- Установка и настройка удалённых приложений RemoteApp в Windows Server 2016
- Оглавление
- Что такое служба удалённых приложений RemoteApp?
- Установка ролей и служб RemoteApp
- Настройка коллекции и добавление удалённых приложений
- Натсройка подключения к RemoteApp приложению
- Supported configurations for Remote Desktop Services
- Best practices
- RD Connection Brokers
- Support for graphics processing unit (GPU) acceleration
- Remote Desktop Session Host support for GPUs
- VDI support for GPUs
- RemoteFX 3D Video Adapter (vGPU) support
- Discrete Device Assignment support
- VDI deployment – supported guest OSes
- Single sign-on
- Using Remote Desktop Services with application proxy services
- RDP-ссылка на RemoteApp в Windows Server 2012 R2
Установка и настройка удалённых приложений RemoteApp в Windows Server 2016
Оглавление
Что такое служба удалённых приложений RemoteApp?
RemoteApp — это часть роли служб терминального сервера Windows Server 2016 и эта служба даёт доступ к приложениям, работающих на терминальном сервере, таким образом, что как будто вы их запускаете у себя на локальном компьютере. Служба терминального сервера, которая берёт на себя все вычислительные ресурсы приложения, а пользователю отправляет только результат. Ещё и называют удалённым приложением RemoteApp.
Установка ролей и служб RemoteApp
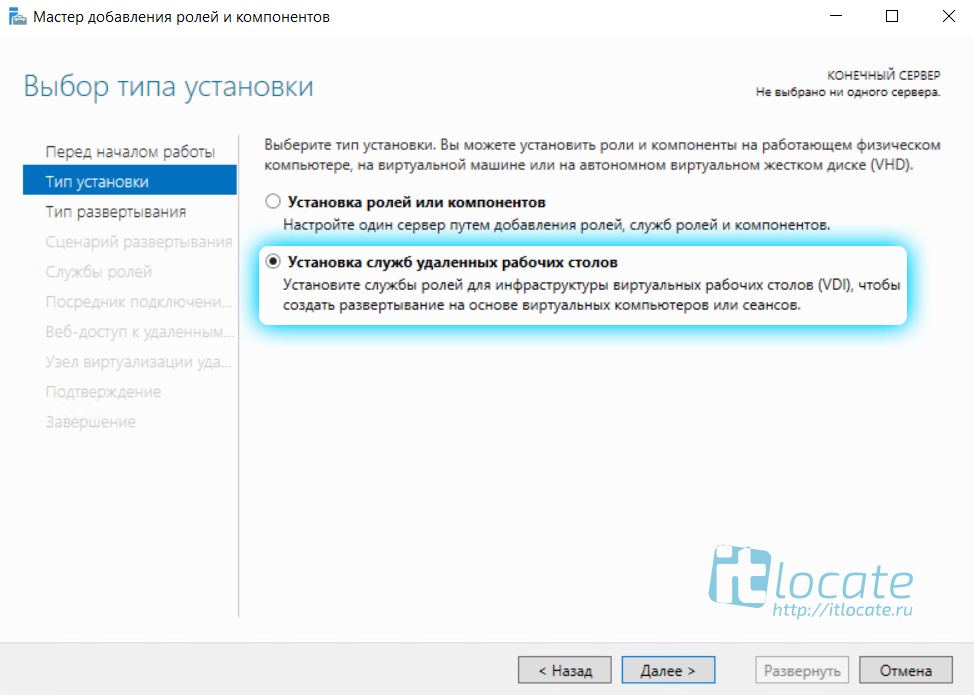
Для установки RemoteApp запускаем Мастер добавления ролей и компонентов и выбираем Тип установки Установка служб удалённых рабочих столов как на скриншоте ниже
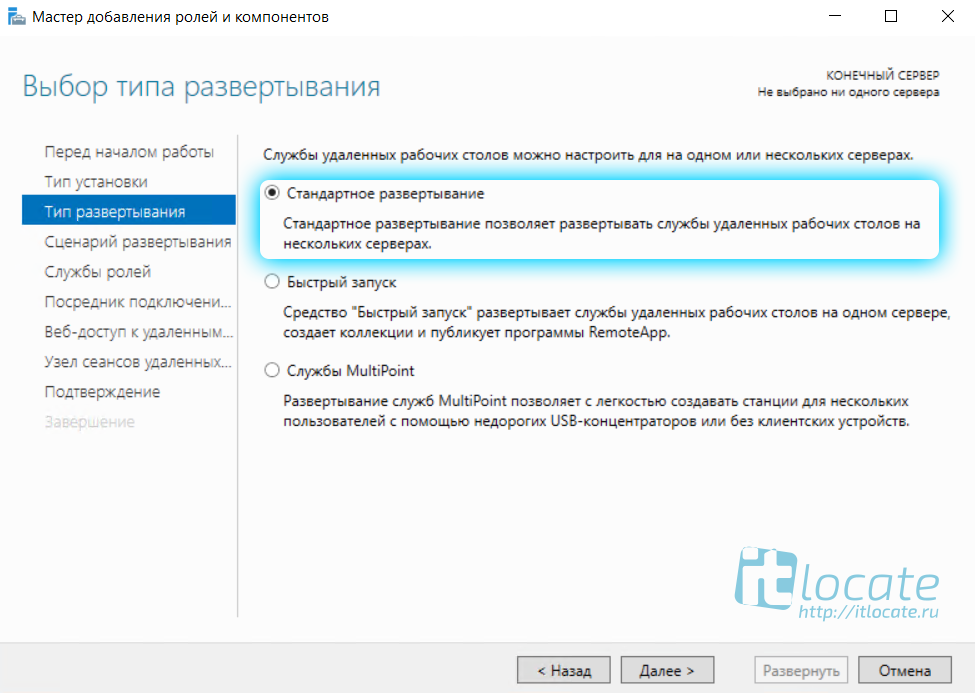
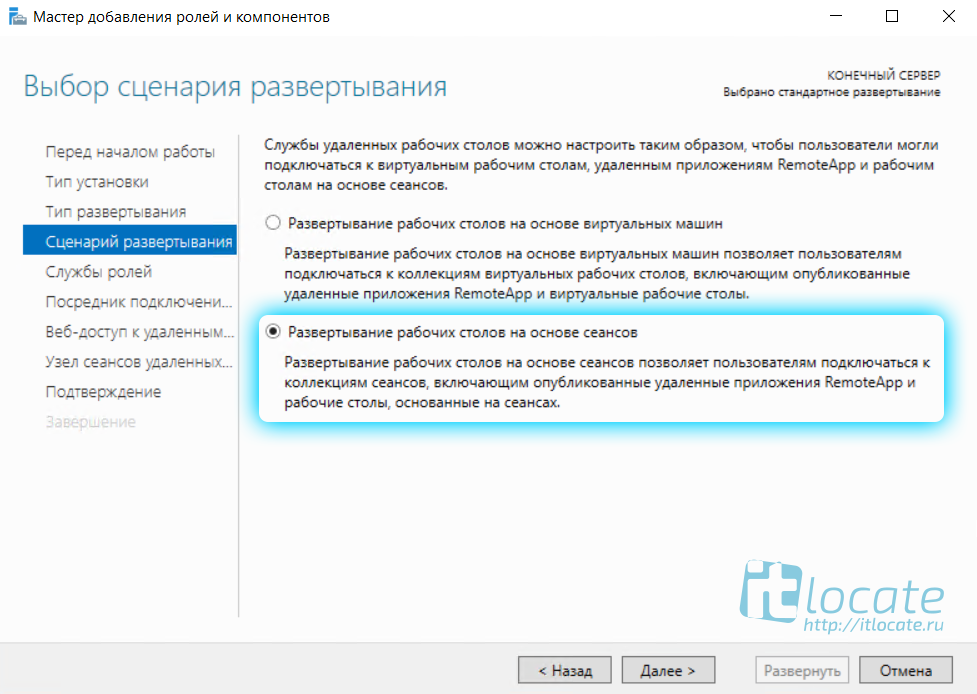
Далее выбираем Стандартное обёртывание xD. И после выбираем Развёртывание рабочих столов на основе сеансов.
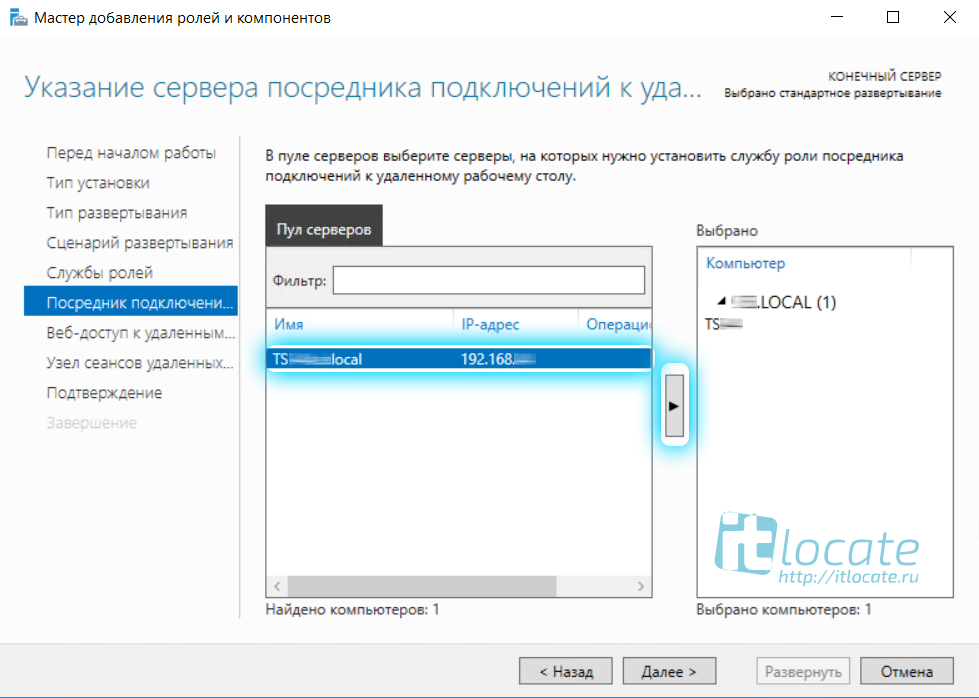
На пункте Посредник подключения выбираем наш сервер из пула серверов и добавляем его в правое поле.
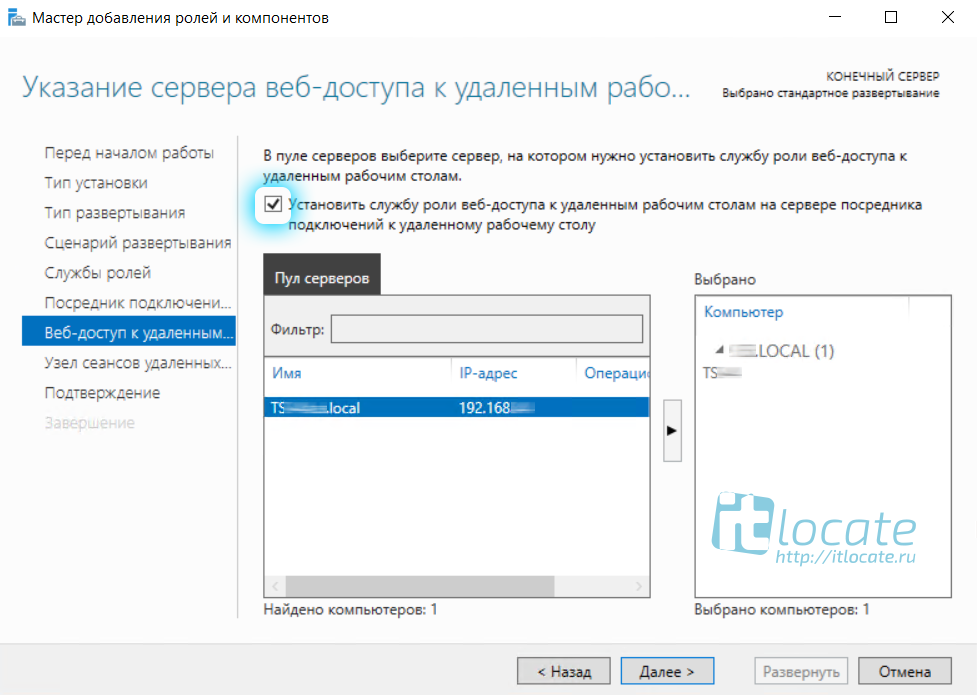
На следующем пункте, обратите внимание, необходимо отметить чекбксом Установить службу роли веб-доступа к удалённым рабочим столам на сервере посредника подключений к удалённому рабочему столу
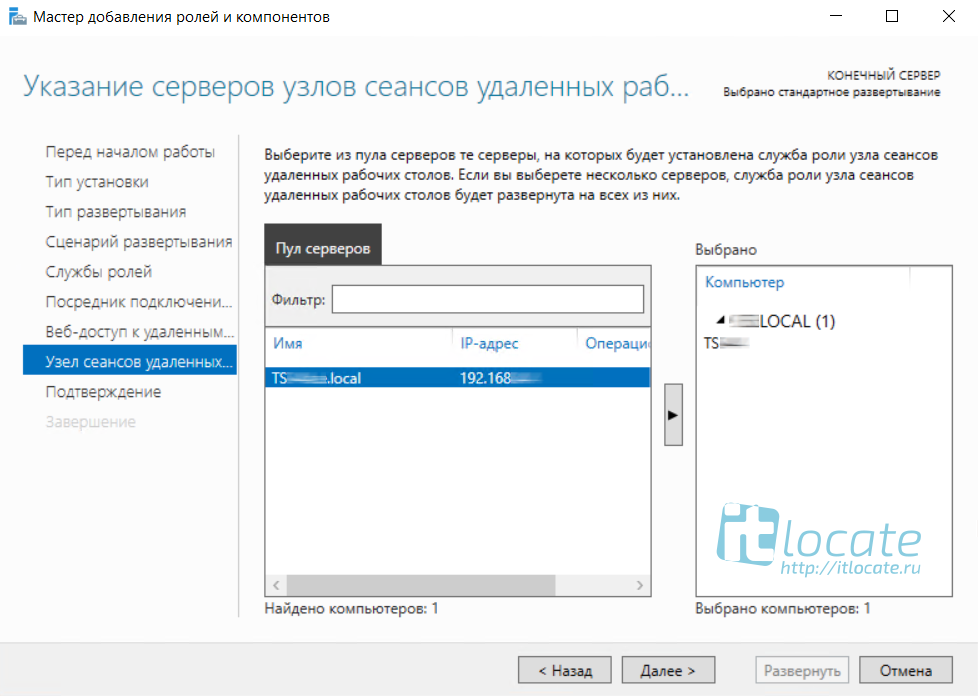
Так же выбираем наш сервер из пула серверов и прожимаем Далее / Развернуть
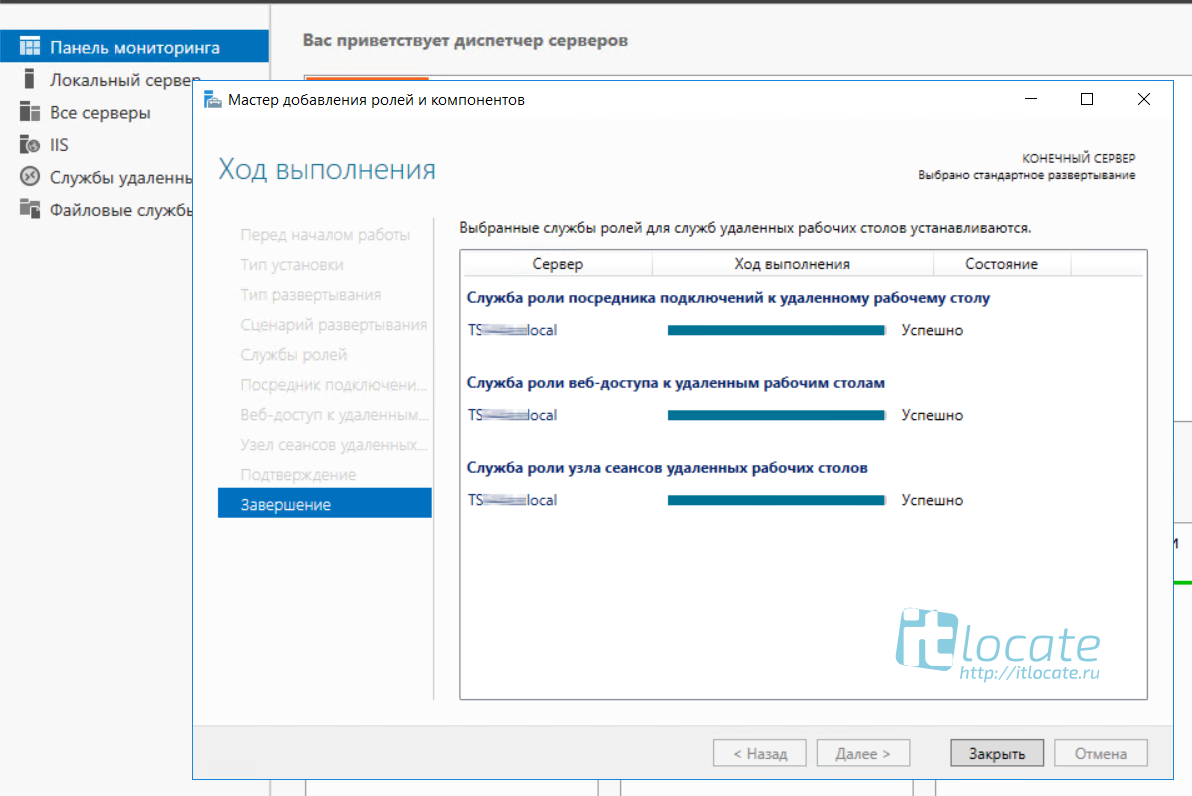
Процесс развёртывания будет отображаться на экране, а по окончанию мы с вами выходим из мастера по нажатию кнопки Закрыть
Настройка коллекции и добавление удалённых приложений
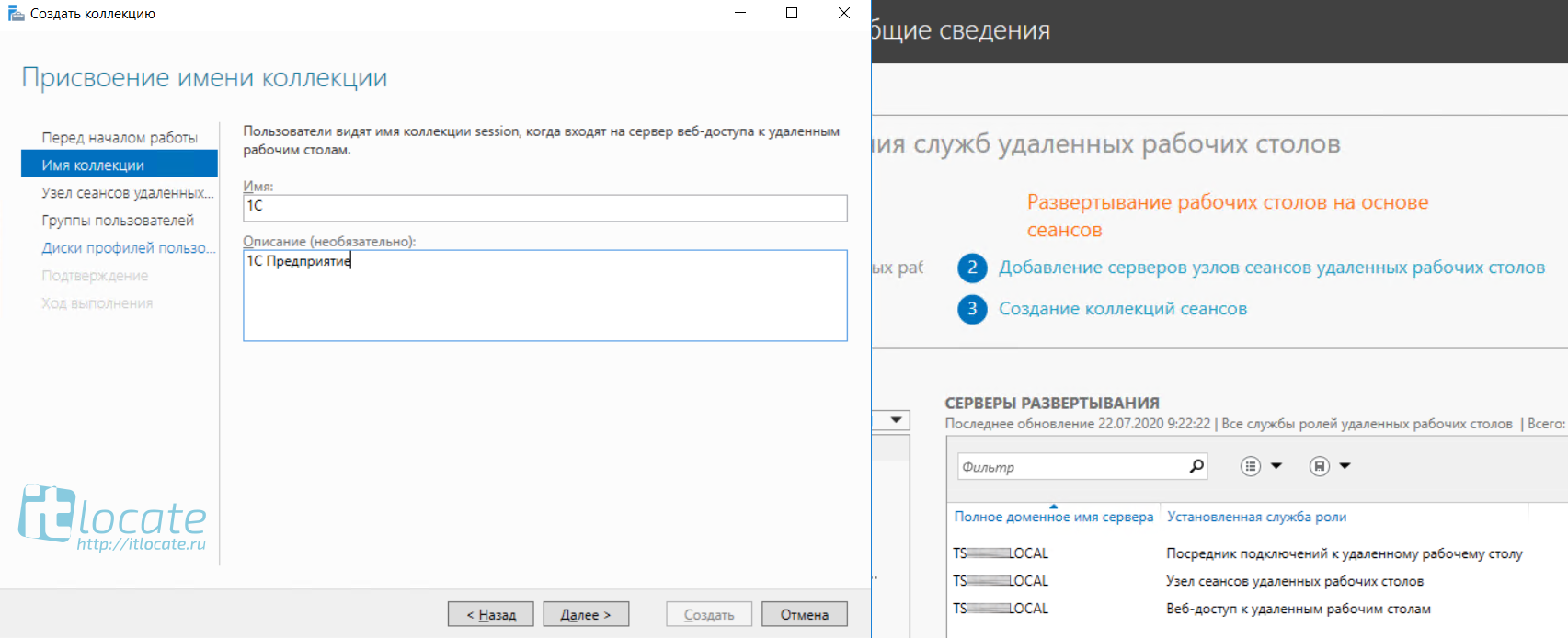
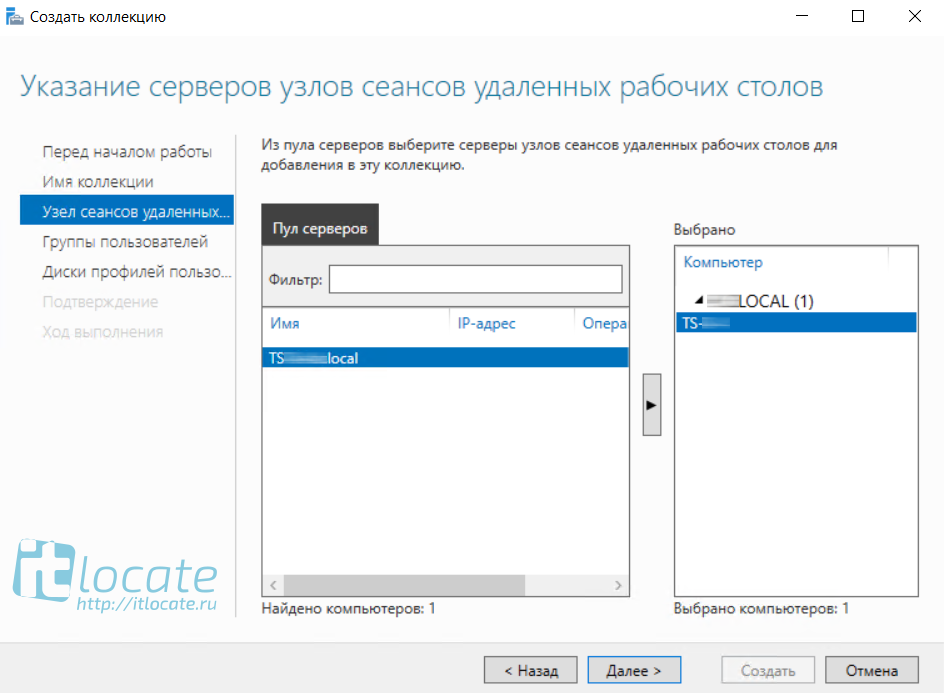
Далее в Диспетчере серверов переходим в Службы удалённых рабочих столов и добавляем коллекцию, присваиваем имя и заполняем описание. Далее
Выбираем сервер из пула. Далее
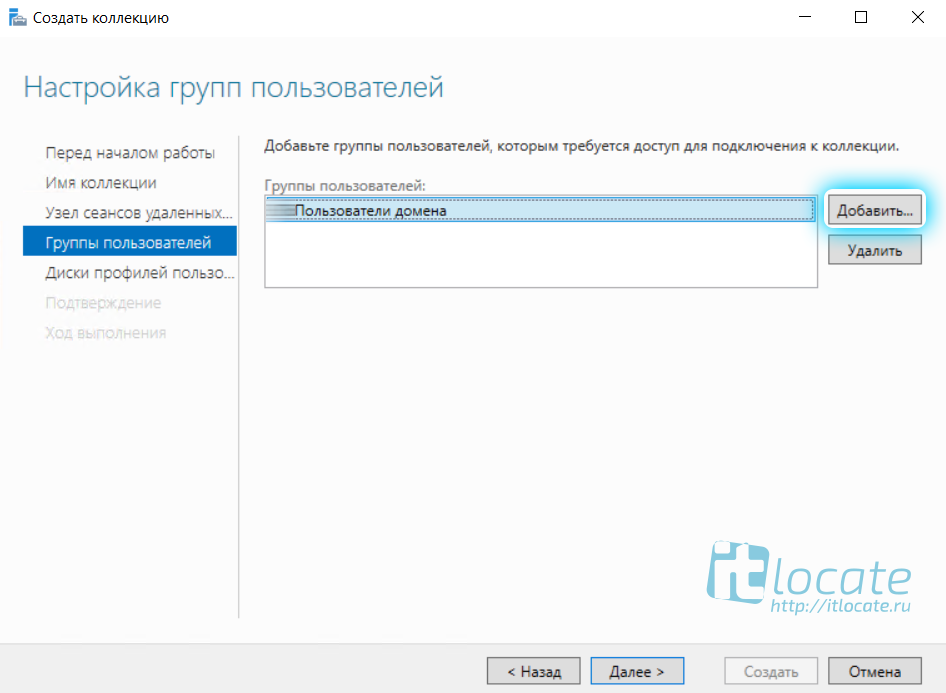
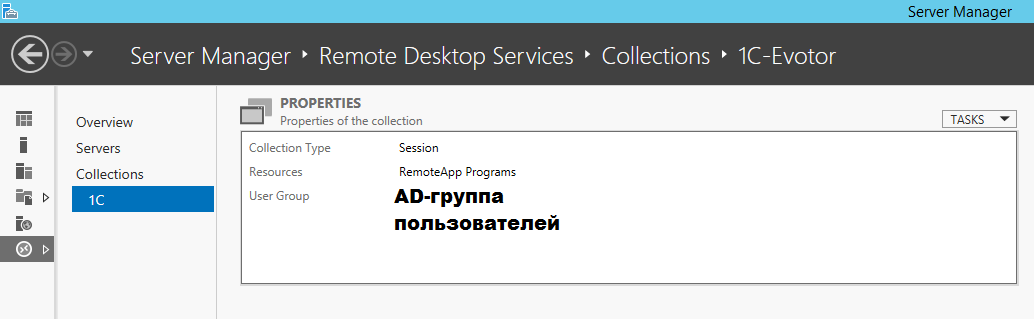
На данном шаге нам необходимо Добавить Группы пользователей, которые будут иметь доступ к данному приложению remoteapp.
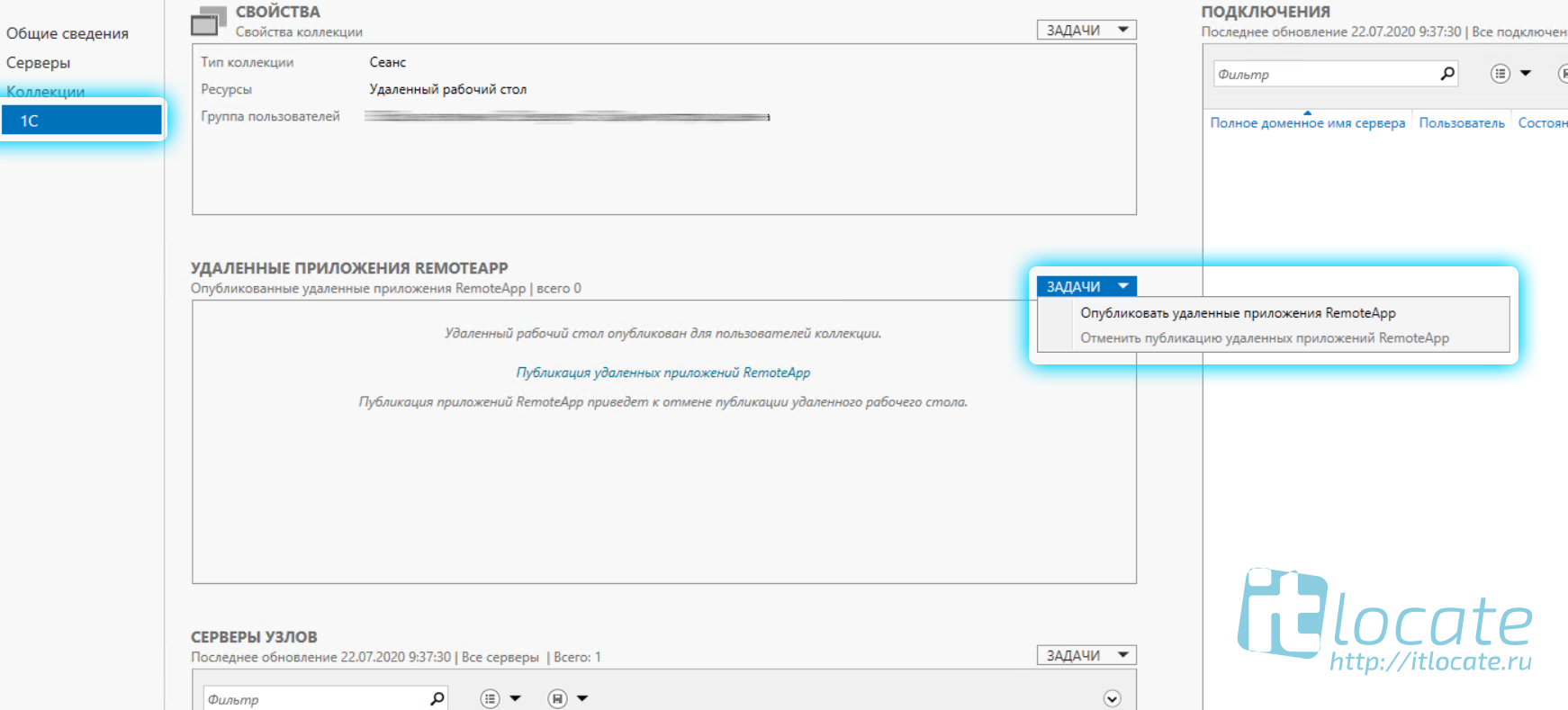
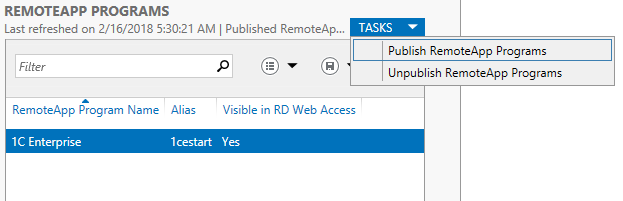
Теперь переходим к завершению настройки удалённого приложения remoteapp, нам нужно зайти в только что созданную нами коллекцию и через Задачи выбрать из выпадающего меню выбрать пункт Опубликовать удалённые приложения RemoteApp
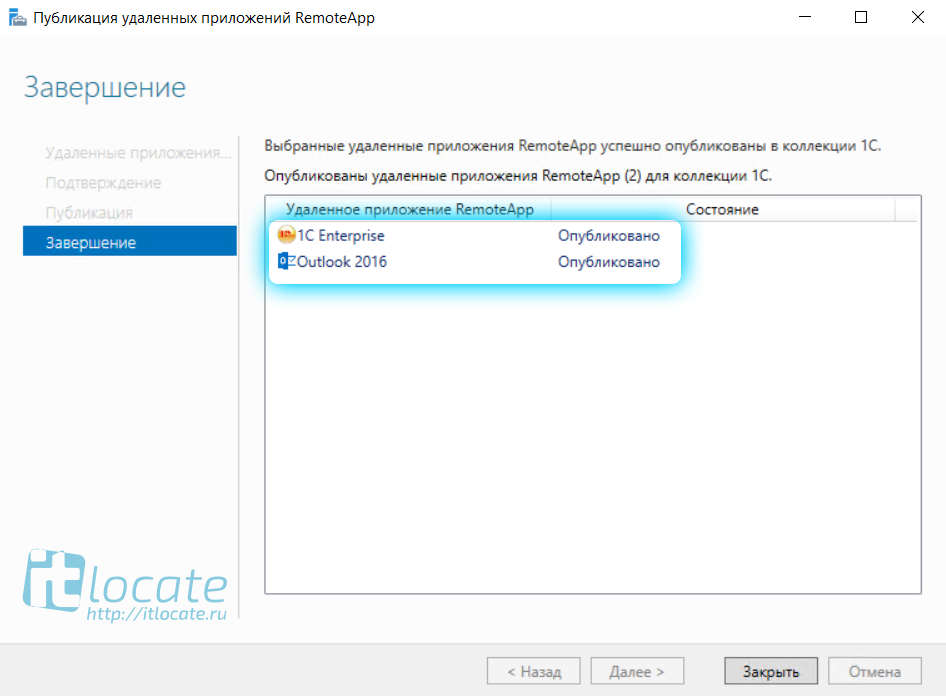
Добавляем нужные нам приложения и финализируем Закрыть
Натсройка подключения к RemoteApp приложению
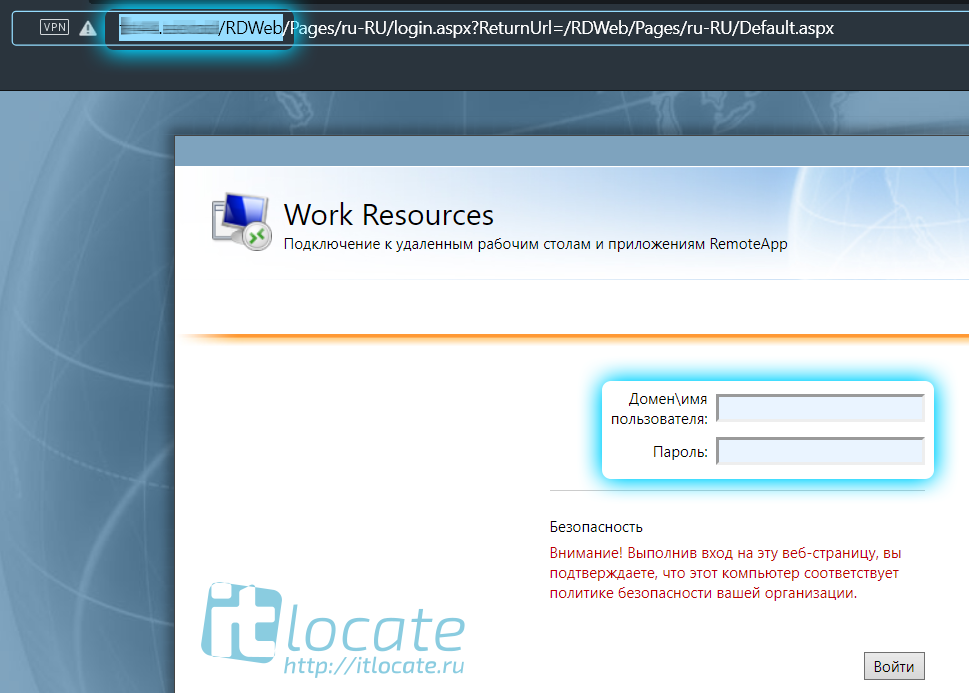
Тут всё ещё проще! Переходим по ссылке http://IP_ADDRES/RDWeb, где указываем имя или ip адрес вашего сервера, логинимся под вашей учётной записью.
Открывается меню Удалённые приложения RemoteApp и рабочие столы, где нам буду доступны только те приложения к которым у нас есть доступ (настраивали ранее). Нажимая на значок приложения начнётся процесс скачивания. После того как вы запустите его вам будет предложено авторизоваться, а уже после чего перед вами откроется уже само приложение 1С RemoteApp или Outlook 2016 RemoteApp.
Приложение RemoteApp будет помечено соответствующим значком
Вот и всё, друзья! Надеюсь я вам смог помочь) Всем спасибо!
Supported configurations for Remote Desktop Services
Applies To: Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019
When it comes to supported configurations for Remote Desktop Services environments, the largest concern tends to be version interoperability. Most environments include multiple versions of Windows Server — for example, you may have an existing Windows Server 2012 R2 RDS deployment but want to upgrade to Windows Server 2016 to take advantage of the new features (like support for OpenGL\OpenCL, Discrete Device Assignment, or Storage Spaces Direct). The question then becomes, which RDS components can work with different versions and which need to be the same?
So with that in mind, here are basic guidelines for supported configurations of Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server.
Best practices
Use Windows Server 2019 for your Remote Desktop infrastructure (the Web Access, Gateway, Connection Broker, and license server). Windows Server 2019 is backward-compatible with these components, which means a Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2012 R2 RD Session Host can connect to a 2019 RD Connection Broker, but not the other way around.
For RD Session Hosts — all Session Hosts in a collection need to be at the same level, but you can have multiple collections. You can have a collection with Windows Server 2016 Session Hosts and one with Windows Server 2019 Session Hosts.
If you upgrade your RD Session Host to Windows Server 2019, also upgrade the license server. Remember that a 2019 license server can process CALs from all previous versions of Windows Server, down to Windows Server 2003.
If you are creating a highly available environment, all of your Connection Brokers need to be at the same OS level.
RD Connection Brokers
Windows Server 2016 removes the restriction for the number of Connection Brokers you can have in a deployment when using Remote Desktop Session Hosts (RDSH) and Remote Desktop Virtualization Hosts (RDVH) that also run Windows Server 2016. The following table shows which versions of RDS components work with the 2016 and 2012 R2 versions of the Connection Broker in a highly available deployment with three or more Connection Brokers.
| 3+ Connection Brokers in HA | RDSH or RDVH 2019 | RDSH or RDVH 2016 | RDSH or RDVH 2012 R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2019 Connection Broker | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Windows Server 2016 Connection Broker | N/A | Supported | Supported |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Connection Broker | N/A | N/A | Not Supported |
Support for graphics processing unit (GPU) acceleration
Remote Desktop Services support systems equipped with GPUs. Applications that require a GPU can be used over the remote connection. Additionally, GPU-accelerated rendering and encoding can be enabled for improved app performance and scalability.
Remote Desktop Services Session Hosts and single-session client operating systems can take advantage of the physical or virtual GPUs presented to the operating system in many ways, including the Azure GPU optimized virtual machine sizes, GPUs available to the physical RDSH server, and GPUs presented to the VMs by supported hypervisors.
GPU vendors may have a separate licensing scheme for RDSH scenarios or restrict GPU use on the server OS, verify the requirements with your favorite vendor.
GPUs presented by a non-Microsoft hypervisor or Cloud Platform must have drivers digitally-signed by WHQL and supplied by the GPU vendor.
Remote Desktop Session Host support for GPUs
The following table shows the scenarios supported by different versions of RDSH hosts.
| Feature | Windows Server 2008 R2 | Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows Server 2016 | Windows Server 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use of hardware GPU for all RDP sessions | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| H.264/AVC hardware encoding (if suppported by the GPU) | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Load balancing between multiple GPUs presented to the OS | No | No | No | Yes |
| H.264/AVC encoding optimizations for minimizing bandwidth usage | No | No | No | Yes |
| H.264/AVC support for 4K resolution | No | No | No | Yes |
VDI support for GPUs
The following table shows support for GPU scenarios in the client OS.
| Feature | Windows 7 SP1 | Windows 8.1 | Windows 10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use of hardware GPU for all RDP sessions | No | Yes | Yes |
| H.264/AVC hardware encoding (if suppported by the GPU) | No | No | Windows 10 1703 and later |
| Load balancing between multiple GPUs presented to the OS | No | No | Windows 10 1803 and later |
| H.264/AVC encoding optimizations for minimizing bandwidth usage | No | No | Windows 10 1803 and later |
| H.264/AVC support for 4K resolution | No | No | Windows 10 1803 and later |
RemoteFX 3D Video Adapter (vGPU) support
Because of security concerns, RemoteFX vGPU is disabled by default on all versions of Windows starting with the July 14, 2020 Security Update and removed starting with the April 13, 2021 Security Update. To learn more, see KB 4570006.
Remote Desktop Services supports RemoteFX vGPUs when VM is running as a Hyper-V guest on Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016. The following guest operating systems have RemoteFX vGPU support:
- Windows 7 SP1
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 10 1703 or later
- Windows Server 2016 in a single-session deployment only
Discrete Device Assignment support
Remote Desktop Services supports Physical GPUs presented with Discrete Device Assignment from Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V hosts. See Plan for deploying Discrete Device Assignment for more details.
VDI deployment – supported guest OSes
Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019 RD Virtualization Host servers support the following guest OSes:
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 8.1 Enterprise
- Windows 7 SP1 Enterprise
- Remote Desktop Services doesn’t support heterogeneous session collections. The OSes of all VMs in a collection must be the same version.
- You can have separate homogeneous collections with different guest OS versions on the same host.
- The Hyper-V host used to run VMs must be the same version as the Hyper-V host used to create the original VM templates.
Single sign-on
Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019 RDS supports two main SSO experiences:
- In-app (Remote Desktop application on Windows, iOS, Android, and Mac)
- Web SSO
Using the Remote Desktop application, you can store credentials either as part of the connection info (Mac) or as part of managed accounts (iOS, Android, Windows) securely through the mechanisms unique to each OS.
To connect to desktops and RemoteApps with SSO through the inbox Remote Desktop Connection client on Windows, you must connect to the RD Web page through Internet Explorer. The following configuration options are required on the server side. No other configurations are supported for Web SSO:
- RD Web set to Forms-Based Authentication (Default)
- RD Gateway set to Password Authentication (Default)
- RDS Deployment set to «Use RD Gateway credentials for remote computers» (Default) in the RD Gateway properties
Due to the required configuration options, Web SSO is not supported with smartcards. Users who login via smartcards might face multiple prompts to login.
For more information about creating VDI deployment of Remote Desktop Services, check out Supported Windows 10 security configurations for Remote Desktop Services VDI.
Using Remote Desktop Services with application proxy services
You can use Remote Desktop Services with Azure AD Application Proxy. Remote Desktop Services does not support using Web Application Proxy, which is included in Windows Server 2016 and earlier versions.
RDP-ссылка на RemoteApp в Windows Server 2012 R2
Говорят, что в Windows Server 2012 выпилили функционал по созданию rdp ярлыков на удалённые приложения. Но это не совсем так. Расскажу как сделать rdp ярлык без особых проблем.
Устанавливаете приложение на сервер. Убедитесь, что входите в группу пользователей, которым доступны удалённые приложения.
Публикуете приложение как RemoteApp.
Если вы знаете ссылку к web-интерфейсу RemoteApp вашего терминального сервера, то хорошо, если не знаете, то запускаете оснастку IIS на терминальном сервере:
В Default Web Site находите приложение RDWeb.
Справа нажимаете Browse *:443.
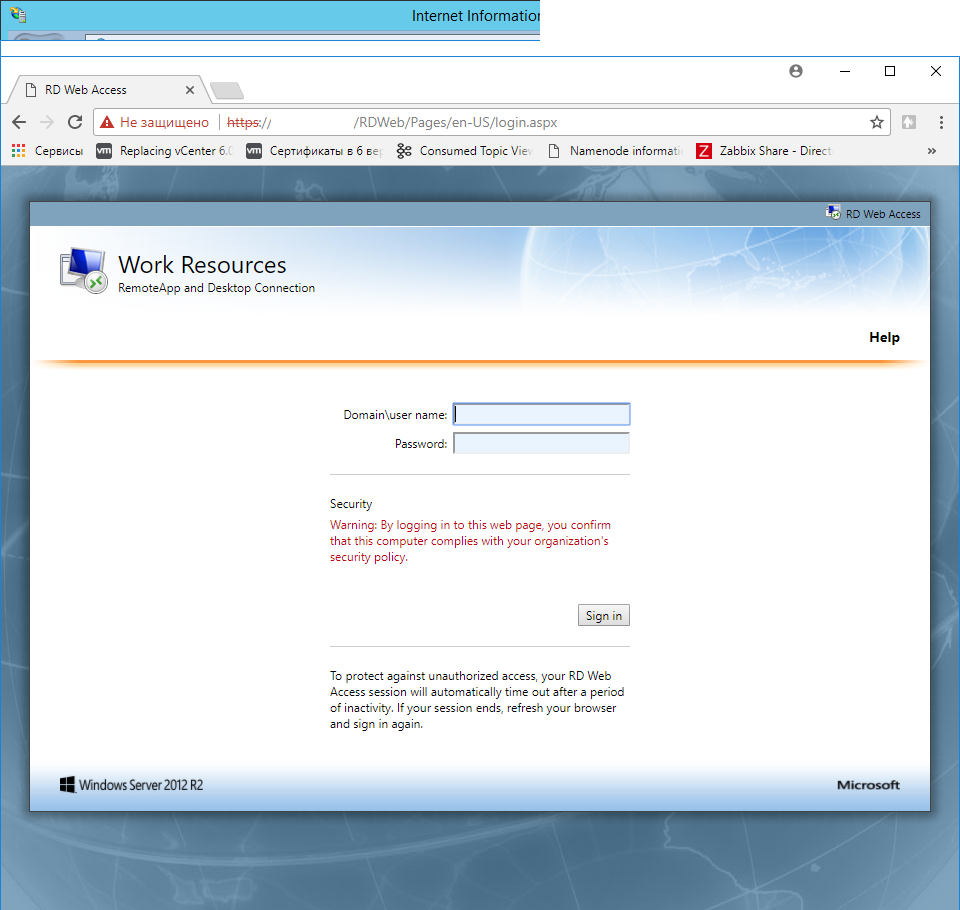
Откроется ссылка вида:
Теперь вы можете открыть эту ссылку в своем браузере (не IE!) Google Chrome, заменив localhost на адрес сервера.
