- Windows start rdp service
- Постановка задачи
- Методы активации доступа по RDP
- Как удаленно включить RDP
- Классический метод включения удаленного рабочего стола
- Как включить удаленный рабочий стол (RDP) через PowerShell
- Как удаленно включить RDP через групповую политику
- General Remote Desktop connection troubleshooting
- Check the status of the RDP protocol
- Check the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer
- Check the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer
- Check whether a Group Policy Object (GPO) is blocking RDP on a local computer
- Check whether a GPO is blocking RDP on a remote computer
- Modifying a blocking GPO
- Check the status of the RDP services
- Check that the RDP listener is functioning
- Check the status of the RDP listener
- Check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate
- Check the permissions of the MachineKeys folder
- Check the RDP listener port
- Check that another application isn’t trying to use the same port
- Check whether a firewall is blocking the RDP port
Windows start rdp service

Постановка задачи
Разобрать все методы, позволяющие вам включать RDP доступ на Windows системах, понимать какие ключи реестра за это отвечают и как это можно применять на практике.
Методы активации доступа по RDP
Я могу выделить вот такие способы:
- Классический метод с использованием оснастки свойств системы Windows
- С помощью оболочки и командлетов PowerShell
- Удаленное включение, через реестр Windows
- Через GPO политику
Как удаленно включить RDP
