- What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
- What is an Operating System?
- History Of OS
- Examples of Operating System with Market Share
- Types of Operating System (OS)
- Batch Operating System
- Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
- Real time OS
- Distributed Operating System
- Network Operating System
- Mobile OS
- Functions of Operating System
- Features of Operating System (OS)
- Advantage of using Operating System
- Disadvantages of using Operating System
- What is a Kernel?
- Features of Kennel
- Types of Kernels
- Operating System Classes
- Desktop
- Drivers
- File System
- Job Objects
- Memory and Page Files
- Multimedia Audio or Visual
- Networking
- Operating System Events
- Operating System Settings
- Processes
- Registry
- Scheduler Jobs
- Security
- Services
- Shares
- Start Menu
- Storage
- Users
- Windows Event Log
- Windows Product Activation
What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
What is an Operating System?
An Operating System (OS) is a software that acts as an interface between computer hardware components and the user. Every computer system must have at least one operating system to run other programs. Applications like Browsers, MS Office, Notepad Games, etc., need some environment to run and perform its tasks.
The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. It is not possible for the user to use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system. 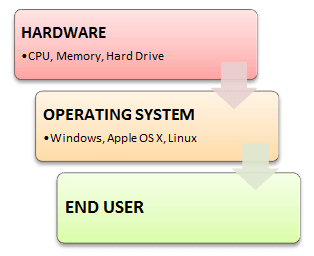
History Of OS
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The General Motors Research Lab implemented the first OS in the early 1950s for their IBM 701
- In the mid-1960s, operating systems started to use disks
- In the late 1960s, the first version of the Unix OS was developed
- The first OS built by Microsoft was DOS. It was built in 1981 by purchasing the 86-DOS software from a Seattle company
- The present-day popular OS Windows first came to existence in 1985 when a GUI was created and paired with MS-DOS.
Examples of Operating System with Market Share
Following are the examples of Operating System with the latest Market Share
| OS Name | Share |
| Windows | 40.34 |
| Android | 37.95 |
| iOS | 15.44 |
| Mac OS | 4.34 |
| Linux | 0.95 |
| Chrome OS | 0.14 |
| Windows Phone OS | 0.06 |
Types of Operating System (OS)
Following are the popular types of Operating System:
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
Time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed as time sharing.
Real time OS
A real time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems are the Real time OS example.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to its users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, user, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.
Functions of Operating System
Below are the main functions of Operating System: 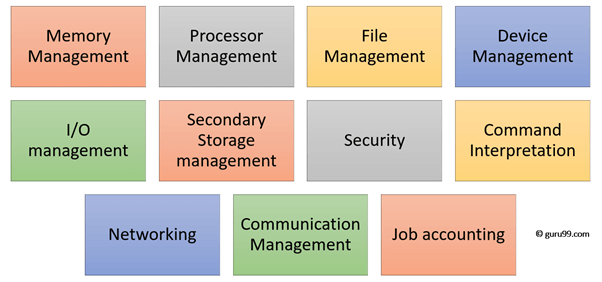
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources.
- File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
- I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware devices from the user.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which includes primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
- Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access.
- Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process that commands.
- Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
- Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users.
- Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and another software resource of the various users of the computer systems.
Features of Operating System (OS)
Here is a list important features of OS:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection

Advantage of using Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware’s and software’s of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- Operating system’s software is quite expensive for small size organization which adds burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
What is a Kernel?
The kernel is the central component of a computer operating systems. The only job performed by the kernel is to the manage the communication between the software and the hardware. A Kernel is at the nucleus of a computer. It makes the communication between the hardware and software possible. While the Kernel is the innermost part of an operating system, a shell is the outermost one.
Features of Kennel
- Low-level scheduling of processes
- Inter-process communication
- Process synchronization
- Context switching
Types of Kernels
There are many types of kernels that exists, but among them, the two most popular kernels are:
1.Monolithic
A monolithic kernel is a single code or block of the program. It provides all the required services offered by the operating system. It is a simplistic design which creates a distinct communication layer between the hardware and software.
