- В чём разница между папками «Program Files (x86)» и «Program Files» в Windows
- 32-битная и 64-разрядная Windows
- Что хранится в каждой папке
- Почему они разделяются
- Почему 32-битная папка называется (x86)
- Обычно это не имеет значения
- Program Files (x86) и Program Files – что это за папки на компьютере
- Программные файлы
- Program Files и Program Files (x86) что это?
- Можно ли удалить Program Files?
- Видео
- How do I use spaces in the Command Prompt?
- 11 Answers 11
- Spaces and Parenthesis in windows PATH variable screws up batch files
- 8 Answers 8
В чём разница между папками «Program Files (x86)» и «Program Files» в Windows
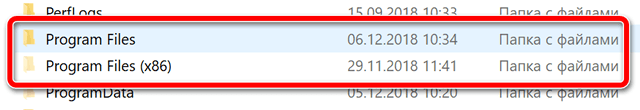
Весьма вероятно, на вашем компьютере Windows Вы обнаружите две папки «Program Files» и «Program Files (x86)». Если вы соскучитесь, вы увидите, что некоторые из ваших программ установлены в одну папку, а некоторые – в другую.
32-битная и 64-разрядная Windows
Первоначально Windows была доступна только в 32-разрядной версии. В 32-битных версиях Windows – даже 32-разрядных версиях Windows 10, которые по-прежнему доступны сегодня, – вы увидите только папку «Program Files».
Эта папка Program Files является рекомендуемым местом, где установленные программы должны хранить исполняемые файлы, данные и другие файлы. Другими словами, программы устанавливаются в папку Program Files.
В 64-разрядных версиях Windows 64-разрядные приложения устанавливаются в папку Program Files. Однако, 64-разрядные версии Windows также поддерживают 32-разрядные программы, и Microsoft не хочет, чтобы 32-битное и 64-битное программное обеспечение смешивались в одном месте. Таким образом, 32-разрядные программы устанавливаются в папку «Program Files (x86)».
Windows запускает 32-разрядные приложения в 64-разрядных версиях Windows с использованием WOW64.
Когда вы запускаете 32-разрядную программу в 64-разрядной версии Windows, уровень эмуляции WOW64 плавно перенаправляет доступ к файлу с «C:\Program Files» на «C:\Program Files (x86)». 64-разрядные программы по-прежнему используют обычную папку Program Files.
Что хранится в каждой папке
Таким образом, в 32-разрядной версии Windows у вас есть только папка «Program Files». Она содержит все установленные вами программы, все из которых являются 32-разрядными.
В 64-разрядной версии Windows 64-разрядные программы хранятся в папке «Program Files», а 32-разрядные программы хранятся в папке «Program Files (x86)».
Вот почему разные программы распределяются между двумя папками Program Files, кажущимися случайными. В папке «Program Files» находятся 64-разрядные, а в папке «Program Files (x86)» – 32-разрядные приложения.
Почему они разделяются
Это функция совместимости предназначена для старых 32-разрядных программ. Эти 32-разрядные программы могут не знать, что 64-разрядная версия Windows даже существует, поэтому Windows изолирует их от 64-битного кода.
32-разрядные программы не могут загружать 64-разрядные библиотеки (DLL-файлы) и могут вылетать, если они попытаются загрузить определенный DLL-файл и обнаружат 64-битную версию вместо 32-разрядной. То же самое касается 64-разрядных программ. Сохранение различных программных файлов для разных архитектур процессоров предотвращает подобные ошибки.
Например, предположим, что Windows использует одну папку Program Files. 32-разрядное приложение может искать файл DLL Microsoft Office, расположенный в C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office, и попытаться загрузить его. Однако, если у вас установлена 64-разрядная версия Microsoft Office, приложение будет аварийно завершено и не будет работать должным образом. С отдельными папками это приложение не сможет найти DLL вообще, потому что 64-разрядная версия Microsoft Office будет в C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office, а 32-разрядное приложение будет искать в C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office.
Это также помогает, когда разработчик создает как 32-битную, так и 64-разрядную версию приложения, особенно если они должны быть установлены сразу обе. 32-разрядная версия автоматически устанавливается в C:\Program Files (x86), а 64-разрядная версия автоматически устанавливается в C:\Program Files. Если бы Windows использовала одну папку, разработчику приложения пришлось бы установить 64-разрядную папку в другую папку, чтобы разделить их.
Почему 32-битная папка называется (x86)
Вы не всегда будете видеть термины «32-разрядная» или «64-битная». Вместо этого иногда вы можете встретить «x86» и «x64» для обозначения этих двух разных архитектур. Это потому, что на ранних компьютерах использовался чип Intel 8086. Исходные чипы были 16-битными, но более новые версии стали 32-битными. «X86» теперь относится к до 32-битной архитектуре – будь то 16-разрядная или 32-разрядная. Новую 64-битную архитектуру называют «x64».
Это означает, что «Program Files (x86)» – это реализация папки Program Files для программ с использованием старой архитектуры процессоров x86. Заметим, однако, что 64-разрядные версии Windows не могут запускать 16-разрядный код .
Обычно это не имеет значения
Обычно не имеет значения, хранятся ли файлы программ в Program Files или Program Files (x86). Windows автоматически устанавливает программы в правильную папку, поэтому вам не нужно об этом думать. Программы отображаются в меню «Пуск» и функционируют нормально, независимо от того, где они установлены. Просто позвольте вашим программам автоматически решать, какую папку Program Files использовать.
Если вы используете переносное приложение, оно может запускаться из любой папки в вашей системе, поэтому вам не нужно беспокоиться о том, где его разместить.
Вместе с тем, иногда нам нужно знать, где хранится программа. Например, вы хотите войти в свой каталог Steam для резервного копирования некоторых файлов. Вы найдете его в C:\Program Files (x86), так как Steam – это 32-разрядная программа.
Program Files (x86) и Program Files – что это за папки на компьютере
Если Вы являетесь пользователем операционной системы от компании Microsoft, то в корне системного диска могли заметить следующий элемент — Program Files x86 что это за папка на компьютере Windows? Предлагаю разобраться в теме и получить максимум ответов!
Программные файлы
Именно так дословно переводиться название каталога. Он является стандартным в ОС, начиная с первых версий Виндовс. Изначально в нём содержится лишь несколько вложенных директорий, связанных с предустановленным функционалом «операционки» — антивирусом, почтовым клиентом, медиа проигрывателем, консолью PowerShell и т.д.:
Но со временем количество содержимого увеличивается. Это связано с установкой различных пользовательских приложений, игр. Скорее всего, Вы обращали внимание, что в процессе инсталляции софта нужно указать — куда копировать контент. Выглядит это примерно следующим образом:
В итоге, папка Program Files увеличивается в размере, в ней появляются дополнительные элементы, некоторые из которых занимают десятки гигабайт (если Вы устанавливаете современные игры). То есть, во вложенных папках хранятся практически все данные программ.
Переходим к следующему вопросу.
Program Files и Program Files (x86) что это?
У некоторых пользователей есть только одна из указанных папок, а другие находят у себя вторую, с окончанием «x86». Где логика? От чего зависит ситуация?
Не нужно пугаться, искать проблему там, где её нет. Многие сразу же думают, что в Виндовс проник вирус, который создал дубликат с похожим названием и содержимым, чтобы незаметно «поедать» личную информацию и нагружать процессор.
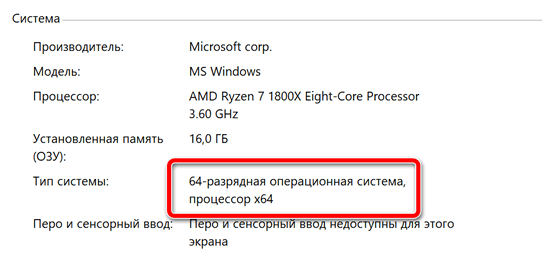
На самом деле, всё зависит от разрядности Windows (переходите по ссылке и читайте детальный обзор, чтобы мне не пришлось повторяться).
- Если у Вас система 32-х битная, то в корне диска С обнаружите только один каталог «Program Files». И все новые программы по умолчанию будут копироваться туда;
- В 64-х битной ОС создается две директории — та, которая заканчивается на «x86» предназначена для расположения софта, разработанного исключительно для систем x64.
В качестве эксперимента, можете перейти на страницу скачивания архиватора 7-Zip , там есть две ссылки Download» для получения установочного файла версии 32-bit или 64-bit. В зависимости от того, какой выберете и запустите, копирование будет осуществляться в разные каталоги на компьютере. Но это только при условии, что у Вас Windows 64 бит и есть обе папки «Програм_Файлс».
Можно ли удалить Program Files?
Если внимательно читали всё вышеизложенное, то вывод напрашивается сам по себе — ничего трогать не нужно. Иначе установленные утилиты перестанут корректно работать.
Даже если не хватает места на системном накопителе, то следует прибегнуть к более эффективным способам освобождения пространства:
Удалить Program Files (x86) целиком нельзя, а вот вложенные объекты — можно. Но поступать так стоит лишь в том случае, если Вы избавились от ненужного приложения, а папка от него осталась. Такое часто случается, я сам периодически захожу в «Програм-файлс», просматриваю содержимое, подчищаю следы уже неактуальных утилит.
Видео

Надеюсь, что эта инструкция немножко прояснила ситуацию и помогла понять — Program Files x86 что это за папка на компьютере Windows.
How do I use spaces in the Command Prompt?
How can I use spaces in the Windows Command Line?
11 Answers 11
Single quotation marks won’t do in that case. You have to add quotation marks around each path and also enclose the whole command in quotation marks:
I just figured out that for a case where the path involves the use of white space characters, for example, when I need to access the app xyz which location is :
To run this from windows cmd prompt, you need to use
If double quotes do not solve the issue then try e.g.
to get a list of alternative file or directory names. Example output:
Now use the short 8 character file or folder name in the 5th column, e.g. PROGRA
1.XML, in your commands. For instance:
Enclose the paths containing spaces with double quotes.
I prefer to enclose the command in () which is valid batch which makes it a bit easier to read:
Try to provide complex pathnames in double-quotes (and include file extensions at the end for files.)
CMD interprets text with double quotes («xyz») as one string and text within single quotes (‘xyz’) as a command. For example:
FOR %%A in (‘dir /b /s *.txt’) do (echo «%%A»)
And one good thing, cmd is not* case sensitive like bash. So «New fiLE.txt» and «new file.TXT» is alike to it.
*Note: The %%A variables in above case is case-sensitive (%%A not equal to %%a).
this worked for me in a batch file
Just add Quotation Mark
Example:«C:\Users\User Name»
Hope it got Solved!
You should try using quotes.
Spaces in the Commend Prompt (in a VBA Shell command code line)
I had a very similar problem which ended up being a space in the command prompt when automating via VBA to get the contents from the command window into a text file. This Thread was one of many I caught along the way that didn’t quite get me the solution.
So this may help others with a similar problem: Since the syntax with quotes is always difficult to get right , I think showing some specific examples is always useful. The additional problem you get using the command prompt in VBA via the Shell thing, is that the code line often won’t error when something goes wrong: in fact a blink of the black commend window misleads into thinking something was done.
As example… say I have a Folder, with a text file in it like at
The space there in the folder name gives the problem.
Something like this would work, assuming the Folder, AlansFolder, exists
This won’t work. (It won’t error).
Including quote pairs around the path will make it work
( By the way, if the text file does not exist, then it will be made).
With the benefit of hindsight, we can see that my solution does tie up approximately with some already given..
Converting that code line to a manual given command we would have
That seems to work
This works also
This final form also works and ties up with the solution from sacra ….” You have to add quotation marks around each path and also enclose the whole command in quotation marks “ …..
Spaces and Parenthesis in windows PATH variable screws up batch files
So, my path variable (System->Adv Settings->Env Vars->System->PATH) is set to:
Although, obviously, without the newlines.
Notice the lines containing PathWithSpaces — the first has no spaces, the second has a space, and the third has a space followed by a parenthesis.
Now, notice the output of this batch file:
or specifically the line:
So, what is this bullshit?
- Directory in path that is properly escaped with quotes, but with no spaces = fine
- Directory in path that is properly escaped with quotes, and has spaces but no parenthesis = fine
- Directory in path that is properly escaped with quotes, and has spaces and has a parenthesis = ERROR
Whats going on here? How can I fix this? I’ll probably resort to a junction point to let my tools still work as workaround, but if you have any insight into this, please let me know 🙂
8 Answers 8
This can happen if there are unescaped parentheses in a line inside a «block» (which also uses parentheses for delimiting).
You can usually fix it by turning on delayed expansion and use variables with !var! instead of %var% . There isn’t much more advice I could give without seeing the code.
Note for Windows users on 64-bit systems
1 = ‘Program Files’ Progra
2 = ‘Program Files(x86)’
There should either (a) not be any quotes in the MS-Windows PATH environmental variable (PATH command) or (b) there should be quotes surrounding the entire expression following the (SET command). Unfortunately, this is not very well documented by MS, although they do state that if quotes are used, they will be included in the value of the variable (Windows XP Command Line Reference).
This can cause problems that are inconsistent and therefore difficult to diagnose. For example if your path includes «C:\Python27», your machine will say «‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.» when you try to execute python. However some libraries may still be available.
You do not need to «escape» spaces or parentheses. If you need to escape special characters, then put quotes around the entire expression, including the variable name.
or you can use parentheses too.
Note, double quotes must come in pairs.
However, there probably are not any characters that are valid pathnames, that would cause a problem with the SET command.
The solution they suggest is to use delayed expansion.
For setting a path in an if block, rather than using SET PATH= , you should probably use the PATH command.
For other variables, another solution may be to use quotes, but around the whole thing:
Joey in his answer says
This can happen if there are unescaped parentheses in a line inside a «block» (which also uses parentheses for delimiting).
and that’s true. If there are unescaped parentheses one should, well escape them. That’s what I did; I replaced
and this solved the problem.
I’ve experienced something similar. Microsoft explains the issue here: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/329308
Basically, instead of changing the Path variable via System->Adv Settings->Env Vars->System->PATH, try
In Windows 8 I’ve found very little success with any of these methods. Parentheses do not work, quotes work, but the «path» you modify this way isn’t the path that gets used for locating executables, instead cmd still seems to be using the system path it inherited when you opened the window.
example: after determining the processor architecture, I want to add a couple of paths to the PATH environment variable. Actually, even just adding them temporarily would work since I only need them while a batch file is running. But that doesn’t even work.
echo %path% displays the system PATH at the time the cmd was launched.
set path=»%path%;%programfiles(x86)%\company\program\subdir» works but now %path% contains everything surrounded by quotes, and if I try to run a program in subdir from somewhere else, it fails. Using parentheses around the whole thing instead of quotes does not work.
Another thing I’ve noticed is that the same command will work if entered interactively in cmd , but not if encountered in a batch file. That’s frightening. Yet another oddity is the intermittent loss of the last character of an environment variable’s value! Another inconsistency is with third party programs: some can handle a %var% as a parameter, others don’t.