- Windows set partition type
- Values
- Valid Configuration Passes
- Parent Hierarchy
- Applies To
- XML Examples
- How to Change Partition Type ID Easily? (2 Ways Included)
- About partition type ID
- How to change partition type ID in Windows 10/8/7 easily?
- Solution 1: change partition type ID with a powerful utility
- Solution 2: set partition type ID via Diskpart
- Conclusion
- New-Partition
- Syntax
- Description
- Examples
- Example 1: Create a new partition on disk 1
- Example 2: Get all RAW disks, initialize the disks, partition, and format them
- Example 3: Create a new EFI partition on GTP disk 2
- Example 4: Create a Windows/system partition on MBR disk 0
- Parameters
- Inputs
- Outputs
Windows set partition type
Type specifies the type of partition to create.
Values
Primary
Creates a primary partition type.
A standard master boot record (MBR)-based hard disk can contain up to four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition. The extended partition can include additional logical drives.
A GUID partition table (GPT)-based hard disk can contain up to 128В primary partitions.
Windows must be installed on either a primary or a logical partition.
EFI
Creates an extensible firmware interface (EFI) partition type.
The EFI partition type configures the partition as an EFI system partition (ESP). This is a required partition for a GUID partition table (GPT)-based disk.
Only a single EFI system partition is required, regardless of how many GPT-based disks exist on a system. For unattended installations, it is possible to create more than one ESP on a hard disk. If there is already an ESP on the hard disk to which you are installing, and you create a new ESP in your answer file, two ESPs will be present on the computer. Two ESPs might be problematic for users, and they will consume additional disk space.
We recommend that you use the WillWipeDisk setting to erase all partitions on the disk before performing an unattended installation.
In attended installations, Windows Setup warns you that an ESP already exists on the hard disk.
Installation will be terminated if you specify Type as EFI and the format of the disk is of type MBR. Only GPT disks can have an EFI System partition.
Extended
Specifies that the partition is an extended partition.
An extended partition can be created only on master boot record (MBR)-based disks.
Only one extended partition can exist on a single disk. If an extended partition already exists on the disk, a second extended partition is not created. If the value for the WillShowUI setting is set to Never, an error is logged, and installation is terminated.
Extended partitions are useful if you intend to create more than four volumes on a basic MBR disk. Unlike primary partitions, you do not format an extended partition with a file system. Instead, you create one or more logical drives within the extended partition.
Logical
Specifies that the partition is a logical partition.
WindowsВ 7 must be installed on either a primary or a logical partition.
A logical partition is a volume that is created inside an extended partition on a basic master boot record (MBR)-based disk.
Logical partitions are similar to primary partitions. However, while only four primary partitions can exist on a single disk, the number of logical partitions that can exist on a disk is unlimited. A logical partition can be formatted and assigned a drive letter.
A logical partition must be created inside an extended partition. If an extended partition does not already exist on the disk or the specified size of the logical drive exceeds the extended partition, no partition is created.
If WillShowUI is set to Never, an error is logged, and installation is terminated.
MSR
Specifies that the partition is a Microsoft reserved (MSR) partition.
The MSR partition type is a required partition for GUID partition table (GPT)-based disks.
The size of the MSR partition varies. For GPT disks that are smaller than 16В GB, the size of the MSR partition is 32В MB. For disks larger than 16В GB, the MSR partition is 128В MB.
If an MSR partition already exists on the same disk, or the format of the disk is MBR, no partition is created. If the value for WillShowUI is set to Never, an error is logged and the installation is terminated.
If an ESP is not detected or an MSR partition does not exist on each GPT disk in the system, no GPT-related disk configurations can be created.
For information about setting other types of partitions, such as utility and recovery partitions, see Microsoft-Windows-Setup/DiskConfiguration/Disk/ModifyPartitions/ModifyPartition/TypeID.
This string type does not support empty elements. Do not create an empty value for this setting.
Valid Configuration Passes
Parent Hierarchy
Applies To
For a list of Windows editions and architectures that this component supports, see Microsoft-Windows-Setup.
XML Examples
The following XML output for the DiskConfiguration setting shows a configuration for a UEFI-based system with four partitions, including an EFI partition, an MSR partition, and two primary partitions.
0 true 1 Primary 250 2 EFI 100 3 MSR 128 4 Primary true 1
How to Change Partition Type ID Easily? (2 Ways Included)
Are you in need of changing partition type ID in Windows? Read this article thoroughly to get two efficient solutions.
By Lily 
Quick Navigation:
About partition type ID
Most computer users may be familiar with partitions and partition types. Actually, there are five partition types: primary, extensible firmware interface (EFI), extended, logical, and Microsoft Reserved (MSR). How about partition type ID?
Partition type ID is a byte value intended to specify the file system a partition contains and/or to flag the special access method used to access the partition.
For MBR disks, the value for the type field is in hexadecimal form. Following are the frequently-used type IDs for MBR-based partitions:
в—Џ 0x01 FAT12
в—Џ 0x04 FAT16, less than 32 MB
в—Џ 0x06 FAT16, greater than 32 MB
в—Џ 0x07 NTFS
в—Џ 0x0B FAT32, used by DOS & Win95
в—Џ 0x0C FAT32 using LBA mode to access to FAT32 partition
в—Џ 0x0E FAT16 using LBA mode to access to FAT16 partition
For GPT disks, the value for the type field is a long string. Recognized GUIDs include:
в—† EFI system partition: c12a7328-f81f-11d2-ba4b-00a0c93ec93b
в—† Basic data partition: ebd0a0a2-b9e5-4433-87c0-68b6b72699c7
◆ Learn more…
Why would someone like to change a partition type ID? Actually, changing type ID is a good way to prevent the system using or initializing partitions. Read on to find out how to change partition type ID in Windows 10/8/7 efficiently.
How to change partition type ID in Windows 10/8/7 easily?
Here I’m going to show you two efficient solutions to change partition type ID in Windows 10. You can set partition type ID in Windows 8/7 with the same methods.
Solution 1: change partition type ID with a powerful utility
With a reliable, specialized utility, you will save much time and efforts. AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional is such a tool you need. It is an all-around partition manager which helps you to move, merge, split and resize partitions. It also offers you the disk conversion feature, such as converting dynamic disk to basic, converting GPT disk to MBR and MBR disk to GPT, etc.
It supports all Windows PC operating systems like Windows 10/8.1/8/7/Vista/XP. If you are running Windows Server, please turn to the Server edition. Now follow the instructions below to change partition type ID via AOMEI Partition Assistant:
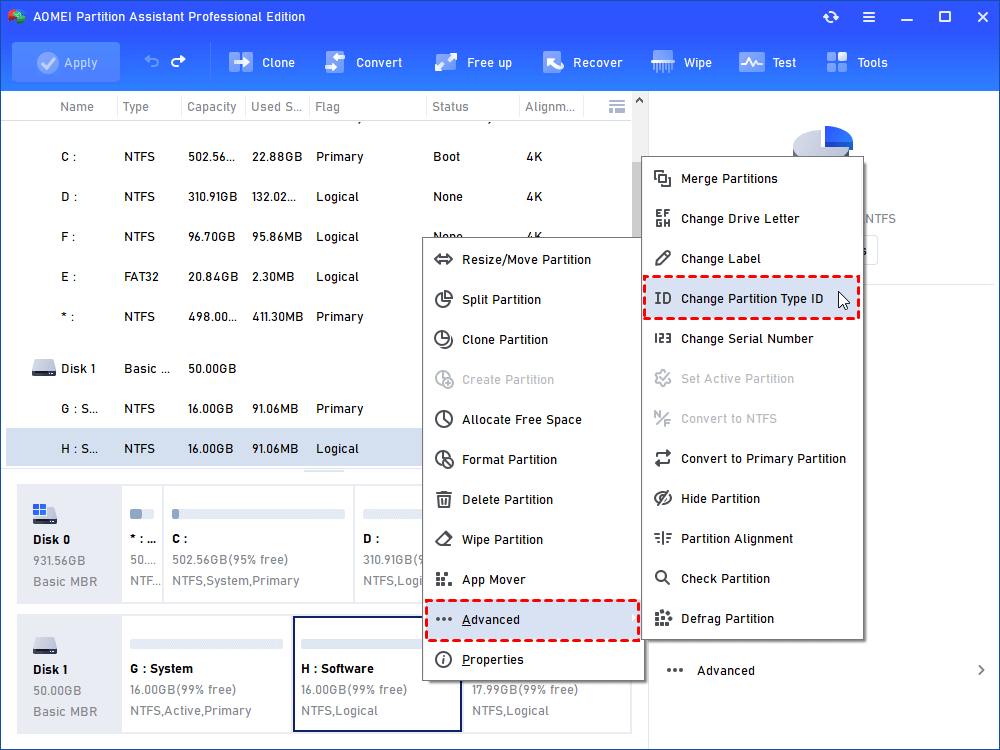
Step 1. Install and launch AOMEI Partition Assistant. Right click the drive of which you want to change partition type ID, select “Advanced” and then “Change Partition Type ID”.
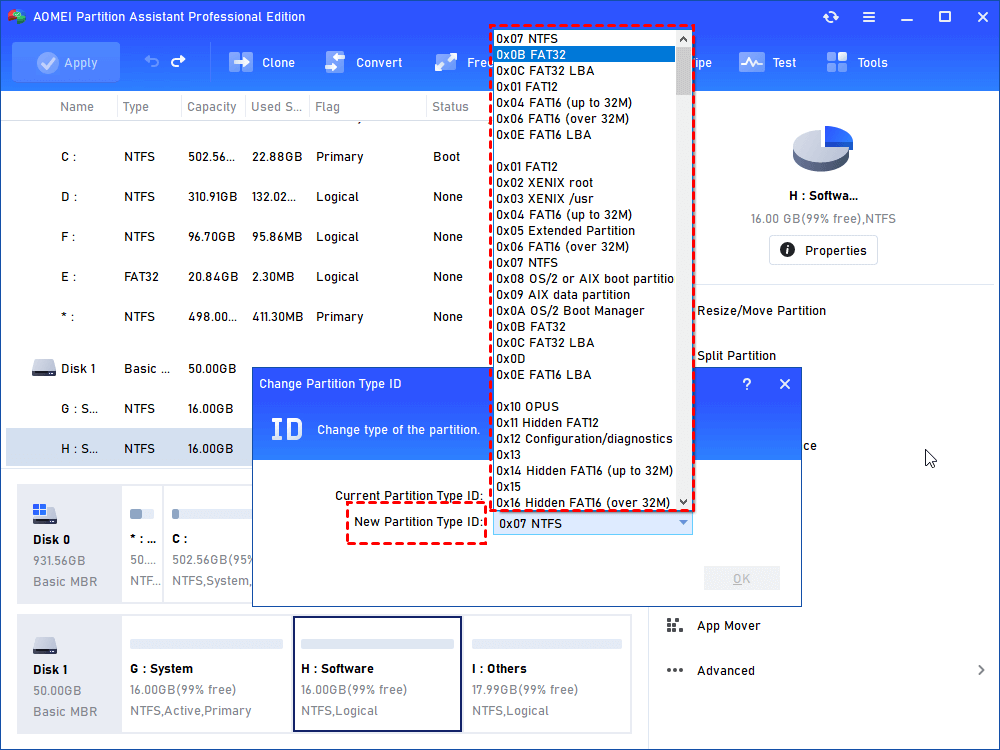
Step 2. In the pop up window, select the new partition type ID and click “OK” to save the change.
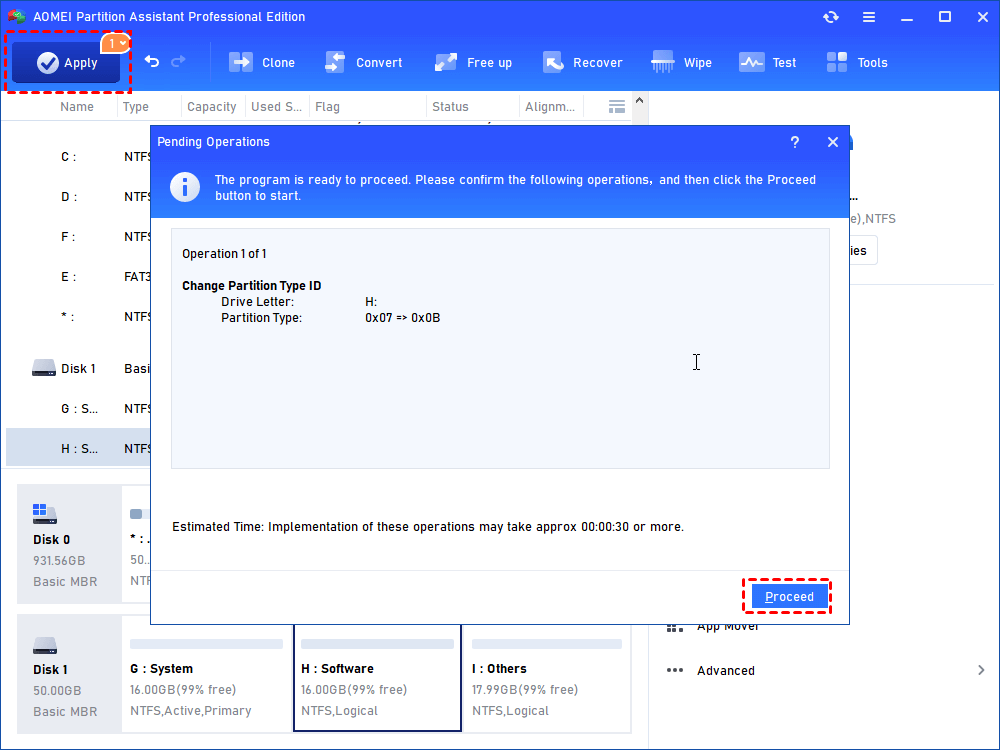
Step 3. Click “Apply” to view pending operation and then “Proceed” to commit the operation.
вњЋ Notes:
в—Џ Changing partition type ID is unavailable for GPT disk partitions in AOMEI Partition Assistant. However, you are allowed to convert between GPT and MBR disks.
● The program won’t delete files while changing partition type ID, so you needn’t be worried about data loss.
Solution 2: set partition type ID via Diskpart
Some people prefer to use command lines. Then, try Diskpart SET ID command in following steps:
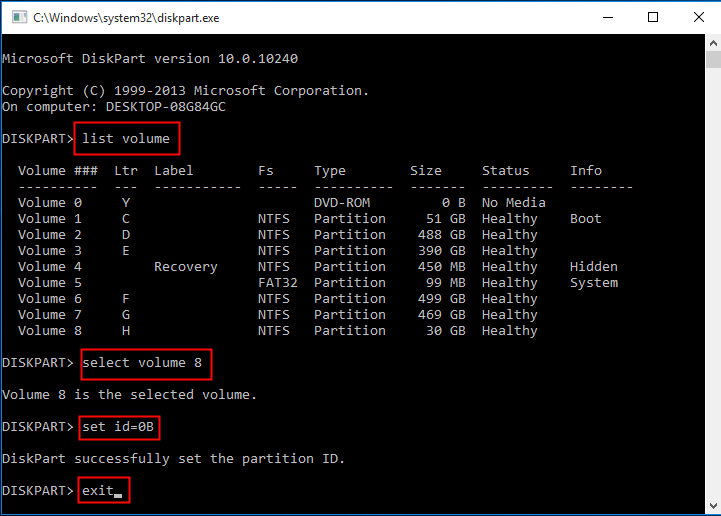
1. Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialogue. Type diskpart and click “OK” or press Enter to run Diskpart.
2. Type list volume and press Enter.
3. Type select volume # (ex: volume 8) and press Enter to select the volume/partition of which you want to change partition type ID.
4. Type set (ex: and press Enter to set a new partition type ID.
(Tips: The leading “0x” of the ID is omitted when specifying the hexadecimal partition type.)
5. Type exit and press Enter to exit Diskpart.
Conclusion
You have learned two efficient ways to change partition type ID in Windows 10/8/7. Apart from setting partition type ID, you can use AOMEI Partition Assistant to remove write protection on micro SD card Samsung and repair pen drive not detected. Go for this tool and enjoy all the wonderful features right now!
New-Partition
Creates a new partition on an existing Disk object.
Syntax
Description
The New-Partition cmdlet creates a partition on a specified Disk object. Note: This cmdlet does not support creating dynamic volumes.
Examples
Example 1: Create a new partition on disk 1
This example creates a new partition on disk 1 using the maximum available space and assigns a drive letter T.
Example 2: Get all RAW disks, initialize the disks, partition, and format them
This example uses five cmdlets and the pipeline to get all disks, filter them for only RAW, unpartitioned disks, initialize the disks, partition the disks, and then to format them.
Example 3: Create a new EFI partition on GTP disk 2
This example creates a new EFI partition on disk 2 with a size of 500 MB.
Example 4: Create a Windows/system partition on MBR disk 0
This example creates a new Windows/system partition on MBR disk 0 with a size of 100 GB.
Parameters
Specifies the alignment boundary in bytes.
| Type: | UInt32 |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Runs the cmdlet as a background job. Use this parameter to run commands that take a long time to complete.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Assigns a drive letter to the new partition.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Runs the cmdlet in a remote session or on a remote computer. Enter a computer name or a session object, such as the output of a New-CimSession or Get-CimSession cmdlet. The default is the current session on the local computer.
| Type: | CimSession [ ] |
| Aliases: | Session |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the ID of the disk on which to create the partition.
| Type: | String [ ] |
| Aliases: | Id |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies an array of disk numbers.
| Type: | UInt32 [ ] |
| Position: | 0 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the path of the disk on which to create the partition.
| Type: | String [ ] |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the specific drive letter to assign to the new partition.
| Type: | Char |
| Aliases: | NewDriveLetter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the type of GPT partition to create (by GUID). The format should be 32 digits separated by hyphens, enclosed in braces and quoted:
By default, the New-Partition cmdlet creates a basic GPT data partition.
The GUIDs of valid types are:
- System Partition — «
« - Microsoft Reserved — «
« - Basic data — «
« - Microsoft Recovery — «
«
| Type: | String |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | « |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the input object that is used in a pipeline command.
| Type: | CimInstance [ ] |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Marks the partition as active:
- On a BIOS-based system, the active partition is the partition the system will boot to. This partition must be a primary partition.
- On a Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)-based system, this setting is not used. The system will always boot to the EFI System Partition (ESP). If Active is set for this partition type, it is ignored.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Creates a hidden partition.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the type of MBR partition to create.
| Type: | MbrType |
| Accepted values: | FAT12, FAT16, Extended, Huge, IFS, FAT32 |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | Huge |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the starting offset, in bytes.
| Type: | UInt64 |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the size of the partition to create. If not specified, then the units will default to Bytes. The acceptable value for this parameter is a positive number followed by the one of the following unit values: Bytes, KB, MB, GB, or TB.
| Type: | UInt64 |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent operations that can be established to run the cmdlet. If this parameter is omitted or a value of 0 is entered, then Windows PowerShellВ® calculates an optimum throttle limit for the cmdlet based on the number of CIM cmdlets that are running on the computer. The throttle limit applies only to the current cmdlet, not to the session or to the computer.
| Type: | Int32 |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Creates the largest possible partition on the specified disk.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Inputs
You can pipe a Disk object to the InputObject parameter.
Outputs
This cmdlet outputs an object that represents the newly created partition.