- Windows server dhcp server log
- Постановка задачи
- Как найти историю аренды ip-адресов DHCP
- Где лежит лог dhcp сервера
- Troubleshoot problems on the DHCP server
- Troubleshooting checklist
- Event logs
- Data collection
- DHCP Server log
- Network trace
- 62.3. Windows DHCP server | Log Collection Solutions
- 62.3. Windows DHCP server
- 62.3.1. DHCP server audit logging
- 62.3.2. DHCP server logs in Windows Event Log
Windows server dhcp server log
Добрый день! Уважаемые читатели и гости одного из популярнейших IT блогов Pyatilistnik.org. В прошлый раз мы с вами разобрали тему по отключению защитника Windows 8.1. Сегодня мы разберем интересную тему по системному администрированию, а именно, как и где посмотреть историю аренды IP-адресов на сервере DHCP в Windows. Я расскажу вам сценарии, при которых эти знания окажутся для вас весьма полезными и необходимыми, да и вообще инженеры очень редко смотрят и изучают логи DHCP сервера.
Постановка задачи
И так у вас развернут DHCP сервер на Windows. В какой-то момент вам потребовалось выяснить, кем был зарезервирован IP-адрес, например несколько дней назад. Когда у вас время аренды большое, это сделать проще, если настроено резервирование, то это еще проще, но мы рассмотрим, что у вас время аренды, пусть будет сутки и резервирования нет. Благодаря моей инструкции вы сможете вычислить компьютер и mac-адрес устройства, кто получал нужный нам ip-адрес.
Как найти историю аренды ip-адресов DHCP
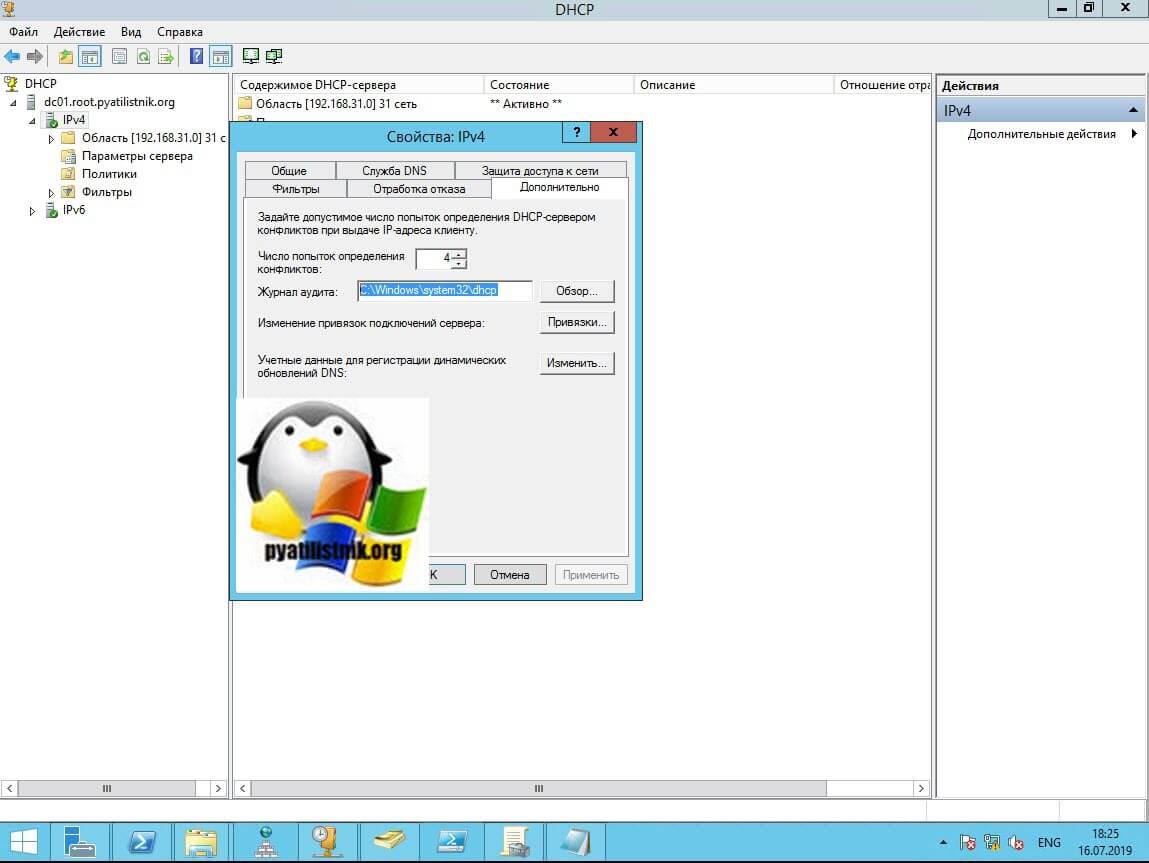
Откройте оснастку DHCP, и откройте свойства вашего пула IPV6 или IPV6. Убедитесь, что у вас включена функция «Вести журнал аудита DHCP«, если нет то включаем ее.
На вкладке «Дополнительно» вы можете посмотреть куда сохраняется журнал с событиями сервера. По умолчанию, это C:\Windows\system32\dhcp.
Переходим в каталог C:\Windows\system32\dhcp. Тут будут нужные нам файлы DhcpSrvLog.log. таких файлов будет 7, на каждый день недели.
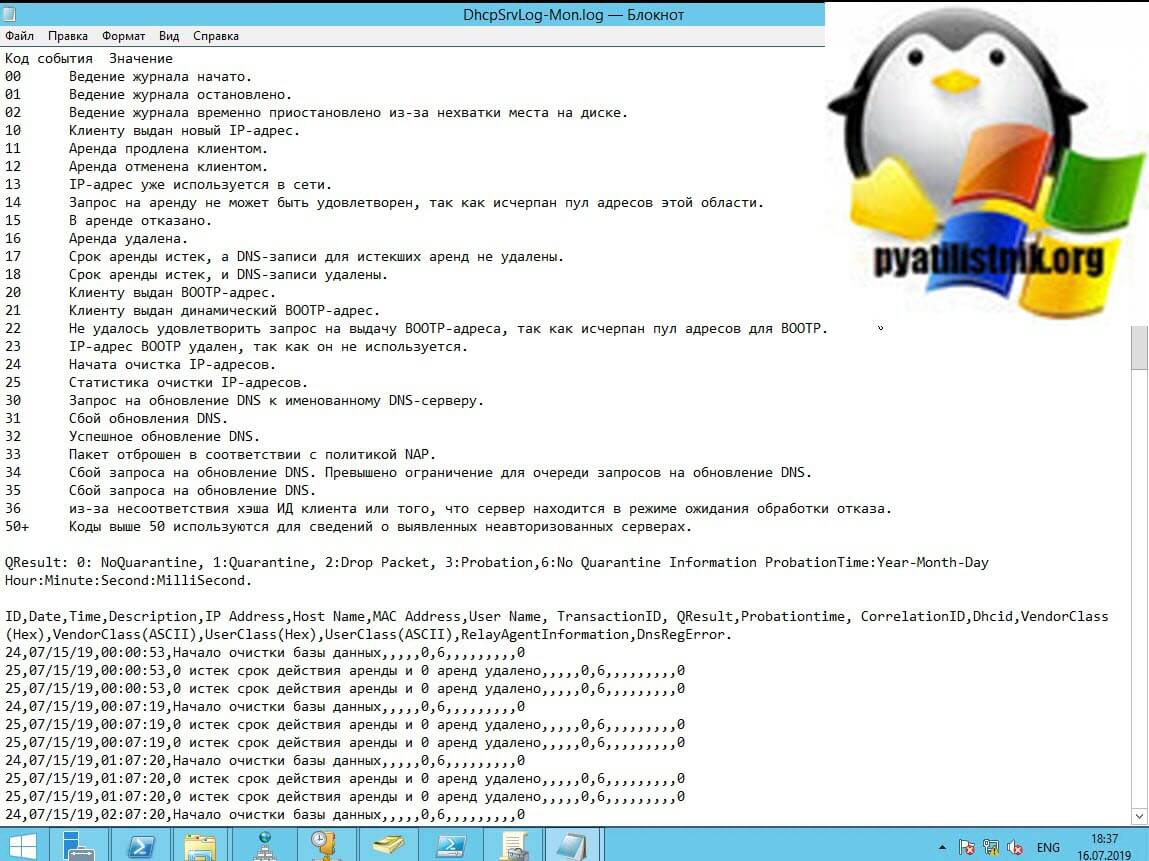
Открыв файл вам сразу выскочит подсказка по кодам событий:
- 00 Ведение журнала начато.
- 01 Ведение журнала остановлено.
- 02 Ведение журнала временно приостановлено из-за нехватки места на диске.
- 10 Клиенту выдан новый IP-адрес.
- 11 Аренда продлена клиентом.
- 12 Аренда отменена клиентом.
- 13 IP-адрес уже используется в сети.
- 14 Запрос на аренду не может быть удовлетворен, так как исчерпан пул адресов этой области.
- 15 В аренде отказано.
- 16 Аренда удалена.
- 17 Срок аренды истек, а DNS-записи для истекших аренд не удалены.
- 18 Срок аренды истек, и DNS-записи удалены.
- 20 Клиенту выдан BOOTP-адрес.
- 21 Клиенту выдан динамический BOOTP-адрес.
- 22 Не удалось удовлетворить запрос на выдачу BOOTP-адреса, так как исчерпан пул адресов для BOOTP.
- 23 IP-адрес BOOTP удален, так как он не используется.
- 24 Начата очистка IP-адресов.
- 25 Статистика очистки IP-адресов.
- 30 Запрос на обновление DNS к именованному DNS-серверу.
- 31 Сбой обновления DNS.
- 32 Успешное обновление DNS.
- 33 Пакет отброшен в соответствии с политикой NAP.
- 34 Сбой запроса на обновление DNS. Превышено ограничение для очереди запросов на обновление DNS.
- 35 Сбой запроса на обновление DNS.
- 36 из-за несоответствия хэша ИД клиента или того, что сервер находится в режиме ожидания обработки отказа.
- 50+ Коды выше 50 используются для сведений о выявленных неавторизованных серверах.
- 11000 Обращение DHCPv6.
- 11001 Объявление DHCPv6.
- 11002 Запрос DHCPv6.
- 11003 Подтверждение DHCPv6.
- 11004 Обновление DHCPv6.
- 11005 Повторная привязка DHCPv6.
- 11006 Отклонение DHCPv6.
- 11007 Освобождение DHCPv6.
- 11008 Запрос информации DHCPv6.
- 11009 Заполнение области DHCPv6.
- 11010 Запуск DHCPv6.
- 11011 Остановка DHCPv6.
- 11012 Приостановка журнала аудита DHCPv6.
- 11013 Файл журнала DHCPv6.
- 11014 Недопустимый DHCPv6-адрес.
- 11015 DHCPv6-адрес уже используется.
- 11016 DHCPv6-клиент удален.
- 11017 DNS-запись DHCPv6 не удалена.
- 11018 Срок действия DHCPv6 истек.
- 11019 Устаревшие и удаленные аренды DHCPv6.
- 11020 Начало очистки базы данных DHCPv6.
- 11021 Окончание очистки базы данных DHCPv6.
- 11022 Запрос обновления DNS для IPv6.
- 11023 Сбой обновления DNS для IPv6.
- 11024 Успешное обновление DNS для IPv6.
- 11028 Сбой запроса обновления DNS для IPv6. Превышен предел очереди запросов на обновление DNS.
- 11029 Сбой запроса обновления DNS для IPv6.
- 11030 Записи DHCPv6-клиента без отслеживания состояния очищены.
- 11031 Запись DHCPv6-клиента без отслеживания состояния очищена, так как для нее истек интервал очистки.
- 11032 Запрос информации DHCPV6 с IPv6-клиента без отслеживания состояния.
Вот для примера, как выглядит продление аренды адреса.
Где лежит лог dhcp сервера
  | Список форумов SYSAdmins.RU -> WINDOWS |
| Автор | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| frie21 Участник форума Зарегистрирован: 08.09.2008
|
| ||
| Вернуться к началу |
| ||
 | |||
| Зарегистрируйтесь и реклама исчезнет! | |||
 | |||
| SergeiS Активный участник Зарегистрирован: 07.04.2006 |
| ||
| Вернуться к началу |
| ||
 | |||
| frie21 Участник форума Зарегистрирован: 08.09.2008 Troubleshoot problems on the DHCP serverThis article discusses how to troubleshoot problems that occur on the DHCP server. Troubleshooting checklistCheck the following settings: The DHCP server service is started and running. To check this setting, run the net start command, and look for DHCP Server. Verify that IP address leases are available in the DHCP server scope for the subnet the DHCP client is on. To do this, see the statistic for the appropriate scope in the DHCP server management console. Check whether any BAD_ADDRESS listings can be found in Address Leases. Check whether any devices on the network have static IP addresses that have not been excluded from the DHCP scope. Verify that the IP address to which DHCP server is bound is within the subnet of the scopes from which IP addresses must be leased out. This is in case no relay agent is available. To do this, run the Get-DhcpServerv4Binding or Get-DhcpServerv6Binding cmdlet. Verify that only the DHCP server is listening on UDP port 67 and 68. No other process or other services (such as WDS or PXE) should occupy these ports. To do this, run the netstat -anb command. Verify that the DHCP server IPsec exemption is added if you are dealing with an IPsec-deployed environment. Verify that the relay agent IP address can be pinged from the DHCP server. Enumerate and check configured DHCP policies and filters. Event logsCheck the System and DHCP Server service event logs (Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > DHCP-Server) for reported issues that are related to the observed problem. Depending on the kind of issue, an event is logged to one of the following event channels: DHCP Server Operational Events DHCP Server Administrative Events DHCP Server System Events DHCP Server Filter Notification Events DHCP Server Audit Events Data collectionDHCP Server logThe DHCP Server service debug logs provide more information about the IP address lease assignment and the DNS dynamic updates that are done by the DHCP server. These logs by default are located in %windir%\System32\Dhcp. For more information, see Analyze DHCP Server Log Files. Network traceA correlating network trace may indicate what the DHCP server was doing at the time that the event was logged. To create such a trace, follow these steps: Go to GitHub, and download the tss_tools.zip file. Copy the Tss_tools.zip file, and expand it to a location on the local disk, such as to the C:\tools folder. Run the following command from C:\tools in an elevated Command Prompt window: 62.3. Windows DHCP server | Log Collection Solutions62.3. Windows DHCP serverDHCP Server events are written to DHCP audit log files (if configured) and to the Windows Event Log. This section provides details about configuring logging and collecting logs with NXLog. | The following sections have been tested on Windows Server 2016. | ||
62.3.1. DHCP server audit logging
The Windows DHCP Server provides an audit logging feature that writes server activity to log files. NXLog can be configured to read and parse these logs.
The log files are named DhcpSrvLog- .log for IPv4 and DhcpV6SrvLog- .log for IPv6. For example, Thursday’s log files are DhcpSrvLog-Thu.log and DhcpV6SrvLog-Thu.log .
The DHCP audit log can be configured with PowerShell or the DHCP Management MMC snap-in.
62.3.1.1. Configuring via PowerShell
To view the current DHCP audit log configuration, run the following command (see Get-DhcpServerAuditLog on Microsoft Docs).
To set the audit log configuration, run this command (see Set-DhcpServerAuditLog on Microsoft Docs).
The DHCP server must be restarted for the configuration changes to take effect.
62.3.1.2. Configuring with the DHCP Management Console
Follow these steps to configure the DHCP audit log. Any changes to the audit log settings apply to both IPv4 and IPv6, once the DHCP server has been restarted.
Run the DHCP MMC snap-in ( dhcpmgmt.msc ), expand the server for which to configure logging, and click on IPv4.
Right-click on IPv4 and click Properties. Note that the context menu is not fully populated until after the IPv4 menu has been expanded at least once.
Make sure Enable DHCP audit logging is checked.
Open the Advanced tab, change the Audit log file path, and click OK.
Restart the DHCP server by right-clicking the server and clicking All Tasks › Restart .
62.3.1.3. Collecting DHCP server audit logs
The DHCP audit logs are stored in CSV format with a large free-form header containing a list of event ID descriptions and other details.
This configuration uses a short batch/PowerShell polyglot script with the include_stdout directive to fetch the DHCP audit log location. The im_file module reads from the files and the xm_csv module parses the lines into fields. Any line that does not match the /^\d+,/ regular expression is discarded with the drop() procedure (all the header lines are dropped). The event ID and QResult codes are resolved automatically, with corresponding $Message and $QMessage fields added where applicable.
62.3.2. DHCP server logs in Windows Event Log
Events are also written to three logs in the Windows Event Log. To make sure the required logs are enabled, open Event Viewer ( eventvwr ) and check the logs under Applications and Services Logs › Microsoft › Windows › DHCP-Server . To enable a log, right-click on it and click Enable Log.
Alternatively, the following PowerShell script will check all three logs, enabling if necessary.
This configuration uses the im_msvistalog module to collect DHCP Server events from the Windows Event Log DhcpAdminEvents , FilterNotifications , and Operational logs.