И так начну с более интересного метода. Предположим, что у вас есть сервер или компьютер, от которого у вас есть учетные данные для входа, но не активен вход через удаленный рабочий стол. И вам хотели бы его активировать. Делается все это просто. Тут мы воспользуемся удаленным доступом через консоль. Откройте окно выполнить (Сочетание клавиш WIN и R одновременно) и в открывшемся окне введите:
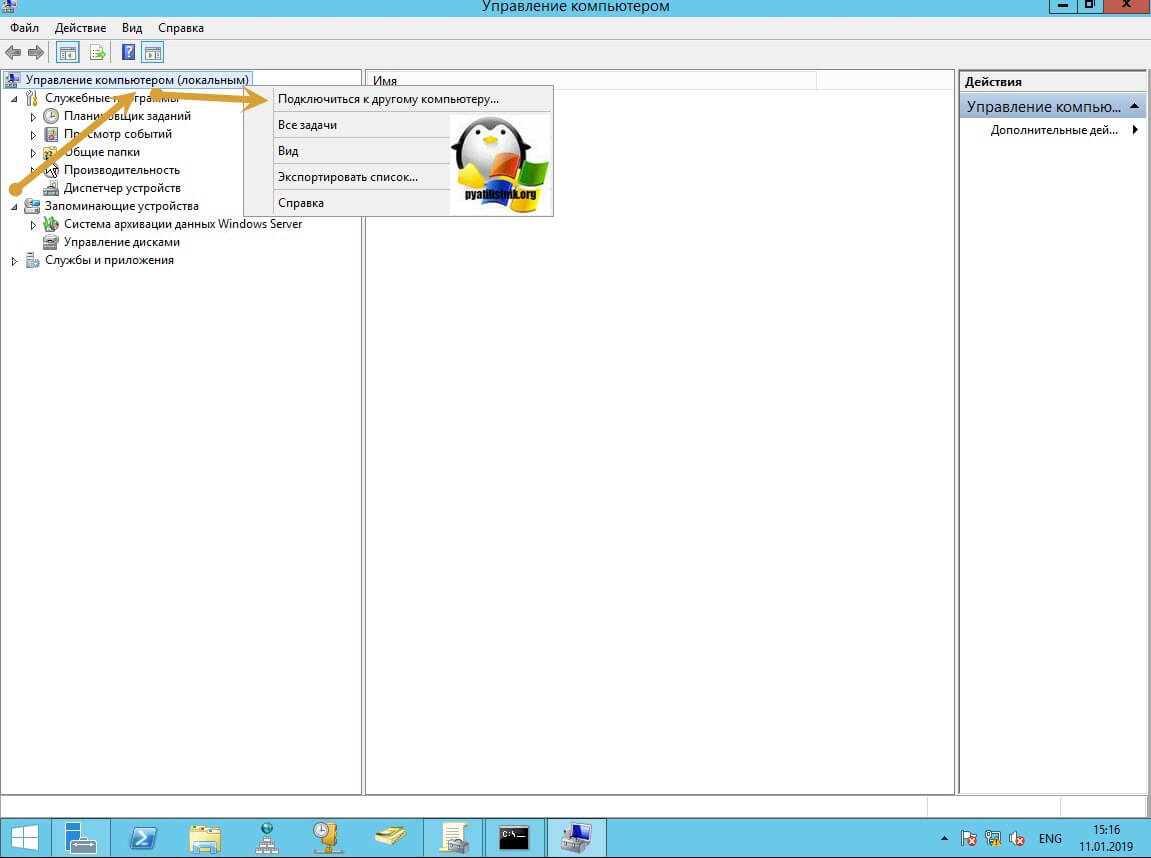
Далее щелкаете по корню «Управление компьютера (локальным)» правым кликом и в открывшемся окне выберите пункт «Подключиться к другому компьютеру»
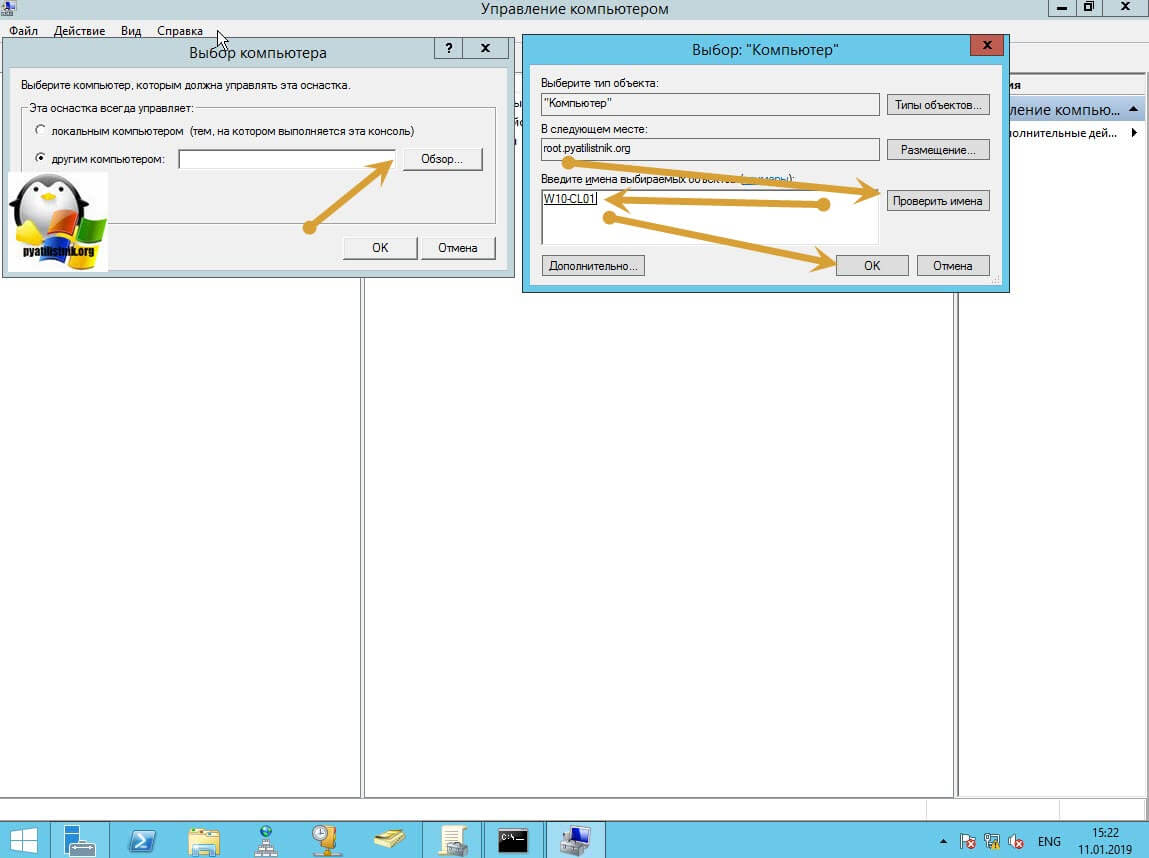
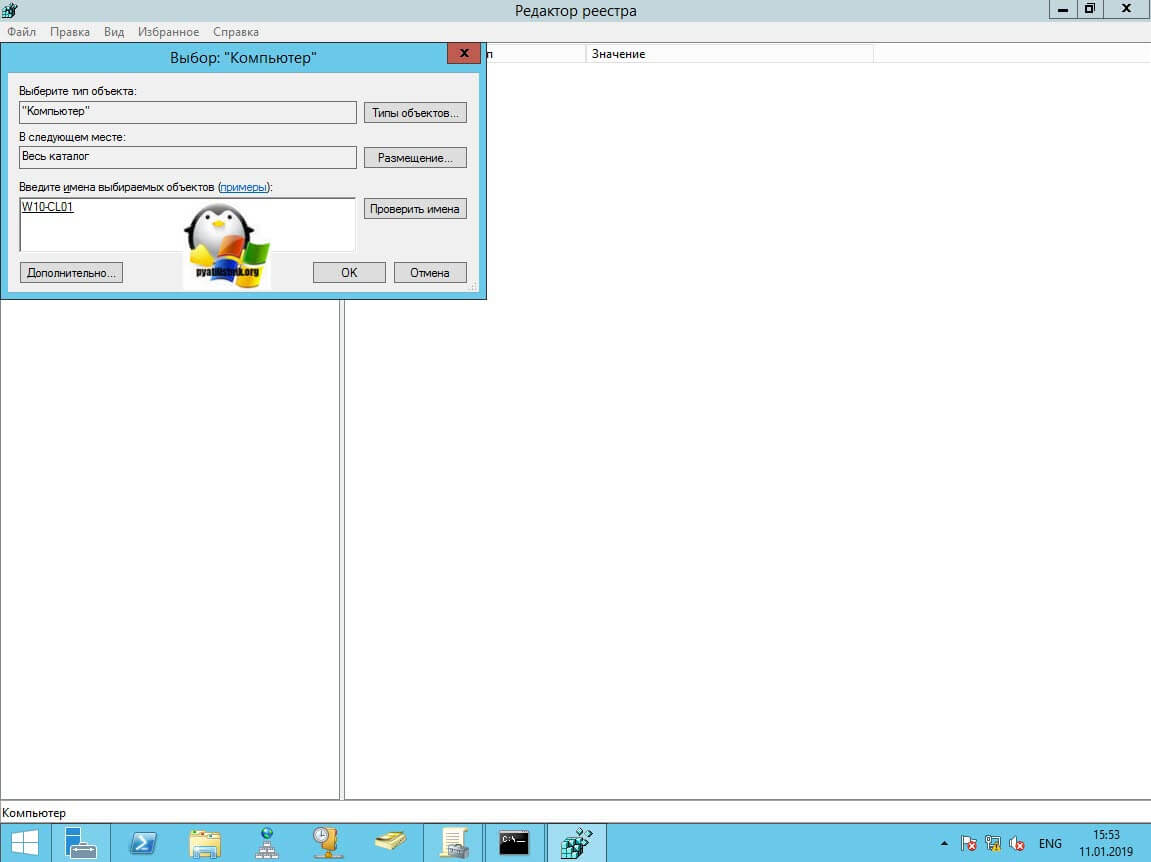
В окне выбора компьютера, вам необходимо нажать кнопку «Обзор», которое откроет второе окошко, где нужно выбрать необходимый компьютер, так как у меня доменная сеть, то мне еще проще. В моем примере это будет компьютер с операционной системой Windows 10 под DNS-именем W10-CL01. Нажимаем ок.
