- How to Run a Program as a Different User (RunAs) in Windows 10?
- How to Run an App as Different User from File Explorer?
- “Run As Different User” Option is Missing in Windows 10
- Using the RunAs Command to Run a Program as Another User from CMD
- How to Use RunAs Without Password Prompt?
- How to Create a Shortcut to Run As Different User?
- How to Run MMC Snap-Ins As a Different User?
- Add “Run As” Option to Start Menu in Windows 10
- Application. Run Метод
- Определение
- Перегрузки
- Исключения
- Комментарии
- См. также раздел
- Применяется к
- Run(ApplicationContext)
- Параметры
- Исключения
- Примеры
- Использование запуска приложения с учетной записи администратора в Windows Server 2003
- Аннотация
- Действия, необходимые для запуска приложения с учетной записи администратора
How to Run a Program as a Different User (RunAs) in Windows 10?
In all supported Windows versions it is possible to run applications on behalf of another user (Run As) in the current session. This allows you to run a script (.bat, .cmd, .vbs, .ps1), an executable (.exe) or an application installation (.msi, .cab) with another user (usually elevated) privileges.
For example, you can use the RunAs to install apps or run MMC snap-ins under the administrator account in an unprivileged user session. The opportunity to run a program as a different user may be useful when an application is configured under another user (and stores its settings in another user’s profile, which the current user cannot access), but it must be started with the same settings in another user’s session.
In Windows 10 there are several ways to run a program/process on behalf of another user.
How to Run an App as Different User from File Explorer?
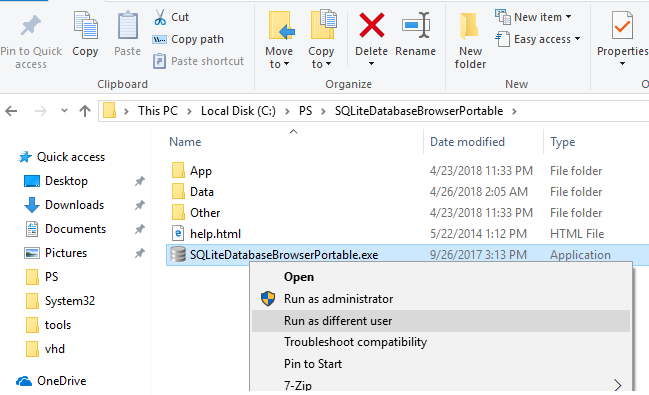
The easiest way to run an application on behalf of another user is to use the Windows File Explorer GUI. Just find an application (or a shortcut) you want to start, press the Shift key and right-click on it. Select Run as different user in the context menu.
[alert]Note. If the menu item “Run as different user” is missing, see the next section.
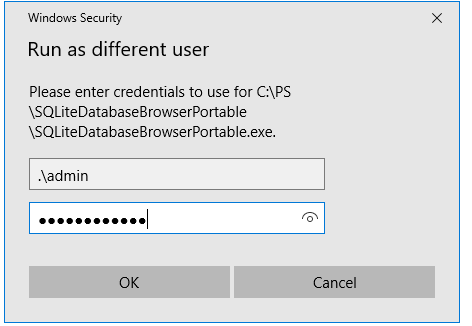
In the next window, specify the name and password of the user under whose account you want to run the application and click OK.
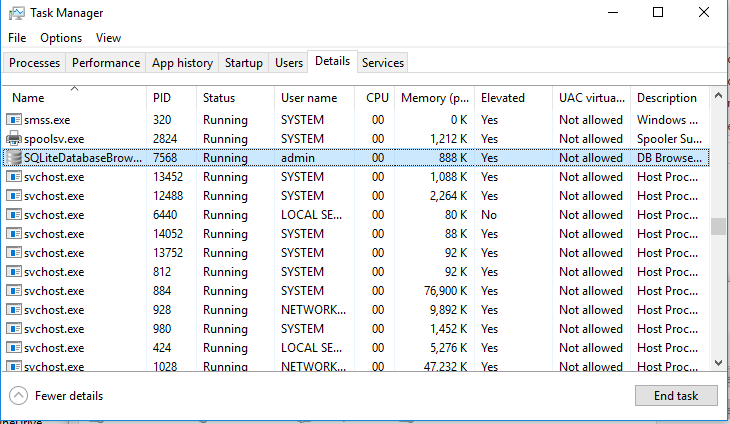
Open the Task Manager and make sure that the application is running under the specified user account.
