- How to use the Windows command line (DOS)
- Get into the Windows command line
- Understanding the prompt
- Key tips
- Listing the files
- Moving into a directory
- Understand the files
- Moving back a directory
- Creating a directory
- Switching drives
- Creating a new file
- Creating a new batch file
- Moving and copying a file
- Rename a file
- Deleting a file
- Renaming a directory
- Removing a directory
- Running a program
- How to list available commands
- Closing or exiting the command line window
- In conclusion
- Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
- Command line syntax
- Options and commands
- Command line argument examples
- Target a specific window
- Open a new profile instance
- Target a directory
- Multiple tabs
- Multiple panes
- Multiple tabs and panes
- Tab title
- Using application title (Preview)
- Tab color
- Color scheme (Preview)
- Tab focus
- Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
- Single quoted parameters
- Escaped quotes
- Using start
How to use the Windows command line (DOS)
This page covers the basics of navigating and using the Microsoft Windows command line. On this page, you learn how to move around in the command line, find files, manipulate files, and other important commands. Keep in mind that there are over 100 different commands used in MS-DOS and the Windows command line. If you are interested in learning about the command line in more detail, see our DOS and command prompt overview, which gives a description and example for every command.
Get into the Windows command line
Open a Windows command line window by following the steps below. If you need additional information or alternative methods for all versions of Windows, see: How to get to an MS-DOS prompt or Windows command line.
- Click Start.
- In the Search or Run line, type cmd (short for command), and press Enter .
Understanding the prompt
After following the steps above, the Windows command line should be shown (similar to the example below). Windows often starts you at your user directory. In the example below, the user is Mrhope. So, C:\Users\Mrhope> is our prompt. This prompt shows that we’re in the C: drive (default hard drive letter) and currently in the Mrhope directory, a subdirectory of the Users directory.
Key tips
- MS-DOS and the Windows command line are notcase sensitive.
- The files and directories shown in Windows are also found in the command line.
- When working with a file or directory with a space, surround it in quotes. For example, the directory My Documents would be «My Documents» when typed.
- File names can have a long file name of 255 characters and a three character file extension.
- When a file or directory is deleted in the command line, it is not moved into the Recycle Bin.
- If you need help with any of command, type /? after the command. For example, dir /? would give the options available for the dir command.
Listing the files
Let’s learn your first command. Type dir at the prompt to list files in the current directory. You should get an output similar to the example image below. Without using any dir options, this is how dir output appears. As shown, you are given lots of useful information including the creation date and time, directories ( ), and the name of the directory or file. In the example below, there are 0 files listed and 14 directories, indicated by the status message at the bottom of the output.
Every command in the command line has options, which are additional switches and commands that can be added after the command. For example, with the dir command, you can type dir /p to list the files and directories in the current directory one page at a time. This switch is useful to see all the files and directories in a directory with dozens or hundreds of files. Each of the command options and switches is listed in our DOS command overview. We offer guides for individual commands, as well. For example, if you want to see all the options for the dir command, refer to our dir command overview for a complete option listing.
The dir command can also be used to search for specific files and directories using wildcards. For example, to list files or directories that begin with the letter «A» you could type dir a* to list only the AppData directory, in this above example. See the wildcard definition for other examples and help with using wildcards.
Moving into a directory
Now that we’ve seen a list of directories (shown below) in the current directory, move into one of those directories. To move into a directory, we use the cd command, so to move into the Desktop type cd desktop and press Enter . Once you’ve moved into a new directory, the prompt changes. So, in our example, the prompt is now C:\Users\Mrhope\Desktop>. You can see what files are found in this directory by typing the dir command again.
Understand the files
In the Desktop directory, as shown in the above example, there are 23 files and 7 directories, representing different file types. In Windows, you are familiar with files having icons that help represent the file type. In the command line, the same thing is accomplished by the file extensions. For example, «forum posts.txt» is a text file because it has a .txt file extension. Time.mp3 is an MP3 music file and minecraft.exe is an executable file.