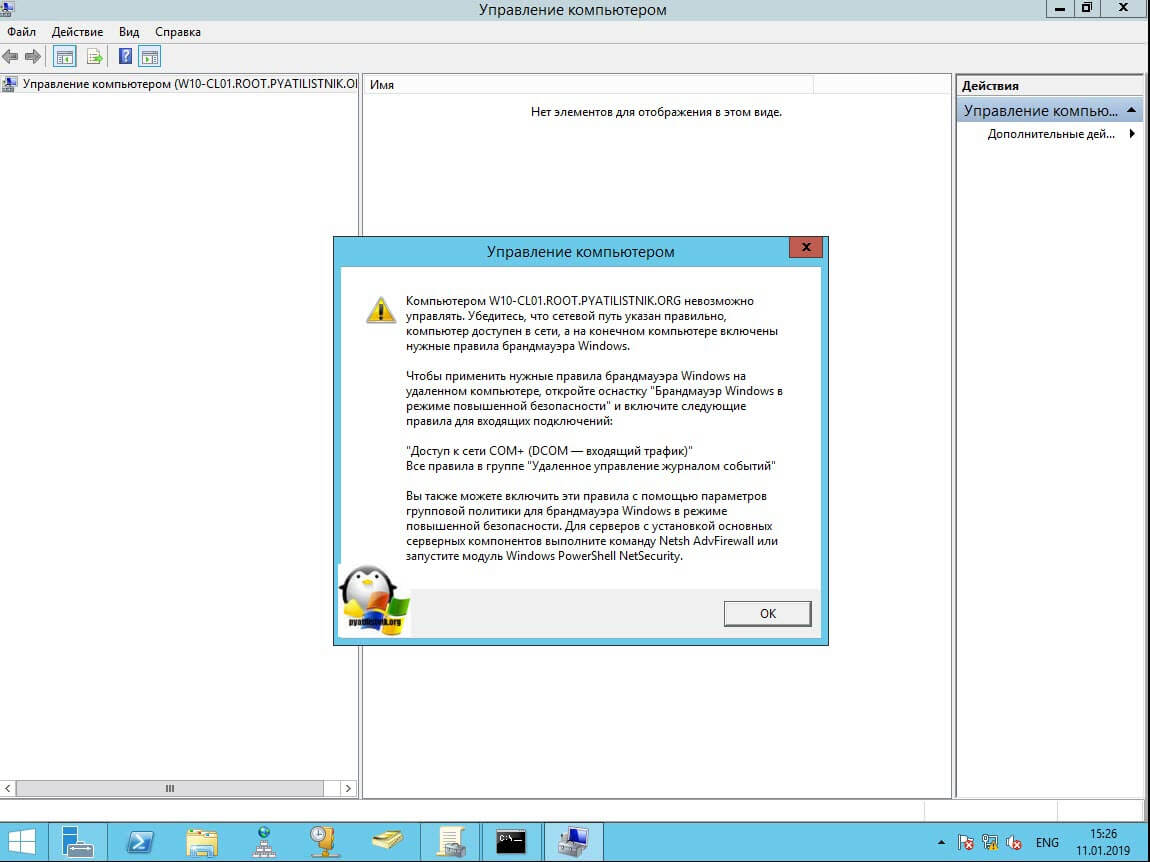
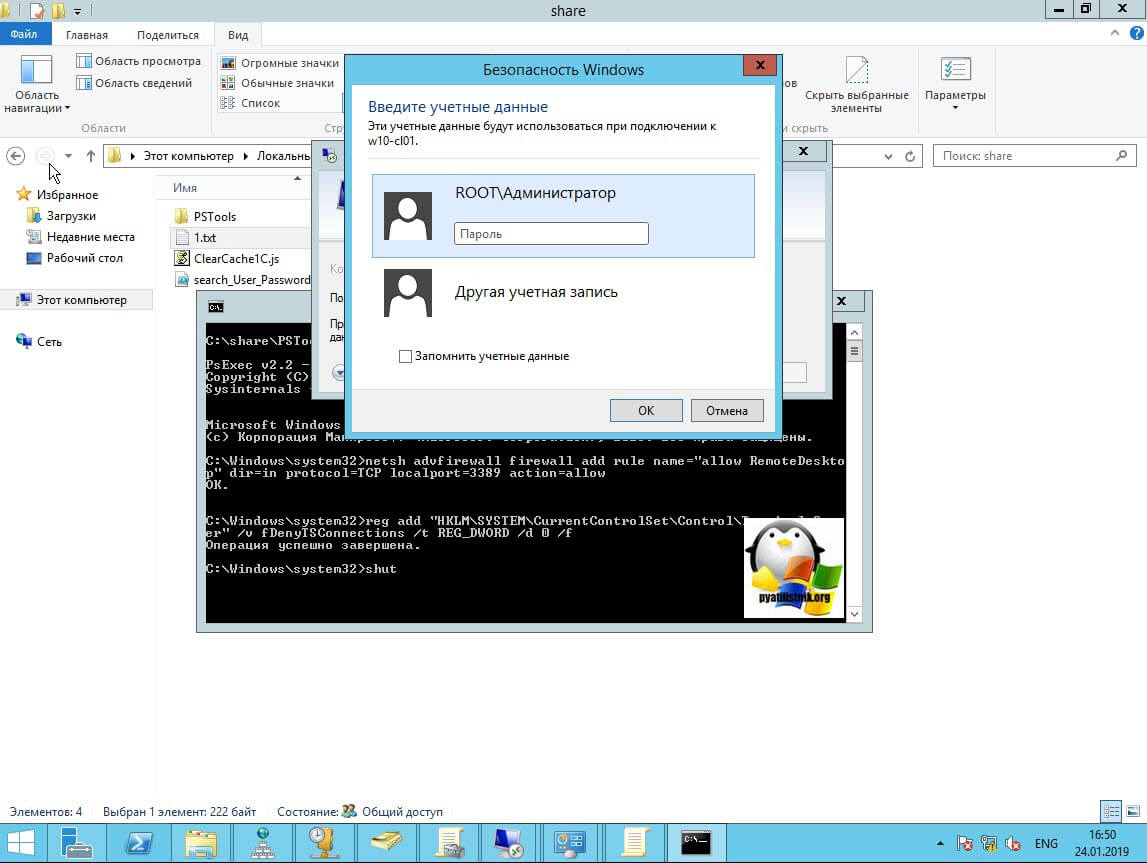
У вас будет произведено подключение к данному компьютеру. Если у вас выскочит ошибка:
В данном случае, нужно проверить две вещи:
- Доступен ли компьютер по сети, для этого проведите элементарный ping компьютера.
- Это нужно на этом компьютере в брандмауэре Windows разрешить «Удаленное управление журналом событий»
