют портом COM.
Отличительной особенностью последовательного порта является его способ организации передачи данных. В этом плане последовательный порт существенно отличается от параллельного порта, стандарт которого предусматривает наличие 8 линий данных, по которым происходит одновременная передача сигналов. Передача данных через последовательный порт осуществляется всего по двум линиям данных, одна из которых предназначена для передачи в одну сторону, от порта к подключенному к нему устройству, а другая – в обратную сторону. Отсылка данных при этом происходит в последовательном режиме, то есть, в режиме передачи битов друг за другом. Кроме того, COM-port имеет несколько служебных линий данных.
К последовательному порту можно подключать различные периферийные устройства. Чаще всего в качестве подобных устройств служат коммуникационные устройства, такие, как модемы, а также мыши. Кроме того, многие встроенные модемы эмулируют работу с COM port-ом.
Всего, как правило, в системе может быть не более 4 последовательных портов (COM1, COM2, COM3 и COM4). Для каждого из них в системе отводится определенное аппаратное прерывание IRQ, а также определенный адрес в памяти, через который порт может обращаться к центральному процессору. Как правило, под последовательные порты отводятся прерывания IRQ3 и IRQ4. Обычно они относятся соответственно к первому и второму последовательным портам. Порты COM3 и COM4 могут использовать прерывания, установленные соответственно для первого и второго портов.
Так как в персональном компьютере может быть не один COM-port, то в BIOS могут существовать две аналогичные друг другу опции, например, Serial Port 1 и Serial Port 2, предназначенные для настройки двух пар портов (нечетных и четных), расположенных на материнской плате. Опция Serial Port также может иметь и другие названия, например, COM Port, Serial Port Address, Onboard UART или Onboard Serial Port.
Опция Serial Port может принимать различные значения. Наиболее часто используется вариант значения Auto (Автоматический выбор). Выбор подобного варианта позволит BIOS автоматически настроить адрес ввода-вывода и номер прерывания соответствующего порта.
Также пользователь может указать значение адреса ввода-вывода и номер прерывания, выбрав его из набора вариантов. При этом варианты значений указываются в виде адрес/прерывание IRQ, например, 2F8/IRQ3. Как правило, пользователь может выбрать всего из двух значений прерывания – IRQ3 или IRQ4, а каждое прерывание имеет лишь два доступных адреса – 3F8, 3E8 для IRQ4 и 2F8, 2E8 для IRQ3. Таким образом, пользователь имеет всего 4 доступных варианта. В большинстве случаев для первого последовательного порта (COM1) в BIOS по умолчанию используется вариант 3F8/IRQ4. Но обычно оба прерывания (IRQ3 и IRQ4) и соответствующие им адреса ввода-вывода равноценны, и не имеет особого значения, какое из них следует выбрать пользователю.
В некоторых BIOS можно встретить и другие номера прерываний (не IRQ3 и IRQ4). Эта возможность может быть полезной в том случае, если прерывания IRQ3 и IRQ4 оказались заняты какими-то другими устройствами.
Иногда в параметре отсутствует выбор значений прерываний и адресов ввода-вывода, зато есть вариант Enabled (Включено). После выбора данного варианта становятся доступными две вложенные опции – Base I/O Address и Interrupt, которые предназначены соответственно для выбора адресов ввода-вывода и номеров прерываний. Такая конфигурация опции обычно встречается на материнских платах Intel.
Часто в опции Serial Port может встретиться также значение Disabled (Отключить). Установка данного значения позволяет отключить последовательный порт. При отключении port-а ресурсы, используемые им – прерывание и адрес ввода-вывода становятся свободными и могут быть использованы другими устройствами.
Какое значение выбрать?
В большинстве случаев лучше всего выбрать значение Auto, чтобы BIOS смогла бы автоматически выбрать нужные варианты прерываний и адресов ввода-вывода. Кроме того, современные операционные системы, такие, как Windows, умеют автоматически распределять адреса и прерывания устройств, поэтому их ручная настройка средствами BIOS не требуется. Тем не менее, если у вас установлена старая операционная система, такая, как MS-DOS, то в ряде случаев может потребоваться ручная установка прерываний. В частности, могут встречаться DOS-программы, которые требуют работы с COM-портом, имеющим определенное прерывание и определенное значение адреса ввода-вывода. В таком случае опция Serial Port может стать незаменимой для пользователя.
