- File sharing over a network in Windows 10
- Fix problems in Windows Search
- Check for updates
- Run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter
- Restart Windows Search or your device
- Reset Windows Search
- Windows 10, version 1809 and earlier
- Windows 10, version 1903 and later
- Help us improve Search in Windows 10
- Общий доступ к файлам Windows Windows file sharing
- Доступ к файлам с помощью общего доступа к файлам Windows Accessing your files using Windows file sharing
- Запуск и остановка сервера общего доступа к файлам Starting and stopping the file sharing server
- Отключение и включение сервера общего доступа к файлам при запуске Disabling and enabling the file sharing server on startup
- Windows Search Overview
- Introduction
- Windows Search Service
- Development Platform
- User Interface
- Technical Prerequisites
- SDK Download and Contents
- Windows Search SDK Documentation
- History of Windows Search
File sharing over a network in Windows 10
In Windows 10, some features of file and folder sharing over a network have changed, including the removal of HomeGroup. Read on for answers to common questions about other changes to file and folder sharing in Windows 10.
To share a file or folder in File Explorer, do one of the following:
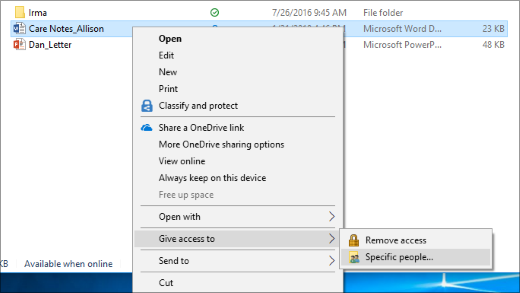
Right-click or press a file, select Give access to > Specific people.
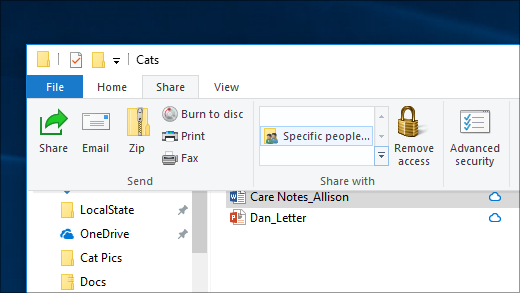
Select a file, select the Share tab at the top of File Explorer, and then in the Share with section select Specific people.
If you select multiple files at once, you can share them all in the same way. It works for folders, too—share a folder, and all files in it will be shared.
To stop sharing in File Explorer, do one of the following:
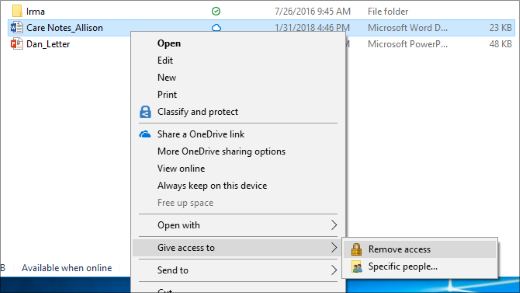
Right-click or press a file or folder, then select Give access to > Remove access.
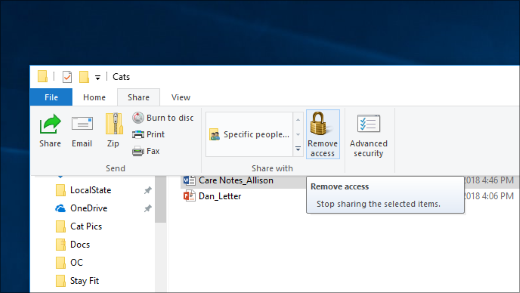
Select a file or folder, select the Share tab at the top of File Explorer, and then in the Share with section select Remove access.
File Explorer shows the «Remove access» option («Stop sharing» in older versions of Windows 10) for all files, even those that aren’t being shared over a network.
Open File Explorer, then type \\localhost into the address bar.
Note: When you’ve shared a file from a folder in your user profile and you go to \\localhost, you’ll see your user profile and all its files there. This doesn’t mean that all of your files are shared—just that you have access to all your own files.