“Run As Different User” Option is Missing in Windows 10
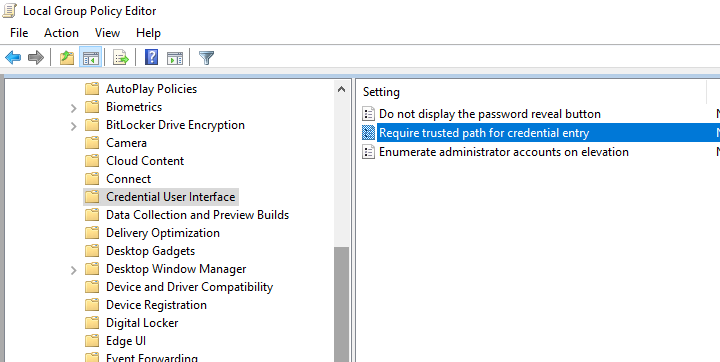
If there is no Run as different user option in the File Explorer context menu, open the Local Group Policy Editor ( gpedit.msc ) and make sure that the Require trusted path for credential entry policy is disabled (or not configured) in Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Credential User Interface.
Using the RunAs Command to Run a Program as Another User from CMD
You can use the Windows built-in cli tool runas.exe to run apps applications as a different user from the command prompt. The runas command also lets you to save the user’s password to the Windows Credential Manager so that you don’t have to enter it every time.
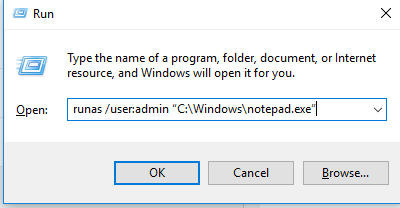
Open the command prompt (or the Run window by pressing Win+R). To start the Notepad.exe under the administrator account, run this command:
runas /user:admin «C:\Windows\notepad.exe»
runas /user:»antony jr» notepad.exe
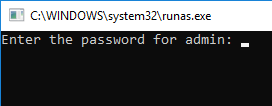
In the next window, the prompt “Enter the password for admin” appears, where you have to enter the user’s password and press Enter.
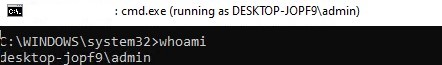
Your application should open. In my case, this is cmd.exe. The window title says “running as PCName\username“:
For example, you can open the Control Panel under a different user:
runas /user:admin control
If you need to run a program under a domain user, use the following name format: UserName@DomainName or DomainName\UserName . For example, to open a text file using notepad on behalf of a domain user, use the command:
runas /user:corp\server_admin «C:\Windows\system32\notepad.exe C:\ps\region.txt»
Sometimes you need to run a program as a domain user from a computer that is not joined to the AD domain. In this case, you need to use the following command (It is assumed that the DNS server specified in your computer’s network settings can resolve this domain name):
runas /netonly /user:contoso\bmorgan cmd.exe
If you don’t want to load user profile when starting the program as different user, use the /noprofile parameter. This allows the application to launch much faster, but may cause incorrect operation of programs that store app data in the user’s profile.
How to Use RunAs Without Password Prompt?