Most users are only concerned with executable files, which as mentioned above, are files ending with .exe, .com, and .bat. When the file name is typed in the command line, the program runs, which is the same as double-clicking a file in Windows. For example, if we wanted to run minecraft.exe, typing minecraft at the prompt runs that program.
Keep in mind that if the executable file you are trying to run is not in the current directory, you get an error. Unless you have set a path for the directory with the executable file, which is how the command line finds external commands.
If you want to view the contents of a file, most versions of the command line use the edit command. For example, if we wanted to look at the log file hijackthis.log, we would type edit hijackthis.log at the prompt. For 64-bit versions of Windows that do not support this command, you can use the start command (e.g., type start notepad hijackthis.log) to open the file in Notepad. Additional information about opening and editing a file from the command line is available on the page linked below.
Moving back a directory
You learned earlier the cd command can move into a directory. This command also allows you to go back a directory by typing cd.. at the prompt. When this command is typed, you’ll be moved out of the Desktop directory and back into the user directory. To move back to the root directory type cd\ to get to the C:\> prompt. If you know the name of the directory you want to move into, you can also type cd\ and the directory name. For example, to move into C:\Windows>, type cd\windows at the prompt.
Creating a directory
Now with your basic understanding of navigating the command line, let’s start creating new directories. To create a directory in the current directory, use the mkdir command. For example, create a directory called «test» by typing mkdir test at the prompt. If created successfully, you are returned to the prompt with no error message. After the directory is created, move into that directory with the cd command.
Switching drives
In some circumstances, you may want to copy or list files on another drive. To switch drives in the Windows command line, type the drive letter of the drive followed by a colon. For example, if your CD-ROM drive is the D drive, you would type d: and press Enter . If the drive exists, the prompt changes to that drive letter. If the drive does not exist or is not accessible (e.g., no disc in CD-ROM drive), you get an error.
Creating a new file
You can create a new file from the command line using the edit command, copy con command, or using the start command to open a file.
Creating a new batch file
In the new test directory, let’s create your first file. In most circumstances, you never need to create any file at the command line, but it is still good to understand how files are created. In this example, we are creating a batch file. A batch file is a file that ends with .bat and helps automate frequently used commands in the command line. We are calling this batch file example, so type edit example.bat at the prompt. As mentioned in the document on creating a file, if the edit command does not work, use the start command to open the batch file in Notepad. To perform this action, you type start notepad example.bat into the prompt.
Both of the commands above open a new blank example.bat window. In the file, type the three lines below, which clear the screen with the cls command and run the dir command.
After these three lines are typed into the file, save, and exit the file. If you are in the edit command, click File (or press Alt + F ) and then Save. After the file is saved and you are back at the command prompt, typing dir displays the «example.bat» file in the test directory.
Now, run the batch file to get a better understanding of what a batch file does. To run the batch file, type example at the prompt, which executes the batch file, clears the screen, and runs the dir command.
Moving and copying a file
Now that we’ve created a file, let’s move it into an alternate directory. To help make things easier, create another directory for the files. So, type mkdir dir2 to create a new directory in the test directory called dir2. After the new directory is created, use the move command to move the example.bat file into that directory. To do this, type move example.bat dir2 at the prompt. If done successfully, you get a message indicating the file was moved. You could also substitute the move command for the copy command to copy the file instead of moving it.
Rename a file
After the file is moved into the dir2 directory, move into that directory with the cd command to rename the file. In the dir2 directory, use the rename command to rename the example file into an alternate name. Type rename example.bat first.bat at the prompt to rename the file to «first.bat.» Now, when using the dir command, you see «first.bat» as the only file.
When renaming any file, make sure the file has the same file extension. If you were to rename the .bat file to a .txt file, it is no longer an executable file only a text file. Also, keep in mind that renaming the file to a different file extension does not convert the file. For example, if you renamed the file as an .MP3, it may look like an MP3 in Windows, but it’s not going to play music.