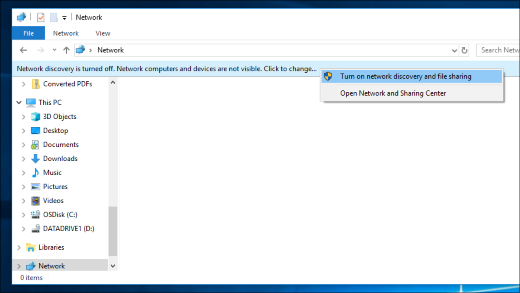
If you open File Explorer, go to Network, and see an error message («Network discovery is turned off….»), you’ll need to turn on Network discovery to see devices on the network that are sharing files. To turn it on, select the Network discovery is turned off banner, then select Turn on network discovery and file sharing.
To troubleshoot problems with sharing files or folders, follow the steps below on all computers from which you’re trying to share.
Make sure the computers are on the same network. For example, if your computers connect to the internet through a wireless router, make sure they all connect through the same wireless router.
If you’re on a Wi-Fi network, set it to Private. To find out how, read Make a Wi-Fi network public or private in Windows 10.
Turn on network discovery and file and printer sharing, and turn off password protected sharing.
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Network & Internet , and on the right side, select Sharing options.
Under Private, select Turn on Network discovery and Turn on file and printer sharing.
Under All Networks, select Turn off password protected sharing.
Make sharing services start automatically.
Press the Windows logo key + R.
In the Run dialog box, type services.msc, and then select OK.
Right-click each of the following services, select Properties, if they’re not running, select Start, and next to Startup type, select Automatic:
Fix problems in Windows Search
If Windows Search is unresponsive or the search results don’t appear as expected, try any of the following solutions in this article.
If you’re running Windows 10 May 2019 Update (version 1903) or later versions and Windows can detect a problem, we’ll run the Search troubleshooter automatically. This troubleshooter will reset Windows Search back to the default experience. View your troubleshooter history under Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > View History. Follow the steps below if your issue is still not resolved.
Original product version: В Windows 10 — all editions
Original KB number: В 4520146
Check for updates
Windows 10 lets you choose when and how to get the latest updates to keep your device running smoothly and securely. To manage your options and see any available updates, select the Start button, and then go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates. Install any available updates, and then restart your computer if the updates require it.
For more information, see Update Windows 10.
Run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter
Your PC automatically indexes content to deliver faster search results. Learn more about Search indexing in Windows 10.
Use the Windows Search and Indexing troubleshooter to try to fix any problems that may arise. To use the troubleshooter, follow these steps:
- Select Start, then select Settings.
- In Windows Settings, select Update & Security >Troubleshoot. Under Find and fix other problems, select Search and Indexing.
- Run the troubleshooter, and select any problems that apply. Windows will try to detect and solve them.
You can also use a command prompt to open the troubleshooter. Press Windows logo key+R, enter cmd in the Open box, and then select OK. At the command prompt, run the following command:
Restart Windows Search or your device
End the SearchUI process to restart Windows Search by following these steps:
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete, and select Task Manager.
- In the Task Manager window, select the Details tab.
- In the Name column, right-click SearchUI.exe, and then select End task.
- When you’re prompted to end SearchUI.exe, select End process.
The Windows Search process will automatically restart the next time that you search.
If this solution doesn’t fix your problem, try restarting your device. Restarting will also install any pending updates.
You may want to bookmark this page before you restart.
Reset Windows Search
Try resetting Windows Search by using the method that’s appropriate for your version of Windows.
To determine which version of Windows your device is running, follow these steps:
Select Start > Settings > System > About.
Under Windows specifications, check which version of Windows your device is running.
Resetting Windows Search does not affect your files. However, it may temporarily affect the relevance of search results.
Windows 10, version 1809 and earlier
If the Windows 10 October 2018 Update or an earlier update is installed, reset Cortana to reset Windows Search by following these steps:
- Select Start, right-click Cortana, select More, and then select App settings.
- In the Cortana settings, select Reset.
Windows 10, version 1903 and later
If the Windows 10 May 2019 Update or a later update is installed, use Windows PowerShell to reset Windows Search by following these steps:
You must have administrator permissions to run this script.
Download the ResetWindowsSearchBox.ps1 script from the Reset Windows Search PowerShell script, and save the file to a local folder.
Right-click the file that you saved, and select Run with PowerShell.
If you’re asked the following question, select Yes.
Do you want to allow this app to make changes to your device?
The PowerShell script resets the Windows Search feature. When the word Done appears, close the PowerShell window.
If you receive the following error message:
Cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system
enter the following command on the command line of the PowerShell window, and then press Enter:
The current policy appears in the window. For example, you might see Restricted. We recommend that you note this value because you’ll have to use it later.
Enter the following command on the command line of the PowerShell window, and then press Enter:
You’ll receive a warning message that explains the security risks of an execution policy change. Press Y, and then press Enter to accept the change.
To learn more about PowerShell execution policies, see About Execution Policies.
After the policy change is completed, close the window, and then repeat steps 2-4. However, when the Done message appears this time, DON’T close the PowerShell window. Instead, press any key to continue.
Revert to your previous PowerShell execution policy setting. Enter the following command on the command line of the PowerShell window, press the Spacebar, enter the policy value that you noted in step 5, and then press Enter:
For example, if the policy that you noted in step 5 was Restricted, the command would resemble the following one:
You’ll receive a warning message that explains the security risks of an execution policy change. Press Y, and then press Enter to accept the change and revert to your previous policy setting.
Close the PowerShell window.
If your organization has disabled the ability to run scripts, contact your administrator for help.
Help us improve Search in Windows 10
If the previous suggestions don’t fix the problem, let us know by sending feedback in the Feedback Hub. Provide details, such as a description of the problem, screenshots, log files, and any other information that might be helpful. In the Feedback Hub, select the appropriate category and subcategory. In this case, submit your feedback in the Cortana and Search category.
Общий доступ к файлам Windows Windows file sharing
Для перемещения файлов на устройство и с него можно использовать общий доступ к файлам Windows. You can use Windows file sharing to transfer files to and from your device.
Доступ к файлам с помощью общего доступа к файлам Windows Accessing your files using Windows file sharing
Сервер общего доступа к файлам на устройстве Windows IoT базовая запускается автоматически при загрузке. The file sharing server on your Windows IoT Core device starts automatically on boot. Для подключения к нему требуется IP-адрес устройства. In order to connect to it, you need the IP address of your device. IP-адрес можно найти в приложении по умолчанию, которое загружается при запуске устройства. You can find the IP address on the default app that boots when your device starts.
Получив IP-адрес, откройте проводник на компьютере и введите \\ \c$ , где — это имя или IP-адрес устройства Windows IOT базовая, а затем нажмите клавишу ВВОД. Once you have the IP, open up File Explorer on your computer and type \\ \c$ , where is either the name or the IP Address of your Windows IoT Core device, then hit Enter.
При появлении запроса введите имя пользователя и пароль администратора. Enter your administrator username and password if prompted. Имя пользователя должно иметь префикс с IP-адресом устройства Windows IoT базовая. The username should be prefixed with the IP Address of your Windows IoT Core device. Пример: username: 192.168.1.118\Administrator пароль:
- Теперь вы можете получить доступ к файлам на устройстве, используя общий доступ к файлам Windows. Now you can access the files on your device using Windows file sharing.
Запуск и остановка сервера общего доступа к файлам Starting and stopping the file sharing server
Подключитесь к устройству с помощью PowerShell или SSH. Connect to your device through PowerShell or SSH.
По умолчанию сервер совместного использования файлов запускается при загрузке устройства. By default the file sharing server is started when the device is booted.
Чтобы отключить сервер общего доступа к файлам, введите net stop Server /y To stop the file sharing server, type net stop Server /y
Чтобы запустить сервер общего доступа к файлам, введите net start Server To start the file sharing server, type net start Server
Отключение и включение сервера общего доступа к файлам при запуске Disabling and enabling the file sharing server on startup
Подключитесь к устройству с помощью PowerShell или SSH. Connect to your device through PowerShell or SSH.
По умолчанию сервер совместного использования файлов запускается при загрузке устройства. By default the file sharing server is started when the device is booted.
Чтобы отключить сервер совместного использования файлов, чтобы он не запускался при запуске устройства, введите reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\lanmanserver /v Start /t REG_DWORD /d 0x3 /f To disable the file sharing server so that it does not start when the device starts, type reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\lanmanserver /v Start /t REG_DWORD /d 0x3 /f
Чтобы включить сервер общего доступа к файлам, который запускается при запуске устройства, введите reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\lanmanserver /v Start /t REG_DWORD /d 0x2 /f To enable the file sharing server, so that starts when the device starts, type reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\lanmanserver /v Start /t REG_DWORD /d 0x2 /f
Windows Search Overview
Windows Search is a desktop search platform that has instant search capabilities for most common file types and data types, and third-party developers can extend these capabilities to new file types and data types.
This topic is organized as follows:
Introduction
Windows Search is a standard component of WindowsВ 7 and WindowsВ Vista, and is enabled by default. Windows Search replaces Windows Desktop Search (WDS), which was available as an add-in for WindowsВ XP and Windows ServerВ 2003.
Windows Search is composed of three components:
Windows Search Service
The WSS organizes the extracted features of a collection of documents. The Windows Search Protocol enables a client to communicate with a server that is hosting a WSS, both to issue queries and to enable an administrator to manage the indexing server. When processing files, WSS analyzes a set of documents, extracts useful information, and then organizes the extracted information so that properties of those documents can be efficiently returned in response to queries.
A collection of documents that can be queried comprises a catalog, which is the highest-level unit of organization in Windows Search. A catalog represents a set of indexed documents that can be queried. A catalog consists of a properties table with the text or value and corresponding location (locale) stored in columns of the table. Each row of the table corresponds to a separate document in the scope of the catalog, and each column of the table corresponds to a property. A catalog may contain an inverted index (for quick word matching) and a property cache (for quick retrieval of property values).
The indexer process is implemented as a Windows service running in the LocalSystem account and is always running for all users (even if no user is logged in), which permits Windows Search to accomplish the following:
- Maintain one index that is shared among all users.
- Maintain security restrictions on content access.
- Process remote queries from client computers on the network.
The Search service is designed to protect the user experience and system performance when indexing. The following conditions cause the service to throttle back or pause indexing:
- High CPU usage by non-search-related processes.
- High system I/O rate including file reads and writes, page file and file cache I/O, and mapped file I/O.
- Low memory availability.
- Low battery life.
- Low disk space on the drive that stores the index.
Development Platform
The preferred way to access the Search APIs and create Windows Search applications is through a Shell data source. A Shell data source is a component that is used to extend the Shell namespace and expose items in a data store. A data store is a repository of data. A data store can be exposed to the Shell programming model as a container that uses a Shell data source. The items in a data store can be indexed by the Windows Search system using a protocol handler.
For example, ISearchFolderItemFactory is a component that can create instances of the search folder data source, which is a sort of «virtual» data source provided by the Shell that can execute queries over other data sources in the Shell namespace and enumerate results. It can do so either by using the indexer or by manually enumerating and inspecting items in the specified scopes. This interface permits you to set up the parameters of the search by using methods that create and modify search folders. If methods of this interface are not called, default values are used instead.
Accessing the Windows Search capability indirectly through the Shell data model is preferred because it provides access to full Shell functionality at the level of the Shell data model. For example, you can set the scope of a search to a library (which is a feature available in WindowsВ 7 and later) to use the library folders as the scope of the query. Windows Search then aggregates the search results from those locations if they are in different indexes (if the folders are on different computers). The Shell data layer also creates a more complete view of items’ properties, synthesizing some property values. It also provides access to search features for data stores that are not indexed by Windows Search. For example, you can search a Universal Serial Bus (USB) storage devices, portable device that uses the MTP protocol, or an File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server through the Shell data sources that provides access to those storage systems. Doing so ensures a better user experience.
Windows Search has a cache of property values that is used in the implementation of the Windows Search Service (WSS). These property values can be programmatically queried by using the Windows Search OLEВ DB provider, or through ISearchFolderItemFactory, which represents items in search results and query-based views. Windows Search then collects and stores properties emitted by filter handlers or property handlers when an item such as a Word document is indexed. This store is discarded and rebuilt when the index is rebuilt.
Third-party developers can create applications that consume the data in the index through programmatic queries, and can extend the data in the index for custom file and item types to be indexed by Windows Search. If you want to show query results in Windows Explorer, you must implement a Shell data source before you can create a protocol handler to extend the index. However, if all queries are programmatic (through OLEВ DB for example) and interpreted by the application’s code rather than the Shell, a Shell namespace is still preferred but not required.
A protocol handler is required for Windows to obtain information about file contents, such as items in databases or custom file types. While Windows Search can index the name and properties of the file, Windows has no information about the content of the file. As a result, such items cannot be indexed or exposed in the Windows Shell. By implementing a custom protocol handler, you can expose these items. For a list of handlers identified by the developer scenario you are trying to achieve, see «Overview of Handlers» in Windows Search as a Development Platform.
A Shell data source is sometimes known as a Shell namespace extension. A handler is sometimes known as a Shell extension or a Shell extension handler.
User Interface
In WindowsВ Vista and later, Windows Search is integrated into all Windows Explorer windows for instant access to search. This enables users to quickly search for files and items by file name, properties, and full-text contents. Results can also be filtered further to refine the search. Here are some more features of Windows Search:
- An instant search box in every window enables instant filtering of all items currently in view. Instant search boxes appear in the Start menu to search for programs or files, and in the upper-right corner of all Windows Explorer windows to filter the results shown. Instant search is also integrated into some other Windows features, such as Windows Media Player, to find related files.
- Documents can be tagged with keywords to group them by custom criteria that are defined by the user. Tags are metadata items that are assigned by the user or applications to make it easier to find files based on keywords that may not be in the item name or contents. For example, a set of pictures might be tagged as «Arizona Vacation 2009» to quickly retrieve later by searching for any of the included words.
- Enhanced column headers in Windows Explorer views enable sorting and grouping documents in different ways. For example, files can be sorted according to name, date modified, type, size, and tags. Documents can also be grouped according to any of these properties and each group can be filtered (hidden or displayed) as desired.
- Documents can be stacked according to name, date modified, type, size, and tags. Stacks include all documents that have the specified property and are located within any subfolder of the selected folder.
- Searches can be saved (to be retrieved later) by clicking the Save Search button in the search pane in Windows Explorer. The results will be dynamically repopulated based on the original criteria when the saved search is opened. For instructions, see Save Your Search Results.
- Preview handlers and thumbnail handlers enable users to preview documents in Windows Explorer without having to open the application that created them.
Technical Prerequisites
Before you start reading the Windows Search SDK documentation, you should have a fundamental understanding of the following concepts:
- How to implement a Shell data source.
- How to implement a handler.
- How to work in native code.
A Shell data source is a component that is used to extend the Shell namespace and expose items in a data store. In the past, the Shell data source was referred to as the Shell namespace extension. A handler is a Component Object Model (COM) object that provides functionality for a Shell item. For a list of handlers identified by the developer scenario you are trying to achieve, see «Overview of Handlers» in Windows Search as a Development Platform.
For more information about the Windows Search SDK interoperability assembly for working with COM objects that are exposed by Windows Search and other programs that use managed code, see Using Managed Code with Shell Data and Windows Search. However, note that filters, property handlers, and protocol handlers must be written in native code. This is due to potential common language runtime (CLR) versioning issues with the process that multiple add-ins run in. Developers who are new to C++ can get started with the Visual C++ Developer Center and Windows Development Getting Started.
SDK Download and Contents
In addition to meeting the listed technical prerequirements, you must also download the Windows SDK to get the Windows Search libraries. The Windows Search SDK Samples contain useful code samples and an interoperability assembly for developing with managed code. For more information on using the code samples, see Windows Search Code Samples.
Windows Search SDK Documentation
The contents of the Windows Search SDK documentation are as follows:
Outlines the main development scenarios in Windows Search. Provides a list of handlers identified by the development scenario you are trying to achieve, add-in installer guidelines, and implementation notes.
Describes the Search API code samples that are available.
Describes WindowsВ 7 support for search federation to remote data stores using OpenSearch technologies that enable users to access and interact with their remote data from within Windows Explorer.
Lists technologies related to Windows Search: Enterprise Search, SharePoint Enterprise Search, and legacy applications such as Windows Desktop Search 2.x and Platform SDK: Indexing Service.
Defines essential terms used in Windows Search and Shell technologies.
History of Windows Search
Windows Search replaces Windows Desktop Search (WDS), which was available as an add-in for WindowsВ XP and Windows ServerВ 2003. WDS replaced the legacy Indexing Service from previous versions of Windows with enhancements to performance, usability, and extensibility. The new development platform supports requirements that produce a more secure and stable system. While the new querying platform is not compatible with MicrosoftВ Windows Desktop Search (WDS) 2.x, filters and protocol handlers written for previous versions of WDS can be updated to work with Windows Search. Windows Search also supports a new property system. For information on filters, property handlers, and protocol handlers, see Extending the Index.
Windows Search is built into WindowsВ Vista and later, and is available as a redistributable update to WDS 2.x, to support the following operating systems:
- 32-bit versions of WindowsВ XP with Service Pack 2 (SP2).
- All x64-based versions of WindowsВ XP.
- Windows ServerВ 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) and later.
- All x64-based versions of Windows ServerВ 2003.
Systems running these operating systems must have Windows Search installed in order to run applications written for Windows Search. For more information, see KB article 917013: Description of Windows Desktop Search 3.01 and the Multilingual User Interface Pack for Windows Desktop Search 3.01.