- How To Check Process Start Time in Windows?
- Как получить время работы процесса?
- The Core Technologies Blog
- Our Software // Windows Services // 24×7 Operation
- When did my Windows Service Start?
- Solution #1: Search the Windows Event Logs with PowerShell
- Solution #2: Search the Windows Event Logs using the Event Viewer
- Solution #3: Figure out when the Service’s Process was Started
- Solution #4: Use the System Boot/Up Time (for Automatic Windows Services)
- Управление процессами с помощью командлетов Process Managing Processes with Process Cmdlets
- Получение процессов (Get-Process) Getting Processes (Get-Process)
- Остановка процессов (Stop-Process) Stopping Processes (Stop-Process)
- Остановка всех остальных сеансов Windows PowerShell Stopping All Other Windows PowerShell Sessions
- Запуск, отладка и ожидание процессов Starting, Debugging, and Waiting for Processes
How To Check Process Start Time in Windows?
One of the essential tasks to find out during application troubleshooting.
Did you ever wonder how to check for how long, particular process is running in Windows?
Lately, I was working on the Windows server and had to find out for how long the process is running.
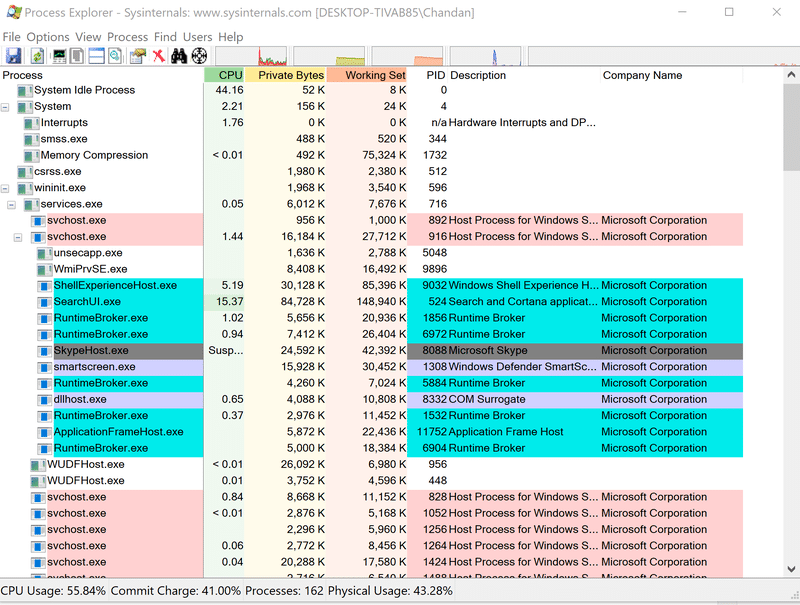
After some research, I found you could easily find out process start time in Windows by using the Process Explorer tool.
This article will guide you on how to install & check process start time on Windows operating system.
- Download Process Explorer from Microsoft download page
- Extract the downloaded zip file
Now, you are ready to use Process Explorer
- Double click on procexp to open it, it will look like below
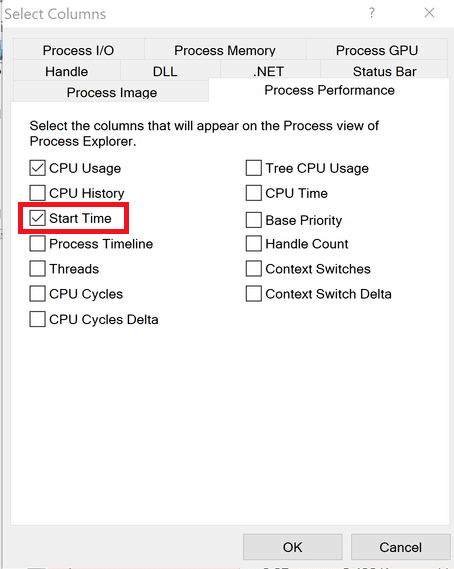
- Click on View >> Select Columns
- Click on Process Performance tab and select Start Time
- Click on Ok
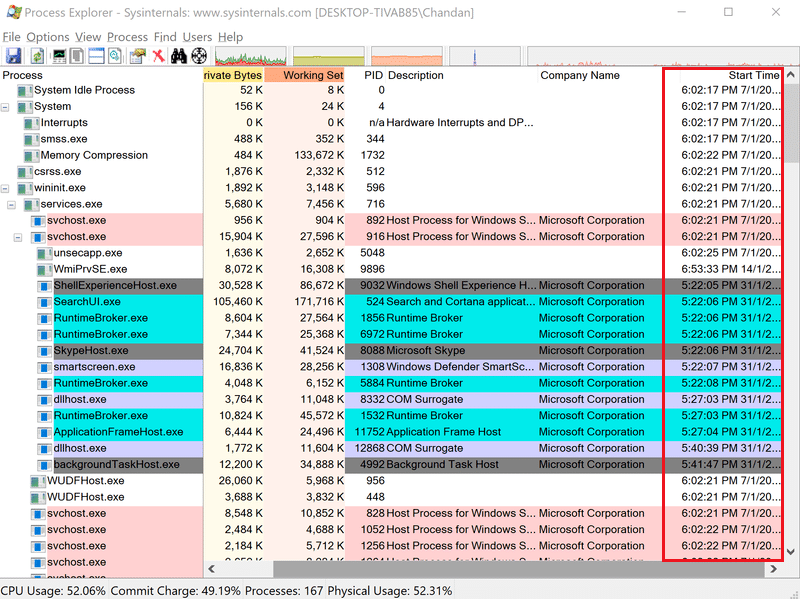
- You will notice an additional column is added called Start Time in Process Explorer.
I hope this helps you with your application troubleshooting procedure. If you are looking to learn Windows server administration, then check out this Udemy course.
