- Windows Service Account Password Reset
- (Feature available only in Premium and Enterprise Editions)
- How does windows service account reset work?
- How to setup Windows Service Account Password Reset?
- Work flow Summary: Setting up Windows Service Account Password & Scheduled Task Password Reset
- Steps to configure Windows Service Account Password Reset
- Viewing Service Account Status
- Service Accounts
- Overview
- Standalone managed service accounts
- Software requirements
- Group managed service accounts
- Practical applications
- Software requirements
- Virtual accounts
- Software requirements
- See also
Windows Service Account Password Reset
(Feature available only in Premium and Enterprise Editions)
Windows Service Accounts, used by system programs to run application software services or processes, often possess higher or even excessive privileges than normal user accounts. These are indeed very powerful accounts that run critical business processes and services. Many third-party services or scheduled tasks or processes might make use of the same service account, resulting in a complex interconnection.
Typically, specific windows domain accounts are used as service accounts in services running in Windows servers, that need network access. Password Manager Pro has the ability to identify the service accounts associated with a particular domain account. While resetting the password of a domain account managed in Password Manager Pro, it will find out the services which use that particular domain account as service account. It will automatically reset the service account password when the domain password is changed.
In certain cases, you will require to restart the services for the service account password reset to take effect. The windows service account password reset feature of PMP helps achieve this precisely, fully automated.
How does windows service account reset work?
For every Windows domain account for which the service account reset is enabled, Password Manager Pro will find out the services which use that particular domain account as service account, and automatically reset the service account password if this domain password is changed.
How to setup Windows Service Account Password Reset?
The following are mandatory:
(1) Microsoft .Net framework 4.5.2 or above must be installed.
(2) Microsoft Visual C++ 2015 redistributable must be installed.
Before enabling windows service account reset, ensure if the following services are enabled in the servers where the dependent services are running:
(1) Windows RPC service should have been enabled
(2) Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) service should have been enabled
Work flow Summary: Setting up Windows Service Account Password & Scheduled Task Password Reset
- You have a Service Account SA1
- You have four servers Win1, Win2, Win3 & Win4 that make use of SA1
- Your domain name is MyDomain and the SA1 is present in this domain
- Your domain administrator account is DomainAdmin
For enabling Windows Service Account Reset, you need to do the following:
- Create Windows resources for each of the servers that use service accounts. In the above example, you need to create Win1, Win2, Win3 & Win4 as four separate resources (with resource type ‘Windows’). (In the case of service accounts spread across multiple domains, Password Manager Pro uses the local administrator account to login. So, if you wish to have service account password reset for multiple domains, ensure that you have entered local administrator account while creating the resource).
- Create a resource group consisting of these resources — say RG1
- Create a Windows Domain resource. In the above example, it will be MyDomain with resource type Windows Domain
- Inside the domain account, add the individual domain account. In the above example, add SA1 as domain account
- Specify the Resource Group (the group that contains the resources that use the domain account as the service account) that are associated with the domain account. In the above example, associate SA1 with RG1
- Specify the domain administrator account. In this example, it is DomainAdmin . This is required for resetting the service account
Note: The above steps are automated, and PMP will fetch the service accounts associated with the services in the domain members (from v8300 and above) during the privileged accounts discovery process.
Now, when the domain account password is reset
- It is modified immediately in the domain
- Password Manager Pro iterates through the associated resource group and for each resource find the list of services and scheduled tasks which use this domain account as their service account.
- Password Manager Pro uses the domain administrator credentials to log in to the servers and forcefully modify the service account password and scheduled task passwords too and restart the services.
Steps to configure Windows Service Account Password Reset
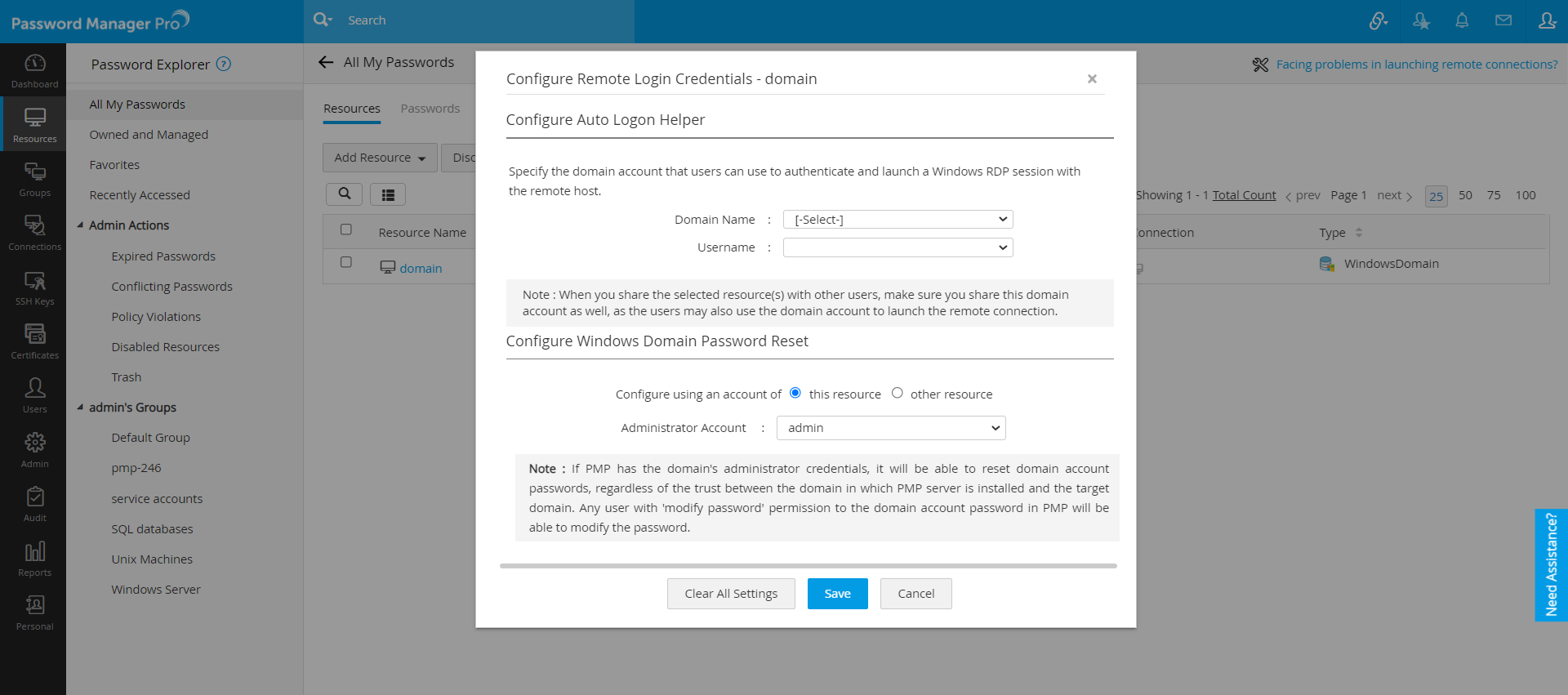
- Add the Domain controller as ‘Windows Domain’ resource type. Make sure that you specify the DNS name and Domain name.
- Add the domain administrator account to this ‘Windows Domain’ resource.
- Add the service account which is used as logon account to this ‘Windows Domain’ resource.
- Add each machine in which services are running as individual resource with resource type ‘Windows’.
- Create a resource group which contains all these windows machines. For example: Service Account group.
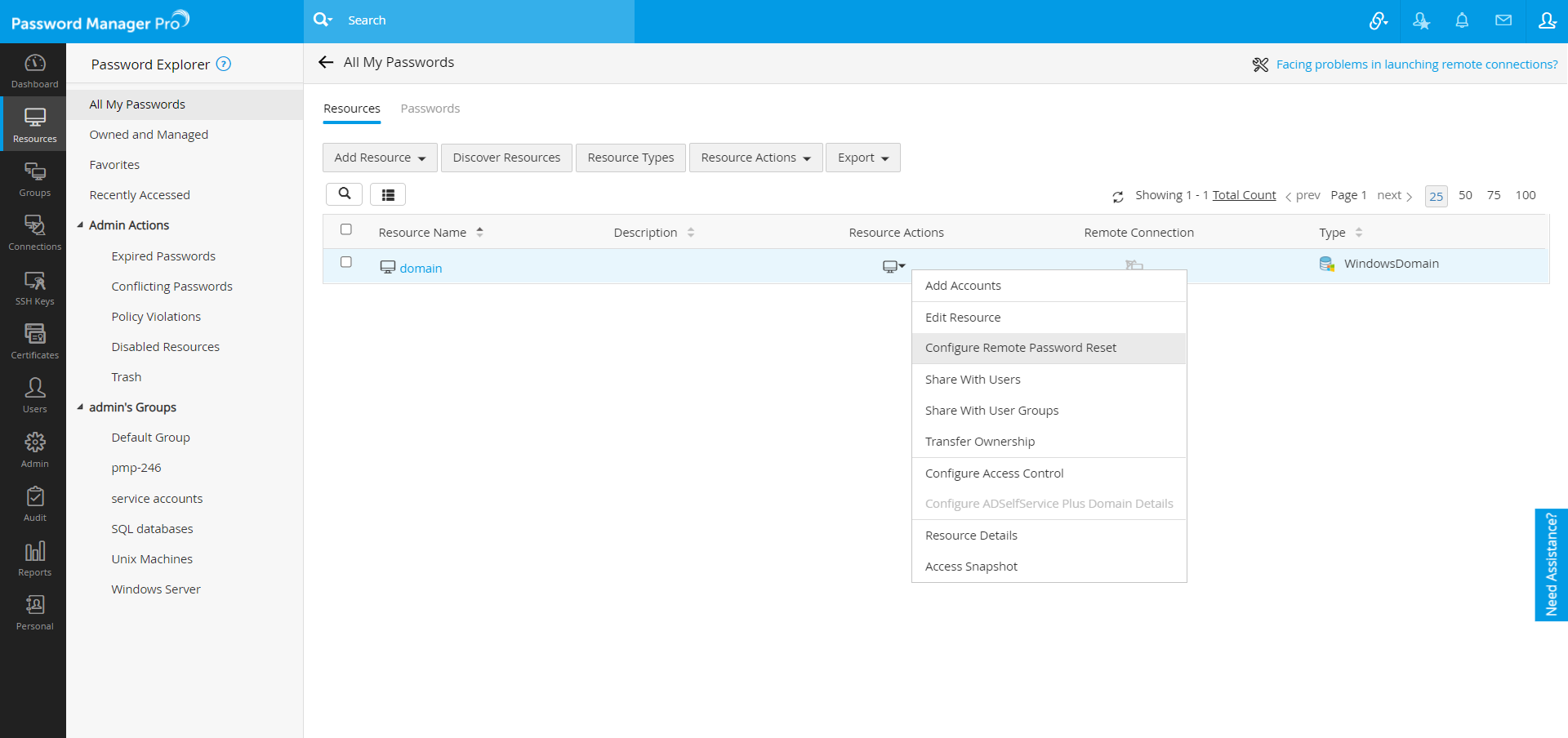
- Click the «Resource Actions» icon against WindowsDomain resource and select «Configure Remote Password Reset» from the drop down.
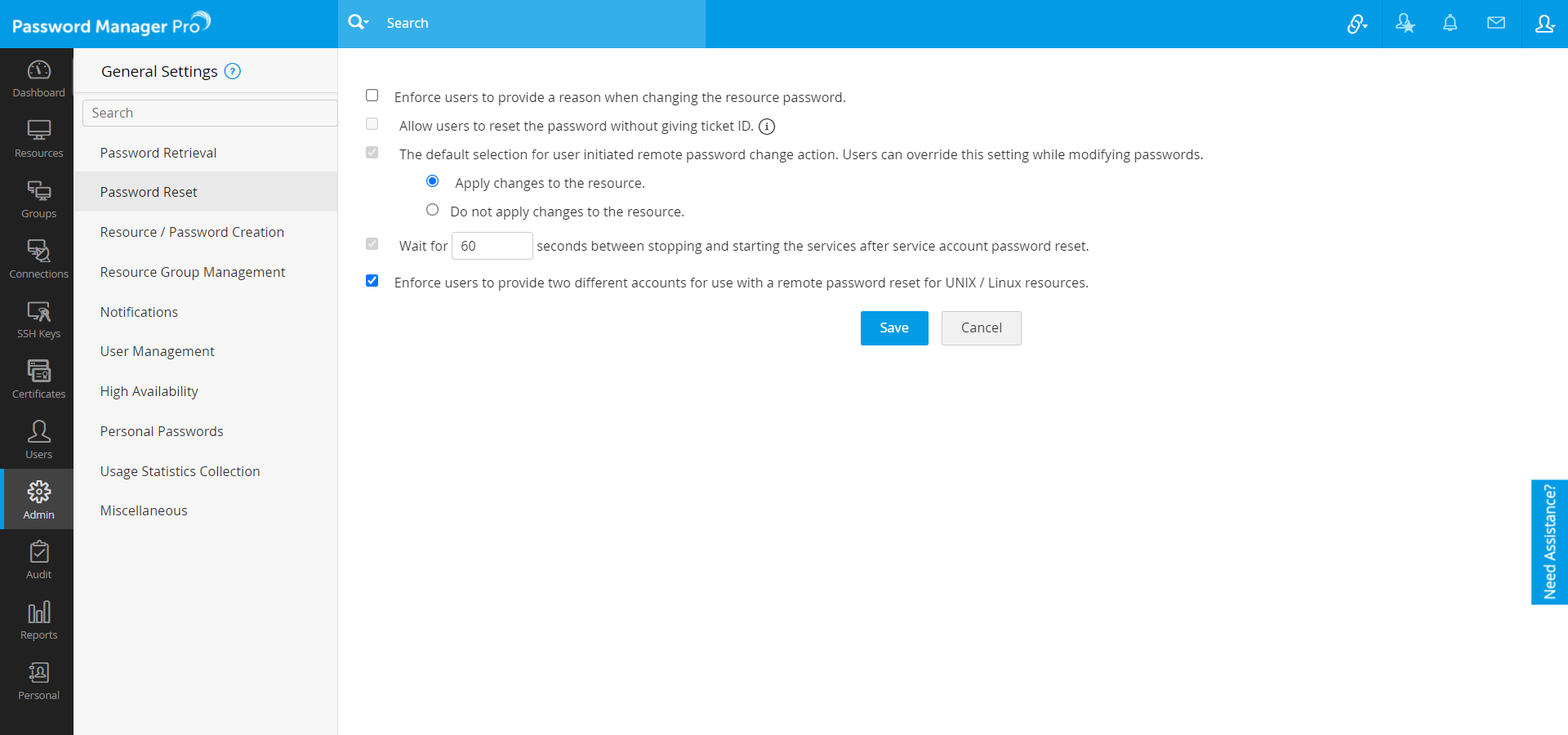
Note: In certain cases, there would be requirements for stopping and starting the services during domain account reset. In such cases, through «General Settings» you can configure Password Manager Pro to wait for a specified time period (in seconds) between stopping and starting the services.
To configure this,
- Navigate to Admin >> Settings >> General Settinngs.
Viewing Service Account Status
For any windows domain account (for which you have enabled Windows service account reset), you can view the list of associated service accounts, scheduled tasks and information on whether the service accounts and scheduled tasks were reset upon the corresponding domain account reset.
To view this information,
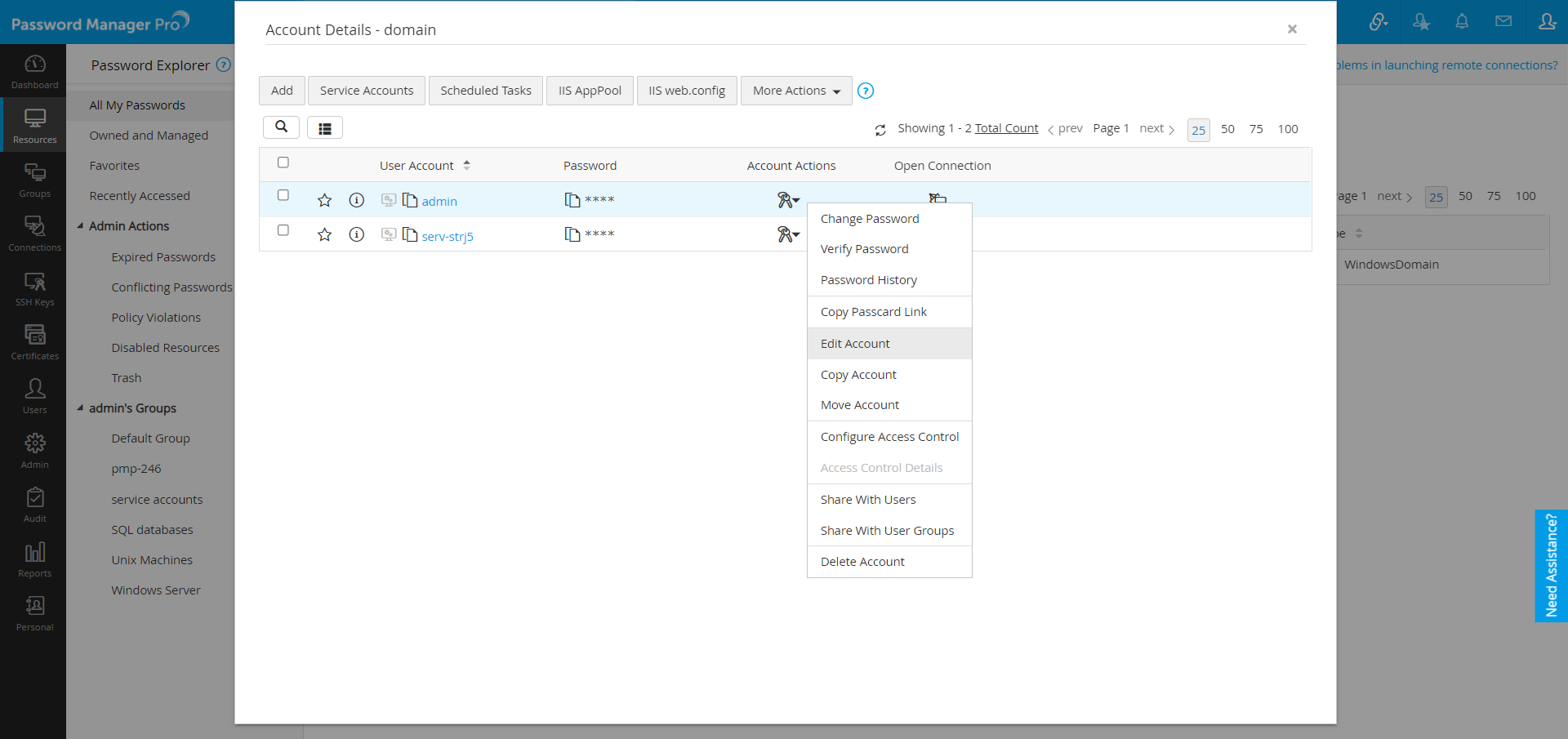
- Go to «Resources» tab and click the name of the resource.
- In the UI that opens, select the domain account of the resource for which you wish to know the status of service account reset and click «Service Account» button at the top of the list of acounts.
- In the dialog box that opens, switch to «Service Account Status» tab.
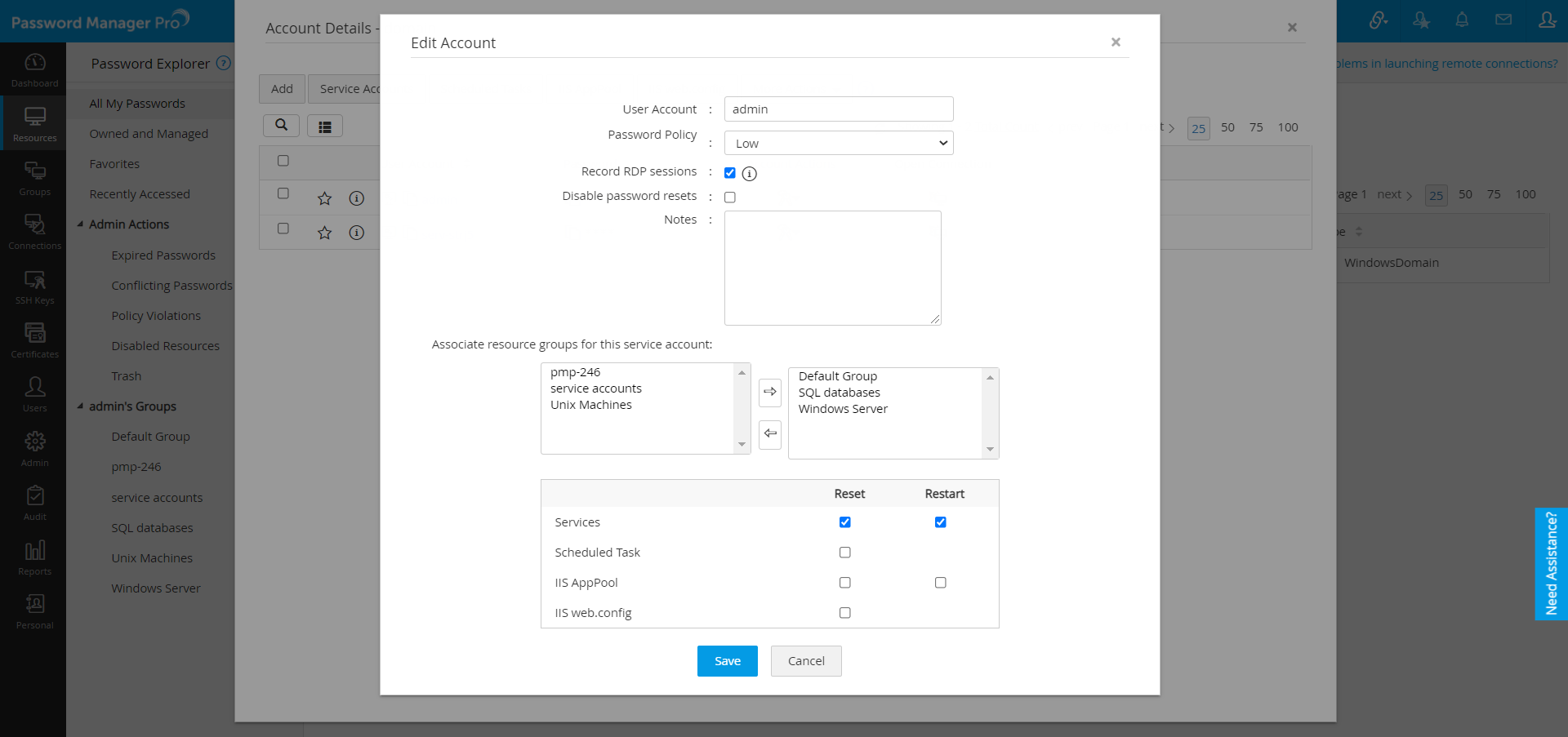
(1) Whenever the password of the domain account is changed, the windows service account associated with it will also be changed. In case, you have created schedules for rotating domain accounts, the service account reset will also follow the schedule.
(2) Once you create Windows Service Account Reset, the passwords of the Windows scheduled tasks associated with the service accounts will also be reset.
Service Accounts
Applies to
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
This topic for the IT professional explains group and standalone managed service accounts, and the computer-specific virtual computer account, and it points to resources about these service accounts.
Overview
A service account is a user account that is created explicitly to provide a security context for services running on Windows Server operating systems. The security context determines the service’s ability to access local and network resources. The Windows operating systems rely on services to run various features. These services can be configured through the applications, the Services snap-in, or Task Manager, or by using Windows PowerShell.
This topic contains information about the following types of service accounts:
Standalone managed service accounts
A managed service account is designed to isolate domain accounts in crucial applications, such as Internet Information Services (IIS), and eliminate the need for an administrator to manually administer the service principal name (SPN) and credentials for the accounts.
To use managed service accounts, the server on which the application or service is installed must be running at least Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. One managed service account can be used for services on a single computer. Managed service accounts cannot be shared between multiple computers, and they cannot be used in server clusters where a service is replicated on multiple cluster nodes. For this scenario, you must use a group managed service account. For more information, see Group Managed Service Accounts Overview.
In addition to the enhanced security that is provided by having individual accounts for critical services, there are four important administrative benefits associated with managed service accounts:
You can create a class of domain accounts that can be used to manage and maintain services on local computers.
Unlike domain accounts in which administrators must reset manually passwords, the network passwords for these accounts are automatically reset.
You do not have to complete complex SPN management tasks to use managed service accounts.
Administrative tasks for managed service accounts can be delegated to non-administrators.
Software requirements
Managed service accounts apply to the Windows operating systems that are designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic.
Group managed service accounts
Group managed service accounts are an extension of the standalone managed service accounts, which were introduced in Windows ServerВ 2008В R2. These are managed domain accounts that provide automatic password management and simplified service principal name (SPN) management, including delegation of management to other administrators.
The group managed service account provides the same functionality as a standalone managed service account within the domain, but it extends that functionality over multiple servers. When connecting to a service that is hosted on a server farm, such as Network Load Balancing, the authentication protocols that support mutual authentication require all instances of the services to use the same principal. When group managed service accounts are used as service principals, the Windows Server operating system manages the password for the account instead of relying on the administrator to manage the password.
The Microsoft Key Distribution Service (kdssvc.dll) provides the mechanism to securely obtain the latest key or a specific key with a key identifier for an Active Directory account. This service was introduced in Windows Server 2012, and it does not run on previous versions of the Windows Server operating system. The Key Distribution Service shares a secret, which is used to create keys for the account. These keys are periodically changed. For a group managed service account, the domain controller computes the password on the key that is provided by the Key Distribution Services, in addition to other attributes of the group managed service account.
Practical applications
Group managed service accounts provide a single identity solution for services running on a server farm, or on systems that use Network Load Balancing. By providing a group managed service account solution, services can be configured for the group managed service account principal, and the password management is handled by the operating system.
By using a group managed service account, services or service administrators do not need to manage password synchronization between service instances. The group managed service account supports hosts that are kept offline for an extended time period and the management of member hosts for all instances of a service. This means that you can deploy a server farm that supports a single identity to which existing client computers can authenticate without knowing the instance of the service to which they are connecting.
Failover clusters do not support group managed service account s. However, services that run on top of the Cluster service can use a group managed service account or a standalone managed service account if they are a Windows service, an App pool, a scheduled task, or if they natively support group managed service account or standalone managed service accounts.
Software requirements
Group managed service accounts can only be configured and administered on computers running at least Windows Server 2012, but they can be deployed as a single service identity solution in domains that still have domain controllers running operating systems earlier than Windows Server 2012. There are no domain or forest functional level requirements.
A 64-bit architecture is required to run the Windows PowerShell commands that are used to administer group managed service accounts.
A managed service account is dependent on encryption types supported by Kerberos. When a client computer authenticates to a server by using Kerberos protocol, the domain controller creates a Kerberos service ticket that is protected with encryption that the domain controller and the server support. The domain controller uses the account’s msDS-SupportedEncryptionTypes attribute to determine what encryption the server supports, and if there is no attribute, it assumes that the client computer does not support stronger encryption types. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) should always be explicitly configured for managed service accounts. If computers that host the managed service account are configured to not support RC4, authentication will always fail.
NoteВ В Introduced in WindowsВ ServerВ 2008В R2, the Data Encryption Standard (DES) is disabled by default. For more information about supported encryption types, see Changes in Kerberos Authentication.
Group managed service accounts are not applicable in Windows operating systems prior to Windows Server 2012.
Virtual accounts
Virtual accounts were introduced in Windows ServerВ 2008В R2 and WindowsВ 7, and are managed local accounts that provide the following features to simplify service administration:
The virtual account is automatically managed.
The virtual account can access the network in a domain environment.
No password management is required. For example, if the default value is used for the service accounts during SQL Server setup on Windows ServerВ 2008В R2, a virtual account that uses the instance name as the service name is established in the format NT SERVICE\ .
Services that run as virtual accounts access network resources by using the credentials of the computer account in the format \ $.
For information about how to configure and use virtual service accounts, see Service Accounts Step-by-Step Guide.
Software requirements
Virtual accounts apply to the Windows operating systems that are designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic.
See also
The following table provides links to additional resources that are related to standalone managed service accounts, group managed service accounts, and virtual accounts.