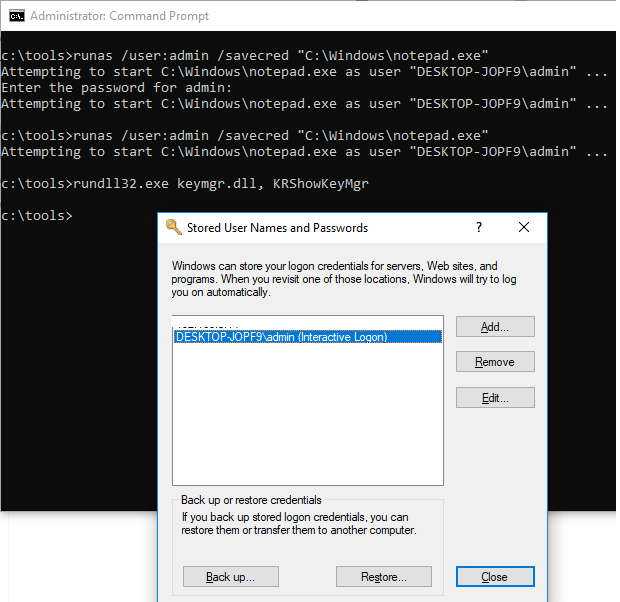
You can save the user credentials (with password) that you enter. The /savecred parameter is used for this.
runas /user:admin /savecred “C:\Windows\cmd.exe”
After specifying the password, it will be saved to the Windows Credential Manager.
The next time you run the runas command under the same user with the /savecred key, Windows will automatically use the saved password from the Credential Manager without prompting to enter it again.
To display a list of saved credentials in Credential Manager, use the following command:
rundll32.exe keymgr.dll, KRShowKeyMgr
However, using the /savecred parameter is not safe. Because a user, in which profile it is saved, can use it to run any command with these privileges and even change another user password. Also, it is easy to steal passwords saved in the Credential Manager so it is recommended to prevent a Windows from saving passwords (and never save the password of the privileged administrator accounts).
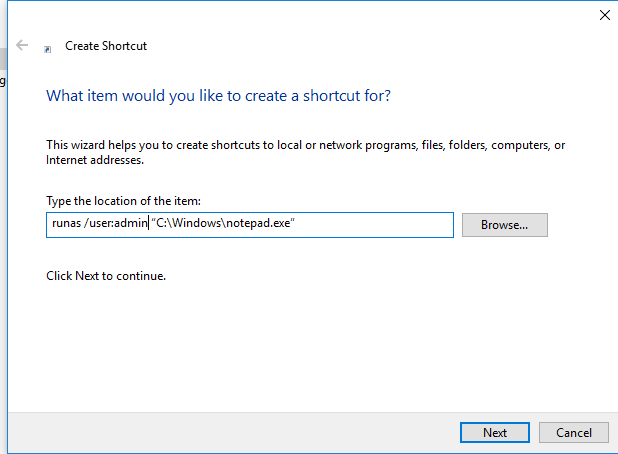
How to Create a Shortcut to Run As Different User?
You can create a shortcut on your desktop that allows you to run the program as a different user. Just create a new shortcut, and specify the runas command with the necessary parameters in the Location field
When you run such a shortcut, you will be prompted to enter a user password.
If you additionally specify the /savecred parameter in the runas shortcut, then the password will be prompted only once. The password will be saved in Credential Manager and automatically used when you running the shortcut without prompting for a password.
Such shortcuts are quite often used to run programs that require elevated permissions to run. However, there are safer ways to run a program without administrator privileges, or disable the UAC prompt for a specific application.
How to Run MMC Snap-Ins As a Different User?
In some cases, you have to run one of Windows management snap-ins as a different user. For example, you can use the following command to run the Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) RSAT snap-in as a different user:
runas.exe /user:DOMAIN\USER «cmd /c start \»\» mmc %SystemRoot%\system32\dsa.msc»
In the same way you can run any other snap-in (if you know its name).