Как получить время работы процесса?
Всем привет, подскажите пожалуйста, как получить время работы процесса с помощью powerShell. Как я понял сделать это можно с помощью new-timespan. Время запуска процесса, например notepad получаем так
gps -Name notepad | select starttime
Собственно вопрос заключается в том, как передать переменную времени запуска из gps -Name notepad | select starttime в new-timespan. А также из всего вывода получить числовую переменную сколько минут запущен процесс.
Добавлено через 18 минут
Разобрался

Собственно говоря нужно в powershell написать скрипт, выводящий время работы системы и отправляющий.
Получить время с удалённого компьютера и перезагрузить его, если время превышает заданное
Доброго времени суток всем Вам! Многим из вас моя проблема покажется крайне легкой, но для меня.

по идее он должен показывать еще и время запуска но почему то не показывает в чем проблема PS.
Как узнать время работы процесса
Как узнать время работы процесса в формате 00:00:00 И как его выключить из программы
The Core Technologies Blog
Our Software // Windows Services // 24×7 Operation
When did my Windows Service Start?
Here are four ways to determine when your windows service last started.
Solution #1: Search the Windows Event Logs with PowerShell
The Windows Event Logs hold a wealth of information about your computer’s activities. Indeed, a new record is added to the System event log whenever a windows service starts or stops.
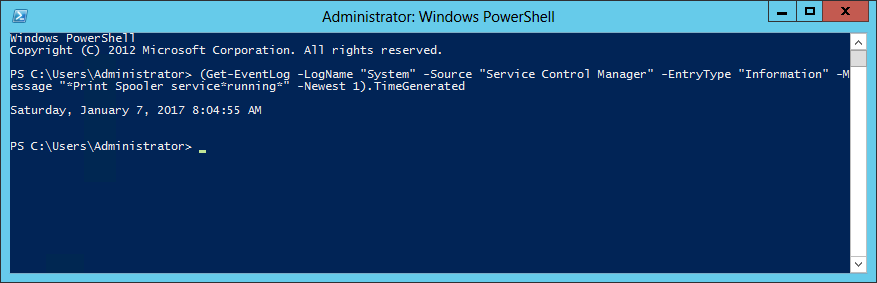
The easiest way to find your service’s most recent start time is to use a specially crafted PowerShell command to search the System event log. For example, the following line will return the last time the “Print Spooler” service was started:
(Get-EventLog -LogName «System» -Source «Service Control Manager» -EntryType «Information» -Message «*Print Spooler service*running*» -Newest 1).TimeGenerated
Be sure to replace «Print Spooler» with the display name of the service you are investigating!
