- How to find program location in registry, if I know MSI GUID?
- 7 Answers 7
- How do I open and edit the Windows registry?
- How to open the Windows registry
- Windows 10
- Windows 8
- Windows 7 and earlier
- How to browse the Windows registry
- How to edit a Windows registry value
- How to delete a Windows registry value
- Windows registry shorthand and abbreviations
- Enable Windows Installer logging
- Windows Installer logging
- Enable Windows Installer logging manually
- Enable Windows Installer logging with Group Policies
- Изменения реестра в 64-х версиях Windows
- Аннотация
- Перенаправление реестра
- Поднаправления реестра, включенные в перенаправление
- Отражение реестра
- Общие разделы реестра
- Изменения редактора реестра
- Запуск 64-битной версии редактора реестра
- Запуск 32-битной версии редактора реестра
- Техническая поддержка для версий Windows на основе x64
How to find program location in registry, if I know MSI GUID?
I have installed some MSI with GUID (0733556C-37E8-4123-A801-D3E6C5151617). The program registered in the registry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Uninstall \ ()
Value UninstallString = MsiExec.exe / I (0733556C-37E8-4123-A801-D3E6C5151617)
My question is: how utility MsiExec.exe knows the name and path to the file you want to run when you remove programs? Where in the registry this information can be found?
7 Answers 7
Windows keeps Windows Installer configuration information hidden and encrypted in the Registry. It is not browseable with the human eye as other parts of the Registry are.
To query/modify/delete this information, you’ll need to use MSI functions.
(Installer Function Reference)
For your particular question, try the function MsiGetProductInfo.
Here’s a simple c# program that uses MsiGetProductInfo, as William Leara says, to get the actual location of the cached installer on disk.
You could try, from the command line:
You don´t need any software. This is working in Windows 10 and I think its valid for windows 7 as well.
If your Product Code is 0733556C-37E8-4123-A801-D3E6C5151617. Try to find the key C65533708E7332148A103D6E5C516171 (basically it’s reversed) once you found it, browse for InstallProperties subkey, if doesn´t exists, try to find other result. Once you found InstallProperties, open and find the LocalPackage Key. And then you have the path for the msi packeage that MSI saves as Cache when you installed your application.
There is a free utility from Tarma Software Research that I found helpful for this. Get it from their website.
The premise of this question is misleading because the UninstallString in the registry is not used when doing the uninstall. Go ahead and change the string to test this — it won’t use your altered string.
Although references to stuff in the registry might be appealing, the short answer is that Windows Installer data in the registry is implementation detail. The question is basically asking how MsiConfigureProduct(. INSTALLSTATE_ABSENT. ) works, and it’s pointless to guess at the implementation details and where it might be in the registry. It’s APIs all the way down. There might have been an actual task the poster may have wanted to accomplish, but it is masked by a question of how uninstalls work.
That key maps to HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Installer\Products\ .
How do I open and edit the Windows registry?
Fixing Windows errors, tweaking Windows features, or completely removing a program can sometimes require you to edit the Windows registry. This page provides help on how to open and view the Windows registry, edit, and delete registry values.
Before editing or changing anything in the Microsoft Windows registry, we recommend you back up the registry. For help with backing up the registry, see: How to back up and restore the Windows registry.
How to open the Windows registry
To open the Windows registry, follow the steps below for your version of Windows.
If you have restricted access to the Windows computer you’re logged in to, you may not be able to access the Windows registry.
Windows 10
- Type regedit in the Windows search box on the taskbar and press Enter .
- If prompted by User Account Control, click Yes to open the Registry Editor.
- The Windows Registry Editor window should open and look similar to the example shown below.
Windows 8
- Type regedit on the Start screen and select the regedit option in the search results.
- If prompted by User Account Control, click Yes to open the Registry Editor.
- The Windows Registry Editor window should open and look similar to the example shown below.
Windows 7 and earlier
- Click Start or press the Windows key .
- In the Start menu, either in the Run box or the Search box, type regedit and press Enter . In Windows 8, you can type regedit on the Start screen and select the regedit option in the search results. In Windows 10, type regedit in the Search box on the taskbar and press Enter .
- If prompted by User Account Control, click Yes to open the Registry Editor.
- The Windows Registry Editor window should open and look similar to the example shown below.
