- “Register” an .exe so you can run it from any command line in Windows
- 20 Answers 20
- Simple Bash-like aliases in Windows
- «Install» Your Aliases Path
- Add Your Alias
- Open in New Shell Window
- Execute in Current Shell Window
- Execute in Current Shell Window 2
- How to Run Program from CMD (Command Prompt) Windows 10 [MiniTool News]
- Summary :
- How to Run a Program from CMD in Windows 10
- How to Run EXE in CMD on Windows 10
- Bottom Line
- ABOUT THE AUTHOR
- path path
- Синтаксис Syntax
- Параметры Parameters
- Комментарии Remarks
- Примеры Examples
“Register” an .exe so you can run it from any command line in Windows
How can you make a .exe file accessible from any location in the Windows command window? Is there some registry entry that has to be entered?
20 Answers 20
You need to make sure that the exe is in a folder that’s on the PATH environment variable.
You can do this by either installing it into a folder that’s already on the PATH or by adding your folder to the PATH .
You can have your installer do this — but you may need to restart the machine to make sure it gets picked up.
Windows 10, 8.1, 8
Open start menu,
- Type Edit environment variables
- Open the option Edit the system environment variables
- Click Environment variables. button
- There you see two boxes, in System Variables box find path variable
- Click Edit
- a window pops up, click New
- Type the Directory path of your .exe or batch file ( Directory means exclude the file name from path)
- Click Ok on all open windows and
restart your systemrestart the command prompt.
You can add the following registry key:
In this key, add the default string value containing the path to the exe file.
You have to put your .exe file’s path into enviroment variable path. Go to «My computer -> properties -> advanced -> environment variables -> Path» and edit path by adding .exe ‘s directory into path.
Another solution I personally prefer is using RapidEE for a smoother variable editing.
Rather than putting the executable into a directory on the path, you should create a batch file in a directory on the path that launches the program. This way you don’t separate the executable from its supporting files, and you don’t add other stuff in the same directory to the path unintentionally.
Such batch file can look like this:
Let’s say my exe is C:\Program Files\AzCopy\azcopy.exe
I can now simply type and use azcopy from any location from any shell inc command prompt, powershell, git bash etc
it’s amazing there’s no simple solution for such a simple task on windows, I created this little cmd script that you can use to define aliases on windows (instructions are at the file header itself):
this is pretty much the same approach used by tools like NPM or ruby gems to register global commands.
It is very simple and it won’t take more than 30 seconds.
For example the software called abc located in D:/Softwares/vlc/abc.exe Add the folder path of abc.exe to system environment variables.
My Computer -> Click Properties -> Click Advanced system settings -> Click Environment Variables
now you can just open cmd prompt and you can launch the software from anywhere. to use abc.exe just type abc in the command line.
- If you want to be able to run it inside cmd.exe or batch files you need to add the directory the .exe is in to the %path% variable (System or User)
- If you want to be able to run it in the Run dialog (Win+R) or any application that calls ShellExecute, adding your exe to the app paths key is enough (This is less error prone during install/uninstall and also does not clutter up the path variable)
You may also permanently (after reboots) add to the Path variable this way:
Right click My Computer -> Click Properties -> Click Advanced system settings -> Click Environment Variables
Simple Bash-like aliases in Windows
To get global bash-like aliases in Windows for applications not added to the path automatically without manually adding each one to the path, here’s the cleanest solution I’ve come up with that does the least amount of changes to the system and has the most flexibility for later customization:
«Install» Your Aliases Path
Add Your Alias
Open in New Shell Window
To start C:\path to\my program.exe , passing in all arguments, opening it in a new window, create c:\aliases\my program.bat file with the following contents(see NT Start Command for details on the start commmand):
Execute in Current Shell Window
To start C:\path to\my program.exe , passing in all arguments, but running it in the same window (more like how bash operates) create c:\aliases\my program.bat file with the following contents:
Execute in Current Shell Window 2
If you don’t need the application to change the current working directory at all in order to operate, you can just add a symlink to the executable inside your aliases folder:
Put it in the c:\windows directory or add your directory to the «path» in the environment-settings (windows-break — tab advanced)
Add to the PATH, steps below (Windows 10):
- Type in search bar «environment. » and choose Edit the system environment variables which opens up the System Properties window
- Click the Environment Variables. button
- In the Environment Variables tab, double click the Path variable in the System variables section
- Add the path to the folder containing the .exe to the Path by double clicking on the empty line and paste the path.
