- Windows. Devices. Usb Namespace
- Device Support
- USB Device Capabilities
- Troubleshooting
- Classes
- Enums
- USB over Network
- Share and access USB devices over local network or the Internet. Available for Windows and Linux.
- Overview
- How it works
- Real USB virtualization technology
- Works with any USB devices
- Support for both Windows and Linux
- Driver-free solution
- USB port sharing
- SSL Security
- Password protection
- Reversed device connections
- Per-interface sharing
- Advanced sharing rules
- USB server auto discovery
- OEM License Benefits
- What Customers Say
Windows. Devices. Usb Namespace
This namespace defines Windows Runtime classes that a UWP app can use to communicate with WinUSB devices. These devices are handled by the inbox winusb.sys driver and are identified by a specific Microsoft OS Descriptor.
A valid WinUSB device will have a compatible id of USB\MS_COMP_WINUSB
Device Support
This namespace supports most WinUSB devices. However, it does not provide access to USB devices with device classes of the following:
- Audio ( 0x01 )
- HID ( 0x03 )
- Image ( 0x06 )
- Printer ( 0x07 )
- Mass Storage ( 0x08 )
- Smart Card ( 0x0B )
- Audio/Video ( 0x10 )
- Wireless Controller ( 0xE0 )
USB Device Capabilities
A UWP app that accesses a USB device must include specific device capability data in the capabilities node of its manifest. This data identifies the device and its purpose (or function). Note that some devices may have multiple functions.
Since Windows 10, version 1809 (October 2018 Update)
Before Windows 10, version 1809 (October 2018 Update)
Since 1809, the VendorId/ProductId and function-type no longer need to be specified and will be ignored on newer systems. If targeting systems below 1809, then see legacy USB device capabilities.
Troubleshooting
- Verify the USB capability ( usb ) is in the application manifest.
- Verify the user has granted permission for the application to utilize USB devices.
- Validate the device type is not one designated as inaccessible.
- Machine-internal devices ( DEVPKEY_Device_InLocalMachineContainer == TRUE ) are generally not accessible unless running on a SKU with embedded mode and lowLevelDevices capability.
- Devices with stacks that contain upper/lower filter drivers are generally not accessible. These are sometimes added by 3rd parties to enable additional functionality for custom hardware.
- Device restriction is partially determined by winusb.sys during device enumeration, which may set the device interface property DEVPKEY_DeviceInterface_Restricted to TRUE on the WinUSB Device Interface GUID_DEVINTERFACE_WINUSB_WINRT based on the presence of device/class filters.
- The presence of device UpperFilter/LowerFilter drivers can be determined using DeviceManager by looking for UpperFilters and LowerFilters properties.
- The presence of WinUSB class UpperFilter/LowerFilter drivers can be determined using DeviceManager by looking for Class upper filters and Class lower filters properties.
- Device Interface properties can be inspected by calling CM_Get_Device_Interface_Property where pszDeviceInterface is the same string as would be passed to FromIdAsync.
- These restrictions can be bypassed when making a custom device by working with the driver-developer to create a Hardware Support App
Classes
The endpoint descriptor for a USB bulk IN endpoint. The descriptor specifies the endpoint type, direction, number and also the maximum number of bytes that can be read from the endpoint, in a single transfer.
Represents the pipe that the underlying USB driver opens to communicate with a USB bulk IN endpoint of the device. The app can get an input stream from the pipe and access data is being read from the endpoint.
The endpoint descriptor for a USB bulk OUT endpoint. The descriptor specifies the endpoint type, direction, number and also the maximum number of bytes that can be written to the endpoint, in a single transfer.
Represents the pipe that the underlying USB driver opens to communicate with a USB bulk OUT endpoint of the device. The object provides access to an output stream to which the app can write data to send to the endpoint.
Provides information about a USB configuration, its descriptors and the interfaces defined within that configuration. For an explanation of a USB configuration, see Section 9.6.3 in the Universal Serial Bus (USB) specification.
Derives information from the first 9 bytes of a USB configuration descriptor. The information includes the power capabilities of the device when the configuration is active and the number of interfaces included in that configuration. For an explanation of a configuration descriptor, Section 9.6.3 Universal Serial Bus Specification. For information about descriptor fields, see:
- Table 9.15 in the Universal Serial Bus 3.0 Specification
- Table 9.10 in the Universal Serial Bus Specification (version 2.0)
Provides information about the USB control transfer, the type of control request, whether the data is sent from or to the host, and the recipient of the request in the device.
Provides information about the type of descriptor, its size (in bytes), and gets the descriptor data.
Represents a USB device. The object provides methods and properties that an app can use to enumerate WinUSB devices and send IN and OUT control transfers.
Provides a way for the app to get an Advanced Query Syntax (AQS) string by specifying the class code, subclass code, and the protocol code defined by the device. The properties in this class are passed in the call to GetDeviceClassSelector.
Provides a way for you to retrieve a UsbDeviceClass object based on the USB device class of a device. The properties defined in this class represent the supported USB device classes, and they return UsbDeviceClass objects.
For information about USB device classes, see the official USB Website for Approved Class Specification Documents.
Derives information from the USB device descriptor of the device. For an explanation of the device descriptor, see Table 9.8 in the Universal Serial Bus Specification.
Derives information from the USB endpoint descriptor of the endpoint, such as type, direction, and endpoint number. This object also gets the specific endpoint descriptors based on the type of endpoint. For an explanation of an endpoint descriptor, see Section 9.6.5 in the Universal Serial Bus Specification:
- Table 9.18 in the Universal Serial Bus 3.0 Specification
- Table 9.13 in the Universal Serial Bus Specification (version 2.0)
Provides information about the USB interface including its endpoints, the number of alternate settings the interface supports, and gets the entire descriptor set for those settings. It also obtains pipes associated with the endpoints that the interface supports.
Describes a USB alternate setting (of an interface) in an interface descriptor. For an explanation of an interface descriptor, see Section 9.6.5 in the Universal Serial Bus Specification:
- Table 9.15 in the Universal Serial Bus 3.0 Specification
- Table 9.12 in the Universal Serial Bus Specification (version 2.0)
Provides information about an alternate setting and select that setting. The app can get the USB interface descriptors for the setting and its endpoints, and determine whether this setting is currently selected.
The endpoint descriptor for a USB interrupt IN endpoint. The descriptor specifies the endpoint type, direction, number and also the maximum number of bytes that can be read from the endpoint, in a single transfer. The app can also get information about how often the host polls the endpoint for data.
Represents the object that is passed as a parameter to the event handler for the DataReceived event.
Represents the pipe that the underlying USB driver opens to communicate with a USB interrupt IN endpoint of the device. The object also enables the app to specify an event handler. That handler that gets invoked when data is read from the endpoint.
The endpoint descriptor for a USB interrupt OUT endpoint. The descriptor specifies the endpoint type, direction, number and also the maximum number of bytes that can be written to the endpoint, in a single transfer. The app can also get information about how often the host polls the endpoint to send data.
Represents the pipe that the underlying USB driver opens to communicate with a USB interrupt OUT endpoint of the device. The object provides access to an output stream to which the app can write data to send to the endpoint.
Describes the setup packet for a USB control transfer. For an explanation of the setup packet, see Table 9.2 in the Universal Serial Bus (USB) specification.
Enums
Defines constants that indicate the recipient of a USB control transfer. The recipient is defined in the setup packet of the control request. See Table 9.2 of section 9.3 of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) specification (www.usb.org).
Defines constants that indicate the type of USB control transfer: standard, class, or vendor.
Defines constants that indicate the type of USB endpoint: control, bulk, isochronous, or interrupt.
Defines constants for configuration flags that can be set for a USB pipe that the host opens for a USB bulk IN endpoint.
Defines constants that indicate the direction of USB transfer: IN or OUT transfers.
Defines constants for configuration flags that can be set for a USB pipe that the host opens for a USB OUT endpoint.
USB over Network
Share and access USB devices over local network or the Internet.
Available for Windows and Linux.
Overview
USB over Network allows to use remote USB devices shared over a local network or the Internet.
It does not matter if you are located in another office or even country, now you can use any USB device remotely as if it was attached to your computer locally.
How it works
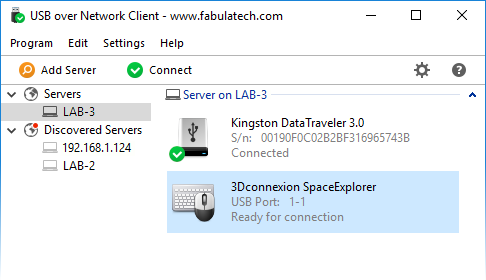
The program consists of two parts — Server and Client. The Server part is installed on a PC where USB devices are physically plugged in, making it possible to share the devices for remote connection. The Client should be installed on computers where you need to get access to remote shared USB devices.
When you connect remote USB device using a Client part on your PC, it appears as if the device was attached directly to your computer.
Real USB virtualization technology
Thanks to many years of research and development we were able to release unique USB virtualization technology. It fully emulates the USB stack of remote USB devices on the client side creating the exact virtual copy of each shared hardware USB device.
Works with any USB devices
The program is not limited to some specific models of USB devices. It is compatible with any of them. So, it is really universal solution for the remote access to USB devices. Even the most exotic USB devices can be accessed over network or the Internet.
Support for both Windows and Linux
USB over Network supports both WIndows and Linux on both sides. Any compatible Windows and Linux distribution can be used on Client side for accessing remote USB devices shared on Windows or Linux Servers.
Driver-free solution
USB over Network does not require USB device drivers on the Server side. This feature really simplifies everything, since it allows to share USB devices even when their drivers was not installed locally (or in case if the device is not supported by Server side OS). Keep in mind, that USB device drivers are required on the Client side anyway.
USB port sharing
In some cases it is really convenient to use some dedicated USB port for device sharing. So any USB device being plugged into it becomes shared automatically. This won’t affect other USB devices plugged into other USB ports.
SSL Security
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a server and a client. This layer protects your private information and keeps the data safe.
Password protection
In order to provide more security, it’s possible to protect USB devices or the whole USB server by password. So, only authorized users will be able to access specified USB devices remotely.
Reversed device connections
Sometimes it’s needed to initiate device connection from Server side to Client side. So instead of connecting remote USB device, end user can “push” the local USB device to the remote computer. The call-back connection feature is especially useful in case if the Server is behind a firewall or on a NAT network.
Per-interface sharing
There is a possibility of per-interface sharing for composite devices that usually contain several USB devices. For example, if you use the webcam with built-in speaker, it’s no problem to share the webcam for remote access but leave the speakers for local use only.
Advanced sharing rules
The system of Sharing Rules allows fine-tuning of the sharing process both of the concrete device and of the group of USB devices with the same characteristics. Built-in Sharing Rules Manager makes the process of rules creation really easy.
USB server auto discovery
USB over Network Client can discover USB Servers installed in your local network. So, in most cases, it’s even not needed to specify remote IP address or hostname of the Server. Just choose the needed server from the list in order to connect the Server permanently.
OEM License Benefits
USB over Network functionality can be easily integrated into your application. So you can share USB devices or connect them up from your application directly. Read more…
What Customers Say
The developmental goals of remotely operated vehicle are aimed at exploring the implementation of robotics in subsea exploration.
As part of this project, our team will be using software developed by FabulaTech for the transmission of control signal from the surface laptop. Using the server-client USB over Network program developed by FabulaTech, the surface control laptop acts as the server, while the client is the onboard RaspberryPi.