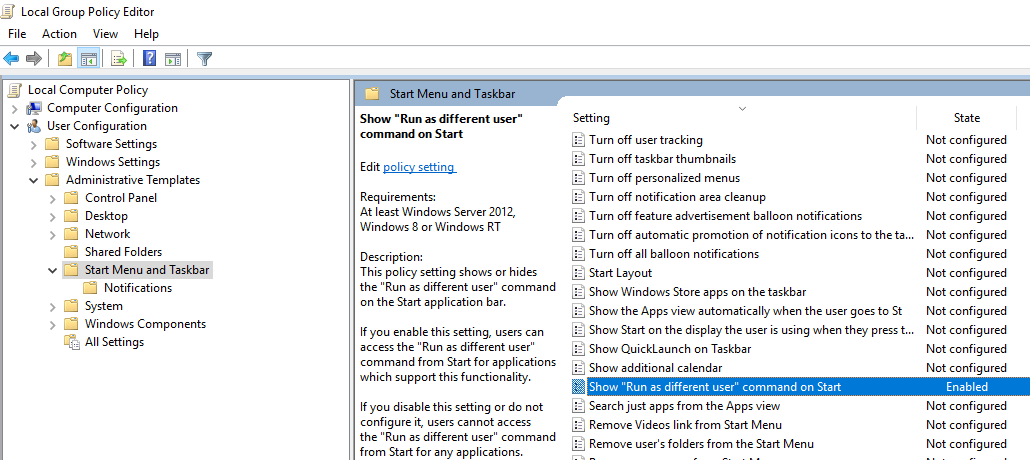
Add “Run As” Option to Start Menu in Windows 10
By default in Windows 10 Start Menu items do not have the “Run As” option. To add the context menu “Run as different user”, enable the “Show Run as different user command on Start” policy in User Configuration -> Administrative Templates ->Start Menu and Taskbar section of the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc).
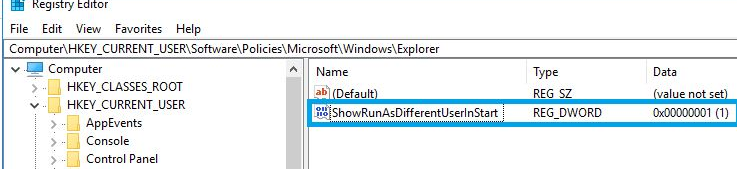
Or, if the gpedit.msc is missing, create a new DWORD parameter with the name ShowRunasDifferentuserinStart and value 1 in the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer. You can use the following PowerShell command to add the reg parameter:
New-ItemProperty -Path «HKCU:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer» -Name ShowRunasDifferentuserinStart -Value 1 -PropertyType DWORD -Force
Update the Group Policy settings ( gpupdate /force ) and make sure that a new context menu More -> Run as different user has appeared for the programs in the Start menu.
Application. Run Метод
Определение
Запускает стандартный цикл обработки сообщений приложения в текущем потоке. Begins running a standard application message loop on the current thread.
Перегрузки
Запускает стандартный цикл обработки сообщений приложения в текущем потоке, без формы. Begins running a standard application message loop on the current thread, without a form.
Запускает стандартный цикл обработки сообщений приложения в текущем потоке с ApplicationContext. Begins running a standard application message loop on the current thread, with an ApplicationContext.
Запускает стандартный цикл обработки сообщений приложения в текущем потоке и делает указанную форму видимой. Begins running a standard application message loop on the current thread, and makes the specified form visible.
Запускает стандартный цикл обработки сообщений приложения в текущем потоке, без формы. Begins running a standard application message loop on the current thread, without a form.
Исключения
Основной цикл обработки сообщений уже запущен в данном потоке. A main message loop is already running on this thread.
Комментарии
В приложении на основе Win32 или Windows Forms цикл обработки сообщений является подпрограммой в коде, который обрабатывает события пользователя, такие как щелчки мыши и клавиатуры. In a Win32-based or Windows Forms application, a message loop is a routine in code that processes user events, such as mouse clicks and keyboard strokes. Для каждого работающего приложения на основе Windows требуется активный цикл обработки сообщений, который называется основным циклом обработки сообщений. Every running Windows-based application requires an active message loop, called the main message loop. Когда главный цикл обработки сообщений закрыт, приложение завершает работу. When the main message loop is closed, the application exits. В Windows Forms этот цикл закрывается при Exit вызове метода или при ExitThread вызове метода в потоке, выполняющем основной цикл обработки сообщений. In Windows Forms, this loop is closed when the Exit method is called, or when the ExitThread method is called on the thread that is running the main message loop.