Solution #2: Search the Windows Event Logs using the Event Viewer
Instead of running a PowerShell command, you can also search the Event Log manually.
To find the event log record showing when your service was last started:
Open the Event Viewer from the Control Panel (search for it by name).
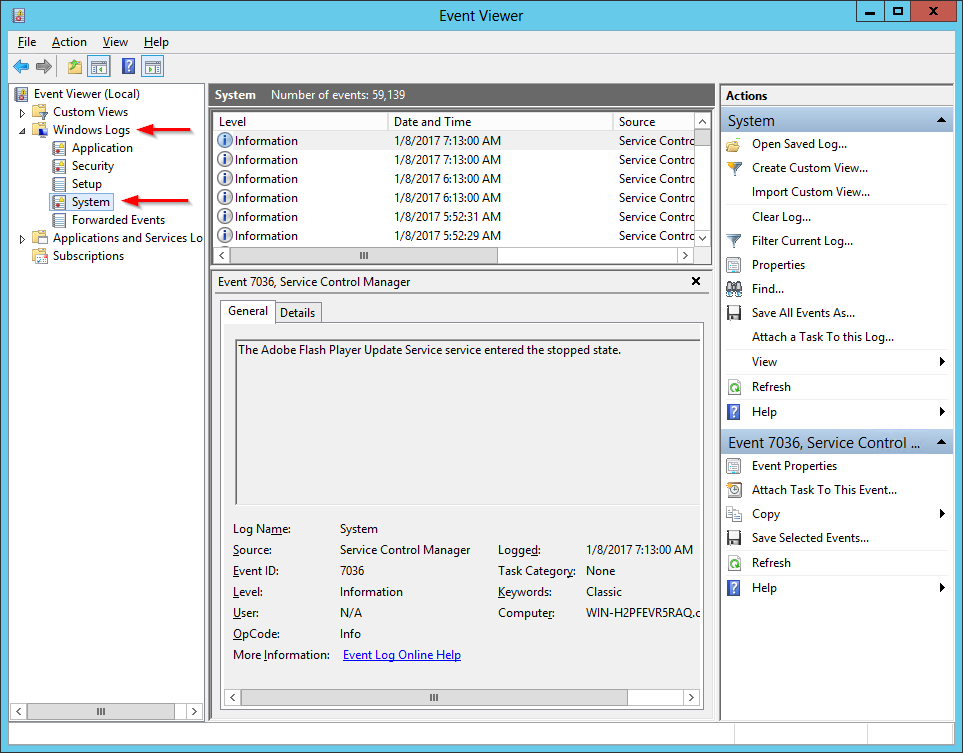
In the left-hand column, navigate to Windows Logs > System:
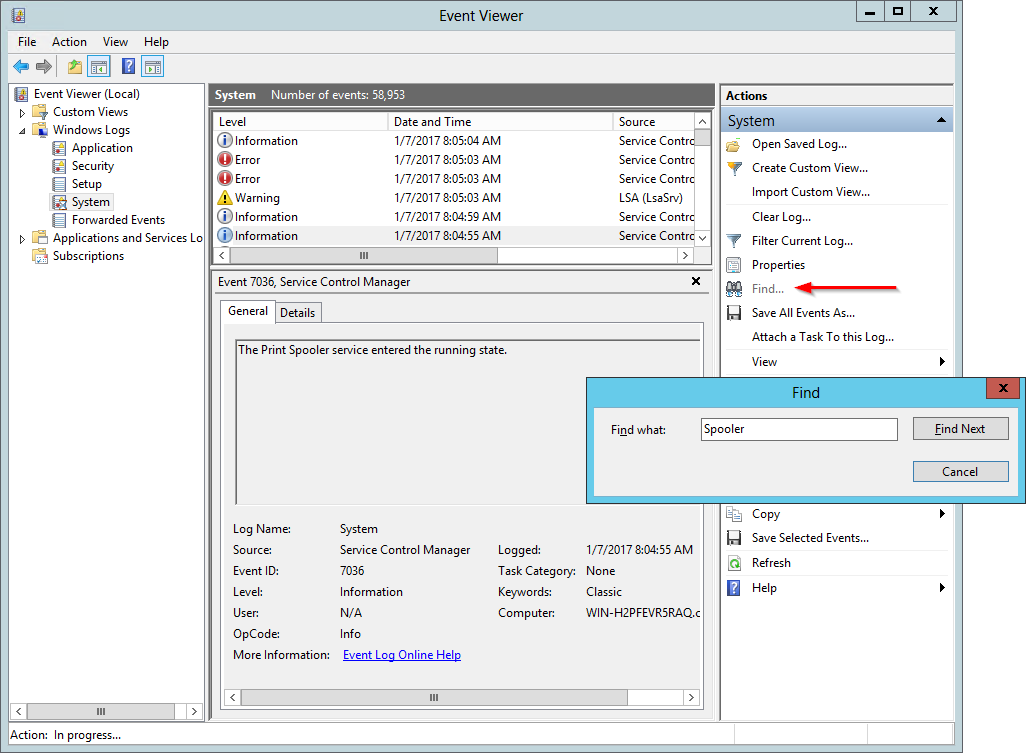
Click Find… on the right to bring up the Find window. Enter the name of the service and click the Find Next button to highlight the first matching record in the middle panel. We have entered Spooler, for the Windows Spooler service:
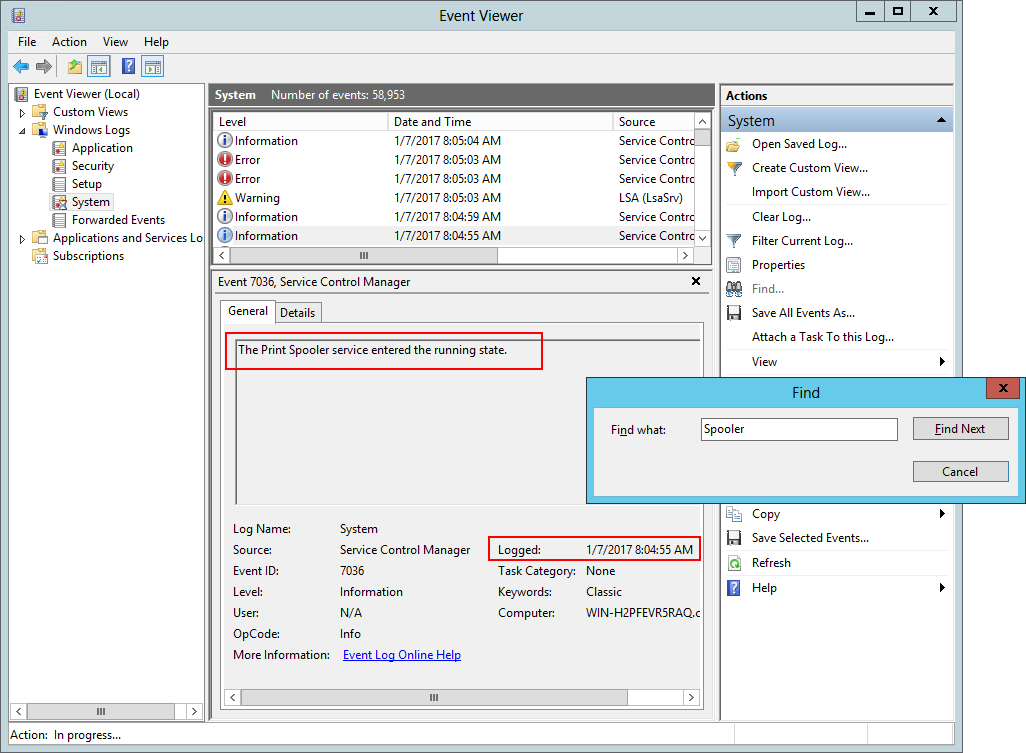
If necessary, keep clicking the Find Next button until a record saying that your service has “entered the running state” comes up. The Source should be Service Control Manager, and the time your service started will be displayed in the Logged value. The screenshot show that the Print Spooler service last started at 8:04:55 AM on January 7th 2017:
Solution #3: Figure out when the Service’s Process was Started
Each running windows service is backed by an underlying process. 99.9% of the time, that process was launched immediately when the service started. So finding the process start time will give us the service start time.