Deleting a file
Now that we’ve had our fun with our new file, delete the file with the del command. Type del first.bat to delete the first.bat file. If successful, you are returned to the prompt with no errors, and the dir command shows no files in the current directory.
When deleting files, you can also use wildcards to delete multiple files at once. For example, if the directory contained several .GIF image files you could type del *.gif to delete all files ending with the .gif file extension.
Renaming a directory
Go back one directory to get back to the test directory using the cd.. command mentioned earlier. Now, rename our dir2 directory to something else using the same rename command we used earlier. At the prompt, type rename dir2 hope to rename the directory to «hope.» After this command is completed, type dir and you see one directory called «hope.»
Removing a directory
While still in the test directory, remove the hope directory using the rmdir command. At the prompt, type rmdir hope to remove the hope directory.
If the directory you are trying to remove contains any files or directories, you’ll receive an error. To prevent this error, use the /s option. For example, if the hope directory still had the first.bat file, you would need to type rmdir /s hope at the prompt.
Running a program
Any executable file can run from the command line by typing the name of the file. For example, if you listed files using the dir command and see a file named «myfile.exe,» typing «myfile» at the command line runs that program.
How to list available commands
After getting a good understanding of using the command line from the steps shown above, you can move on to other available commands by typing help at the command line. Typing «help» displays a list of available commands with a brief description of each command.
Closing or exiting the command line window
After you are done with the Windows command line, you can type exit to close the window.
In conclusion
Now you have a good understanding of how to navigate the command line, create directories and files, rename directories and files, and delete. As mentioned earlier, there are hundreds of other commands you can use at the command line. If you want to expand your knowledge further, we recommend looking at the options available for each command above and reviewing our commands overview page. You can also use our search to find any command by the name of the command or by the action it performs.
Using command line arguments for Windows Terminal
You can use wt.exe to open a new instance of Windows Terminal from the command line. You can also use the execution alias wt instead.
If you built Windows Terminal from the source code on GitHub, you can open that build using wtd.exe or wtd .
Command line syntax
The wt command line accepts two types of values: options and commands. Options are a list of flags and other parameters that can control the behavior of the wt command line as a whole. Commands provide the action, or list of actions separated by semicolons, that should be implemented. If no command is specified, then the command is assumed to be new-tab by default.
To display a help message listing the available command line arguments, enter: wt -h , wt —help , wt -? , or wt /? .
Options and commands
Below is the full list of supported commands and options for the wt command line.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| —help , -h , -? , /? | Displays the help message. |
| —maximized , -M | Launches the terminal maximized. |
| —fullscreen , -F | Launches the terminal as full screen. |
| —focus , -f | Launches the terminal in the focus mode. Can be combined with maximized . |
| —window , -w | Launches the terminal in a specific window. |
| Command | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| new-tab , nt | —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , commandline , —title , —tabColor | Creates a new tab. |
| split-pane , sp | -H, —horizontal , -V, —vertical , —profile, -p profile-name , —startingDirectory, -d starting-directory , —title , —tabColor , —size, -s size , commandline , -D, —duplicate | Splits a new pane. |
| focus-tab , ft | —target, -t tab-index | Focuses on a specific tab. |
| move-focus , mf | direction | Move focus between panes in the given direction. Accepts one of up , down , left , right . |
When opening Windows Terminal from cmd (Command Prompt), if you want to use your custom «cmd» profile settings, you will need to use the command wt -p cmd . Otherwise, to run your default profile settings, just use wt cmd .
The -D, —duplicate parameter for split-pane is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Command line argument examples
Commands may vary slightly depending on which command line you’re using.
Target a specific window
The ability for the —window,-w parameter to accept window names is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Below are examples of how to target specific windows using the —window,-w option.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Open a new profile instance
To open a new terminal instance, in this case the command will open the profile named «Ubuntu-18.04», enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
The -p flag is used to specify the Windows Terminal profile that should be opened. Substitute «Ubuntu-18.04» with the name of any terminal profile that you have installed. This will always open a new window. Windows Terminal is not yet capable of opening new tabs or panes in an existing instance.
Target a directory
To specify the folder that should be used as the starting directory for the console, in this case the d:\ directory, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
Multiple tabs
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running.
To open a new terminal instance with multiple tabs, in this case a Command Prompt profile and a PowerShell profile, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Multiple panes
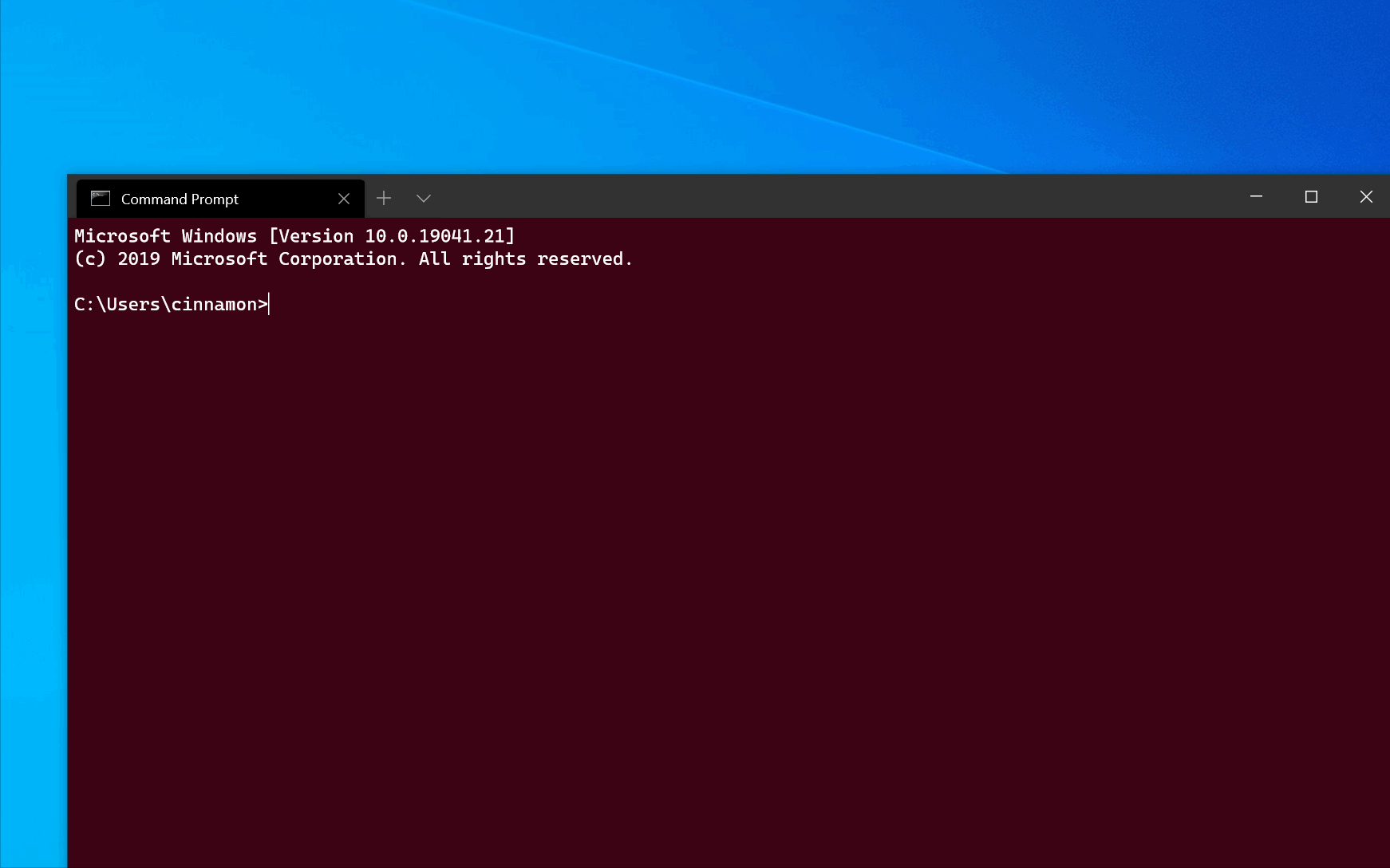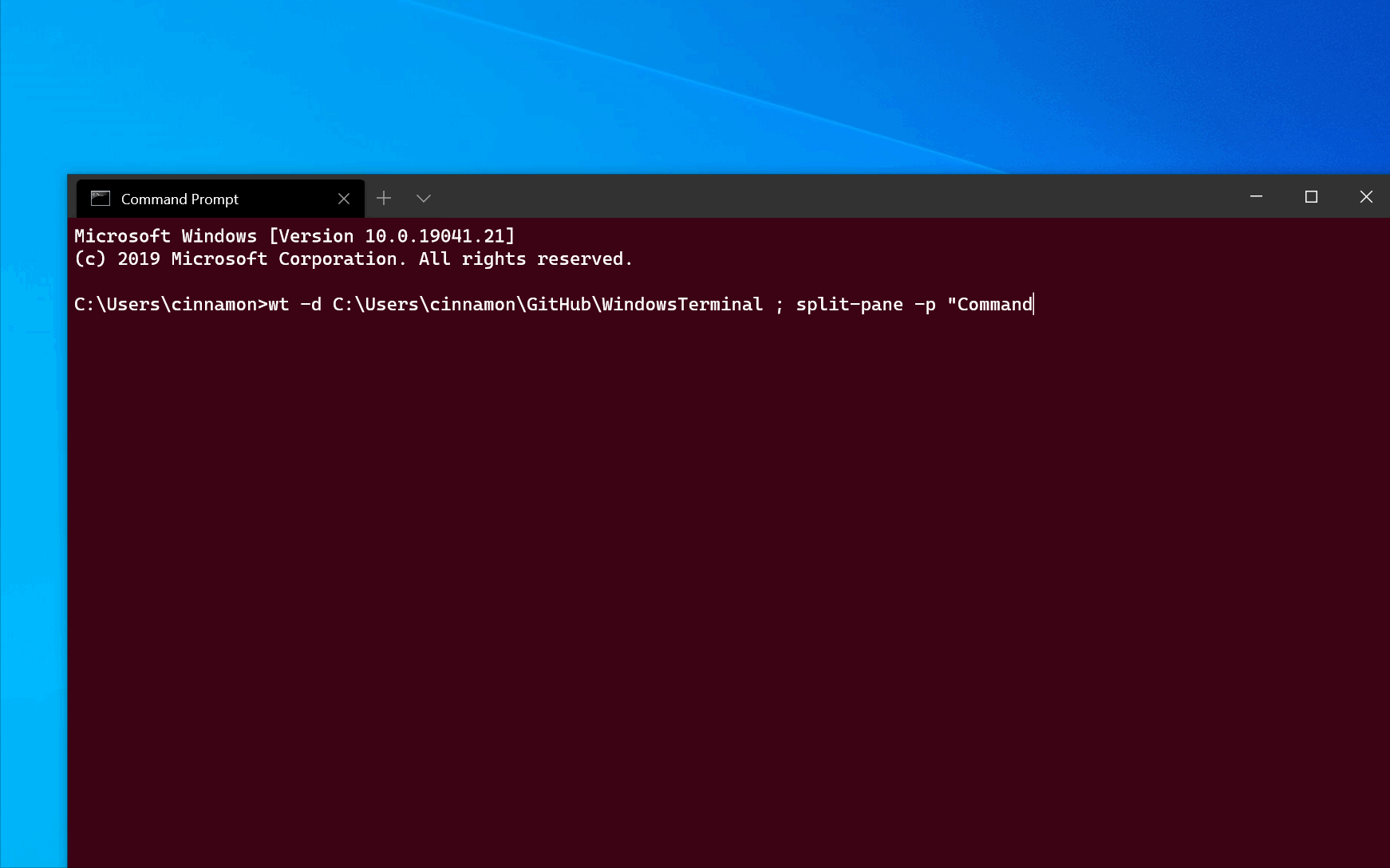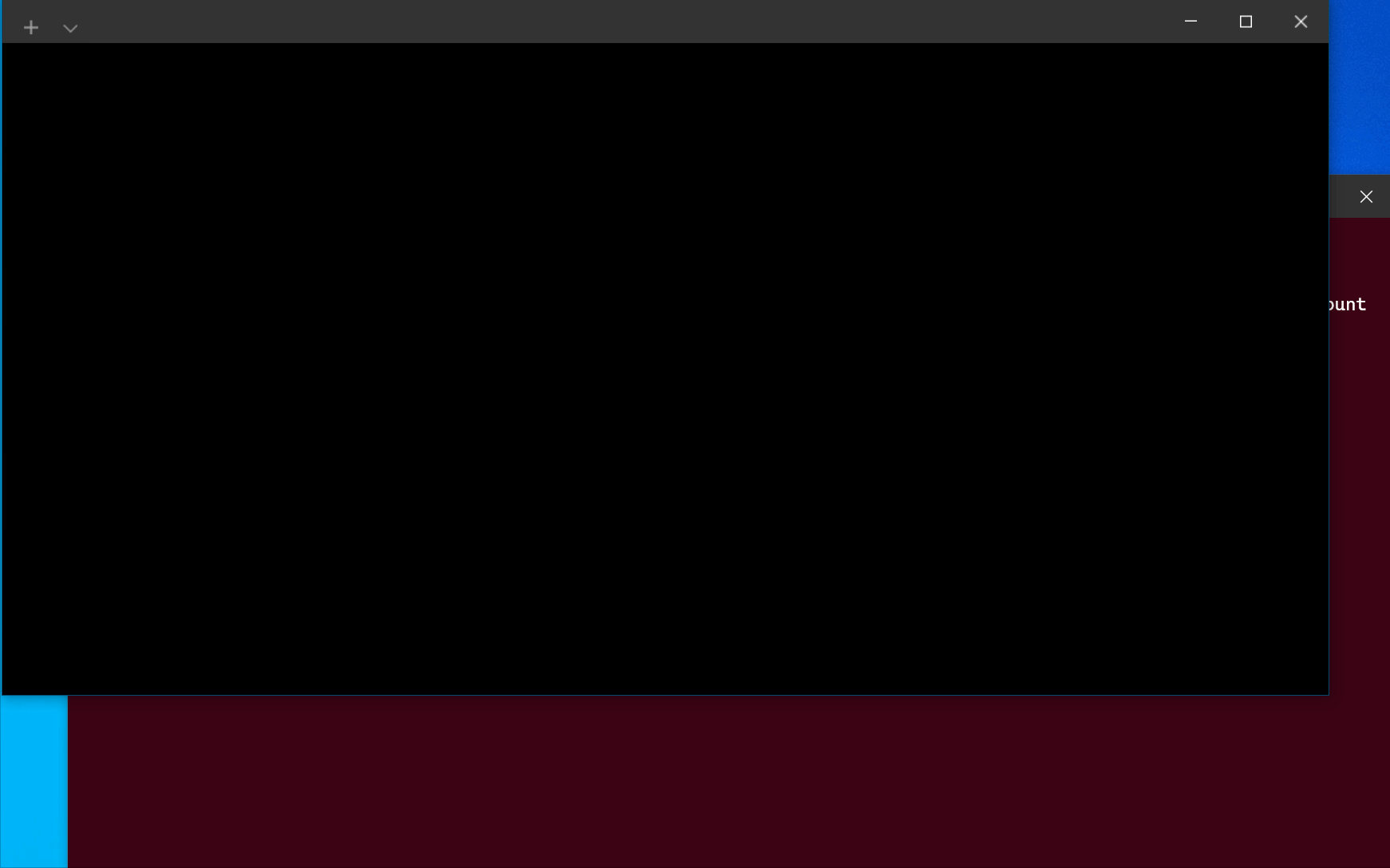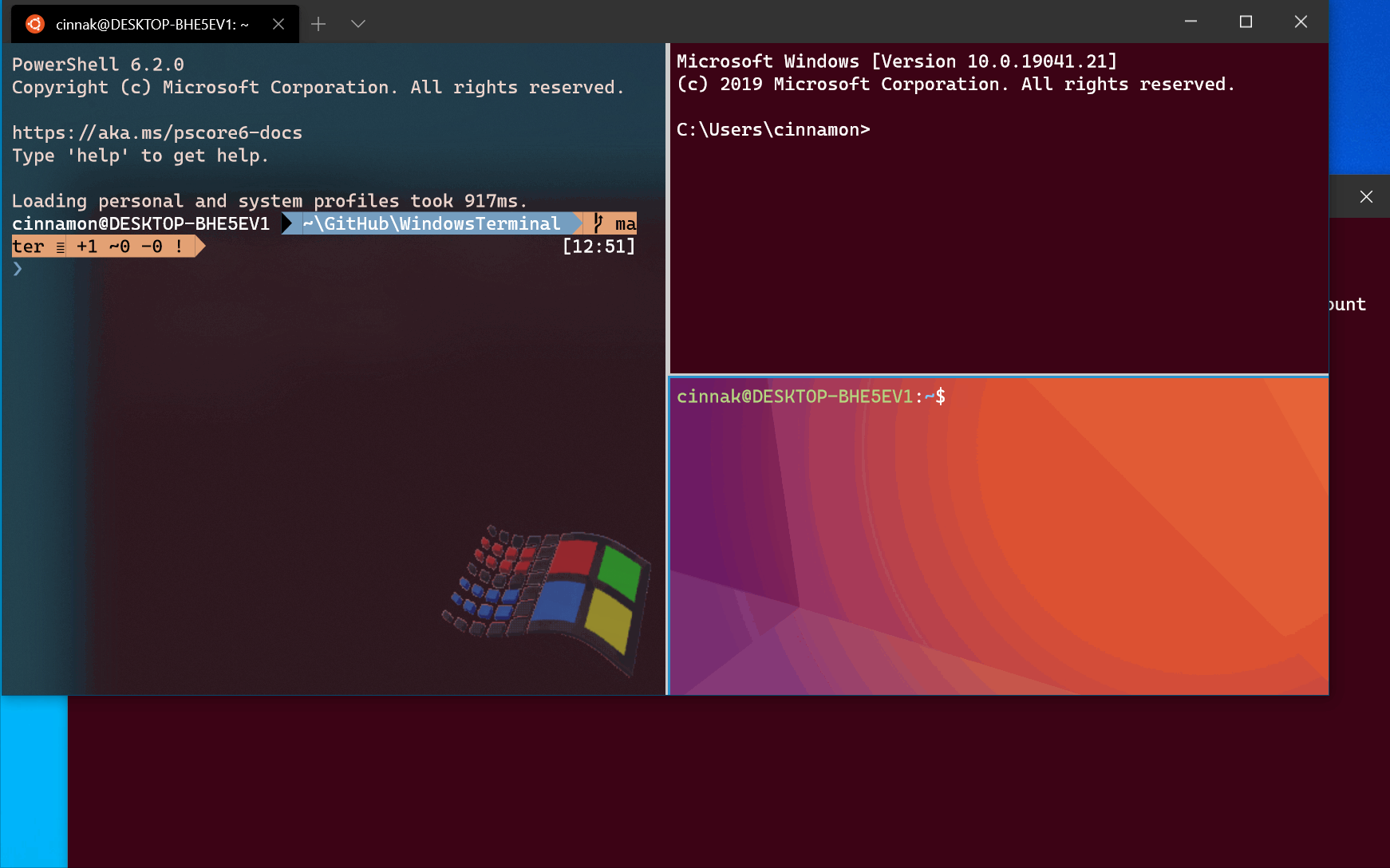
To open a new terminal instance with one tab containing three panes running a Command Prompt profile, a PowerShell profile, and your default profile running a WSL command line, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
The -H flag (or —horizontal ) indicates that you would like the panes to be split horizontally. The -V flag (or —vertical ) indicates that you would like the panes split vertically.
Multiple tabs and panes
The new-tab and split-pane commands can be sequenced to get multiple tabs, each with split panes. To open a new terminal instance with two tabs, each with two panes running a Command Prompt and a WSL command line, with each tab in a different directory, enter:
PowerShell uses a semicolon ; to delimit statements. To interpret a semicolon ; as a command delimiter for wt command-line arguments, you need to escape semicolon characters using backticks. PowerShell also has the stop parsing operator (—%), which instructs it to stop interpreting anything after it and just pass it on verbatim.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands. Note to specify a Windows directory as the starting directory for wsl.exe that two backslashes \\ are required.
Tab title
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab titles, use the —title argument. To set the title of each tab when opening two tabs, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; forward-slash + semicolon separates commands.
Using application title (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance allowing applications within it to set the tab title by sending title change messages, use the —useApplicationTitle flag. To suppress these messages, use the —suppressApplicationTitle flag. If none of these flags are provided, the behavior is inherited from the profile’s settings. To open a tab with title tabname that will not be overridden by the application, enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab color
To open a new terminal instance with custom tab colors, use the —tabColor argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile, but can be overridden as well using the tab color picker. In the following example, a new terminal is created with two tabs of different colors:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
When —tabColor is set for a tab, it is associated with the first pane of this tab. Hence in a tab with multiple panes, the color will be applied only if the first pane is in focus. To set the tab color for additional panes, you will need to add the —tabColor parameter to the split-pane subcommand as well. In the example below, a tab with two panes is created with tab colors specified for each pane:
Color scheme (Preview)
To open a new terminal instance with a specific color scheme (instead of the colorScheme set in the profile), use the —colorScheme argument. This argument overrides the value defined in the profile.
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and \; separates commands.
This feature is only available in Windows Terminal Preview.
Tab focus
To open a new terminal instance with a specific tab in focus, use the -t flag (or —target ), along with the tab-index number. To open your default profile in the first tab and the «Ubuntu-18.04» profile focused in the second tab ( -t 1 ), enter:
Execution aliases do not work in WSL distributions. If you want to use wt.exe from a WSL command line, you can spawn it from CMD directly by running cmd.exe . The /c option tells CMD to terminate after running and the \; backslash + semicolon separates commands.
Examples of multiple commands from PowerShell
Windows Terminal uses the semicolon character ; as a delimiter for separating commands in the wt command line. Unfortunately, PowerShell also uses ; as a command separator. To work around this, you can use the following tricks to run multiple wt commands from PowerShell. In all the following examples, a new terminal window is created with three panes — one running Command Prompt, one with PowerShell, and the last one running WSL.
The following examples use the Start-Process command to run wt . For more information on why the terminal uses Start-Process , see Using start below.
Single quoted parameters
In this example, the wt parameters are wrapped in single quotes ( ‘ ). This syntax is useful if nothing is being calculated.
Escaped quotes
When passing a value contained in a variable to the wt command line, use the following syntax:
Note the usage of ` to escape the double-quotes ( » ) around «Windows PowerShell» in the -p parameter to the split-pane parameter.
Using start
All the above examples explicitly used start to launch the terminal.
The following examples do not use start to run the command line. Instead, there are two other methods of escaping the command line:
- Only escaping the semicolons so that PowerShell will ignore them and pass them straight to wt .
- Using —% , so PowerShell will treat the rest of the command line as arguments to the application.
In both of these examples, the newly created Windows Terminal window will create the window by correctly parsing all the provided command-line arguments.
However, these methods are not recommended currently, as PowerShell will wait for the newly-created terminal window to be closed before returning control to PowerShell. By default, PowerShell will always wait for Windows Store applications (like Windows Terminal) to close before returning to the prompt. Note that this is different than the behavior of Command Prompt, which will return to the prompt immediately.