How to browse the Windows registry
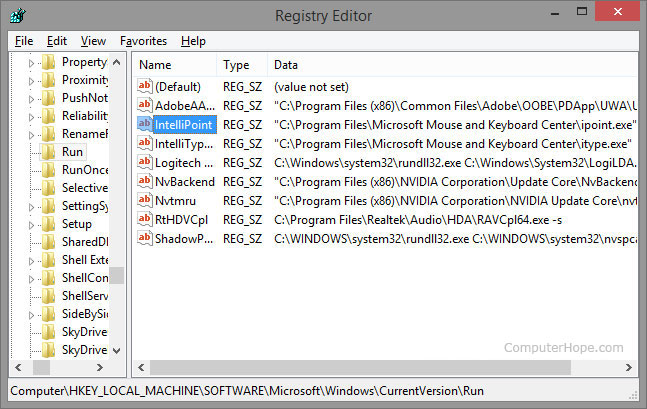
When most users need to edit their registry, they’re given the location or path of where the registry value is located and what to change. Below is an example path for a commonly accessed registry subkey. To browse to this location, you first start by opening the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE key (folder). In this key, you see the SOFTWARE folder, then Microsoft, Windows, CurrentVersion, and finally the Run folder.
Each backslash («\») in a registry path represents another folder in the registry, with the name of that folder following the backslash.
After navigating to the registry path above, you’ll see a window similar to the example below. In this example, you can see four different string value keys, which are pointing to the programs that run each time the computer is turned on or restarted.
How to edit a Windows registry value
To edit a registry value, double-click the name of the value you want to edit. For example, if we double-clicked the ‘IntelliPoint’ value in the example above, a new window appears that would allow us to change the value of the data. In this case, we could change the file path of where the «ipoint.exe» file is located for the IntelliPoint driver.
How to delete a Windows registry value
To delete a registry value, highlight any registry Name and then press the Del on the keyboard. For example, if we did not want the IntelliPoint program to load each time Windows starts, we could highlight IntelliPoint and then press the Del .
Windows registry shorthand and abbreviations
In some documentation and online forums, the registry values may be abbreviated. For example, instead of saying «HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,» it is easier to say and write «HKLM.» For a listing of registry terms and shorthand, see our registry definition.
Enable Windows Installer logging
Windows includes a registry-activated logging service to help diagnose Windows Installer issues. This article describes how to enable this logging service.
Original product version: В Windows 10 — all editions, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: В 223300
The registry entry in this article is valid for all Windows operating systems.
Windows Installer logging
Windows Installer can use logging to help assist in troubleshooting issues with installing software packages. This logging is enabled by adding keys and values to the registry. After the entries have been added and enabled, you can retry the problem installation and Windows Installer will track the progress and post it to the Temp folder. The new log’s file name is random. However, the first letters are Msi and the file name has a .log extension. To locate the Temp folder, type the following line at a command prompt:
To enable Windows Installer logging manually, see the following section.
Enable Windows Installer logging manually
This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, see How to back up and restore the registry in Windows.
To enable Windows Installer logging yourself, open the registry by using Regedit.exe, and then create the following subkey and keys:
- Path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer
- Type: Reg_SZ
- Value: Logging
- Data: voicewarmupx
The letters in the value field can be in any order. Each letter turns on a different logging mode. Each letter’s actual function is as follows for MSI version 1.1:
- v — Verbose output
- o — Out-of-disk-space messages
- i — Status messages
- c — Initial UI parameters
- e — All error messages
- w — Non-fatal warnings
- a — Start up of actions
- r — Action-specific records
- m — Out-of-memory or fatal exit information
- u — User requests
- p — Terminal properties
- + — Append to existing file
- ! — Flush each line to the log
- x — Extra debugging information. The x flag is available only in Windows Server 2003 and later operating systems, and on the MSI redistributable version 3.0, and on later versions of the MSI redistributable.
- * — Wildcard. Log all information except the v and the x option. To include the v and the x option, specify /l*vx.
This change should be used only for troubleshooting and should not be left on because it will have adverse effects on system performance and disk space. Each time that you use the Add or Remove Programs item in Control Panel, a new Msi*.log file is created. To disable the logging, remove the Logging registry value.
Enable Windows Installer logging with Group Policies
You can enable logging with Group Policies by editing the appropriate OU or Directory Group Policy. Under Group Policy, expand Computer Configuration, expand Administrative Templates, expand Windows Components, and then select Windows Installer.
Double-click Logging, and then click Enabled. In the Logging box, enter the options you want to log. The log file, Msi.log, appears in the Temp folder of the system volume.
For more information about MSI logging, see Windows Help. To do this, search by using the phrase msi logging, and then select Managing options for computers through Group Policy.
The addition of the x flag is available natively in Windows Server 2003 and later operating systems, on the MSI redistributable version 3.0, and on later versions of the MSI redistributable.
Изменения реестра в 64-х версиях Windows
В этой статье описываются некоторые изменения реестра, внесенные в 64-х версиях Microsoft Windows Server 2003 и Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64 Edition. В ней описывается, как операционная система Windows x64 Edition хранит сведения реестра для 32-битных и 64-битных программ.
Исходная версия продукта: Windows 10 — все выпуски, Windows Server 2012 R2
Исходный номер КБ: 896459
Аннотация
В этот раздел, описание метода или задачи включены действия, содержащие указания по изменению параметров реестра. Однако неправильное изменение параметров реестра может привести к возникновению серьезных проблем. Поэтому следует в точности выполнять приведенные инструкции. Для дополнительной защиты создайте резервную копию реестра, прежде чем редактировать его. Так вы сможете восстановить реестр, если возникнет проблема. Для получения дополнительных сведений о том, как создать и восстановить реестр, щелкните следующий номер статьи, чтобы просмотреть статью в базе знаний Майкрософт: 322756 Как создать и восстановить реестр в Windows
Компьютеры с 64-й версией Microsoft Windows Server 2003 или Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64 Edition используют другой макет реестра для обработки как 32-, так и 64-битных программ. Изменения макета реестра в версиях x64 Edition операционной системы Windows не перезаписывают программные жестко заданные пути DLL, параметры программы и другие значения параметров.
Чтобы 32-bit registry settings from overwriting the 64-bit registry settings, computers that are running an x64-based version of Microsoft Store the settings for 32-bit programs in a new branch in the registry. Во время установки программы пользователи не замечают никаких изменений. Процесс перенаправления реестра позволяет установкам программ и настройкам конфигурации программы получать доступ к правильному поднайму реестра без вмешательства пользователя.
32-bit programs and 64-bit programs that are running on an x64-based version of Windows operate in different modes and use the following sections in the registry:
64-битные программы в режиме native запускаются в режиме Native и имеют доступ к ключам и значениям, которые хранятся в следующем поднайке реестра:
32-bit programs run in WOW64 mode and access keys and values that are stored in the following registry subkey:
Перенаправление реестра
Для поддержки сосуществования 32-битной и 64-битной регистрации COM и состояния программ подсистема WOW64 представляет 32-битные программы с помощью другого представления реестра. Подсистема WOW64 использует перенаправление реестра для перехвата вызовов реестра на уровне бита. Перенаправление реестра также позволяет убедиться, что вызовы реестра направляются в правильные ветви реестра.
При установке новой программы или при запуске программы на компьютере с Windows x64 Edition вызовы реестра, сделанные 64-битным программным обеспечением, будут получать доступ к поднаправлению реестра без перенаправления. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software WOW64 перехватывает вызовы реестра, сделанные 32-битным программным путем, а затем перенаправляет их в HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\WOW6432node подмайк. Перенаправляя только 32-битные вызовы программ, WOW64 позволяет убедиться, что программы всегда записывают их в соответствующий поднаправление реестра. Перенаправление реестра не требует изменения кода программы, и этот процесс является прозрачным для пользователя.
Поднаправления реестра, включенные в перенаправление
Следующие поднаправления реестра перенаправляются в текущих версиях операционной системы Windows x64 Edition:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Ole
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Rpc
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\COM3
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\EventSystem
Перенаправление ключа реестра может измениться в более поздних версиях операционной системы. Разработчикам программного обеспечения рекомендуется избегать написания программного кода, основанного на ранее задокументированных списках перенаправленных ключей. Вместо этого следует написать код для проверки состояния перенаправления перед вызовом 32-битного или 64-битного логического представления реестра.
Отражение реестра
Отражение реестра предоставляет метод в режиме реального времени для постоянного открытия 32- и 64-битных разделов реестра. Например, рассмотрим 32-битную программу с именем Hello.exe, которая действует как 32-битный сервер OLE, но также может обслуживать запросы от 64-битных клиентов. Отражение реестра позволяет программе Hello.exe оставить 32-битный и 64-битный реестр открытыми для обработки вызовов как 32-, так и 64-битных программ.
Отражение позволяет наличия двух физических копий одного реестра для поддержки одновременных операций native и WOW64. Большинство отражающихся ключей являются ключами класса. Ключи класса написаны с помощью «последней писательской» концепции, а handle to the key is closed when either the 32-bit or 64-bit class key is written and closed.
В следующем списке представлены некоторые примеры того, как «последний писатель одерживает выигрыш» в этой концепции:
- После чистой установки операционной системы Windows x64 Edition 64-Wordpad.exe для обработки DOC-файлов. Отражаатель реестра копирует регистрацию DOC из 64-битного раздела реестра в 32-битный раздел реестра.
- При установке 32-Microsoft Office Winword.exe регистрируется для обработки DOC-файлов в 32-битной версии реестра. Отражачик реестра копирует эти сведения в 64-битный раздел реестра. Поэтому 32- и 64-битные программы запускают 32-Winword.exe для DOC-файлов.
- При установке 64-Microsoft Office 64-битной версии Winword.exe регистрируется в разделе реестра 64-битной версии для обработки DOC-файлов. Отражачик реестра также копирует эти сведения в 32-битный раздел реестра, чтобы 32- и 64-битные программы запускали 64-Winword.exe для DOC-файлов.
