Realtek HD Audio Manager
Realtek HD Audio Manager R2.82 LATEST
Windows Vista / Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 10
Realtek HD Audio Manager 2021 full offline installer setup for PC 32bit/64bit
Realtek HD Audio Manager is one of the most widely available sound card driver applications, dedicated to provide users with the tool sound chips on their motherboard with the most accurate sound quality, access to all features of the onboard hardware, resolve compatibility issues that may be present with basic Windows drivers, fix various errors that may appear during the throughout the product’s usage, and add support for new operating systems.
This driver package comes with the support for all the major sound codecs, giving your PC support to process audio, playback multimedia, record audio, manage speakers, and more. How to reinstall Realtek HD audio manager on Windows 10? Check out now!
Installation and Use
Realtek HD Audio Manager comes in a single installation package that can be easily installed on any supported Windows OS (Windows XP, 7, Vista, 8, 8.1, and 10) by simply following on-screen instructions.
In addition to automatic install, you can also install the Realtek sound driver via the Update Driver Software feature found in Device Manager. Use “Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer” and “Have Disk” buttons and point the update tool toward the folder where you have extracted the .cab file from the Realtek driver package. After either automatic or manual installation, make sure to restart your PC.
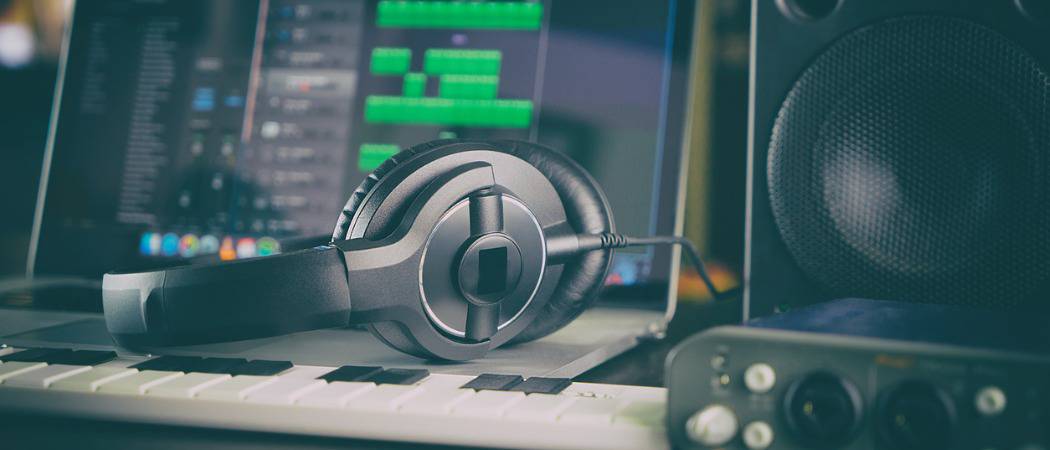
The main interface of the HD Audio Manager can be accessed via icon in the Windows taskbar. The user interface of the app features two tabs (for management of Speakers or Microphone), with in-depth mixing for both Left/Side ratio and Volume, Speaker configuration, surround sound tweaking, and audio jack source re-tasking. Sound Effect tab can be used for choosing the emulated sound environment, equalizer presets, or tweaking of mic sound for Karaoke.
Features and Highlights
In addition to providing deep driver support, the tool features an excellent user-accessible utility for managing your sound card capabilities. Its streamlined UI can be used to manage sound inputs, re-assign audio ports to any of the preferred inputs/outputs, flexible mixing, fine grain coordinating functions, and setting up of the sound stage (headphones, stereo, surround, with dB gain and distance settings). The audio manager can also be used to set up 3D sound rendering and speech synthesis.
Options for audio input (microphone) are also fully featured, including an equalizer, noise suppression, beam formation, and Acoustic Echo Cancelation.
Users on laptops can also take advantage of the Power Management feature that can be accessed via a little battery icon in the bottom corner of the HD Audio software window. In it, you can disable various power-draining audio features when your laptop is running on battery power.
How to Manage Audio Devices in Windows 10
Audio plays a critical role in our experiences when using Windows. Whether it is listening to music, movies or communicating with family and friends over Skype. Depending on the type of computer you own, your choice of audio output might be different. Laptops and some desktops will have onboard audio while both can accommodate external speakers to enhance sound quality.
Adjust Volume and Audio Settings in Windows 10
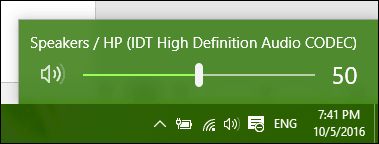
Basic audio settings can be accessed from the Speakers notification on the taskbar. You can use the slider to increase or lower the volume.
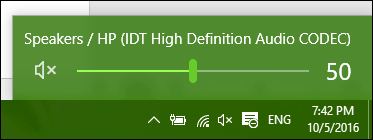
Audio can mute audio by clicking the speaker icon on the new volume menu.
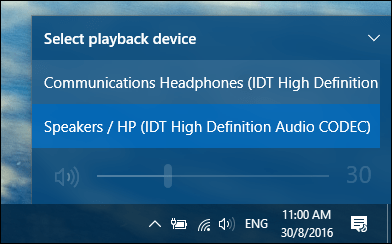
The Windows 10 Anniversary Update now makes it easier to switch between different audio devices. To do so, click the audio icon in the Notification Area.
Click the audio out put device you would like to use. This is especially handy if you want to switch between built in audio or your headphones.
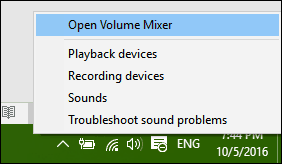
Additional audio options can be accessed from a right-click menu.
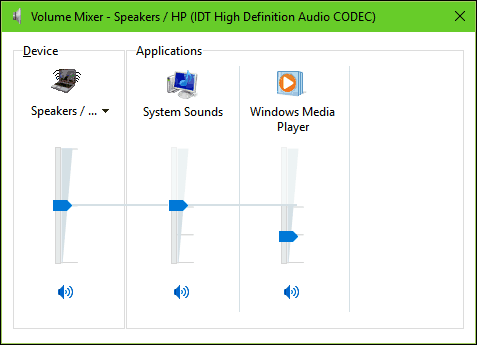
The Volume Mixer provides options for managing volume per desktop application. Not all applications support this feature, though. If they do, you’ll see them in the Mixer and can adjust the volume levels. For example, you might want to mute specific applications such as system sounds when watching a movie.
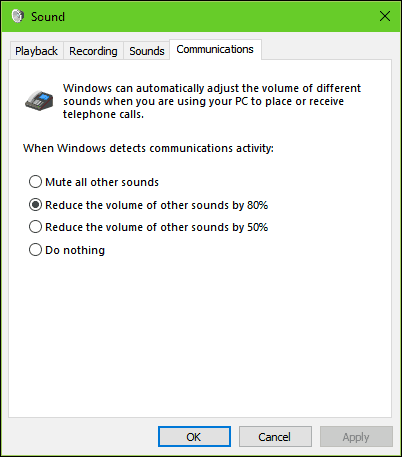
A handy function of the Windows sound settings is the ability to modify audio behavior when multi-tasking. If you use a smartphone, you might be aware of an option which lowers the audio of the active application when you receive a notification. If you use an application such as Skype to send and receive video calls, Windows can be set to adjust the volume automatically when communication activity is detected.
Connected external audio devices such as speakers or headphones can be modified from the Sound Settings playback options. Enhancements such as bass, loudness, and surround sound quality can be applied.
Troubleshooting Audio In Windows 10
If you’re unable to hear audio, there are some things you can try. First, check if the volume is turned down or muted.
If you have recently upgraded to Windows 10, your previous audio driver might not be compatible. Uninstalling and reinstalling your audio device might resolve the issue. Press Windows Key + X and click Device Manager. Then expand Sound > video and game controller. Select your audio device, right-click it and Uninstall. Restart your computer and let Windows redetect it. You can also check Windows Update for the latest drivers for your sound card.
If the problem persists, try running the Troubleshooting audio playback fix it.
Check out our other articles about managing audio:
Fix sound problems in Windows 10
If you’re having audio problems, the following suggestions might help. The tips are listed in order, so start with the first one, see if that helps, and then continue to the next one if it doesn’t.
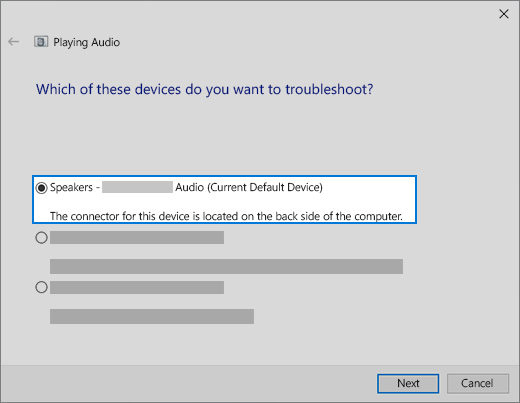
If multiple audio output devices are available, check that you have the appropriate one selected. Here’s how:
Select the Speakers icon on the taskbar.
Next, select the arrow to open a list of audio devices connected to your computer.
Check that your audio is playing to the audio device you prefer, such as a speaker or headphones.
If this doesn’t help, continue to the next tip.
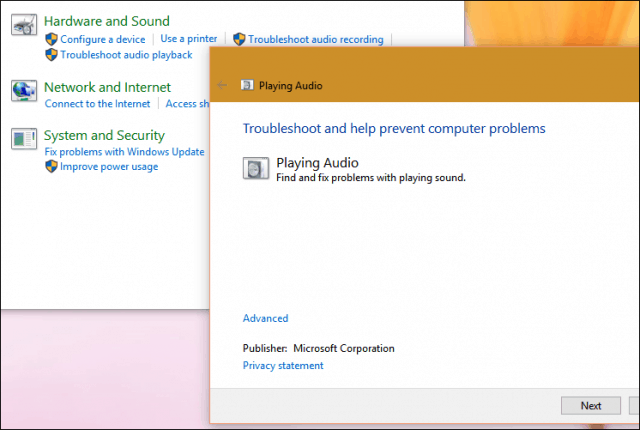
The audio troubleshooter might be able to fix audio problems automatically.
To run the troubleshooter
In the search box on the taskbar, type audio troubleshooter, select Fix and find problems with playing sound from the results, then select Next.
Select the device you want to troubleshoot and then continue through the troubleshooter.
You can also launch the troubleshooter from audio Settings. Select Start > Settings > System > Sound > Troubleshoot.
If running the troubleshooter doesn’t help, continue to the next tip.
To check for updates
Select Start > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates.
Do one of the following:
If the status says «You’re up to date, go to the next tip.
If the status says «Updates are available,» select Install now.
Select the updates you want to install, then select Install.
Restart your PC and see if your sound is working properly.
If that didn’t solve your problem, continue to the next tip.
Try these steps
Check your speaker and headphone connections for loose cords or cables. Make sure all cords and cables are plugged in.
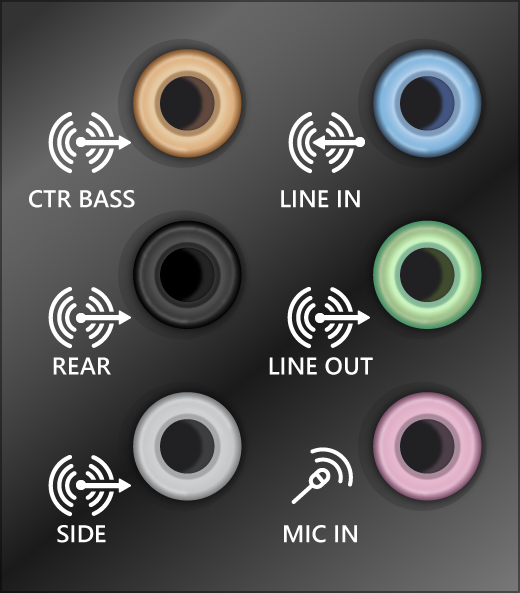
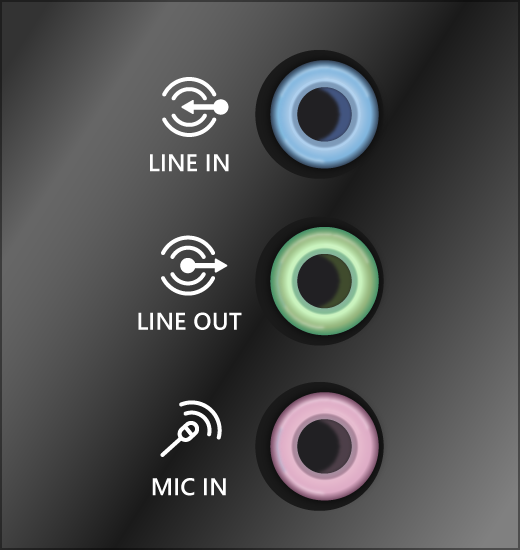
If you have multiple 5mm jacks to plug into, especially on a surround sound system, make sure all cords and cables are plugged into the correct jack.
If it’s not clear which jack goes with which cord, consult your hardware manufacturer, or try the most obvious outputs one at a time and see if they work.
Note: Some systems use a green jack for output and pink for mic input and others will be labeled «headphone» or «microphone.»
Make sure the power is turned on and check the volume level.
Make sure the mute setting is not turned on, and try turning up all the volume controls.
Remember some speakers and apps have their own volume controls. Be sure to check them all.
Try connecting your speaker and headphones to a different USB port.
It’s possible that your speakers won’t work when your headphones are plugged in. Unplug your headphones and see if that helps.
If your cables and volume are OK, see the next sections for additional troubleshooting.
Check to make sure your audio devices aren’t muted and haven’t been disabled.
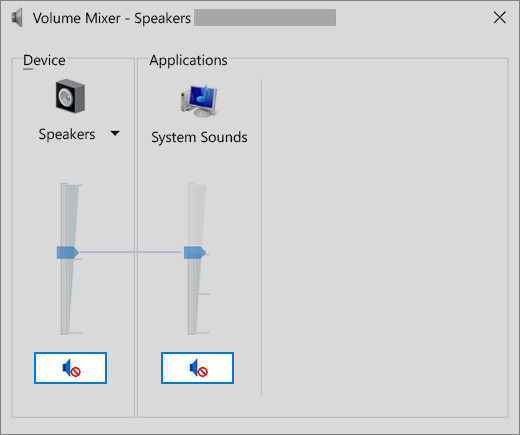
Right-click the Speakers icon on the taskbar, and then select Open Volume mixer.
You’ll see a set of volume controls for your devices. Make sure none of them are muted. If any of them are muted, you’ll see a red circle with a line through it next to the volume control. In that case, select the volume control to unmute.
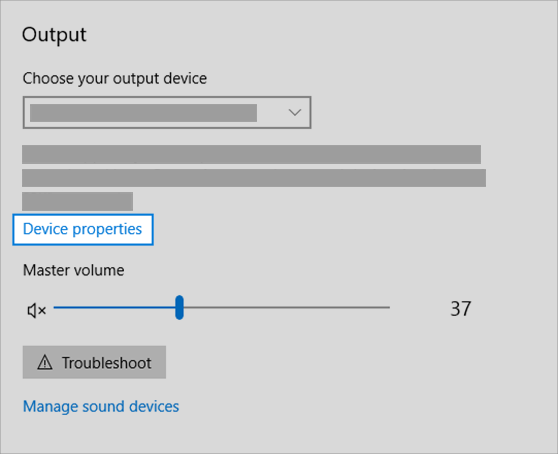
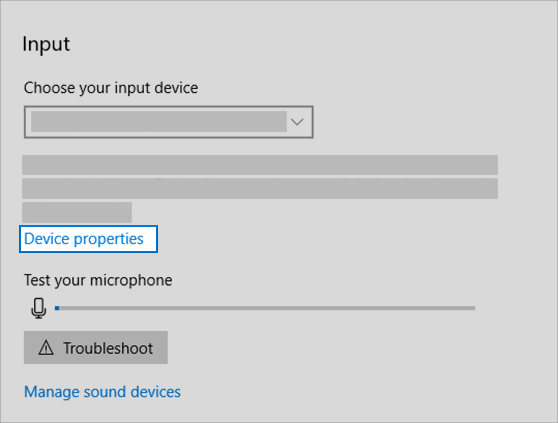
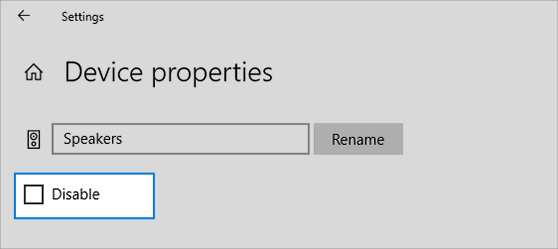
Check your device properties to make sure that your devices have not been disabled by mistake. Select Start > Settings > System > Sound .
Select your audio device, and then select Device properties. Be sure to select Device properties for both the output and input devices.
Make sure the Disable check box is cleared for the output and input devices.
If that didn’t solve your problem, continue to the next tip.
Hardware problems can be caused by outdated or malfunctioning drivers. Make sure your audio driver is up to date and update it if needed. If that doesn’t work, try uninstalling the audio driver (it will reinstall automatically). If that doesn’t work, try using the generic audio driver that comes with Windows. If you’re having audio issues after installing updates, try rolling back your audio driver.
To update your audio driver automatically
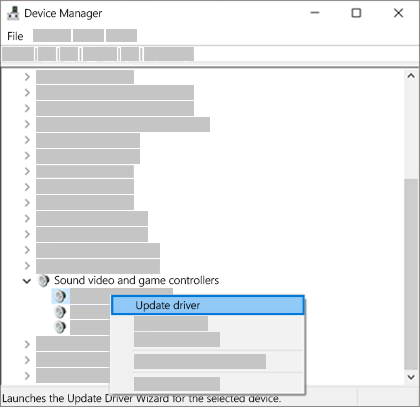
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
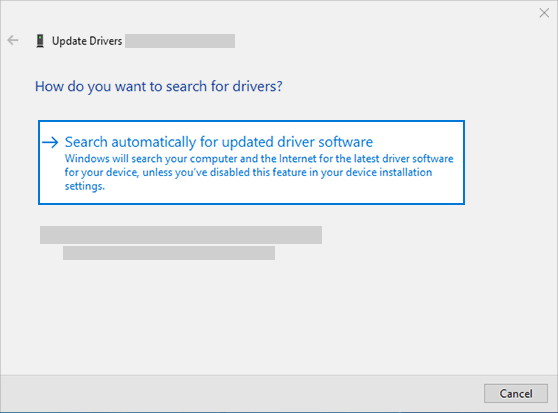
Right-click the listing for your sound card or audio device, such as headphones or speakers, select Update driver, then select Search automatically for updated driver software. Follow the instructions to complete the update.
If Windows doesn’t find a new driver, look for one on the device manufacturer’s website and follow those instructions. If that doesn’t work, try uninstalling your audio driver.
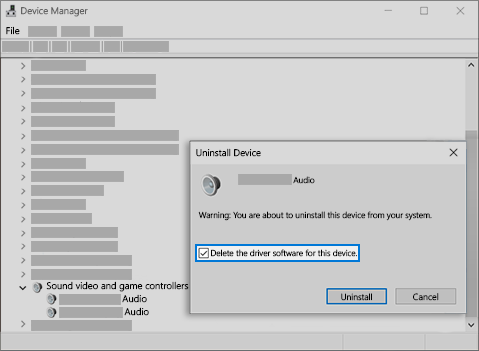
To uninstall your audio driver
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
Right-click the listing for your sound card or audio device, select Uninstall device, select the Delete the driver software for this device check box, and then select Uninstall.
Restart your PC.
Note: Be sure to save documents and any other current work before you restart.
This restart will automatically prompt your PC to reinstall your audio driver.
To restart, select Start > Power > Restart .
If those options didn’t work, try using the generic audio driver that comes with Windows.
To use the generic audio driver that comes with Windows
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
Right-click the listing for your sound card or audio device, then select Update driver > Browse my computer for driver software > Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer.
Select the audio device whose driver you want to update, select Next, and then follow the instructions to install it.
If these steps didn’t solve your audio issue, visit your device manufacturer’s website and install the most recent audio/sound drivers for your device. Following is an example of a driver download page for a sound device manufacturer.
If you have audio issues after installing updates
If your audio was working before you ran Windows Update and now isn’t working, try rolling back your audio driver.
To roll back your audio driver
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
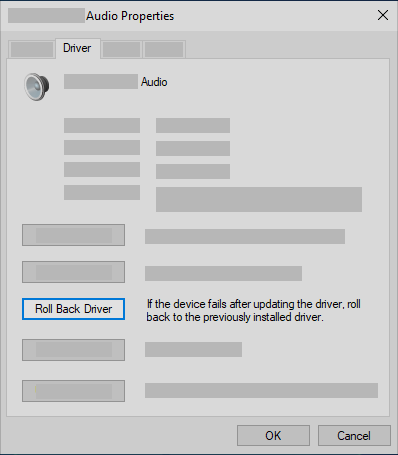
Right-click the listing for your sound card or audio device, then select Properties.
Select the Driver tab, then select Roll Back Driver.
Read and follow the instructions and then select Yes if you want to roll back your audio driver.
If rolling back your audio driver didn’t work or wasn’t an option, you can try to restore your PC from a system restore point.
Restore your PC from a system restore point
When Microsoft installs updates on your system, we create a system restore point in case problems arise. Try restoring from that point and see if that fixes your sound problems. For more info, see «Restore from a system restore point» in Recovery options in Windows 10.
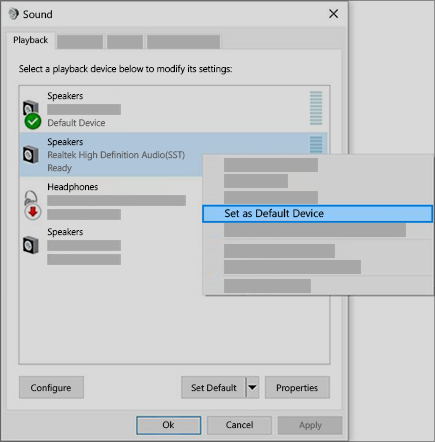
If you’re connecting to an audio device—such as headphones or speakers—using USB or HDMI, you might need to set that device as the default audio device. If you’re using an external monitor that doesn’t have built-in speakers, make sure that the monitor isn’t already selected as your default output device. if it is, you won’t have any audio. You can check that when you set your default output audio device. Here’s how:
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel, then select it from the results.
Select Hardware and Sound from the Control Panel, and then select Sound.
On the Playback tab, right-click the listing for your audio device, select Set as Default Device, and then select OK.
If setting your audio device as the default device doesn’t help, continue to the next tip for additional troubleshooting.
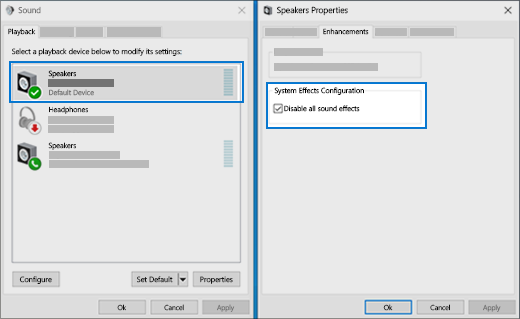
Sometimes having audio enhancements on can result in audio issues. Disabling them may resolve your issue.
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel, then select it from the results.
Select Hardware and Sound from the Control Panel, and then select Sound.
On the Playback tab, right-click the Default Device, and then select Properties.
On the Enhancements tab, select either the Disable all enhancements or the Disable all sound effects check box (depending on which option you see), select OK, and try to play your audio device.
If that doesn’t work, on the Playback tab, select another default device (if you have one), select either the Disable all enhancements or the Disable all sound effects check box (depending on which option you see), select OK, and try to play audio again. Do this for each default device.
If turning off audio enhancements doesn’t help, see the next sections for additional troubleshooting.
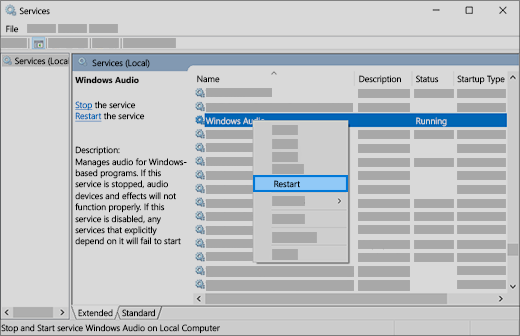
In the search box on the taskbar, type services, then select it from the results.
Select each of the following services, right-click, and then select Restart:
Windows Audio Endpoint Builder
Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
If restarting these services doesn’t resolve your issue, see the next sections for more troubleshooting.
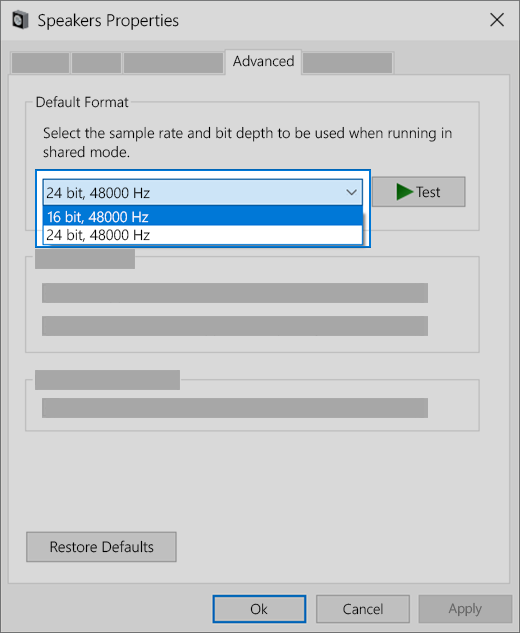
In the search box on the taskbar, type control panel, and then select it from the results.
Select Hardware and Sound from the Control Panel, and then select Sound.
On the Playback tab, right-click (or press and hold) Default Device, and then select Properties.
On the Advanced tab, under Default Format, change the setting, select OK,and then test your audio device. If that doesn’t work, try changing the setting again.
If trying different audio formats doesn’t help, see the next sections for additional troubleshooting.
Many updates require you to restart your device.
To check and see if you have installed updates pending and need to restart
Save your work and close all open applications.
Select Start > Power . If you have installed updates pending, you’ll see options to Update and restart and Update and shut down.
Select one of those restart options to apply the updates
If restarting doesn’t help, see the next section for additional troubleshooting.
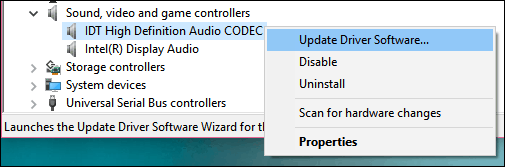
Some audio problems might be caused by an issue with the audio system’s IDT High Definition Audio CODEC. This can be fixed with a manual driver update which allows you to choose the sound driver you want to use.
Note: Not all systems will have an IDT High Definition Audio CODEC.
To check and see if you have one, and to manually update the driver
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager, then select it from the results.
Select the arrow next to Sound, video and game controllers to expand it.
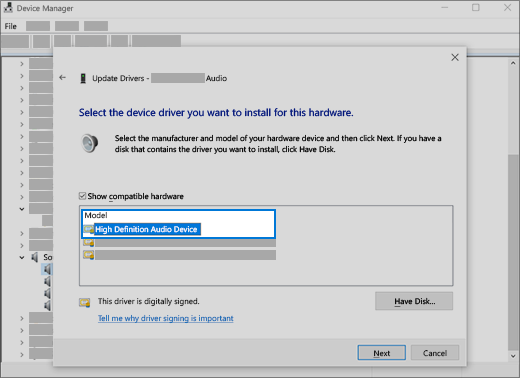
Look for IDT High Definition Audio CODEC. If it’s listed, right-click it and select Update driver, then select Browse my computer for driver software > Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer.
You’ll see a list of pre-installed drivers. Select High Definition Audio Device, and then select Next.
1. Select Start > Settings > Privacy , and then select Microphone from the left menu.
Under Allow access to the microphone on this device, select Change. Make sure the toggle is turned On.
If you’re having this issue with a specific app, scroll down to Choose which Microsoft Store apps can access your microphone and make sure that the toggle next to that app is turned On as well.