Также часто бывает так, что на материнской плате не существует ни одного последовательного порта, или существуют, но они не нужны пользователю. В подобном случае можно беспрепятственно отключить его, выбрав вариант Disabled. Эта операция позволит высвободить прерывание, что может оказаться полезным тогда, когда на материнской плате установлено множество устройств, между которыми могут случаться конфликты за прерывания. Кроме того, отключение COM port-а в BIOS может пригодиться и в том случае, если в системе установлен внутренний модем, использующий тот же самый порт – эта операция также позволит избежать конфликтов за ресурсы.
Win32_SerialPort class
The Win32_SerialPort WMI class represents a serial port on a computer system running Windows.
The following syntax is simplified from Managed Object Format (MOF) code and includes all of the inherited properties. Properties are listed in alphabetic order, not MOF order.
Syntax
Members
The Win32_SerialPort class has these types of members:
Methods
The Win32_SerialPort class has these methods.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Reset | Not implemented. To implement this method, see the Reset method in CIM_SerialController. |
| SetPowerState | Not implemented. To implement this method, see the SetPowerState method in CIM_SerialController. |
Properties
The Win32_SerialPort class has these properties.
Availability
Data type: uint16
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («MIF.DMTF|Operational State|003.5», «MIB.IETF|HOST-RESOURCES-MIB.hrDeviceStatus»)
Availability and status of the device.
Other (1)
Unknown (2)
Running/Full Power (3)
Running or Full Power
Warning (4)
In Test (5)
Not Applicable (6)
Power Off (7)
Off Line (8)
Off Duty (9)
Degraded (10)
Not Installed (11)
Install Error (12)
Power Save — Unknown (13)
The device is known to be in a power save mode, but its exact status is unknown.
Power Save — Low Power Mode (14)
The device is in a power save state but still functioning, and may exhibit degraded performance.
Power Save — Standby (15)
The device is not functioning, but could be brought to full power quickly.
Power Cycle (16)
Power Save — Warning (17)
The device is in a warning state, though also in a power save mode.
Paused (18)
The device is paused.
Not Ready (19)
The device is not ready.
Not Configured (20)
The device is not configured.
Quiesced (21)
The device is quiet.
Binary
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
If TRUE, the serial port is configured for binary data transfer. Because the Windows API does not support nonbinary mode transfers, this property must be TRUE.
Capabilities
Data type: uint16 array
Access type: Read-only
Array of chip-level compatibility for the serial controller. This property describes the buffering and other capabilities of the serial controller that may be inherent in the chip hardware. The property is an enumerated integer.
Other (1)
Unknown (2)
XT/AT Compatible (3)
16450 Compatible (4)
16550 Compatible (5)
16550A Compatible (6)
8251 Compatible (160)
8251FIFO Compatible (161)
CapabilityDescriptions
Data type: string array
Access type: Read-only
Array of free-form strings providing more detailed explanations for any of the serial controller features indicated in the Capabilities array. Note, each entry of this array is related to the entry in the Capabilities array that is located at the same index.
Caption
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Short description of the object.
ConfigManagerErrorCode
Data type: uint32
Access type: Read-only
Win32 Configuration Manager error code.
This device is working properly. (0)
Device is working properly.
This device is not configured correctly. (1)
Device is not configured correctly.
Windows cannot load the driver for this device. (2)
The driver for this device might be corrupted, or your system may be running low on memory or other resources. (3)
Driver for this device might be corrupted, or the system may be low on memory or other resources.
This device is not working properly. One of its drivers or your registry might be corrupted. (4)
Device is not working properly. One of its drivers or the registry might be corrupted.
The driver for this device needs a resource that Windows cannot manage. (5)
Driver for the device requires a resource that Windows cannot manage.