Большинству Windows Forms разработчикам не потребуется использовать эту версию метода. Most Windows Forms developers will not need to use this version of the method. Используйте Run(Form) перегрузку для запуска приложения с главной формой, чтобы приложение завершается при закрытии главной формы. You should use the Run(Form) overload to start an application with a main form, so that the application terminates when the main form is closed. Во всех остальных ситуациях используйте Run(ApplicationContext) перегрузку, которая поддерживает предоставление ApplicationContext объекта для лучшего контроля за временем существования приложения. For all other situations, use the Run(ApplicationContext) overload, which supports supplying an ApplicationContext object for better control over the lifetime of the application.
См. также раздел
Применяется к
Run(ApplicationContext)
Запускает стандартный цикл обработки сообщений приложения в текущем потоке с ApplicationContext. Begins running a standard application message loop on the current thread, with an ApplicationContext.
Параметры
Объект ApplicationContext, в котором запускается приложение. An ApplicationContext in which the application is run.
Исключения
Основной цикл обработки сообщений уже запущен в данном потоке. A main message loop is already running on this thread.
Примеры
В примере показаны две формы и выход из приложения при закрытии обеих форм. The example displays two forms and exits the application when both forms are closed. Когда приложение запускается и завершает работу, сохраняется расположение каждой формы. When the application starts and exits, the position of each form is remembered. В этом примере показано, как использовать ApplicationContext , вместе с Application.Run(context) методом, чтобы отобразить несколько форм при запуске приложения. This example demonstrates how to use an ApplicationContext, along with the Application.Run(context) method, to display multiple forms when the application starts.
Класс MyApplicationContext наследует от ApplicationContext и отслеживает, когда закрывается каждая форма, и завершает текущий поток, когда они оба. The class MyApplicationContext inherits from ApplicationContext and keeps track when each form is closed, and exits the current thread when they both are. Класс хранит позиции каждой формы для пользователя. The class stores the positions of each form for the user. Данные о положении формы хранятся в файле Appdata.txt , созданном в расположении, определенном параметром UserAppDataPath . The form position data is stored in a file titled Appdata.txt that is created in the location determined by UserAppDataPath. Main Метод вызывает, Application.Run(context) чтобы запустить приложение, используя ApplicationContext . The Main method calls Application.Run(context) to start the application given the ApplicationContext.
Код для AppForm1 AppForm2 форм и не показан в целях краткости. The code for the AppForm1 and AppForm2 forms is not shown for the purpose of brevity. ApplicationContextПолный листинг кода см. в обзоре класса. See the ApplicationContext class overview for the whole code listing.
Использование запуска приложения с учетной записи администратора в Windows Server 2003
В этой статье описывается использование команды для запуска Run as приложения в качестве администратора.
Исходная версия продукта: Windows Server 2003
Исходный номер КБ: 325362
Аннотация
Можно использовать для запуска приложения в качестве администратора, если вы хотите выполнять административные задачи при входе в систему в качестве члена другой группы, например «Пользователи» или Run as «Power Users».
Действия, необходимые для запуска приложения с учетной записи администратора
Чтобы запустить Run as приложение в качестве администратора, выполните следующие действия.
- Найдите приложение, которое нужно запустить в проводнике Windows, консоли управления (MMC) или панели управления.
- Нажимайте и удерживайте клавишу SHIFT, щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши исполняемый файл или значок приложения, а затем выберите «Запустить как».
- Выберите следующего пользователя.
- В полях «Имя пользователя»и «Пароль» введите учетную запись администратора и пароль, а затем выберите «ОК».
- Некоторые приложения могут не поддерживать использование Run as команды.
- Возможно, вы не сможете запустить приложение, консоль MMC или средство панели управления из сетевого расположения с помощью команды, если учетные данные, используемые для подключения к сетевой сети, отличаются от учетных данных, используемых для запуска Run as приложения. Учетные данные, используемые для запуска приложения, могут не разрешить доступ к одной сетевой сети.
- Вы также можете использовать Run as команду из командной строки. Для получения дополнительных сведений выберите «Начните» и выберите «Выполнить». В поле «Открыть» введите cmd и выберите «ОК». В командной подсказке введите runas /?, а затем нажмите ввод.