- Click ok and exit. Open a new cmd prompt and hit the command from any folder and it should work.
Use a 1 line batch file in your install:
run the bat file
Now place your .exe in c:\windows, and you’re done.
you may type the ‘exename’ in command-line and it’ll run it.
Another way could be through adding .LNK to your $PATHEX. Then just create a shortcut to your executable (ie: yourshortcut.lnk) and put it into any of the directories listed within $PATH.
WARNING NOTE: Know that any .lnk files located in any directories listed in your $PATH are now «PATH’ed» as well. For this reason, I would favor the batch file method mentionned earlier to this method.
In order to make it work
You need to modify the value of the environment variable with the name key Path , you can add as many paths as you want separating them with ; . The paths you give to it can’t include the name of the executable file.
If you add a path to the variable Path all the excecutable files inside it can be called from cmd or porweshell by writing their name without .exe and these names are not case sensitive.
Here is how to create a system environment variable from a python script:
It is important to run it with administrator privileges in order to make it work. To better understand the code, just read the comments on it.
Tested on Windows 10
You can find more information in the winreg documentation
How to Run Program from CMD (Command Prompt) Windows 10 [MiniTool News]
By Alisa | Follow | Last Updated June 10, 2020
Summary :
You can run a program or an exe file from Command Prompt. Check how to do it in this tutorial. MiniTool software, not only provides many useful computer solutions, but also provides users many useful computer software like data recovery program, disk partition manager, system backup and restore software, video editor, etc.
If you want to run program from CMD (Command Prompt) on Windows 10, you can check the detailed steps below.
How to Run a Program from CMD in Windows 10
You can only run the applications that are installed in Windows-created folders like Explorer in Command Prompt.
Step 1. Open Command Prompt in Windows 10
At first, you should open Command Prompt application on your Windows 10 computer. You can press Windows + R, type cmd, and press Enter to open normal Command Prompt or press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open elevated Command Prompt on Windows 10.
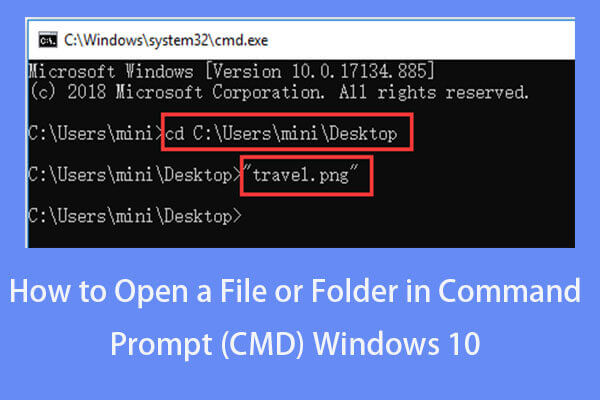
Learn how to open a file/folder in Command Prompt (cmd) on Windows 10. Step-by-step guide is included.
Step 2. Run Program from CMD on Windows 10
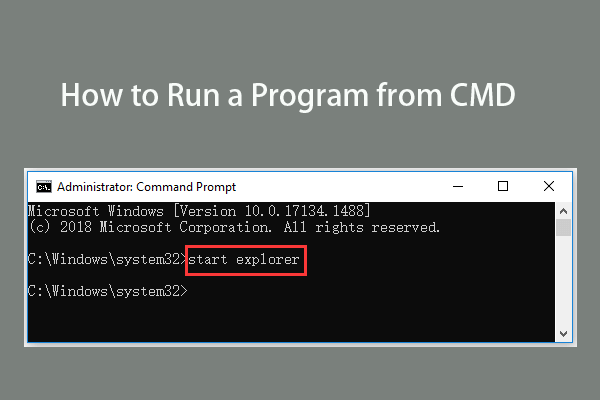
Next you can type start
command in Command Prompt window, and press Enter to open the target application in CMD. Replace the “program name” with the exact file’s system name of the program but not its shortcut name. For instance: start explorer.
The file’s system name of some common programs in Windows are as follows:
- Command Prompt: cmd
- File Explorer: explorer
- Task Manager: taskmgr
- Calculator: calc
- Notepad: notepad
- Paint: mspaint
- Windows Media Player: wmplayer
How to Run EXE in CMD on Windows 10
You can follow the instructions below to run an exe file in Command Prompt.