Выполняете вход под доменной учёткой.
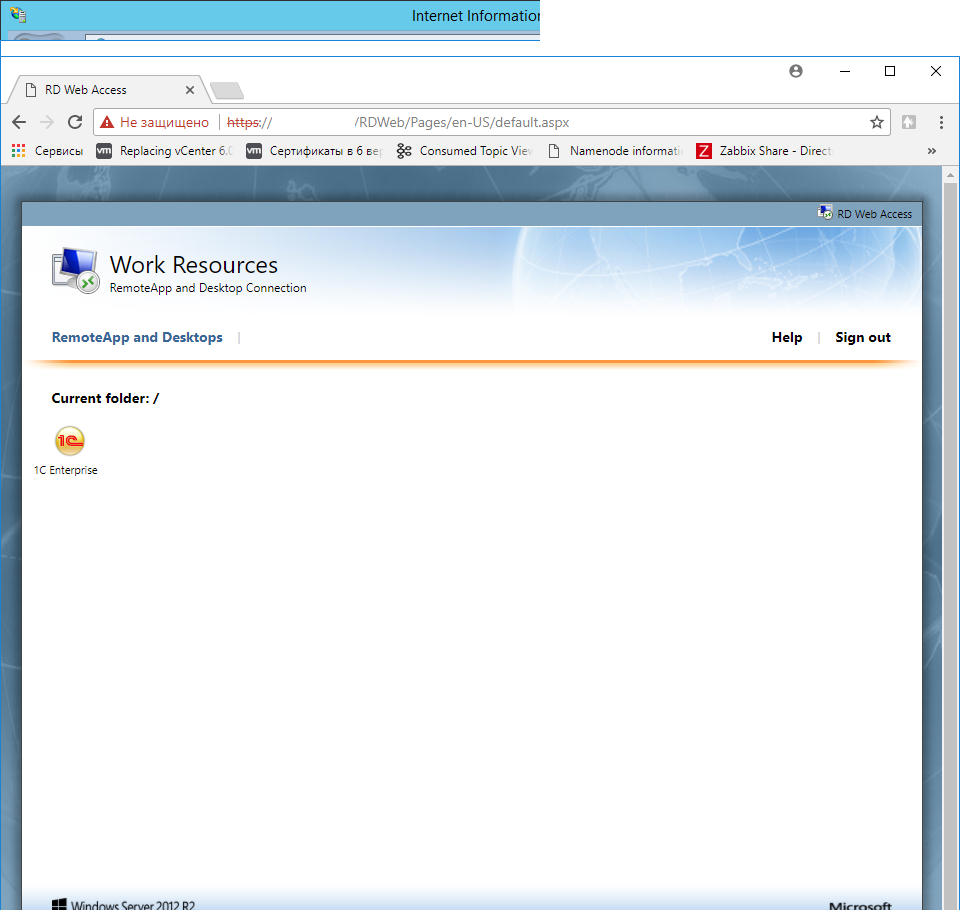
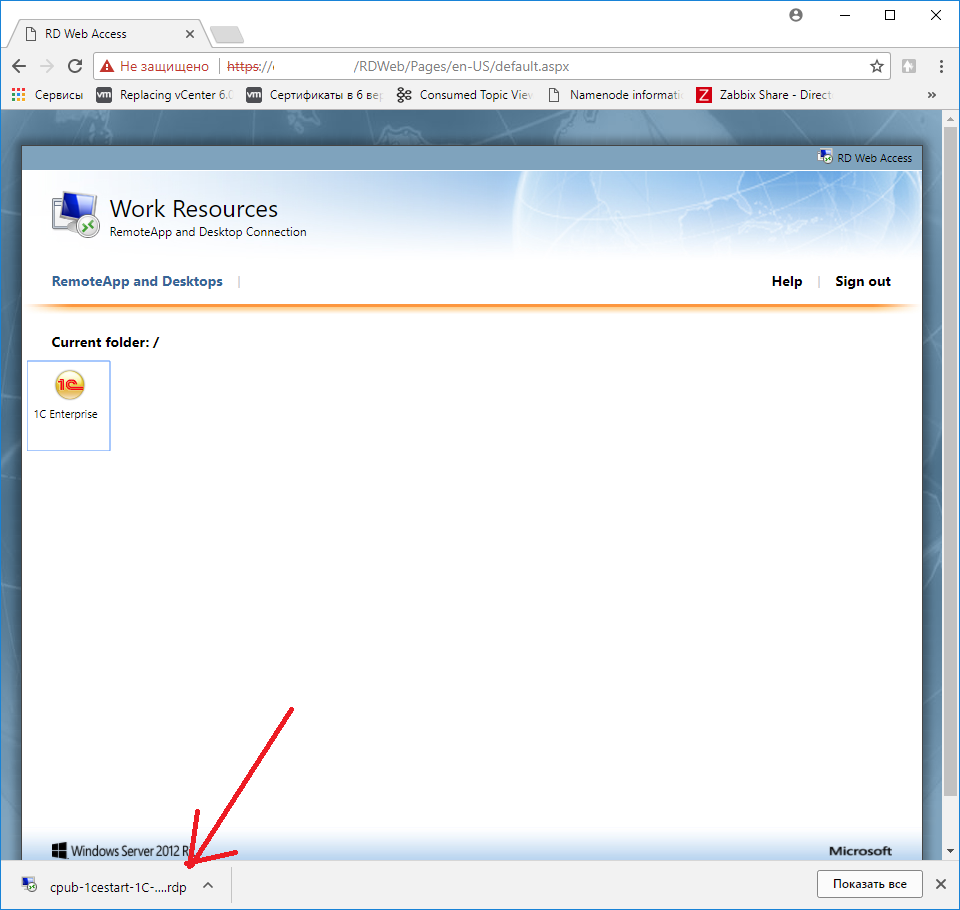
Кликаете на нужное приложение. и получаете требуемый rdp файлик.
Теперь этот файлик можно красиво переименовать и рассылать своим пользователям.