The boot configuration for this device conflicts with other devices. (6)
Boot configuration for the device conflicts with other devices.
Cannot filter. (7)
The driver loader for the device is missing. (8)
Driver loader for the device is missing.
This device is not working properly because the controlling firmware is reporting the resources for the device incorrectly. (9)
Device is not working properly. The controlling firmware is incorrectly reporting the resources for the device.
This device cannot start. (10)
Device cannot start.
This device failed. (11)
This device cannot find enough free resources that it can use. (12)
Device cannot find enough free resources to use.
Windows cannot verify this device’s resources. (13)
Windows cannot verify the device’s resources.
This device cannot work properly until you restart your computer. (14)
Device cannot work properly until the computer is restarted.
This device is not working properly because there is probably a re-enumeration problem. (15)
Device is not working properly due to a possible re-enumeration problem.
Windows cannot identify all the resources this device uses. (16)
Windows cannot identify all of the resources that the device uses.
This device is asking for an unknown resource type. (17)
Device is requesting an unknown resource type.
Reinstall the drivers for this device. (18)
Device drivers must be reinstalled.
Failure using the VxD loader. (19)
Your registry might be corrupted. (20)
Registry might be corrupted.
System failure: Try changing the driver for this device. If that does not work, see your hardware documentation. Windows is removing this device. (21)
System failure. If changing the device driver is ineffective, see the hardware documentation. Windows is removing the device.
This device is disabled. (22)
Device is disabled.
System failure: Try changing the driver for this device. If that doesn’t work, see your hardware documentation. (23)
System failure. If changing the device driver is ineffective, see the hardware documentation.
This device is not present, is not working properly, or does not have all its drivers installed. (24)
Device is not present, not working properly, or does not have all of its drivers installed.
Windows is still setting up this device. (25)
Windows is still setting up the device.
Windows is still setting up this device. (26)
Windows is still setting up the device.
This device does not have valid log configuration. (27)
Device does not have valid log configuration.
The drivers for this device are not installed. (28)
Device drivers are not installed.
This device is disabled because the firmware of the device did not give it the required resources. (29)
Device is disabled. The device firmware did not provide the required resources.
This device is using an Interrupt Request (IRQ) resource that another device is using. (30)
Device is using an IRQ resource that another device is using.
This device is not working properly because Windows cannot load the drivers required for this device. (31)
Device is not working properly. Windows cannot load the required device drivers.
ConfigManagerUserConfig
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
If TRUE, the device is using a user-defined configuration.
CreationClassName
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Name of the first concrete class to appear in the inheritance chain used in the creation of an instance. When used with the other key properties of the class, the property allows all instances of this class and its subclasses to be uniquely identified.
Description
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Description of the object.
DeviceID
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Unique identifier of the serial port with other devices on the system.
ErrorCleared
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
If TRUE, the error reported in LastErrorCode is now cleared.
ErrorDescription
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Free-form string supplying more information about the error recorded in LastErrorCode, and information about any corrective actions that may be taken.
InstallDate
Data type: datetime
Access type: Read-only
Date and time the object was installed. This property does not need a value to indicate that the object is installed.
LastErrorCode
Data type: uint32
Access type: Read-only
Last error code reported by the logical device.
MaxBaudRate
Data type: uint32
Access type: Read-only
Maximum baud rate (in bits per second) supported by the serial controller.
MaximumInputBufferSize
Data type: uint32
Access type: Read-only
Maximum size of the serial port driver’s internal input buffer. A value of 0 (zero) indicates that no maximum value is imposed by the serial provider.
MaximumOutputBufferSize
Data type: uint32
Access type: Read-only
Maximum size of the serial port driver’s internal output buffer. A value of 0 (zero) indicates that no maximum value is imposed by the serial provider.
MaxNumberControlled
Data type: uint32
Access type: Read-only
Maximum number of directly addressable entities supportable by this controller. A value of 0 (zero) should be used if the number is unknown.
Name
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Label by which the object is known. When subclassed, the property can be overridden to be a key property.
OSAutoDiscovered
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
If TRUE, the instances of this class were automatically discovered by the operating system. If, for example, hardware was added through Control Panel, the operating system finds instances of this class by querying hardware from the instances of this class.
PNPDeviceID
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Windows Plug and Play device identifier of the logical device.
PowerManagementCapabilities
Data type: uint16 array
Access type: Read-only
Array of the specific power-related capabilities of a logical device.
This property is inherited from CIM_LogicalDevice.
Unknown (0)
Not Supported (1)
Disabled (2)
Enabled (3)
The power management features are currently enabled but the exact feature set is unknown or the information is unavailable.
Power Saving Modes Entered Automatically (4)
The device can change its power state based on usage or other criteria.
Power State Settable (5)
The SetPowerState method is supported. This method is found on the parent CIM_LogicalDevice class and can be implemented. For more information, see Designing Managed Object Format (MOF) Classes.
Power Cycling Supported (6)
The SetPowerState method can be invoked with the PowerState parameter set to 5 (Power Cycle).
Timed Power On Supported (7)
Timed Power-On Supported
The SetPowerState method can be invoked with the PowerState parameter set to 5 (Power Cycle) and Time set to a specific date and time, or interval, for power-on.
PowerManagementSupported
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
If TRUE, the device can be power-managed (can be put into suspend mode, and so on). The property does not indicate that power management features are currently enabled, only that the logical device is capable of power management.
ProtocolSupported
Data type: uint16
Access type: Read-only
Protocol used by the controller to access «controlled» devices.
This property is inherited from CIM_Controller. The following list shows the possible values.
Other (1)
Unknown (2)
EISA (3)
ISA (4)
PCI (5)
ATA/ATAPI (6)
Flexible Diskette (7)
1496 (8)
SCSI Parallel Interface (9)
SCSI Fibre Channel Protocol (10)
SCSI Serial Bus Protocol (11)
SCSI Serial Bus Protocol-2 (1394) (12)
SCSI Serial Storage Architecture (13)
VESA (14)
PCMCIA (15)
Universal Serial Bus (16)
Parallel Protocol (17)
ESCON (18)
Diagnostic (19)
I2C (20)
Power (21)
HIPPI (22)
MultiBus (23)
VME (24)
IPI (25)
IEEE-488 (26)
RS232 (27)
IEEE 802.3 10BASE5 (28)
IEEE 802.3 10BASE2 (29)
IEEE 802.3 1BASE5 (30)
IEEE 802.3 10BROAD36 (31)
IEEE 802.3 100BASEVG (32)
IEEE 802.5 Token-Ring (33)
ANSI X3T9.5 FDDI (34)
MCA (35)
ESDI (36)
IDE (37)
CMD (38)
ST506 (39)
DSSI (40)
QIC2 (41)
Enhanced ATA/IDE (42)
AGP (43)
TWIRP (two-way infrared) (44)
FIR (fast infrared) (45)
SIR (serial infrared) (46)
IrBus (47)
ProviderType
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Communications provider type.
«FAX Device» «LAT Protocol» «Modem Device» «Network Bridge» «Parallel Port» «RS232 Serial Port» «RS422 Port» «RS423 Port» «RS449 Port» «Scanner Device» «TCP/IP TelNet» «X.25» «Unspecified»
FAX Device («FAX Device»)
LAT Protocol («LAT Protocol»)
Modem Device («Modem Device»)
Network Bridge («Network Bridge»)
Parallel Port («Parallel Port»)
RS232 Serial Port («RS232 Serial Port»)
RS422 Port («RS422 Port»)
RS423 Port («RS423 Port»)
RS449 Port («RS449 Port»)
Scanner Device («Scanner Device»)
TCP/IP TelNet («TCP/IP TelNet»)
X.25 («X.25»)
Unspecified («Unspecified»)
SettableBaudRate
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
If TRUE, the baud rate can be changed for this serial port.
SettableDataBits
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwSettableParams|SP_DATABITS»)
If TRUE, data bits can be set for this serial port.
SettableFlowControl
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwSettableParams|SP_HANDSHAKING»)
If TRUE, flow control can be set for this serial port.