Разработчики могут использовать функцию RegQueryReflectionKey для определения состояния отражения для определенного ключа и использовать функцию RegDisableReflectionKey и функцию RegEnableReflectionKey, чтобы программно отключить и включить отражение реестра для определенного ключа.
Общие разделы реестра
Некоторые подмеки реестра содержат константную информацию, которая существует только в одной копии реестра, хотя эти ключи отображаются как в 32-битных, так и в 64-битных представлениях реестра. Это называется отражением реестра.
В текущих версиях операционных систем Windows x64 Edition следующие разделы реестра совместно распределены по 32- и 64-битным программам и не переописываются на основе 32- или 64-битного уровня программы или процесса:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\SYSTEMCERTIFICATES
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\CRYPTOGRAPHY\SERVICES
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\CLASSES\HCP
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\ENTERPRISECERTIFICATES
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\MSMQ
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\NETWORKCARDS
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\PROFILELIST
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\PERFLIB
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\PRINT
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\PORTS
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\CONTROL PANEL\CURSORS\SCHEMES
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\TELEPHONY\LOCATIONS
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\POLICIES
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\GROUP POLICY
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\POLICIES
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\SETUP\OC MANAGER
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\SHARED TOOLS\MSINFO
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\SETUP
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\CTF\TIP
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\CTF\SYSTEMSHARED
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\FONTS
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\FONTSUBSTITUTES
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\FONTDPI
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\FONTMAPPER
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\RAS
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\DRIVER SIGNING
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\NON-DRIVER SIGNING
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\CRYPTOGRAPHY\CALAIS\CURRENT
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\CRYPTOGRAPHY\CALAIS\READERS
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS NT\CURRENTVERSION\TIME ZONE
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\TRANSACTION SERVER
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\DFS
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\TERMSERVLICENSING
Отражение ключа реестра может измениться в более поздних версиях операционной системы. Разработчикам программного обеспечения рекомендуется избегать написания программного кода, основанного на ранее задокументированных списках отражающих ключей. Вместо этого следует написать код для проверки состояния отражения, прежде чем программа будет звонить в 32- или 64-битное логическое представление реестра.
Изменения редактора реестра
Как 32-, так и 64-битные версии редактора реестра включены в операционные системы x64 Edition. Чтобы лучше понять 64-битные и 32-битные разделы реестра на компьютере с Windows x64 Edition, используйте один из следующих методов.
Запуск 64-битной версии редактора реестра
- Войдите на компьютер с Windows x64 Edition, используя учетную запись с административными разрешениями.
- Нажмите кнопку Пуск, выберите команду Выполнить, в поле Открыть введите regedit и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- В редакторе реестра найдите и изучите следующий подкомедий реестра: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\WOW6432node
Запуск 32-битной версии редактора реестра
Нажмите кнопку «Начните», нажмите кнопку «Выполнить», введите букву диска, на котором вы установили Windows x64 Edition\Windows\syswow64\regedit.exe m в поле «Открыть», а затем нажмите кнопку «ОК». Переключатель m позволяет запускать несколько экземпляров редактора реестра.
При входе на компьютер с Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 1 (SP1) или более поздней версии или на компьютере под управлением Windows x64 Edition и использовании протокола удаленного рабочего стола (RDP) для подключения к другому компьютеру с Windows Server 2003 с sp1 или более поздней версии или компьютеру на базе Windows x64 Edition можно просмотреть 64-битный раздел реестра на удаленном компьютере. Однако при входе на компьютер с Microsoft Windows Server 2003, который не был обновлен до версии SP1 или любой другой 32-битной операционной системы Windows, можно просмотреть только 32-битный раздел реестра на удаленном компьютере.
Техническая поддержка для версий Windows на основе x64
Если ваше оборудование уже установлено с выпуском Windows x64, изготовитель оборудования предоставляет техническую поддержку и поддержку для выпуска Windows x64. В этом случае изготовитель оборудования обеспечивает поддержку, так как в ваше оборудование включен выпуск Windows x64. Возможно, изготовитель оборудования настроил установку выпуска Windows x64 с помощью уникальных компонентов. Уникальные компоненты могут включать определенные драйверы устройств или необязательные параметры для повышения производительности оборудования. Корпорация Майкрософт предоставит разумные усилия, если вам нужна техническая помощь в выпуске Windows x64. Однако может потребоваться связаться с производителем напрямую. Изготовитель лучше всего поддерживает программное обеспечение, установленное на оборудовании. Если вы приобрели выпуск Windows x64, например Выпуск Windows Server 2003 x64 отдельно, обратитесь за технической поддержкой в корпорацию Майкрософт.