2. Microkernels
Microkernel manages all system resources. In this type of kernel, services are implemented in different address space. The user services are stored in user address space, and kernel services are stored under kernel address space. So, it helps to reduce the size of both the kernel and operating system.
Operating System Classes
The Operating System category groups classes that represent operating system related objects. They denote the various configurations and settings that define a computing environment. Examples include: the boot configuration, Component Object Model (COM) settings, desktop environment settings, drivers, security settings, user settings, and registry settings.
The Operating System category is grouped into the following subcategories:
The COM subcategory groups classes that represent COM and DCOM settings, classes, and client application settings.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_ClassicCOMApplicationClasses | Association class Relates a DCOM application and a COM component grouped under it. |
| Win32_ClassicCOMClass | Instance class Represents the properties of a COM component. |
| Win32_ClassicCOMClassSettings | Association class Relates a COM class and the settings used to configure instances of the COM class. |
| Win32_ClientApplicationSetting | Association class Relates an executable and a DCOM application that contains the DCOM configuration options for the executable file. |
| Win32_COMApplication | Instance class Represents a COM application. |
| Win32_COMApplicationClasses | Association class Relates a COM component and the COM application where it resides. |
| Win32_COMApplicationSettings | Association class Relates a DCOM application and its configuration settings. |
| Win32_COMClass | Instance class Represents the properties of a COM component. |
| Win32_ComClassAutoEmulator | Association class Relates a COM class and another COM class that it automatically emulates. |
| Win32_ComClassEmulator | Association class Relates two versions of a COM class. |
| Win32_ComponentCategory | Instance class Represents a component category. |
| Win32_COMSetting | Instance class Represents the settings associated with a COM component or COM application. |
| Win32_DCOMApplication | Instance class Represents the properties of a DCOM application. |
| Win32_DCOMApplicationAccessAllowedSetting | Association class Relates the Win32_DCOMApplication instance and the user security identifications (SID) that can access it. |
| Win32_DCOMApplicationLaunchAllowedSetting | Association class Relates the Win32_DCOMApplication instance and the user SIDs that can launch it. |
| Win32_DCOMApplicationSetting | Instance class Represents the settings of a DCOM application. |
| Win32_ImplementedCategory | Association class Relates a component category and the COM class using its interfaces. |
Desktop
The Desktop subcategory groups classes that represent objects that define a specific desktop configuration.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_Desktop | Instance class Represents the common characteristics of a user’s desktop. |
| Win32_Environment | Instance class Represents an environment or system environment setting on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_TimeZone | Instance class Represents the time zone information for a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_UserDesktop | Association class Relates a user account and the desktop settings that are specific to it. |
Drivers
The Drivers subcategory groups classes that represent virtual device drivers and system drivers for base services.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_SystemDriver | Instance class Represents the system driver for a base service. |
File System
The File System subcategory groups classes that represent the way a hard disk is logically arranged. This includes the type of file system used, the directory structure, and way the disk is partitioned.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_CIMLogicalDeviceCIMDataFile | Association class Relates logical devices and data files, indicating the driver files used by the device. |
| Win32_Directory | Instance class Represents a directory entry on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_DirectorySpecification | Instance class Represents the directory layout for the product. |
| Win32_DiskDriveToDiskPartition | Association class Relates a disk drive and a partition existing on it. |
| Win32_DiskPartition | Instance class Represents the capabilities and management capacity of a partitioned area of a physical disk on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_DiskQuota | Association class Tracks disk space usage for NTFS file system volumes. |
| Win32_LogicalDisk | Represents a data source that resolves to an actual local storage device on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_LogicalDiskRootDirectory | Association class Relates a logical disk and its directory structure. |
| Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition | Association class Relates a logical disk drive and the disk partition it resides on. |
