В какой папке Windows хранит ярлыки меню «Пуск»
В этой статье вы узнаете, как открыть папку «Пуск» в Windows 10.
Вам нравится держать меню Пуск в чистоте, порядке и организованно? Все, что вам нужно сделать, это открыть специальную папку «Пуск» и упорядочить все, что душе угодно. Далее показано, как управлять ярлыками в главном меню Windows.
В Windows 10 предусмотрены различные способы настройки меню «Пуск», но вы все равно можете организовать свои приложения так же, как всегда — упорядочив содержимое папки «Пуск» в Windows. Со всеми изменениями меню «Пуск» за последние годы способ открытия папки «Пуск» изменился от версии к версии. Мы расскажем, как открыть папку «Пуск» в Windows 10, этот способ также подходит для предыдущих версий Windows.
Организация списка «Все приложения» в Windows 10 несколько сложнее, чем в предыдущих версиях. Следует иметь в виду одно большое отличие: в Windows 10 используется внутренняя база данных для создания списка «Все приложения» в меню «Пуск». Это означает, что папка будет отображать не всё содержимое вашего меню «Пуск» — только обычные приложения для рабочего стола. Вы не увидите приложения, загруженные из магазина Windows, поэтому вам придётся управлять ими в другом месте.
Следует также помнить, что Windows создаёт меню «Пуск» из двух мест. Одна папка содержит общесистемные папки и ярлыки, которые появляются в меню «Пуск» любого пользователя, вошедшего в систему. Существует также папка для конкретного пользователя, которая содержит ярлыки и папки, отображаемые только для текущего пользователя, вошедшего в систему. Если вы когда-либо устанавливали приложение и должны были выбрать, устанавливать ли его только для текущего пользователя или для всех пользователей, то вы должны понимать, что это значит. Эти две папки объединяются для создания элементов, которые вы видите в меню «Пуск».
Windows 10: как открыть меню «Пуск» в проводнике
Вы всегда можете получить доступ к папкам «Пуск» в вашей системе в проводнике. Просто запустите его и перейдите в одно из следующих мест (совет: вы можете скопировать эти места и вставить их в адресную строку Проводника).
Вот местоположение глобальной папки «Пуск» для всех пользователей:
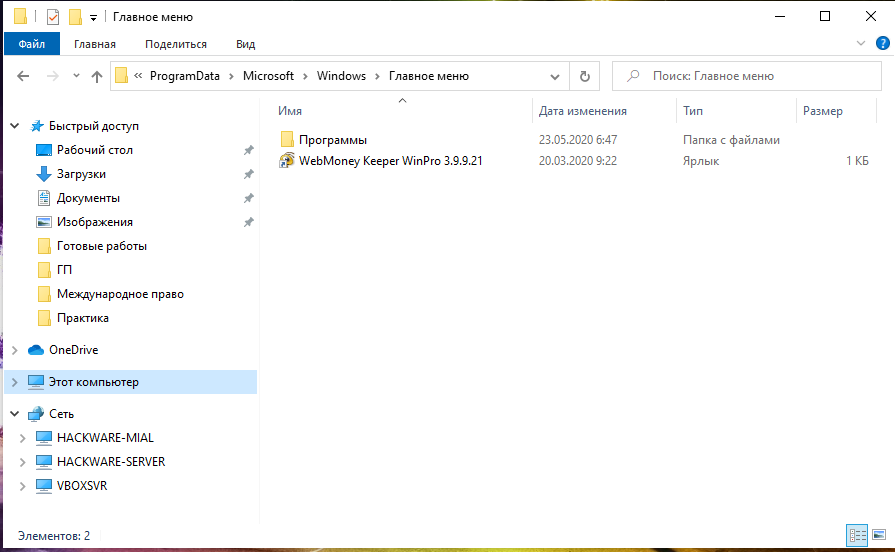
А вот местоположение личной папки «Пуск» для текущего пользователя, вошедшего в систему:
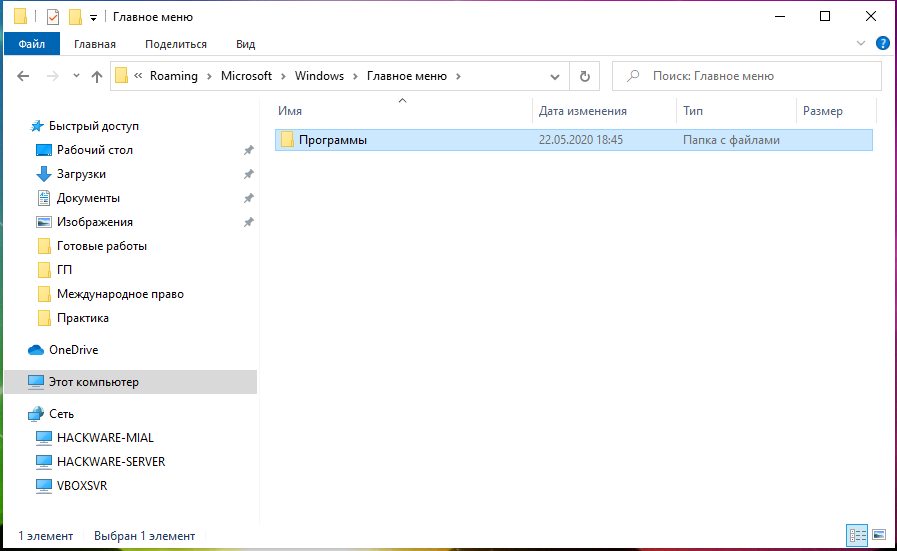
Обратите внимание, что переменная %appdata% — это просто ярлык, который приведёт вас в папку AppData\Roaming внутри структуры папок текущего пользователя.
Поэтому, если по какой-то причине вам нужно организовать личную папку «Пуск» для другой учётной записи пользователя, отличной от той, в которой вы в данный момент вошли, вы можете просто перейти в то же место в их пользовательской папке. Например, если имя учётной записи пользователя было «mial», вы можете перейти в следующее местоположение:
И если вы думаете, что будете регулярно посещать эти папки, сделайте для них ярлыки, чтобы их было легче найти в следующий раз.
start
Starts a separate Command Prompt window to run a specified program or command.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Specifies the title to display in the Command Prompt window title bar. | |
| /d |
. ]]
Remarks
You can run non-executable files through their file association by typing the name of the file as a command.
If you run a command that contains the string CMD as the first token without an extension or path qualifier, CMD is replaced with the value of the COMSPEC variable. This prevents users from picking up cmd from the current directory.
If you run a 32-bit graphical user interface (GUI) application, cmd does not wait for the application to quit before returning to the command prompt. This behavior does not occur if you run the application from a command script.
If you run a command that uses a first token that does not contain an extension, Cmd.exe uses the value of the PATHEXT environment variable to determine which extensions to look for and in what order. The default value for the PATHEXT variable is:
Note that the syntax is the same as the PATH variable, with semicolons (;) separating each extension.
When searching for an executable file, if there is no match on any extension, start checks to see if the name matches a directory name. If it does, start opens Explorer.exe on that path.
Examples
To start the Myapp program at the command prompt and retain use of the current Command Prompt window, type:
To view the start command-line help topic in a separate maximized Command Prompt window, type:
Windows commands
All supported versions of Windows (server and client) have a set of Win32 console commands built in.
This set of documentation describes the Windows Commands you can use to automate tasks by using scripts or scripting tools.
Prerequisites
The information that is contained in this topic applies to:
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel)
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows 10
- Windows 8.1
Command shell overview
The Command shell was the first shell built into Windows to automate routine tasks, like user account management or nightly backups, with batch (.bat) files. With Windows Script Host you could run more sophisticated scripts in the Command shell. For more information, see cscript or wscript. You can perform operations more efficiently by using scripts than you can by using the user interface. Scripts accept all Commands that are available at the command line.
Windows has two command shells: The Command shell and PowerShell. Each shell is a software program that provides direct communication between you and the operating system or application, providing an environment to automate IT operations.
PowerShell was designed to extend the capabilities of the Command shell to run PowerShell commands called cmdlets. Cmdlets are similar to Windows Commands but provide a more extensible scripting language. You can run Windows Commands and PowerShell cmdlets in Powershell, but the Command shell can only run Windows Commands and not PowerShell cmdlets.
For the most robust, up-to-date Windows automation, we recommend using PowerShell instead of Windows Commands or Windows Script Host for Windows automation.
You can also download and install PowerShell Core, the open source version of PowerShell.
Incorrectly editing the registry may severely damage your system. Before making the following changes to the registry, you should back up any valued data on the computer.
To enable or disable file and directory name completion in the Command shell on a computer or user logon session, run regedit.exe and set the following reg_DWOrd value:
To set the reg_DWOrd value, use the hexadecimal value of a control character for a particular function (for example, 0 9 is Tab and 0 08 is Backspace). User-specified settings take precedence over computer settings, and command-line options take precedence over registry settings.
Command-line reference A-Z
To find information about a specific command, in the following A-Z menu, click the letter that the command starts with, and then click the command name.
start start
Запускает отдельное окно командной строки для запуска указанной программы или команды. Starts a separate Command Prompt window to run a specified program or command.
Синтаксис Syntax
Параметры Parameters
| Параметр Parameter | Описание Description |
|---|---|
| Задает заголовок, отображаемый в строке заголовка окна командной строки . Specifies the title to display in the Command Prompt window title bar. | |
| /d |
. ]]
Комментарии Remarks
Вы можете запускать неисполняемые файлы с помощью сопоставления файлов, вводя имя файла в виде команды. You can run non-executable files through their file association by typing the name of the file as a command.
При выполнении команды, содержащей строку CMD в качестве первого маркера без квалификатора расширения или пути, команда CMD заменяется значением переменной COMSPEC. If you run a command that contains the string CMD as the first token without an extension or path qualifier, CMD is replaced with the value of the COMSPEC variable. Это не позволяет пользователям выбирать cmd из текущего каталога. This prevents users from picking up cmd from the current directory.
Если вы запускаете приложение с 32-битным графическим пользовательским интерфейсом (GUI), программа cmd не ждет завершения работы приложения, прежде чем вернуться в командную строку. If you run a 32-bit graphical user interface (GUI) application, cmd does not wait for the application to quit before returning to the command prompt. Такое поведение не происходит при запуске приложения из командного скрипта. This behavior does not occur if you run the application from a command script.
При выполнении команды, использующей первый токен, который не содержит расширение, Cmd.exe использует значение переменной среды ПАСЕКСТ, чтобы определить, какие расширения следует искать и в каком порядке. If you run a command that uses a first token that does not contain an extension, Cmd.exe uses the value of the PATHEXT environment variable to determine which extensions to look for and in what order. Значение по умолчанию для переменной ПАСЕКСТ: The default value for the PATHEXT variable is:
Обратите внимание, что синтаксис аналогичен переменной PATH с точкой с запятой (;) Отделение каждого расширения. Note that the syntax is the same as the PATH variable, with semicolons (;) separating each extension.
При поиске исполняемого файла, если нет совпадения с каким-либо расширением, запустите проверку, чтобы проверить, совпадает ли имя с именем каталога. When searching for an executable file, if there is no match on any extension, start checks to see if the name matches a directory name. Если это так, то Start открывает Explorer.exe по этому пути. If it does, start opens Explorer.exe on that path.
Примеры Examples
Чтобы запустить программу MyApp из командной строки и использовать текущее окно командной строки , введите: To start the Myapp program at the command prompt and retain use of the current Command Prompt window, type:
Чтобы просмотреть раздел справки по командной строке в отдельном окне командной строки с развернутым окном, введите: To view the start command-line help topic in a separate maximized Command Prompt window, type:



