- Create an Application without a Window
- 7 Answers 7
- How do I launch a program from command line without opening a new cmd window?
- 9 Answers 9
- 6 ways to open the Run command window in Windows
- 1. Open the Run command window with a keyboard shortcut
- 2. Use Search to open the Run command window
- 3. Open the Run command window from the Start Menu
- 4. Use the Command Prompt (CMD) to open the Run window
- 5. Open the Run command window with PowerShell
- 6. Use the WinX power user menu to open the Run window in Windows 10
- What do you want to access using the Run window?
- How to Run a Program as a Different User (RunAs) in Windows 10?
- How to Run an App as Different User from File Explorer?
- “Run As Different User” Option is Missing in Windows 10
- Using the RunAs Command to Run a Program as Another User from CMD
- How to Use RunAs Without Password Prompt?
- How to Create a Shortcut to Run As Different User?
- How to Run MMC Snap-Ins As a Different User?
- Add “Run As” Option to Start Menu in Windows 10
Create an Application without a Window
How would you program a C/C++ application that could run without opening a window or console?
7 Answers 7
When you write a WinMain program, you automatically get the /SUBSYSTEM option to be windows in the compiler. (Assuming you use Visual Studio). For any other compiler a similar option might be present but the flag name might be different.
This causes the compiler to create an entry in the executable file format (PE format) that marks the executable as a windows executable.
Once this information is present in the executable, the system loader that starts the program will treat your binary as a windows executable and not a console program and therefore it does not cause console windows to automatically open when it runs.
But a windows program need not create any windows if it need not want to, much like all those programs and services that you see running in the taskbar, but do not see any corresponding windows for them. This can also happen if you create a window but opt not to show it.
All you need to do, to achieve all this is,
The reason you require a WinMain itself is that once you mark the subsystem as Windows, the linker assumes that your entry point function (which is called after the program loads and the C Run TIme library initializes) will be WinMain and not main. If you do not provide a WinMain in such a program you will get an un-resolved symbol error during the linking process.
How do I launch a program from command line without opening a new cmd window?
I’m trying to programmatically execute an external file from cmd using this command:
Where «filepath» is the path of my file. It opens fine but it also open a new command prompt window.
So, which is the right command for opening an external program without opening a new window?
9 Answers 9
In Windows 7+ the first quotations will be the title to the cmd window to open the program:
Formatting your command like the above will temporarily open a cmd window that goes away as fast as it comes up so you really never see it. It also allows you to open more than one program without waiting for the first one to close first.
Add /B, as documented in the command-line help for start:
Just remove the double quote, this works in Windows 7:
If you want to maximize the window, try this:
Your command START «filepath» will start a command prompt and change the command prompt title to filepath .
Try to run start /? in windows command prompt and you will get more info.
I think if you closed a program
end, so if you want to start a program that you can use
(/norma,/max/min are that process value cpu)
start «filepath»
if you want command line without openning an new window you write that
start /b «filepath»
/B is Start application without creating a new window. The application has ^C handling ignored. Unless the application enables ^C processing, ^Break is the only way to interrupt the application.
If you’re doing it via CMD as you say, then you can just enter the command like so:
which will open it within the same window. For example in C++:
will open your.exe in the current CMD window. Likewise to start with a new window, just go for:
If you go for the first option, you would have to clear your screen unless you wanted to have the command to open your.exe on the screen still.
You can use the call command.
Usage: call [drive:][path]filename [batch-parameters]
For example call «Example File/Input File/My Program.bat» [This is also capable with calling files that have a .exe, .cmd, .txt, etc.
NOTE: THIS COMMAND DOES NOT ALWAYS WORK.
Not all computers are capable to run this command, but if it does work than it is very useful, and you won’t have to open a brand new window.
6 ways to open the Run command window in Windows
The Run command window allows you to launch programs, open files and folders, and access internet resources in Windows. Just type a path or a quick command into the Windows Run box, and then click OK or press Enter to use a Run command. Although the Run shortcut is not as easy to find in recent Windows versions, the tool still exists, and there are plenty of ways to access it. This tutorial illustrates how to open Run in Windows 10 and Windows 7:
1. Open the Run command window with a keyboard shortcut
The fastest way to access the Run command window is to use the keyboard shortcut Windows + R. On top of being very easy to remember, this method is universal for all versions of Windows. Hold down the Windows key and then press R on your keyboard.