To find out when the service’s process was started:
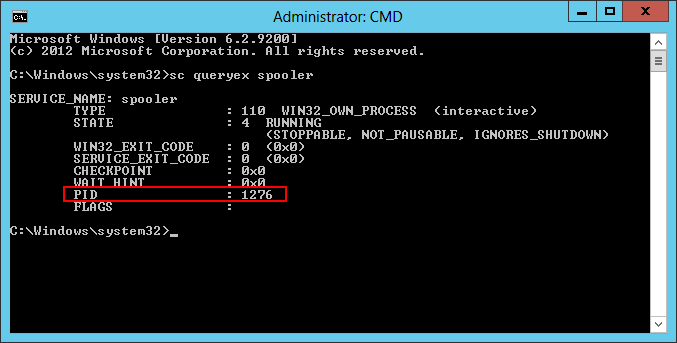
Determine the process identifier (PID) of the service’s process using the SC command. For a service named MyService, run:
(Be sure to enclose the service name in quotes if it contains spaces.)
Here is the result for the Spooler service:
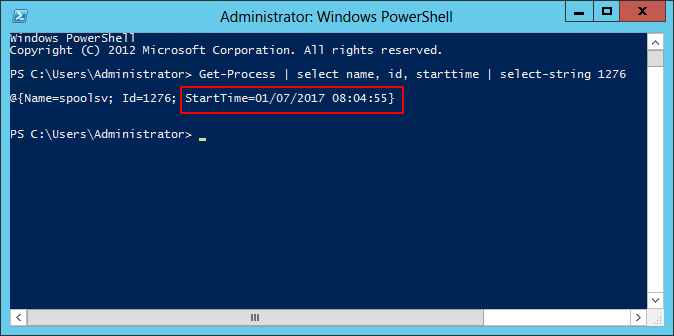
Make a note of the number on the PID line (1276 in the screenshot above).
Get-Process | select name, id, starttime | select-string
is the process identifier from step 1. The start time will come back in the result. Here is what we got for the spooler’s process (#1276):
Solution #4: Use the System Boot/Up Time (for Automatic Windows Services)
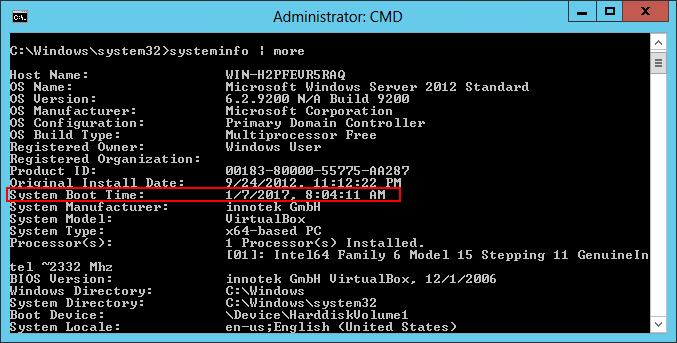
Most Windows Services start when your computer boots and run continuously, 24×7 in the background. For those services, the system boot time is a reasonable approximate.
You can run the built-in systeminfo command to discover when the system last started. Amongst the valuable information systeminfo returns, look for the “System Boot Time” line:
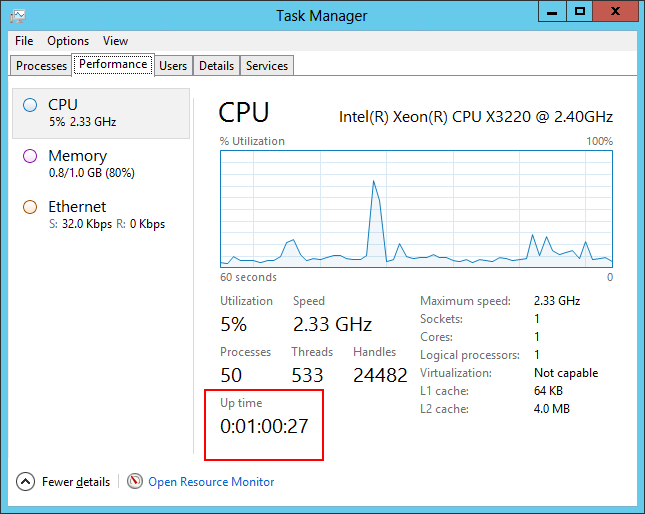
However, if you’re ever in a situation where you can’t remember the command to use, know that the Task Manager’s Performance tab shows how long the computer has been up (“Up time”). The system boot time is a simple calculation away.