Step 1. Access Command Prompt window
You can follow the same operation above to open Command Prompt in Windows 10.
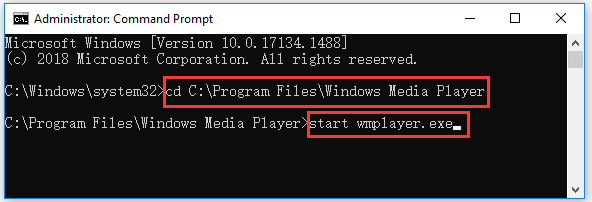
Step 2. Navigate to the folder of the target program
Next you can type cd command in Command Prompt window, and press Enter to navigate to the folder that contains the target exe application. Replace “file path” with the exact file path of the exe file.
You can find the target program folder and click the address bar at the top of File Explorer window to copy the path of the program folder and paste it after cd command. For example, cd C:\Program Files\Windows Media Player.
Step 3. Run exe from CMD
After you are in the target program folder path, then you can type start after the selected file path in CMD, and press Enter to run the exe file in Command Prompt. Replace “filename.exe” with the target program name, e.g. start wmplayer.exe.
Bottom Line
This post introduces how to run a program or exe file from CMD on Windows 10. Hope it helps.
If you need a free data recovery software to recover deleted/lost files from Windows 10 computer or other storage devices, you can try MiniTool Power Data Recovery.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery is a Windows data recovery program that allows you to recover data from PC, external hard drive HDD or SSD, USB drive, SD card, memory card, and more. It is very simple to use and 100% clean.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Position: Columnist
Alisa is a professional English editor with 4-year experience. She loves writing and focuses on sharing detailed solutions and thoughts for computer problems, data recovery & backup, digital gadgets, tech news, etc. Through her articles, users can always easily get related problems solved and find what they want. In spare time, she likes basketball, badminton, tennis, cycling, running, and singing. She is very funny and energetic in life, and always brings friends lots of laughs.
path path
Задает путь к команде в переменной среды PATH, указывающий набор каталогов, используемых для поиска исполняемых файлов (exe). Sets the command path in the PATH environment variable, specifying the set of directories used to search for executable (.exe) files. При использовании без параметров эта команда отображает текущий путь к команде. If used without parameters, this command displays the current command path.
Синтаксис Syntax
Параметры Parameters
| Параметр Parameter | Описание Description |
|---|---|
| [ :] |
Комментарии Remarks
Операционная система Windows выполняет поиск по расширениям имен файлов по умолчанию в следующем порядке приоритета: exe, com, bat и cmd. The Windows operating system searches using default file name extensions in the following order of precedence: .exe, .com, .bat, and .cmd. Это означает, что если вы ищете пакетный файл с именем, acct.bat, но у вас есть приложение с именем acct.exe в том же каталоге, необходимо включить расширение bat в командную строку. Which means if you’re looking for a batch file named, acct.bat, but have an app named acct.exe in the same directory, you must include the .bat extension at the command prompt.
Если два или более файлов в пути команды имеют одинаковое имя файла и расширение, эта команда сначала выполняет поиск указанного имени файла в текущем каталоге. If two or more files in the command path have the same file name and extension, this command first searches for the specified file name in the current directory. Затем он ищет каталоги в пути команды в том порядке, в котором они указаны в переменной среды PATH. Then, it searches the directories in the command path in the order that they’re listed in the PATH environment variable.
При помещении команды path в файл AUTOEXEC. NT операционная система Windows автоматически добавляет указанный путь поиска подсистемы MS-DOS при каждом входе в систему. If you place the path command in your Autoexec.nt file, the Windows operating system automatically appends the specified MS-DOS subsystem search path every time you log on to your computer. Cmd.exe не использует файл AUTOEXEC. NT. Cmd.exe does not use the Autoexec.nt file. При запуске из ярлыка Cmd.exe наследует переменные среды, заданные в Мой компьютер/свойствах/дополнительном/окружении. When started from a shortcut, Cmd.exe inherits the environment variables set in My Computer/Properties/Advanced/Environment.
Примеры Examples
Для поиска по путям к:\усер\таксес, б:\усер\инвест и б:\бин для внешних команд введите: To search the paths c:\user\taxes, b:\user\invest, and b:\bin for external commands, type: