- Корзина Active Directory в Windows Server 2012
- Включаем Active Directory Recycle Bin в домене
- Восстановление удаленных объектов Active Directory из корзины
- Windows server 2012 recycle bin
- AD Recycle Bin in Windows Server 2012 — Part 2: Usage
- Other things to consider ^
- Active Directory Recycle Bin in Windows Server 2012 — Part 1: Enable
- Forest Functional Level ^
- Enable Active Directory Recycle Bin in Windows Server 2012 ^
Корзина Active Directory в Windows Server 2012
Технология корзины AD (Active Directory Recycle Bin) впервые была представлена в Windows Server 2008 R2. В Windows Server 2003 и 2008 восстановить удаленный объект AD можно было только из резервной копии, режима DSRM с помощью команды «ntdsutil authoritative restore» или сторонних утилит (например, ADRestore). Однако во всех этих случаях предполагалась недоступность службы AD во время восстановления объектов. C помощью корзины AD администратор может восстановить любой случайно или преднамеренно удаленный объект Active Directory без прерывания этого сервиса.
В Windows Server 2012 технология корзины Active Directory получила дальнейшее развитие. Одним из главных нововведений в этой технологии является то, что в Windows Server 2012, наконец-то появился графический GUI для работы с корзиной AD Recycle Bin (в Windows 2008 R2 управление корзиной Active Directory Recycle Bin осуществлялось с помощью PowerShell и утилиты LDP.exe). Теперь управление корзиной и возможности восстановления объектов AD доступны из графической консоли Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC).
Кроме того, в новой корзине теперь можно фиксировать информацию об атрибутах объектов и членстве в группах, так что теперь не придется вручную восстанавливать настройки из tombstone объектов.
Удаленные объекты хранятся в корзине AD в течении времени захоронения (tombstonelifetime), заданном для леса. По умолчанию это 180 дней.
Для работы новой ActiveDirectory RecycleBin должны выполняться следующие требования:
- Как минимум один контроллер, сWindows Server 2012 и включенным Active Directory Administrative Center
- Все контролеры домена должны работать под управлением Windows Server 2008 R2 или выше
- Функциональный уровень леса должен быть не менее Windows Server 2008 R2
Включаем Active Directory Recycle Bin в домене
Стоит заранее отметить, что по-умолчанию корзина AD выключена, однако если ее активировать, отключить ее в дальнейшем невозможно. Т.е. включение корзины AD процесс необратимый. Поэтому рекомендуется сначала познакомиться с технологией корзины Active Directory в тестовой среде.
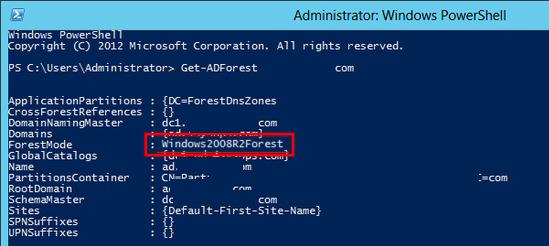
Проверим текущий уровень леса, сделать это можно с помощью команды PoSh:
В нашем случае уровень леса — Windows2008R2Forest, если же уровень леса ниже, его нужно поднять.
Включить корзину Active Directory можно с помощью Powershell:
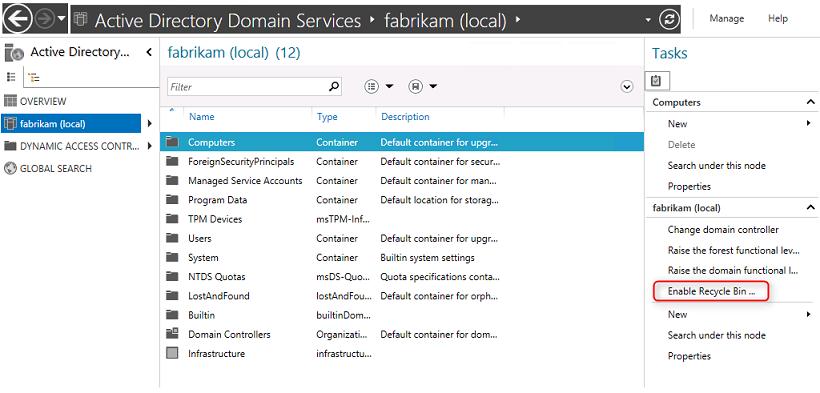
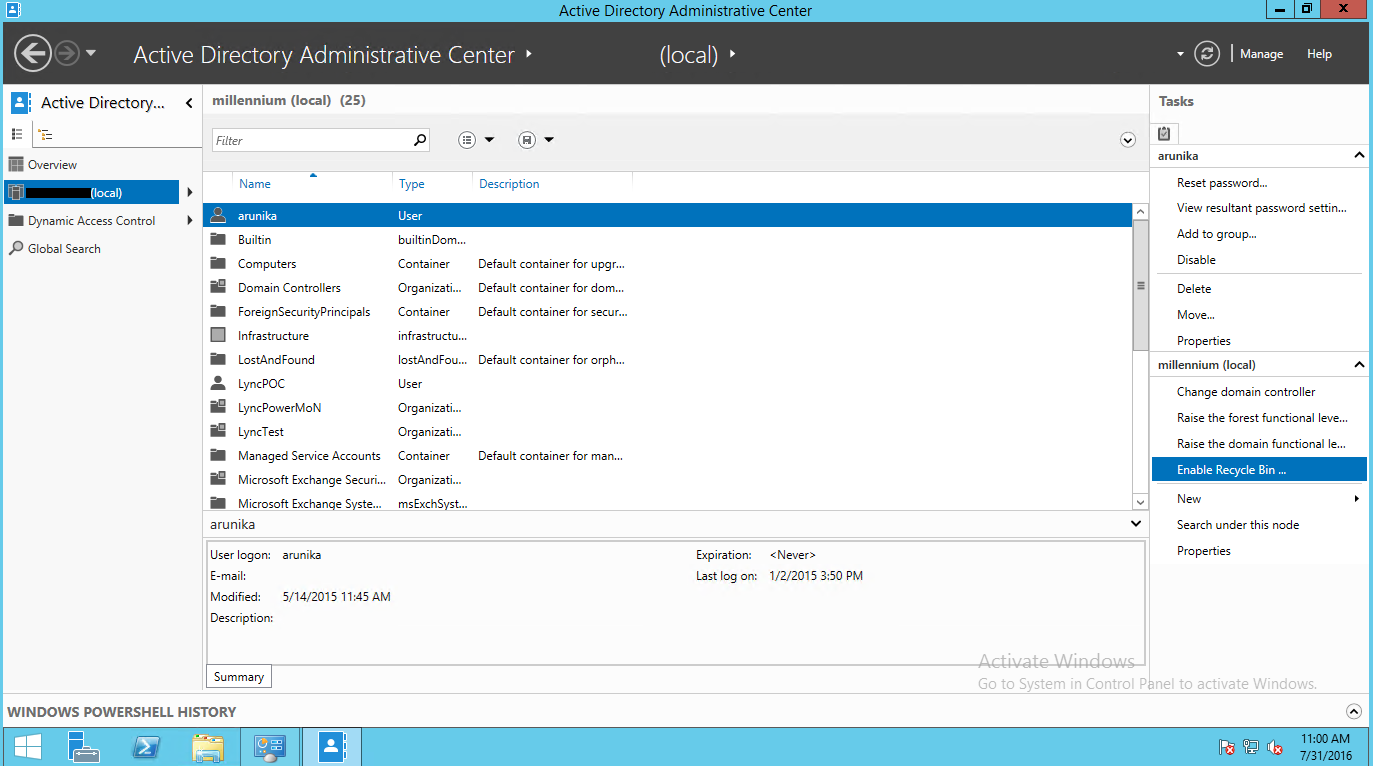
Тоже самое можно сделать из консоли Active Directory Administrative Center. Для этого в консоли нужно выбрать ваш домен и в правой панели найти и нажать кнопку «Enable Recycle Bin».
Примечание . После включения корзины должно пройти некоторое время, прежде чем информация о новой конфигурации реплицируется по всем серверам леса AD.
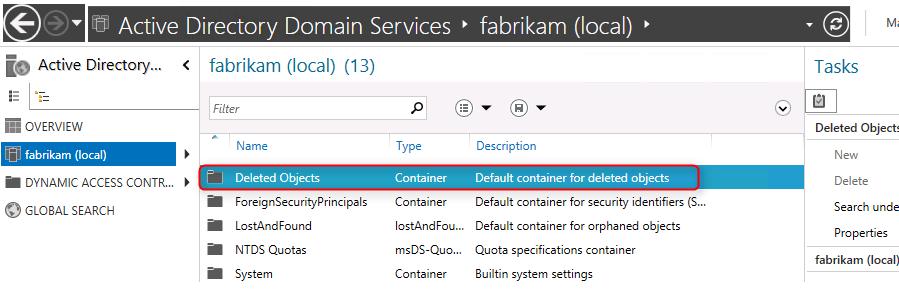
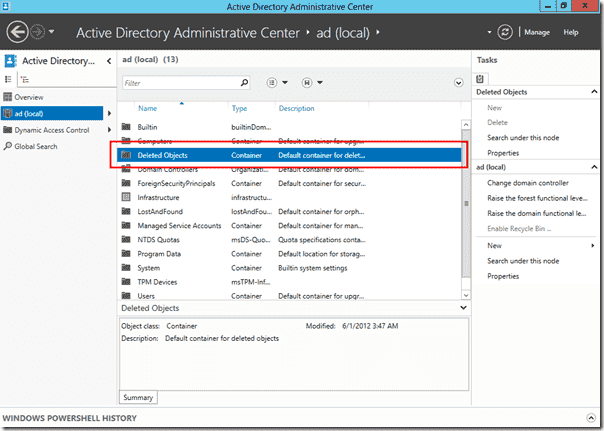
Если обновить консоль, то вы увидите, что в дереве AD появился новый контейнер OU с названием Deleted object
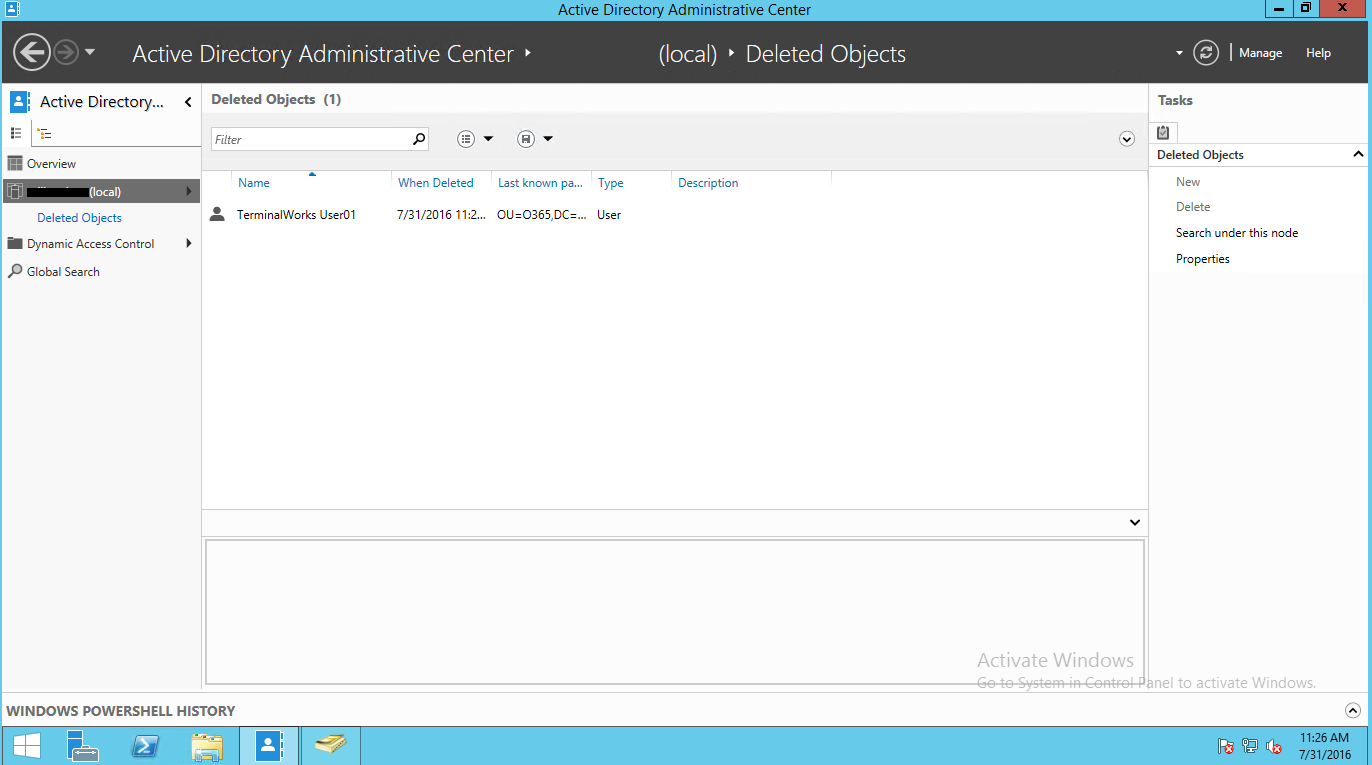
Восстановление удаленных объектов Active Directory из корзины
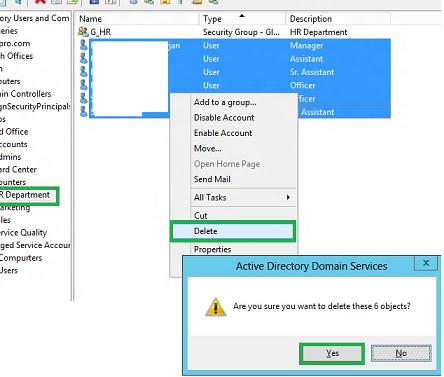
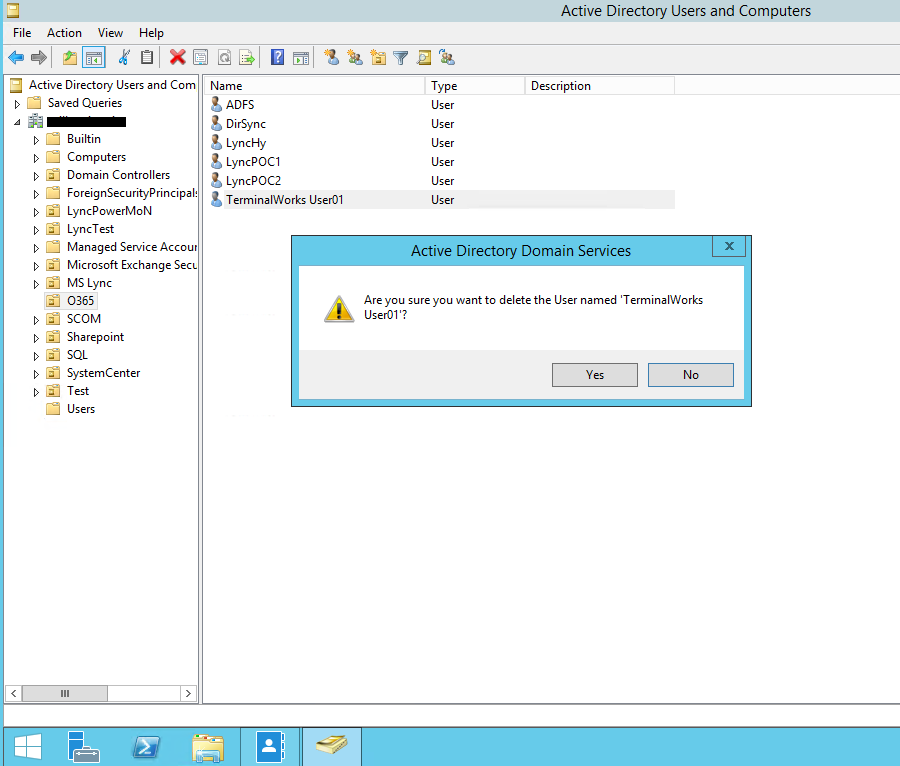
Продемонстрируем работу технологии Active Directory RecycleBin в деле. Попробуем удалить несколько пользователей домена из AD, а затем попробуем их восстановить. Выделим несколько пользователей в тестовой OU и удалим их.
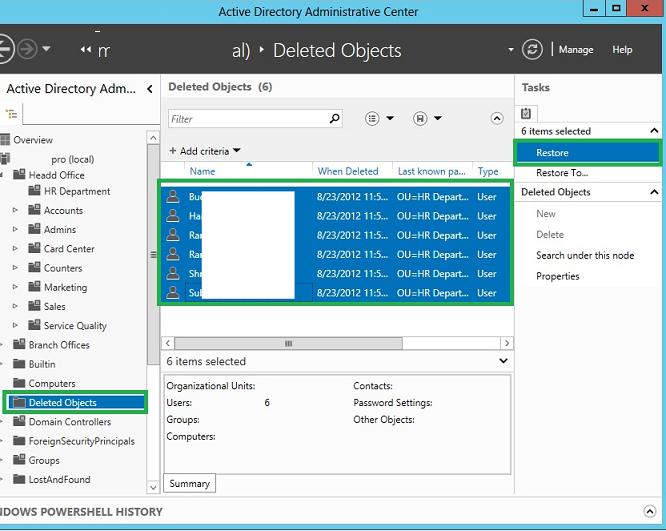
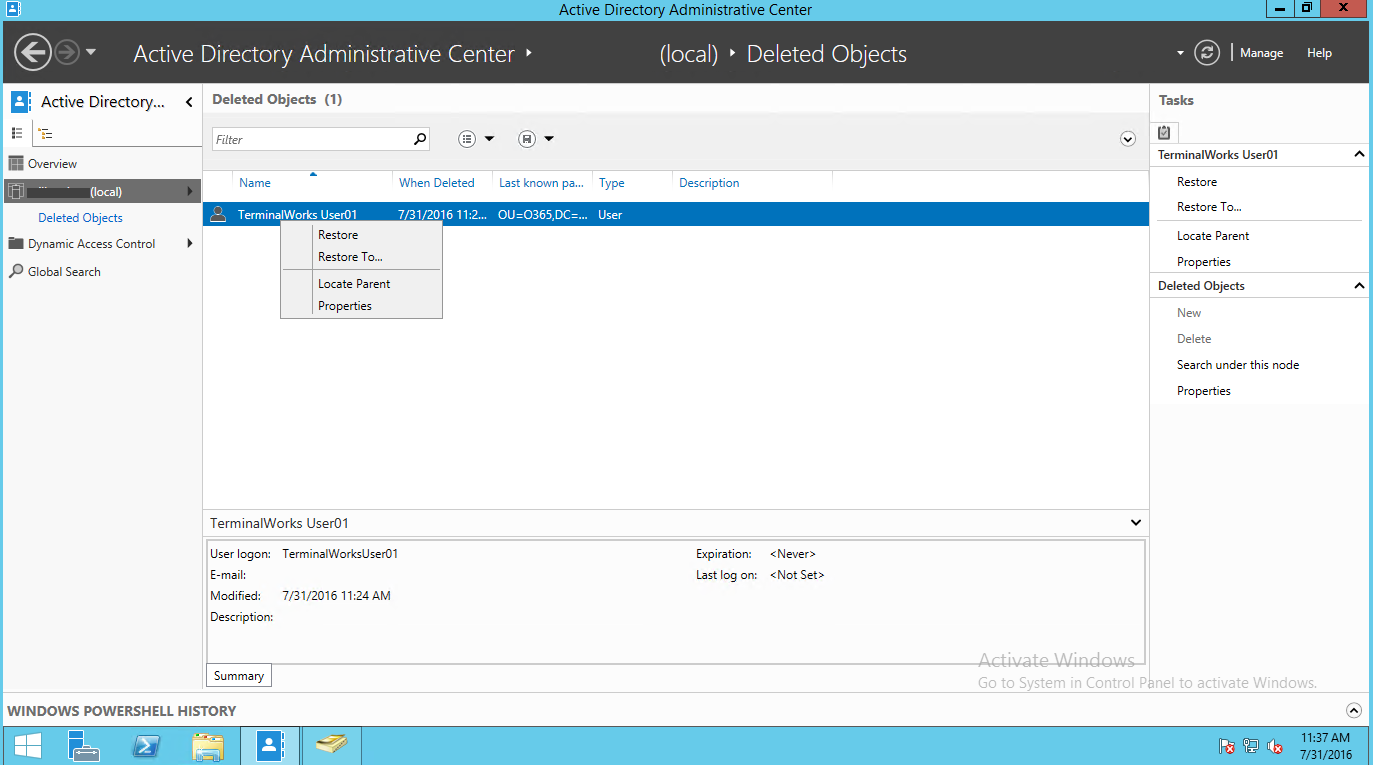
Затем в консоли ADAC перейдем в созданную ранее OU Deleted Objects и в ней должны оказаться все удаленный нами пользователи. Выделим все объекты, которые нужно восстановить и в правой панели нажмем кнопку Restore. Если нужно восстановить объекты в OU, отличную от той, из которой были они удалены, воспользуемся кнопкой Restore To.
После чего можно удостовериться, что все удаленные объекты появятся в исходном контейнере.
Через графический интерфейс отображаются не все атрибуту удаленного объекта (только имя удаленного объекта, last known parent и GUID). Если вам нужна более полная информация об объекте, придется его сначала восстановить, и если это окажется не тот объект, затем удалить. Как вариант выборки элементов с определенными параметрами моно использовать фильтры. Например, выбрав фильтр по атрибуту City и указав Сыктывкар, мы выберем все удаленные объекты, у которых в поле City указана данный город.
Также стоит отметить, что можно восстанавливать не только отдельные объекты AD, но и целиком контейнеры со всеми OU и другими типами объектов в них. Для этого в корзине нужно будет выбрать и объекты и их удаленные родительские OU, а затем нажать кнопку Restore. Одновременно удаленные объекты можно отобрать, отсортировав в корзине с помощь. фильтра по столбцу When Deleted.
Про восстановление удаленных объектов AD с помощью PowerShell есть отдельная статья.
Windows server 2012 recycle bin
Active directory recycle bin is a feature introduced with windows server 2008 R2 to undo or recover a deletion of an Active directory object. With windows server 2012 R2, you can use this feature to recover User objects, Computer objects or Organizational groups when you accidentally or purposefully deleted from the Active directory.
The Feature is rather improved, now it’s a part of the Active Directory administration center. So it’s not required to use PowerShell commands when recovering. AD Administration center has a GUI, which can be used to easily locate a deleted item, and from one click you can restore it to the original location. This is a very useful feature in day to day operations and let’s see how we can enable this.
Enabling AD Recycle Bin
Before enabling this feature you have to check whether your AD functional level is supported. You have to have minimum Windows server 2008R2 Forest functional level or higher. And it’s irreversible, once you have enable it you cannot disable. Also you need to aware that size of the NTDS database will be increase after you enabled the recycle bin. It will keep the deletion data and with time it will increase more, so I suggest you to delete unnecessary data from the bin time to time. Enterprise admin rights are required to access the recycle bin.
- Login to the Domain controller using Enterprise Admin credentials
- Open Active Directory Administration Center from Administration tools
Select the Domain name and click Enable Recycle bin from Right side panel

How to restore an object
To test the configurations, let’s create a test account, delete it and check how to restore it using the Administrative center.
- Create a User account in an OU
- Delete the account
Open Administration Center – Deleted Objects, and you can see the deleted user account
When you right click on the deleted object there is four options to select.
Restore – Restore the object to its original location,
Restore to – Restore it to a new location,
Locate Parent – show where the object existed before the deletion,
Properties – Object properties, Name, Object Class, and UNS,
Right click and select restore
AD Recycle Bin is a useful tool in day to day operations. It will minimize the risk of the operation. You can delegate user operations to the help desk or junior staff, so if they make any mistake you have the option to correct it. Hope this post is useful
AD Recycle Bin in Windows Server 2012 — Part 2: Usage
- Managing shared mailboxes in Office 365 with PowerShell — Thu, May 5 2016
- Managing shared mailboxes in Office 365 with the GUI — Wed, May 4 2016
- Installing and configuring the Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit (EMET) — Wed, Mar 16 2016
Now that the Forest Functional Level is at least Windows Server 2008 R2 and we’ve enabled the Active Directory Recycle Bin, let’s delete some stuff to test it out! The AD Recycle Bin can be accessed in the Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC) on the Start Screen of your Domain Controller.
Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC)
In the ADAC, click on your Domain and then should see a Container called Deleted Objects. Most likely, the Deleted Objects will be empty. Let’s go create some test objects that we can delete. Again, all of my screenshots from this demo were made in a test environment. I highly suggest you do the same before trying this in a production environment. I’ve created several User objects and Security Groups. Now, I’m going to delete them.
Delete User objects in ADAC
In Deleted Objects several items will appear Deleted Objects.
Deleted objects in ADAC
If I select the items I want to restore and click the Restore option, the objects will be restored back to their original OU as if they were never deleted.
AD Recycle Bin Windows Server 2012 — Restore objects
That’s really it. The GUI is rather basic, but a welcome addition to Windows Server 2012. Unfortunately, the items you’ll see in the AD Recycle Bin are limited to the object’s name, last known parent, and GUID. If you need to see more detailed information about a deleted item, you’ll need to restore the object to view its full details and then re-delete it if it isn’t the object you’re looking for.
Other things to consider ^
Deleted items have a lifetime of 180 days in the AD Recycle Bin. For most organization, that is very generous. Should you need to change it, there’s a TechNet article that addresses changing tombstone and deleted item lifetimes.
Enabling the AD Recycle Bin is not reversible. I highly recommend testing this new feature in a test AD environment that mirrors your production environment as much as possible. If your AD environment handles a large number of objects and/or handles a large number of object deletions, you could see your AD database grow significantly. Test these scenarios so you can see if enabling the AD Recycle Bin is going to require memory or storage upgrades for your DC’s.
In addition to using the ADAC, you can also restore AD objects via the Recycle Bin with PowerShell or ldp.exe. Microsoft has an article on TechNet detailing both methods.
The AD Recycle Bin is not a replacement for backups or a disaster recovery strategy! You’ll still want to make sure that you’re performing regular backups of your AD environment. The AD Recycle Bin is typically only going to be helpful in those instances where items are accidentally deleted and need to be recovered with minimal effort.
Active Directory Recycle Bin in Windows Server 2012 — Part 1: Enable
- Managing shared mailboxes in Office 365 with PowerShell — Thu, May 5 2016
- Managing shared mailboxes in Office 365 with the GUI — Wed, May 4 2016
- Installing and configuring the Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit (EMET) — Wed, Mar 16 2016
The Active Directory Recycle Bin isn’t a new feature in Windows Server 2012, but it has gotten a much needed enhancement since it was first made available in Windows Server 2008 R2: a GUI interface. The Active Directory Recycle Bin allows you to restore recently deleted AD objects without having to perform an authoritative restore of your AD or a restore of tombstoned objects. The AD Recycle Bin also has the added bonus of retaining object group membership and attributes so that you don’t have to manually restore settings like you do with tombstoned objects.
Previously, objects in the AD Recycle Bin could only be accessed using PowerShell. In Windows Server 2012, you can now access deleted objects in the Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC) using a GUI. By default – even if you’re creating a new Forest or Domain – the AD Recycle Bin is disabled by default. Once you turn it on, you’re stuck with it. And, because this feature makes changes to how AD stores deleted objects, you’ll definitely want to test this with a copy of your production AD first so you can see how it affects replication and database for your environment.
To get started, you’ll need the following:
- At least one Domain Controller running Windows Server 2012 with the Active Directory Administrative Center enabled.
- All Domain Controllers (or servers running AD LDS) must be running Windows Server 2008 R2 or higher.
- The Forest must be running at Windows Server 2008 R2 functional level.
Forest Functional Level ^
First, let’s verify that our Forest is running at the correct Forest Functional Level. The quickest way to do this is with the PowerShell Cmdlet Get-ADForest. Run the command Get-ADForest yourdomain.local.
Forest Functional Level
As you can see in my PowerShell window, my Forest is running in the Windows 2008 mode and will need to be raised to at least the Windows Server 2008 R2 level. To do this, we’ll run the Set-ADForestMode Cmdlet. Run the command Set-ADForestMode -Identity yourdomain.local -ForestMode Windows2008R2Forest.
After confirming that you want the command to run, you’re done! If we re-run Get-ADForest yourdomain.local, we should be able to confirm that the Forest Functional Level is now at the minimum level to enable the AD Recycle Bin.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Forest Mode
Enable Active Directory Recycle Bin in Windows Server 2012 ^
Now that the Forest Functional Level is at the minimum level, we can enable the AD Recycle Bin. Once again, the quickest, easiest way to do this is with a PowerShell command. The command is:
Enable-ADOptionalFeature –Identity ‘CN=Recycle Bin Feature,CN=Optional Features,CN=Directory Service,CN=Windows NT,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=ad,DC=4sysops,DC=com’ –Scope ForestOrConfigurationSet –Target ‘ad.4sysops.com’
Confirm the action and the Active Directory Recycle Bin is enabled.
Enable Windows Server 2012 Active Directory Recycle Bin