| Win32_MappedLogicalDisk | Represents network storage devices that are mapped as logical disks on the computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_OperatingSystemAutochkSetting | Association class Represents the association between a CIM_ManagedSystemElement instance and the settings defined for it. |
| Win32_QuotaSetting | Instance class Contains setting information for disk quotas on a volume. |
| Win32_ShortcutFile | Instance class Represents files that are shortcuts to other files, directories, and commands. |
| Win32_SubDirectory | Association class Relates a directory (folder) and one of its subdirectories (subfolders). |
| Win32_SystemPartitions | Association class Relates a computer system and a disk partition on that system. |
| Win32_Volume | Instance class Represents an area of storage on a hard disk. |
| Win32_VolumeQuota | Association class Relates a volume to the per volume quota settings. |
| Win32_VolumeQuotaSetting | Association class Relates disk quota settings with a specific disk volume. |
| Win32_VolumeUserQuota | Association class Relates per user quotas to quota-enabled volumes. |
Job Objects
The Job Objects subcategory groups classes that represent classes that provide the means of instrumenting named job objects. An unnamed job object cannot be instrumented.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_CollectionStatistics | Association class Relates a managed system element collection and the class representing statistical information about the collection. |
| Win32_LUID | Instance class Represents a locally unique identifier (LUID) |
| Win32_LUIDandAttributes | Instance class Represents a LUID and its attributes. |
| Win32_NamedJobObject | Instance class Represents a kernel object that is used to group processes for the sake of controlling the life and resources of the processes within the job object. |
| Win32_NamedJobObjectActgInfo | Instance class Represents the I/O accounting information for a job object. |
| Win32_NamedJobObjectLimit | Instance class Represents an association between a job object and the job object limit settings. |
| Win32_NamedJobObjectLimitSetting | Instance class Represents the limit settings for a job object. |
| Win32_NamedJobObjectProcess | Instance class Relates a job object and the process contained in the job object. |
| Win32_NamedJobObjectSecLimit | Instance class Relates a job object and the job object security limit settings. |
| Win32_NamedJobObjectSecLimitSetting | Instance class Represents the security limit settings for a job object. |
| Win32_NamedJobObjectStatistics | Instance class Represents an association between a job object and the job object I/O accounting information class. |
| Win32_SIDandAttributes | Instance class Represents a security identifier (SID) and its attributes. |
| Win32_TokenGroups | Event class Represents information about the group SIDs in an access token. |
| Win32_TokenPrivileges | Event class Represents information about a set of privileges for an access token. |
Memory and Page Files
The Memory and Page files subcategory groups classes that represent page file configuration settings.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_PageFile | Instance class Represents the file used for handling virtual memory file swapping on a Windows system. |
| Win32_PageFileElementSetting | Association class Relates the initial settings of a page file and the state of those settings during normal use. |
| Win32_PageFileSetting | Instance class Represents the settings of a page file. |
| Win32_PageFileUsage | Instance class Represents the file used for handling virtual memory file swapping on a computer system running Windows. |
Multimedia Audio or Visual
The class in the Multimedia Audio or Visual subcategory represents properties of the audio or video codec installed on the computer system.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_CodecFile | Instance class Represents the audio or video codec installed on the computer system. |
Networking
The Networking subcategory groups classes that represent network connections, network clients, and network connection settings such as the protocol used.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_ActiveRoute | Association class Relates the current IP4 route to the persisted IP route table. |
| Win32_IP4PersistedRouteTable | Instance class Represents persisted IP routes. |
| Win32_IP4RouteTable | Instance class Represents information that governs the routing of network data packets. |
| Win32_IP4RouteTableEvent | Event class Represents IP route change events. |
| Win32_NetworkClient | Instance class Represents a network client on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_NetworkConnection | Instance class Represents an active network connection in a Windows environment. |
| Win32_NetworkProtocol | Instance class Represents a protocol and its network characteristics on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_NTDomain | Instance class Represents a Windows NT domain. |
| Win32_PingStatus | Instance class Represents the values returned by the standard ping command. |
| Win32_ProtocolBinding | Association class Relates a system-level driver, network protocol, and network adapter. |
Operating System Events
The Operating System Events subcategory groups classes that represent events in the operating system related to processes, threads, and system shutdown.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_ComputerShutdownEvent | Event class Represents computer shutdown events. |
| Win32_ComputerSystemEvent | Event class Represents events related to a computer system. |
| Win32_DeviceChangeEvent | Event class Represents device change events resulting from the addition, removal, or modification of devices on the computer system. |
| Win32_ModuleLoadTrace | Event class Indicates that a process has loaded a new module. |
| Win32_ModuleTrace | Event class Base event for module events. |
| Win32_ProcessStartTrace | Event class Indicates that a new process has started. |
| Win32_ProcessStopTrace | Event class Indicates that a process has terminated. |
| Win32_ProcessTrace | Event class Base event for process events. |
| Win32_SystemConfigurationChangeEvent | Event class Indicates that the device list on the system has been refreshed (a device has been added or removed, or the configuration changed). |
| Win32_SystemTrace | Event class Base class for all system trace events, including module, process, and thread traces. |
| Win32_ThreadStartTrace | Event class Indicates a new thread has started. |
| Win32_ThreadStopTrace | Event class Indicates that a thread has stopped. |
| Win32_ThreadTrace | Event class Base event class for thread events. |
| Win32_VolumeChangeEvent | Event class Represents a network-mapped drive event resulting from the addition of a network drive letter or mounted drive on the computer system. |
Operating System Settings
The Operating System Settings subcategory groups classes that represent the Operating System and its settings.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_BootConfiguration | Instance class Represents the boot configuration of a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_ComputerSystem | Instance class Represents a computer system operating in a Windows environment. |
| Win32_ComputerSystemProcessor | Association class Relates a computer system and a processor running on that system. |
| Win32_ComputerSystemProduct | Instance class Represents a product. |
| Win32_DependentService | Association class Relates two interdependent base services. |
| Win32_LoadOrderGroup | Instance class Represents a group of system services that define execution dependencies. |
| Win32_LoadOrderGroupServiceDependencies | Instance class Represents an association between a base service and a load order group that the service depends on to start running. |
| Win32_LoadOrderGroupServiceMembers | Association class Relates a load order group and a base service. |
| Win32_OperatingSystem | Instance class Represents an operating system installed on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_OperatingSystemQFE | Association class Relates an operating system and product updates applied as represented in Win32_QuickFixEngineering. |
| Win32_OSRecoveryConfiguration | Instance class Represents the types of information that will be gathered from memory when the operating system fails. |
| Win32_QuickFixEngineering | Instance class Represents system-wide Quick Fix Engineering (QFE) or updates that have been applied to the current operating system. |
| Win32_StartupCommand | Instance class Represents a command that runs automatically when a user logs onto the computer system. |
| Win32_SystemBootConfiguration | Association class Relates a computer system and its boot configuration. |
| Win32_SystemDesktop | Association class Relates a computer system and its desktop configuration. |
| Win32_SystemDevices | Association class Relates a computer system and a logical device installed on that system. |
| Win32_SystemLoadOrderGroups | Association class Relates a computer system and a load order group. |
| Win32_SystemNetworkConnections | Association class Relates a network connection and the computer system on which it resides. |
| Win32_SystemOperatingSystem | Association class Relates a computer system and its operating system. |
| Win32_SystemProcesses | Association class Relates a computer system and a process running on that system. |
| Win32_SystemProgramGroups | Association class Relates a computer system and a logical program group. |
| Win32_SystemResources | Association class Relates a system resource and the computer system it resides on. |
| Win32_SystemServices | Association class Relates a computer system and a service program that exists on the system. |
| Win32_SystemSetting | Association class Relates a computer system and a general setting on that system. |
| Win32_SystemSystemDriver | Association class Relates a computer system and a system driver running on that computer system. |
| Win32_SystemTimeZone | Association class Relates a computer system and a time zone. |
| Win32_SystemUsers | Association class Relates a computer system and a user account on that system. |
Processes
The Processes subcategory groups classes that represent system processes and threads.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_Process | Instance class Represents a sequence of events on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_ProcessStartup | Instance class Represents the startup configuration of a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_Thread | Instance class Represents a thread of execution. |
Registry
The class in the Registry subcategory represents the contents of the Windows registry.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_Registry | Instance class Represents the system registry on a computer system running Windows. |
Scheduler Jobs
The Scheduler Jobs subcategory groups classes that represent scheduled job settings.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_CurrentTime | Abstract class Represents an instance in time as component seconds, minutes, day of the week, and so on. |
| Win32_ScheduledJob | Instance class Represents a job scheduled using the Windows schedule service. |
| Win32_LocalTime | Instance class Represents a point in time returned as Win32_LocalTime objects that result from a query. The Hour property is returned as the local time in a 24-hour clock. |
| Win32_UTCTime | Instance class Represents a point in time that is returned as Win32_UTCTime objects that result from a query. The Hour property is returned as the coordinated universal time (UTC) time in a 24 hour clock. |
Security
The Security subcategory groups classes that represent system security settings.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_AccountSID | Association class Relates a security account instance with a security descriptor instance. |
| Win32_ACE | Instance class Represents an access control entry (ACE). |
| Win32_LogicalFileAccess | Association class Relates the security settings of a file or directory and one member of its discretionary access control list (DACL). |
| Win32_LogicalFileAuditing | Association class Relates the security settings of a file or directory one member of its system access control list (SACL). |
| Win32_LogicalFileGroup | Association class Relates the security settings of a file or directory and its group. |
| Win32_LogicalFileOwner | Association class Relates the security settings of a file or directory and its owner. |
| Win32_LogicalFileSecuritySetting | Instance class Represents security settings for a logical file. |
| Win32_LogicalShareAccess | Association class Relates the security settings of a share and one member of its DACL. |
| Win32_LogicalShareAuditing | Association class Relates the security settings of a share and one member of its SACL. |
| Win32_LogicalShareSecuritySetting | Instance class Represents security settings for a logical file. |
| Win32_PrivilegesStatus | Instance class Represents information about the privileges required to complete an operation. |
| Win32_SecurityDescriptor | Instance class Represents a structural representation of a SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR. |
| Win32_SecuritySetting | Instance class Represents security settings for a managed element. |
| Win32_SecuritySettingAccess | Instance class Represents the rights granted and denied to a trustee for a given object. |
| Win32_SecuritySettingAuditing | Instance class Represents the auditing for a given trustee on a given object. |
| Win32_SecuritySettingGroup | Association class Relates the security of an object and its group. |
| Win32_SecuritySettingOfLogicalFile | Instance class Represents security settings of a file or directory object. |
| Win32_SecuritySettingOfLogicalShare | Instance class Represents security settings of a shared object. |
| Win32_SecuritySettingOfObject | Association class Relates an object to its security settings. |
| Win32_SecuritySettingOwner | Association class Relates the security settings of an object and its owner. |
| Win32_SID | Instance class Represents an arbitrary SID. |
| Win32_Trustee | Instance class Represents a trustee. |
Services
The Services subcategory groups classes that represent services and base services.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_BaseService | Instance class Represents executable objects that are installed in a registry database maintained by the Service Control Manager. |
| Win32_Service | Instance class Represents a service on a computer system running Windows. |
Shares
The Shares subcategory groups classes that represent details of shared resources, such as printers and folders.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_DFSNode | Association class Represents a root or junction node of a domain-based or stand-alone distributed file system (DFS). |
| Win32_DFSNodeTarget | Association class Represents the relationship of a DFS node to one of its targets. |
| Win32_DFSTarget | Association class Represents the target of a DFS node. |
| Win32_ServerConnection | Instance class Represents the connections made from a remote computer to a shared resource on the local computer. |
| Win32_ServerSession | Instance class Represents the sessions that are established with the local computer by users on a remote computer. |
| Win32_ConnectionShare | Association class Relates a shared resource on the computer and the connection made to the shared resource. |
| Win32_PrinterShare | Association class Relates a local printer and the share that represents it as it is viewed over a network. |
| Win32_SessionConnection | Association class Represents an association between a session established with the local server by a user on a remote machine, and the connections that depend on the session. |
| Win32_SessionProcess | Association class Represents an association between a logon session and the processes associated with that session. |
| Win32_ShareToDirectory | Association class Relates a shared resource on the computer system and the directory to which it is mapped. |
| Win32_Share | Instance class Represents a shared resource on a computer system running Windows. |
Start Menu
The Start Menu subcategory groups classes that represent program groups.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_LogicalProgramGroup | Instance class Represents a program group in a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_LogicalProgramGroupDirectory | Association class Relates logical program groups (groupings in the Start menu), and the file directories in which they are stored. |
| Win32_LogicalProgramGroupItem | Instance class Represents an element contained by a Win32_ProgramGroup instance, that is not itself another Win32_ProgramGroup instance. |
| Win32_LogicalProgramGroupItemDataFile | Association class Relates the program group items of the Start menu, and the files in which they are stored. |
| Win32_ProgramGroupContents | Association class Relates a program group order and an individual program group or item contained in it. |
| Win32_ProgramGroupOrItem | Instance class Represents a logical grouping of programs on the user’s Start|Programs menu. |
Storage
The Users subcategory groups classes that represent storage information.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_ShadowBy | Association class Represents the association between a shadow copy and the provider that creates the shadow copy. |
| Win32_ShadowContext | Association class Specifies how a shadow copy is to be created, queried, or deleted. |
| Win32_ShadowCopy | Instance class Represents a duplicate copy of the original volume at a previous time. |
| Win32_ShadowDiffVolumeSupport | Association class Represents an association between a shadow copy provider and a storage volume. |
| Win32_ShadowFor | Association class Represents an association between a shadow copy and the volume for which the shadow copy is created. |
| Win32_ShadowOn | Association class Represents an association between a shadow copy and where the differential data is written. |
| Win32_ShadowProvider | Association class Represents a component that creates and represents volume shadow copies. |
| Win32_ShadowStorage | Association class Represents an association between a shadow copy and where the differential data is written. |
| Win32_ShadowVolumeSupport | Association class Represents an association between a shadow copy provider with a supported volume. |
| Win32_Volume | Instance class Represents an area of storage on a hard disk. |
| Win32_VolumeUserQuota | Association class Represents a volume to the per volume quota settings. |
Users
The Users subcategory groups classes that represent user account information, such as group membership details.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_Account | Instance class Represents information about user accounts and group accounts known to the computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_Group | Instance class Represents data about a group account. |
| Win32_GroupInDomain | Association class Identifies the group accounts associated with a Windows NT domain. |
| Win32_GroupUser | Association class Relates a group and an account that is a member of that group. |
| Win32_LogonSession | Instance class Describes the logon session or sessions associated with a user logged on to Windows. |
| Win32_LogonSessionMappedDisk | Instance class Represents the mapped logical disks associated with the session. |
| Win32_NetworkLoginProfile | Instance class Represents the network login information of a specific user on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_SystemAccount | Instance class Represents a system account. |
| Win32_UserAccount | Instance class Represents information about a user account on a computer system running Windows. |
| Win32_UserInDomain | Association class Relates a user account and a Windows NT domain. |
Windows Event Log
The Windows Event Log subcategory groups classes that represent events, event log entries, event log configuration settings, and so on.
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Win32_NTEventlogFile | Instance class Represents data stored in a Windows Event log file. |
| Win32_NTLogEvent | Instance class Represents Windows events. |
| Win32_NTLogEventComputer | Association class Relates instances of Win32_NTLogEvent and Win32_ComputerSystem. |
| Win32_NTLogEventLog | Association class Relates instances of Win32_NTLogEvent and Win32_NTEventlogFile classes. |
| Win32_NTLogEventUser | Association class Relates instances of Win32_NTLogEvent and Win32_UserAccount. |
Windows Product Activation
Windows Product Activation (WPA) is an antipiracy technology to reduce the casual copying of software.