SettableParity
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwSettableParams|SP_PARITY»)
If TRUE, parity can be set for this serial port.
SettableParityCheck
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwSettableParams|SP_PARITY_CHECK»)
If TRUE, parity checking can be set for this serial port (if parity checking is supported).
SettableRLSD
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
If TRUE, Received Line Signal Detect (RLSD) can be set for this serial port (if RLSD is supported).
SettableStopBits
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwSettableParams|SP_STOPBITS»)
If TRUE, stop bits can be set for this serial port.
Status
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Current status of the object. Various operational and nonoperational statuses can be defined. Operational statuses include: «OK», «Degraded», and «Pred Fail» (an element, such as a SMART-enabled hard disk drive, may be functioning properly but predicting a failure in the near future). Nonoperational statuses include: «Error», «Starting», «Stopping», and «Service». The latter, «Service», could apply during mirror-resilvering of a disk, reload of a user permissions list, or other administrative work. Not all such work is online, yet the managed element is neither «OK» nor in one of the other states.
Values include the following:
OK («OK»)
Error («Error»)
Degraded («Degraded»)
Unknown («Unknown»)
Pred Fail («Pred Fail»)
Starting («Starting»)
Stopping («Stopping»)
Service («Service»)
Stressed («Stressed»)
NonRecover («NonRecover»)
No Contact («No Contact»)
Lost Comm («Lost Comm»)
StatusInfo
Data type: uint16
Access type: Read-only
State of the logical device. If this property does not apply to the logical device, the value 5 (Not Applicable) should be used.
Other (1)
Unknown (2)
Enabled (3)
Disabled (4)
Not Applicable (5)
Supports16BitMode
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_16BITMODE»)
If TRUE, 16-bit mode is supported on this serial port.
SupportsDTRDSR
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_DTRDSR»)
If TRUE, data terminal ready (DTR) and data set ready (DSR) signals are supported on this serial port.
SupportsElapsedTimeouts
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_TOTALTIMEOUTS»)
If TRUE, elapsed time-outs are supported on this serial port. Elapsed timeouts track the total amount of time between data transmissions.
SupportsIntTimeouts
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_INTTIMEOUTS»)
If TRUE, interval time-outs are supported. An interval timeout is the amount of time allowed to elapse between the arrival of each piece of data.
SupportsParityCheck
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_PARITY_CHECK»)
If TRUE, parity checking is supported on this serial port.
SupportsRLSD
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_RLSD»)
If TRUE, Received Line Signal Detect (RLSD) is supported on this serial port.
SupportsRTSCTS
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_RTSCTS»)
If TRUE, ready to send (RTS) and clear to send (CTS) signals are supported on this serial port.
SupportsSpecialCharacters
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_SPECIALCHARS»)
If TRUE, serial port control characters are supported. These characters signal events rather than data. These characters are not displayable and are set by the driver. They include EofChar, ErrorChar, BreakChar, EventChar, XonChar, and XoffChar.
SupportsXOnXOff
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_XONXOFF»)
If TRUE, XON or XOFF flow-control is supported on this serial port.
SupportsXOnXOffSet
Data type: boolean
Access type: Read-only
Qualifiers: MappingStrings («Win32API|Communication Structures|COMMPROP|dwProvCapabilities|PCF_SETXCHAR»)
If TRUE, the communications provider supports configuration of the XONor XOFF flow-control setting.
SystemCreationClassName
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Value of the scoping computer’s CreationClassName property.
SystemName
Data type: string
Access type: Read-only
Name of the scoping system.
TimeOfLastReset
Data type: datetime
Access type: Read-only
Date and time this controller was last reset. This could mean the controller was powered down, or reinitialized.
Remarks
The Win32_SerialPort class is derived from CIM_SerialController.
Examples
For an alternate method of retrieving serial port information (from the registry), see the Enumerate Ports Visual Basic sample.
The List Serial Port Properties PowerShell example returns information about the serial ports installed on a computer.
The following VBScript sample returns information about the serial ports installed on a computer.