- Overview of Windows Server upgrades
- Which version of Windows Server should I upgrade to?
- Windows Server release information
- Windows Server current versions by servicing option
- Информация о выпуске Windows Server Windows Server release information
- Текущие версии Windows Server по варианту обслуживания Windows Server current versions by servicing option
- Windows 10 update history
- Updates for Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows Server, version 20H2
- What’s new for Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows 10, version 2004 release notes
- Current status of Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows Server, version 20H2
- Known issues
- Notes and messages
- General
- Troubleshooting
Overview of Windows Server upgrades
The process of upgrading to a newer version of Windows Server can vary greatly, depending on which operating system you are starting with and the pathway you take. We use the following terms to distinguish between different actions, any of which could be involved in a new Windows Server deployment.
Upgrade. Also known as an «in-place upgrade». You move from an older version of the operating system to a newer version, while staying on the same physical hardware. This is the method we will be covering in this section.
In-place upgrades might also be supported by public or private cloud companies; however, you must check with your cloud provider for the details. Additionally, you’ll be unable to perform an in-place upgrade on any Windows Server configured to Boot from VHD. An In-Place Upgrade from Windows Storage Server Editions to Windows Server 2019 is not supported. You can perform either a Migration or Installation instead.
Installation. Also known as a «clean installation». You move from an older version of the operating system to a newer version, deleting the older operating system.
Migration. You move from an older version of the operating system to a newer version of the operating system, by transferring to a different set of hardware or virtual machine.
Cluster OS Rolling Upgrade. You upgrade the operating system of your cluster nodes without stopping the Hyper-V or the Scale-Out File Server workloads. This feature allows you to avoid downtime which could impact Service Level Agreements. For more information, see Cluster operating system rolling upgrade
License conversion. Convert a particular edition of the release to another edition of the same release in a single step with a simple command and the appropriate license key. We call this «license conversion». For example, if your server is running Windows Server 2016 Standard, you can convert it to Windows Server 2016 Datacenter.
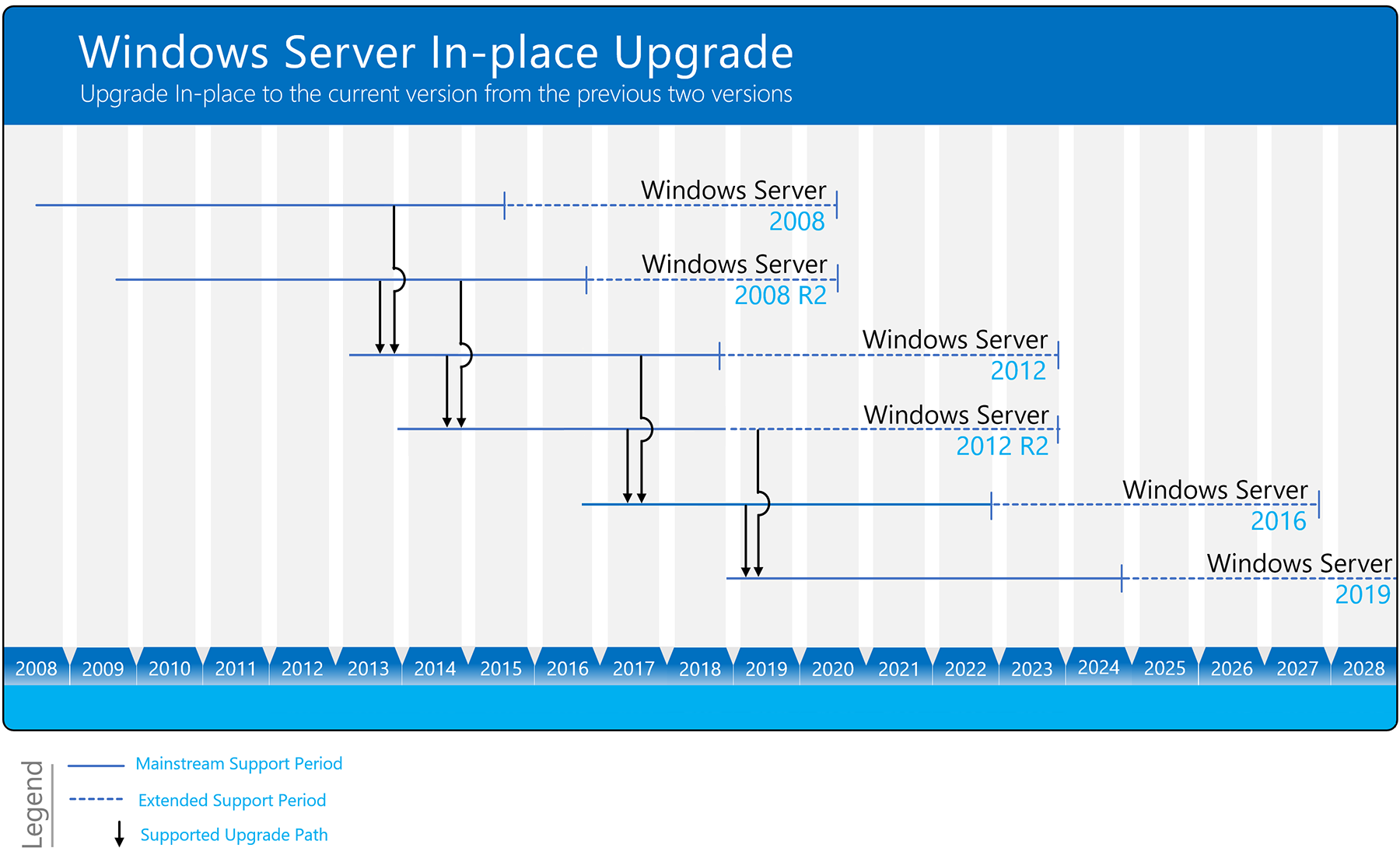
Which version of Windows Server should I upgrade to?
We recommend upgrading to the latest version of Windows Server: Windows Server 2019. Running the latest version of Windows Server allows you to use the latest features – including the latest security features – and delivers the best performance.
However, we realize that’s not always possible. You can use the following diagram to figure out which Windows Server version you can upgrade to, based on the version you’re currently on:
Windows Server can typically be upgraded through at least one, and sometimes even two, versions. For example, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016 can both be upgraded in-place to Windows Server 2019.
You can also upgrade from an evaluation version of the operating system to a retail version, from an older retail version to a newer version, or, in some cases, from a volume-licensed edition of the operating system to an ordinary retail edition. For more information about upgrade options other than in-place upgrade, see Upgrade and conversion options for Windows Server.
Windows Server release information
Microsoft has updated its servicing model. The Semi-Annual Channel is a twice-per-year feature update release with 18-month servicing timelines for each release. This page is designed to help you determine the end of support date for the Semi-Annual Channel releases.
The Semi-Annual Channel provides opportunity for customers who are innovating quickly to take advantage of new operating system capabilities at a faster pace, both in applications — particularly those built on containers and microservices. For more information see the Comparison of servicing channels. Customers also have the option to continue using the Long-Term Servicing Channel releases, which continue to be released every 2-3 years. Each Long-Term Servicing Channel release is supported for 5 years of mainstream support and 5 years of extended support.
Windows Server current versions by servicing option
| Windows Server release | Version | OS Build | Availability | Mainstream support end date | Extended support end date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server, version 20H2 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 20H2 | 19042.508.200927-1902 | 10/20/2020 | 05/10/2022 | Review note |
| Windows Server, version 2004 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 2004 | 19041.264.200508-2205 | 05/27/2020 | 12/14/2021 | Review note |
| Windows Server, version 1909 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 1909 | 18363.418.191007-0143 | 11/12/2019 | 05/11/2021 | Review note |
| Windows Server, version 1903 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 1903 | 18362.30.190401-1528 | 5/21/2019 | 12/08/2020 | Review note |
| Windows Server 2019 (Long-Term Servicing Channel) (Datacenter, Essentials, Standard) | 1809 | 17763.107.1010129-1455 | 11/13/2018 | 01/09/2024 | 01/09/2029 |
| Windows Server, version 1809 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 1809 | 17763.107.1010129-1455 | 11/13/2018 | 11/10/2020 | Review note |
| Windows Server 2016 (Long-Term Servicing Channel) | 1607 | 14393.0 | 10/15/2016 | 01/11/2022 | 01/11/2027 |
End of service for Windows Server, version 1809 has been delayed due to the ongoing public health crisis. For more information, see our Support article.
Windows Server, version 1803 and later are governed by the Modern Lifecycle Policy. See the Windows Lifecycle FAQ and Comparison of servicing channels for details regarding servicing requirements and other important information.
Информация о выпуске Windows Server Windows Server release information
Корпорация Майкрософт обновила модель обслуживания. Microsoft has updated its servicing model. Semi-Annual Channel — это канал, для которого дважды в год выпускаются обновления, с 18-месячными сроками обслуживания для каждого выпуска. The Semi-Annual Channel is a twice-per-year feature update release with 18-month servicing timelines for each release. На этой странице вы сможете определить дату окончания поддержки для выпусков Semi-Annual Channel. This page is designed to help you determine the end of support date for the Semi-Annual Channel releases.
Канал Semi-Annual Channel позволяет клиентам, быстро внедряющим инновации, раньше начать использование возможностей новой операционной системы. Это особенно касается приложений, основанных на контейнерах и микрослужбах. The Semi-Annual Channel provides opportunity for customers who are innovating quickly to take advantage of new operating system capabilities at a faster pace, both in applications — particularly those built on containers and microservices. Подробные сведения см. в статье Windows Server servicing channels: LTSC and SAC (Каналы обслуживания Windows Server: LTSC и SAC). For more information see the Comparison of servicing channels. Клиенты также могут продолжить пользоваться выпусками в канале Long-Term Servicing Channel, которые будут выходить каждые 2–3 года. Customers also have the option to continue using the Long-Term Servicing Channel releases, which continue to be released every 2-3 years. Каждый выпуск Long-Term Servicing Channel получает 5 лет основной поддержки и 5 лет дополнительной поддержки. Each Long-Term Servicing Channel release is supported for 5 years of mainstream support and 5 years of extended support.
Текущие версии Windows Server по варианту обслуживания Windows Server current versions by servicing option
| Выпуск Windows Server Windows Server release | Версия Version | Сборка ОС OS Build | доступность; Availability | Дата окончания основной фазы поддержки Mainstream support end date | Дата окончания дополнительной фазы поддержки Extended support end date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server версии 20H2 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) Windows Server, version 20H2 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 20H2 20H2 | 19042.508.200927-1902 19042.508.200927-1902 | 20.10.2020 10/20/2020 | 10.05.2022 05/10/2022 | См. заметку Review note |
| Windows Server версии 2004 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) Windows Server, version 2004 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 2004 2004 | 19041.264.200508-2205 19041.264.200508-2205 | 27.05.2020 05/27/2020 | 14.12.2021 12/14/2021 | См. заметку Review note |
| Windows Server версии 1909 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) Windows Server, version 1909 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 1909 1909 | 18363.418.191007-0143 18363.418.191007-0143 | 12.11.2019 11/12/2019 | 11.05.2021 05/11/2021 | См. заметку Review note |
| Windows Server версии 1903 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) Windows Server, version 1903 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 1903 1903 | 18362.30.190401-1528 18362.30.190401-1528 | 21.05.2019 5/21/2019 | 08.12.2020 12/08/2020 | См. заметку Review note |
| Windows Server 2019 (Long-Term Servicing Channel) (Datacenter, Essentials, Standard) Windows Server 2019 (Long-Term Servicing Channel) (Datacenter, Essentials, Standard) | 1809 1809 | 17763.107.1010129-1455 17763.107.1010129-1455 | 13.11.2018 11/13/2018 | 09.01.2024 01/09/2024 | 09.01.2029 01/09/2029 |
| Windows Server версии 1809 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) Windows Server, version 1809 (Semi-Annual Channel) (Datacenter Core, Standard Core) | 1809 1809 | 17763.107.1010129-1455 17763.107.1010129-1455 | 13.11.2018 11/13/2018 | 10.11.2020 11/10/2020 | См. заметку Review note |
| Windows Server 2016 (Long-Term Servicing Channel) Windows Server 2016 (Long-Term Servicing Channel) | 1607 1607 | 14393.0 14393.0 | 15.10.2016 10/15/2016 | 11.01.2022 01/11/2022 | 11.01.2027 01/11/2027 |
Завершение работы службы для Windows Server версии 1809 отложено из-за проблем с состоянием здоровья населения. End of service for Windows Server, version 1809 has been delayed due to the ongoing public health crisis. Дополнительная информация приведена в статье о поддержке. For more information, see our Support article.
В отношении Windows Server версии 1803 и более поздних действует современная политика жизненного цикла. Windows Server, version 1803 and later are governed by the Modern Lifecycle Policy. Подробные сведения о требованиях к обслуживанию и другую важную информацию см. в статье с вопросами и ответами о жизненном цикле продуктов Windows и статье со сравнением каналов обслуживания. See the Windows Lifecycle FAQ and Comparison of servicing channels for details regarding servicing requirements and other important information.
Windows 10 update history
Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows Server, version 20H2
Updates for Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows Server, version 20H2
Windows 10 is a service, which means it gets better through periodic software updates.
The great news is you usually don’t have to do anything! If you have enabled automatic updates, new updates will automatically download and install whenever they’re available, so you don’t have to think about it.
On the left side of this page, you’ll find a list of all the updates released for this version of Windows. You can also find more information about releases and any known issues. Installing the most recent update ensures that you also get any previous updates you might have missed, including any important security fixes.
For more information about the update and how to get it, see:
What’s new for Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows 10, version 2004 release notes
Windows 10, versions 20H2 and 2004 share a common core operating system and an identical set of system files. As a result, the release notes for Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows 10, version 2004 will share an update history page. Each release page will contain a list of addressed issues for both 20H2 and 2004 versions. Note that the 20H2 version will always contain the fixes for 2004; however, 2004 will not contain the fixes for 20H2. The update history page will provide you with the build numbers for both 20H2 and 2004 versions so that it will be easier for support to assist you if you encounter issues.
Current status of Windows 10, version 20H2 and Windows Server, version 20H2
For the most up-to-date information about Known Issues for Windows and Windows Server, please go to the Windows release health dashboard.
Known issues
Certain Japanese half-width Katakana and full-width Katakana characters that have a consonant mark aren’t interpreted as the same character. When you use the CompareStringEx() function with the NORM_IGNOREWIDTH flag to compare them, these characters are evaluated as different because of an issue in the sorting rule . This issue affects all the updates starting on October 29, 2020 for Windows 10, version 20H2.
Open the Command Prompt window ( cmd.exe) with elevated privileges.
Run “reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Nls\Sorting\Versions /ve /d 0006020F /f”
Restart the computer or processes to see the full effect.
Important If you have not installed KB4586853or later on the computer, setting an invalid value in this registry might prevent the computer from starting up.
This workaround reverts the National Language Support (NLS) sorting rule to version 6.2, which is used in Windows 10, version 1909 and earlier. When sharing data between systems, consider applying the workaround consistently. If you use this workaround, conduct sufficient testing and evaluations to mitigate problems caused by different sorting rule versions on multiple systems.
Notes and messages
General
IMPORTANT Release notes are changing! To learn about the new URL, metadata updates, and more, see What’s next for Windows release notes.
IMPORTANT Starting in July 2020, we will resume non-security releases for Windows 10 and Windows Server, version 1809 and later. There is no change to the cumulative monthly security updates (also referred to as the «B» release or Update Tuesday release). For more information, see the blog post Resuming optional Windows 10 and Windows Server non-security monthly updates.
IMPORTANT Starting in July 2020, all Windows Updates will disable the RemoteFX vGPU feature because of a security vulnerability. For more information about the vulnerability, seeCVE-2020-1036 and KB4570006. After you install this update, attempts to start virtual machines (VM) that have RemoteFX vGPU enabled will fail, and messages such as the following will appear:
If you re-enable RemoteFX vGPU, a message similar to the following will appear:
“The virtual machine cannot be started because all the RemoteFX-capable GPUs are disabled in Hyper-V Manager.”
“The virtual machine cannot be started because the server has insufficient GPU resources.”
«We no longer support the RemoteFX 3D video adapter. If you are still using this adapter, you may become vulnerable to security risk. Learn more (https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2131976)”
Troubleshooting
If you have questions or need help activating or troubleshooting Windows, see our help topics below:
For information about how to update, see Update Windows 10.
If you have questions about manually installing or removing an update, see Windows Update: FAQ.
Getting an error message when updating? See Troubleshoot problems updating Windows 10.
If you need to activate Windows, see Activation in Windows 10. If you’re having trouble with activation, see Get help with Windows activation errors.
To get the latest major update to Windows 10, see Get the Windows 10 October 2020 Update.