The Run window is immediately displayed in the lower-left corner of the screen.
2. Use Search to open the Run command window
As always in Windows, Search is a great idea to find just about anything. If you are using Windows 10, first type the word “run” inside the Search bar.
Then, click or tap on the relevant search result or press Open from the pane on the right.
In Windows 7, click the Start button and type the word “run” in the Start Menu Search box. Then, click the appropriate result to launch the Run command window.
3. Open the Run command window from the Start Menu
The Start Menu is a reliable way to access features on your Windows computer or device, including the Run window. In Windows 10, access the Start Menu by clicking or tapping on the Windows logo in the lower-left corner or by pressing the Windows button on your keyboard. Then, scroll down to the letter W, open the Windows System folder, and press Run.
In Windows 7, open the Start Menu and then access “All Programs -> Accessories -> Run” to launch the window.
Alternatively, you can also customize your Windows 7 Start Menu to permanently display a Run shortcut in the right-hand pane. To learn how to do that, read The complete guide to the Windows 7 Start Menu.
4. Use the Command Prompt (CMD) to open the Run window
Some of my colleagues love the CMD, so we decided to put this in for other fans, even if it’s not as easy to remember as the other ways illustrated in this article. To open the Windows Run, you can also launch the Command Prompt and enter the following:
explorer.exe Shell.
This method works both in Windows 10 and Windows 7.
5. Open the Run command window with PowerShell
Wondering how to open Run from PowerShell in Windows 10 and Windows 7? First, start PowerShell. Then, copy/paste or type in the following command:
(New-Object -ComObject “Shell.Application”).FileRun()
Press Enter on your keyboard, and the Run command window is immediately opened in the bottom-left corner.
6. Use the WinX power user menu to open the Run window in Windows 10
Windows 10 has a hidden power user menu that includes a shortcut for the Run command window. There are many ways to access this menu, the easiest being to use the Windows + X keyboard shortcut. Then, click or tap on Run or press R on your keyboard to open the Run box in Windows 10.
If the WinX power user menu interests you, you can learn more by reading: What is the WinX menu and how to open it.
What do you want to access using the Run window?
The Run command window was first introduced by Microsoft in Windows 95 and has been with us ever since. Some of us access it pretty often, but plenty of people don’t realize its potential and usefulness yet. We’re happy this feature caught your eye, but we are curious what brought you here. Are you looking for new ways to open the Windows Run command window or are you trying something new on your computer? Let us know in the comments.
How to Run a Program as a Different User (RunAs) in Windows 10?
In all supported Windows versions it is possible to run applications on behalf of another user (Run As) in the current session. This allows you to run a script (.bat, .cmd, .vbs, .ps1), an executable (.exe) or an application installation (.msi, .cab) with another user (usually elevated) privileges.
For example, you can use the RunAs to install apps or run MMC snap-ins under the administrator account in an unprivileged user session. The opportunity to run a program as a different user may be useful when an application is configured under another user (and stores its settings in another user’s profile, which the current user cannot access), but it must be started with the same settings in another user’s session.
In Windows 10 there are several ways to run a program/process on behalf of another user.
How to Run an App as Different User from File Explorer?
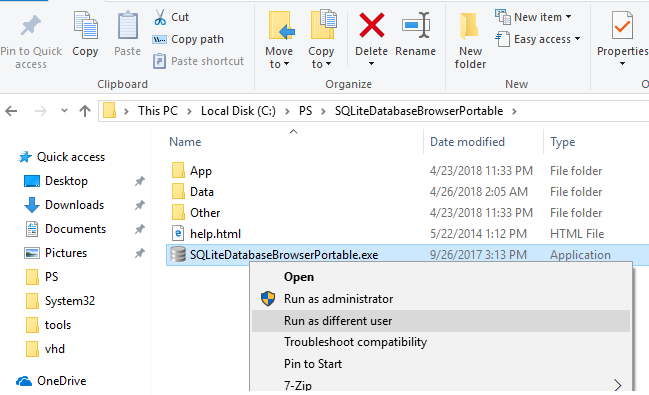
The easiest way to run an application on behalf of another user is to use the Windows File Explorer GUI. Just find an application (or a shortcut) you want to start, press the Shift key and right-click on it. Select Run as different user in the context menu.
[alert]Note. If the menu item “Run as different user” is missing, see the next section.
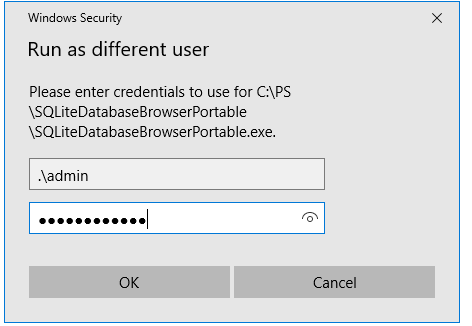
In the next window, specify the name and password of the user under whose account you want to run the application and click OK.
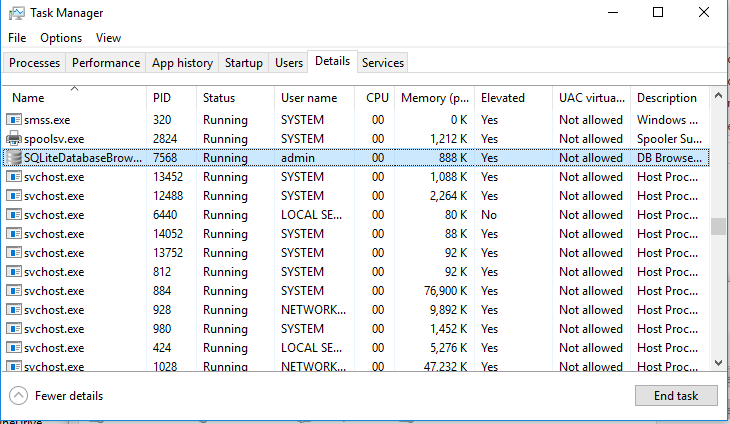
Open the Task Manager and make sure that the application is running under the specified user account.
“Run As Different User” Option is Missing in Windows 10
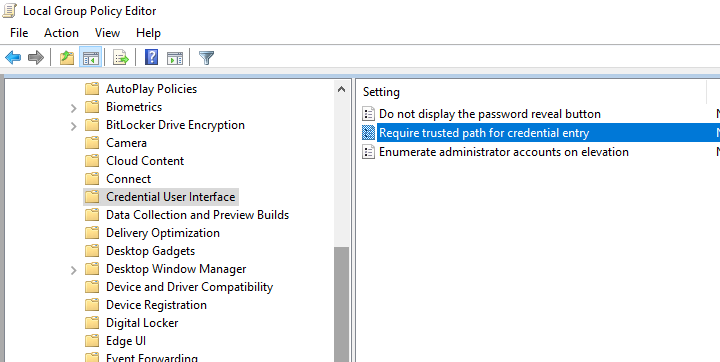
If there is no Run as different user option in the File Explorer context menu, open the Local Group Policy Editor ( gpedit.msc ) and make sure that the Require trusted path for credential entry policy is disabled (or not configured) in Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Credential User Interface.
Using the RunAs Command to Run a Program as Another User from CMD
You can use the Windows built-in cli tool runas.exe to run apps applications as a different user from the command prompt. The runas command also lets you to save the user’s password to the Windows Credential Manager so that you don’t have to enter it every time.
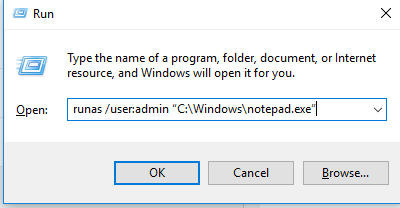
Open the command prompt (or the Run window by pressing Win+R). To start the Notepad.exe under the administrator account, run this command:
runas /user:admin «C:\Windows\notepad.exe»
runas /user:»antony jr» notepad.exe
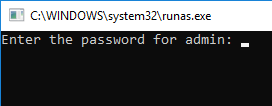
In the next window, the prompt “Enter the password for admin” appears, where you have to enter the user’s password and press Enter.
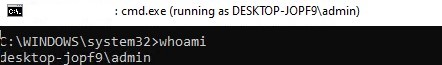
Your application should open. In my case, this is cmd.exe. The window title says “running as PCName\username“:
For example, you can open the Control Panel under a different user:
runas /user:admin control
If you need to run a program under a domain user, use the following name format: UserName@DomainName or DomainName\UserName . For example, to open a text file using notepad on behalf of a domain user, use the command:
runas /user:corp\server_admin «C:\Windows\system32\notepad.exe C:\ps\region.txt»
Sometimes you need to run a program as a domain user from a computer that is not joined to the AD domain. In this case, you need to use the following command (It is assumed that the DNS server specified in your computer’s network settings can resolve this domain name):
runas /netonly /user:contoso\bmorgan cmd.exe
If you don’t want to load user profile when starting the program as different user, use the /noprofile parameter. This allows the application to launch much faster, but may cause incorrect operation of programs that store app data in the user’s profile.
How to Use RunAs Without Password Prompt?
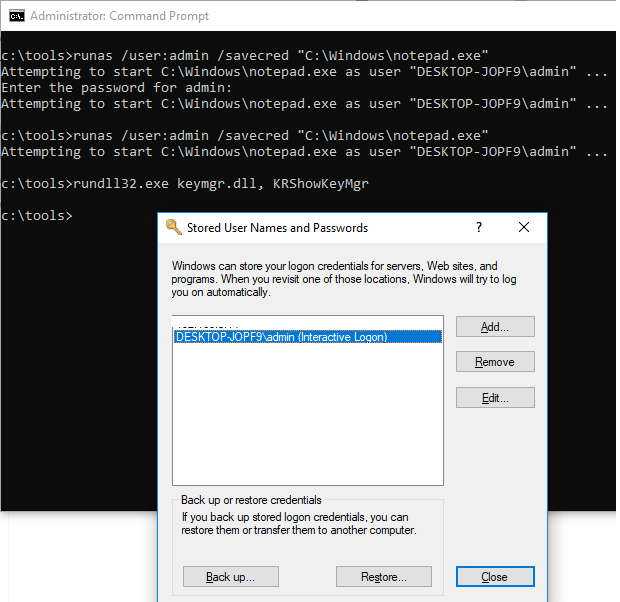
You can save the user credentials (with password) that you enter. The /savecred parameter is used for this.
runas /user:admin /savecred “C:\Windows\cmd.exe”
After specifying the password, it will be saved to the Windows Credential Manager.
The next time you run the runas command under the same user with the /savecred key, Windows will automatically use the saved password from the Credential Manager without prompting to enter it again.
To display a list of saved credentials in Credential Manager, use the following command:
rundll32.exe keymgr.dll, KRShowKeyMgr
However, using the /savecred parameter is not safe. Because a user, in which profile it is saved, can use it to run any command with these privileges and even change another user password. Also, it is easy to steal passwords saved in the Credential Manager so it is recommended to prevent a Windows from saving passwords (and never save the password of the privileged administrator accounts).
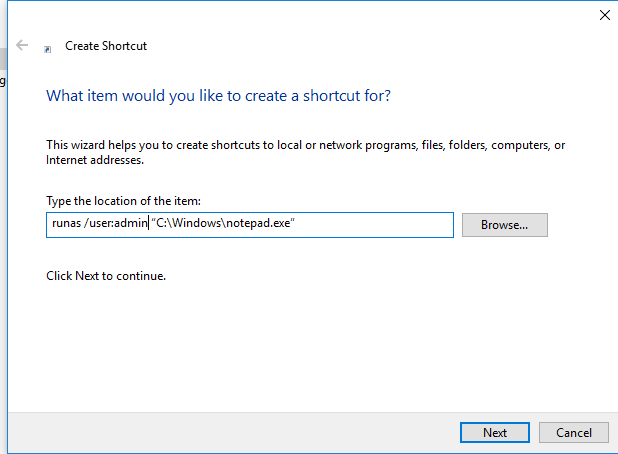
How to Create a Shortcut to Run As Different User?
You can create a shortcut on your desktop that allows you to run the program as a different user. Just create a new shortcut, and specify the runas command with the necessary parameters in the Location field
When you run such a shortcut, you will be prompted to enter a user password.
If you additionally specify the /savecred parameter in the runas shortcut, then the password will be prompted only once. The password will be saved in Credential Manager and automatically used when you running the shortcut without prompting for a password.
Such shortcuts are quite often used to run programs that require elevated permissions to run. However, there are safer ways to run a program without administrator privileges, or disable the UAC prompt for a specific application.
How to Run MMC Snap-Ins As a Different User?
In some cases, you have to run one of Windows management snap-ins as a different user. For example, you can use the following command to run the Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) RSAT snap-in as a different user:
runas.exe /user:DOMAIN\USER «cmd /c start \»\» mmc %SystemRoot%\system32\dsa.msc»
In the same way you can run any other snap-in (if you know its name).
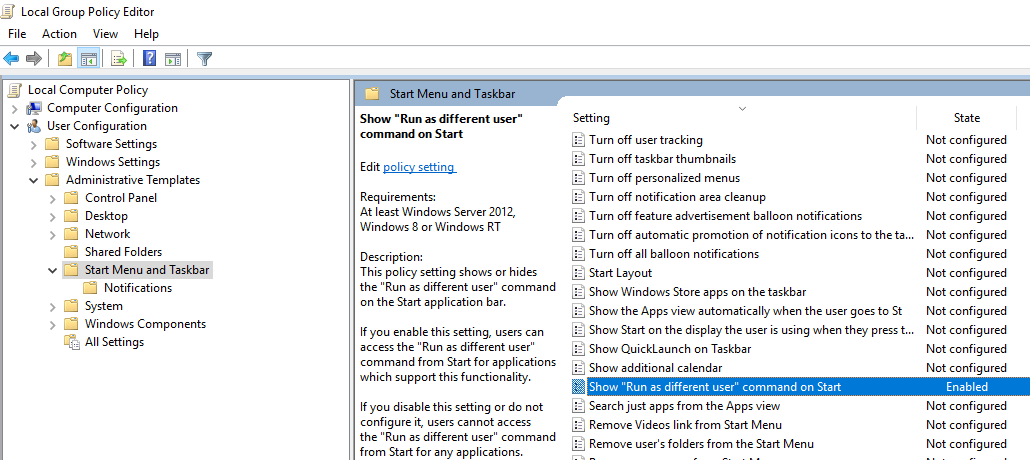
Add “Run As” Option to Start Menu in Windows 10
By default in Windows 10 Start Menu items do not have the “Run As” option. To add the context menu “Run as different user”, enable the “Show Run as different user command on Start” policy in User Configuration -> Administrative Templates ->Start Menu and Taskbar section of the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc).
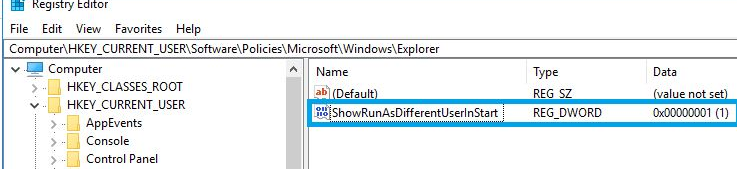
Or, if the gpedit.msc is missing, create a new DWORD parameter with the name ShowRunasDifferentuserinStart and value 1 in the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer. You can use the following PowerShell command to add the reg parameter:
New-ItemProperty -Path «HKCU:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer» -Name ShowRunasDifferentuserinStart -Value 1 -PropertyType DWORD -Force
Update the Group Policy settings ( gpupdate /force ) and make sure that a new context menu More -> Run as different user has appeared for the programs in the Start menu.