So there are four easy ways to find out when your windows service started. Use whichever one best fits your situation. Good luck with your troubleshooting/investigation!
Управление процессами с помощью командлетов Process Managing Processes with Process Cmdlets
Командлеты Process в Windows PowerShell позволяют управлять локальными и удаленными процессами в Windows PowerShell. You can use the Process cmdlets in Windows PowerShell to manage local and remote processes in Windows PowerShell.
Получение процессов (Get-Process) Getting Processes (Get-Process)
Для получения процессов, запущенных на локальном компьютере, выполните командет Get-Process без параметров. To get the processes running on the local computer, run a Get-Process with no parameters.
Отдельные процессы можно получить, указав их имена или идентификаторы. You can get particular processes by specifying their process names or process IDs. Следующая команда возвращает процесс Idle: The following command gets the Idle process:
То, что в некоторых ситуациях командлеты не возвращают данные, является нормальным. Однако если при указании процесса по его идентификатору Get-Process не находит совпадений, он выдает ошибку, так как стандартной целью является получение известного выполняющегося процесса. Although it is normal for cmdlets to return no data in some situations, when you specify a process by its ProcessId, Get-Process generates an error if it finds no matches, because the usual intent is to retrieve a known running process. Если процесс с указанным идентификатором отсутствует, весьма вероятно, что идентификатор неправильный или нужный процесс уже завершился: If there is no process with that Id, it is likely that the Id is incorrect or that the process of interest has already exited:
Параметр Name командлета Get-Process можно использовать для указания подмножества процессов на основе имени процесса. You can use the Name parameter of the Get-Process cmdlet to specify a subset of processes based on the process name. Параметр Name может принимать несколько имен в виде списка с разделителями-запятыми и поддерживает использование подстановочных знаков, что позволяет задавать шаблоны имен. The Name parameter can take multiple names in a comma-separated list and it supports the use of wildcards, so you can type name patterns.
Например, следующая команда возвращает процессы, имена которых начинаются с «ex.». For example, the following command gets process whose names begin with «ex.»
Поскольку класс System.Diagnostics.Process .NET является основой для процессов Windows PowerShell, он удовлетворяет некоторым соглашениям, используемым System.Diagnostics.Process. Because the .NET System.Diagnostics.Process class is the foundation for Windows PowerShell processes, it follows some of the conventions used by System.Diagnostics.Process. Одно из таких соглашений требует, чтобы имя процесса для исполняемого файла никогда не содержало «.exe» в конце имени этого файла. One of those conventions is that the process name for an executable never includes the «.exe» at the end of the executable name.
Get-Process также принимает несколько значений для параметра Name. Get-Process also accepts multiple values for the Name parameter.
Параметр ComputerName командлета Get-Process можно использовать для получения процессов на удаленных компьютерах. You can use the ComputerName parameter of Get-Process to get processes on remote computers. Например, следующая команда получает процессы PowerShell на локальном (представленным «localhost») и двух удаленных компьютерах. For example, the following command gets the PowerShell processes on the local computer (represented by «localhost») and on two remote computers.
Имена компьютеров в этих данных не указаны, однако они хранятся в свойстве MachineName объектов процесса, возвращаемых Get-Process. The computer names are not evident in this display, but they are stored in the MachineName property of the process objects that Get-Process returns. Следующая команда использует командлет Format-Table для отображения свойств ID, ProcessName и MachineName (ComputerName) объектов процесса. The following command uses the Format-Table cmdlet to display the process ID, ProcessName and MachineName (ComputerName) properties of the process objects.
Эта более сложная команда добавляет в стандартные отображаемые данные Get-Process свойство MachineName. This more complex command adds the MachineName property to the standard Get-Process display.
Остановка процессов (Stop-Process) Stopping Processes (Stop-Process)
Windows PowerShell позволяет гибко выводить списки процессов, но как обстоят дела с остановкой процесса? Windows PowerShell gives you flexibility for listing processes, but what about stopping a process?
Командлет Stop-Process принимает имя или идентификатор, указывающие останавливаемый процесс. The Stop-Process cmdlet takes a Name or Id to specify a process you want to stop. Возможность остановки процессов зависит от ваших разрешений. Your ability to stop processes depends on your permissions. Некоторые процессы остановить нельзя. Some processes cannot be stopped. Например, при попытке остановить неактивный процесс возникает ошибка: For example, if you try to stop the idle process, you get an error:
Можно также принудительно вывести запрос с помощью параметра Confirm . You can also force prompting with the Confirm parameter. Он особенно удобен при использовании подстановочного знака в имени процесса, так как случайно может быть определено соответствие с некоторыми процессами, которые не нужно останавливать: This parameter is particularly useful if you use a wildcard when specifying the process name, because you may accidentally match some processes you do not want to stop:
Сложную обработку процессов можно реализовать с помощью командлетов фильтрации объектов. Complex process manipulation is possible by using some of the object filtering cmdlets. Так как объект Process имеет свойство Responding, которое равно true, если он перестал отвечать, вы можете остановить все неотвечающие приложения с помощью следующей команды: Because a Process object has a Responding property that is true when it is no longer responding, you can stop all nonresponsive applications with the following command:
Аналогичный подход возможен и в других ситуациях. You can use the same approach in other situations. Предположим, например, что приложение дополнительной области уведомлений запускается автоматически при открытии другого приложения. For example, suppose a secondary notification area application automatically runs when users start another application. Эта процедура может работать неправильно в сеансах служб терминалов, однако вам все равно нужно сохранить ее в сеансах, выполняемых в консоли физического компьютера. You may find that this does not work correctly in Terminal Services sessions, but you still want to keep it in sessions that run on the physical computer console. Сеансы, подключенные к рабочему столу физического компьютера, всегда имеют идентификатор сеанса 0, поэтому можно остановить все экземпляры процесса, находящиеся в других сеансах, с помощью Where-Object и SessionId процесса: Sessions connected to the physical computer desktop always have a session ID of 0, so you can stop all instances of the process that are in other sessions by using Where-Object and the process, SessionId :
Командлет Stop-Process не использует параметр ComputerName. The Stop-Process cmdlet does not have a ComputerName parameter. Поэтому для выполнения команды остановки процесса на удаленном компьютере необходимо использовать командлет Invoke-Command. Therefore, to run a stop process command on a remote computer, you need to use the Invoke-Command cmdlet. Например, чтобы остановить процесс PowerShell на удаленном компьютере Server01, введите: For example, to stop the PowerShell process on the Server01 remote computer, type:
Остановка всех остальных сеансов Windows PowerShell Stopping All Other Windows PowerShell Sessions
В некоторых случаях может пригодиться возможность остановки всех выполняющихся сеансов Windows PowerShell, отличных от текущего. It may occasionally be useful to be able to stop all running Windows PowerShell sessions other than the current session. Если сеанс использует слишком много ресурсов или недоступен (он может выполняться удаленно или в другом сеансе), возможно, остановить его напрямую не получится. If a session is using too many resources or is inaccessible (it may be running remotely or in another desktop session), you may not be able to directly stop it. При попытке остановить все выполняющиеся сеансы может быть завершен текущий сеанс. If you try to stop all running sessions, however, the current session may be terminated instead.
Каждый сеанс Windows PowerShell имеет переменную среды PID, содержащую идентификатор процесса Windows PowerShell. Each Windows PowerShell session has an environment variable PID that contains the Id of the Windows PowerShell process. Можно проверить переменную $PID на наличие идентификатора каждого сеанса и завершить только сеансы Windows PowerShell с другим идентификатором. Следующая команда конвейера делает именно это и возвращает список завершенных сеансов (из-за использования параметра PassThru ): You can check the $PID against the Id of each session and terminate only Windows PowerShell sessions that have a different Id. The following pipeline command does this and returns the list of terminated sessions (because of the use of the PassThru parameter):
Запуск, отладка и ожидание процессов Starting, Debugging, and Waiting for Processes
Windows PowerShell также имеет командлеты для запуска (или перезапуска), отладки процесса и ожидания завершения процесса перед выполнением команды. Windows PowerShell also comes with cmdlets to start (or restart), debug a process, and wait for a process to complete before running a command. Дополнительные сведения об этих командлетах см. в разделах справки по каждому из них. For information about these cmdlets, see the cmdlet help topic for each cmdlet.