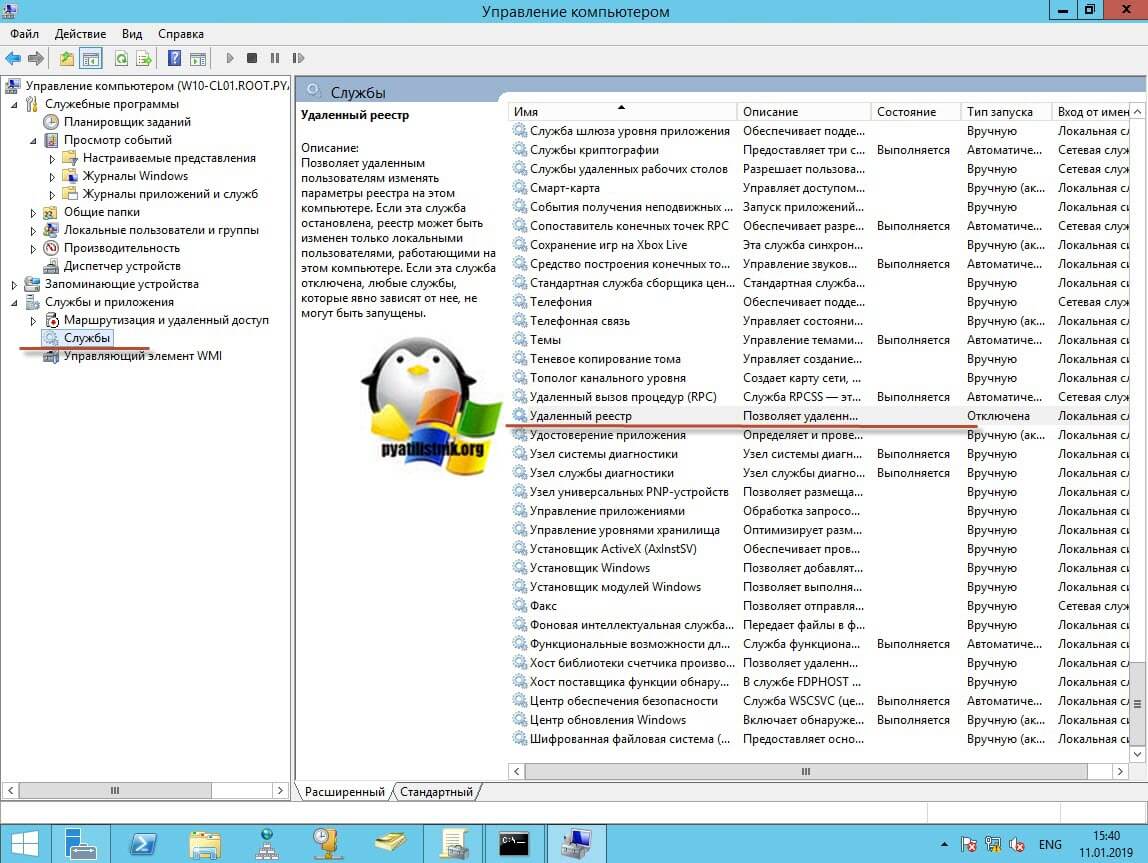
Про то как локально разрешать в брандмауэре службы и порты я говорил, посмотрите по ссылке. Если доступа нет, сделать, это локально, то ниже я приведу пример, как это сделать удаленно. Когда вы подключились к нужному компьютеру или серверу, вам необходимо перед удаленным включением RDP доступа, удостовериться, что у вас на вкладке службы, в активном состоянии запущен сервис «Удаленный реестр».
В моем примере я подключился к удаленным службам, через управление компьютером.
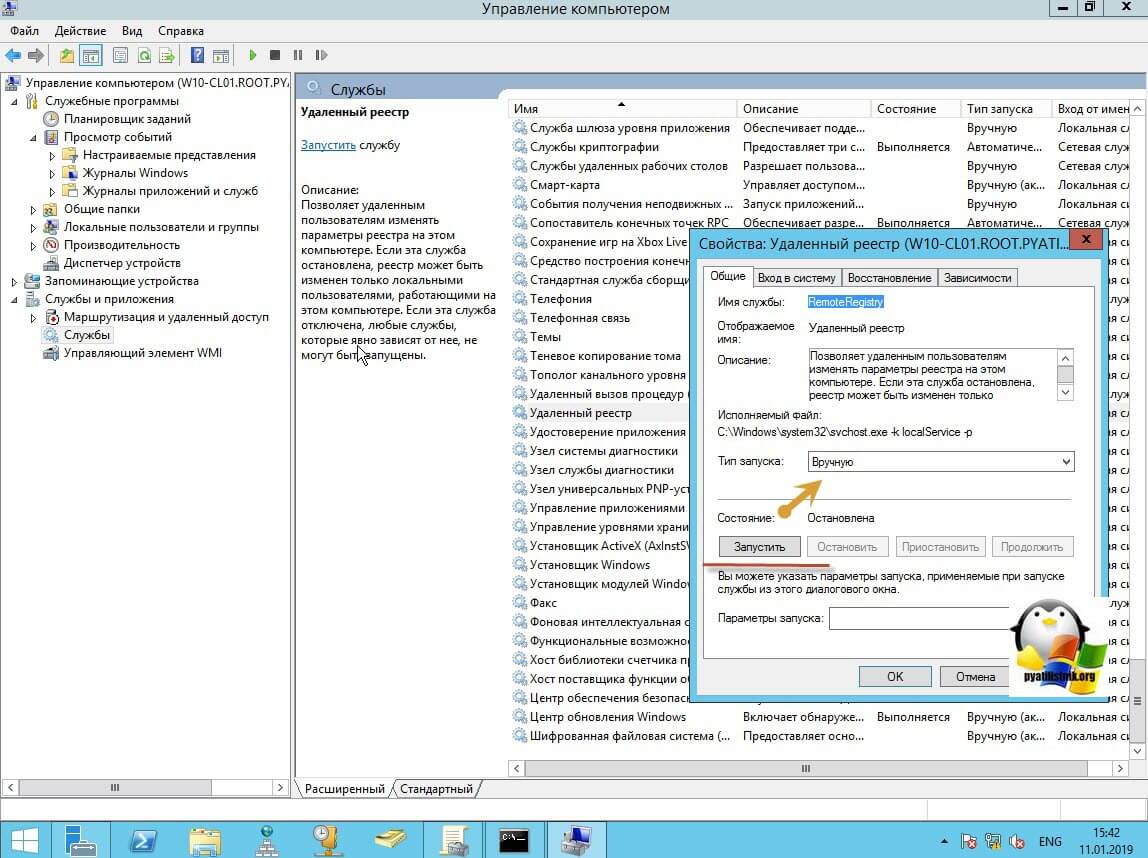
Если этого не сделать, то подключиться к реестру не получиться, и вы не сможете включить RDP по сети. Переходим в свойства данной службы и в типе запуска выставите вручную, после чего нажмите применить. После этого у вас станет активной кнопка запуска, нажимаем ее и проверяем, что сервис стартанул. После этого переходим к редактированию реестра по локальной сети.
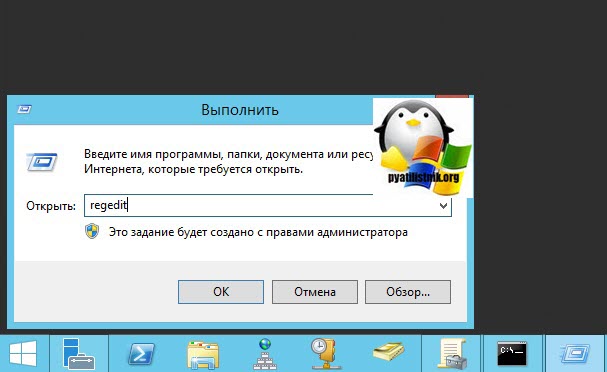
В окне выполнить введите regedit и у вас откроется реестр Windows .
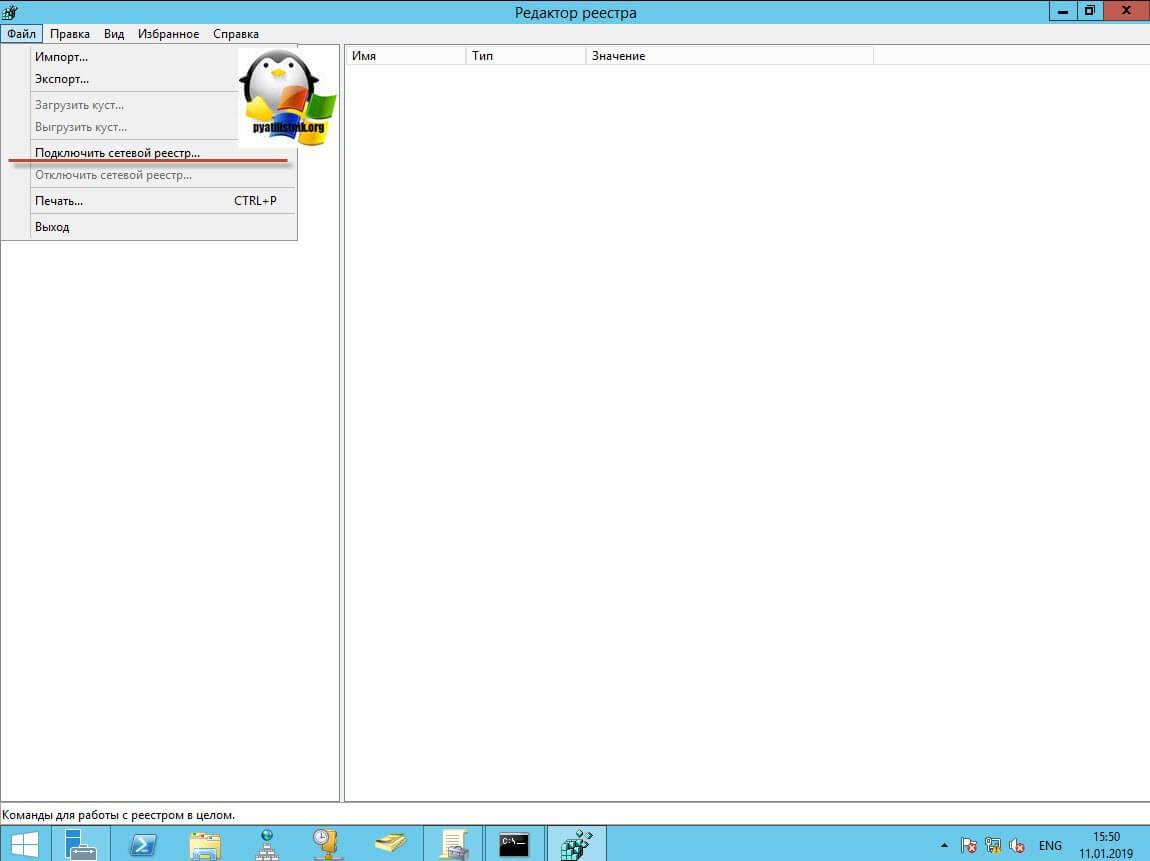
В самом верху есть меню файл, открыв его вам необходимо найти пункт «Подключить сетевой реестр».
У вас откроется окно поиска, где вам необходимо найти нужный вам сетевой компьютер или сервер, после чего нажать ок.
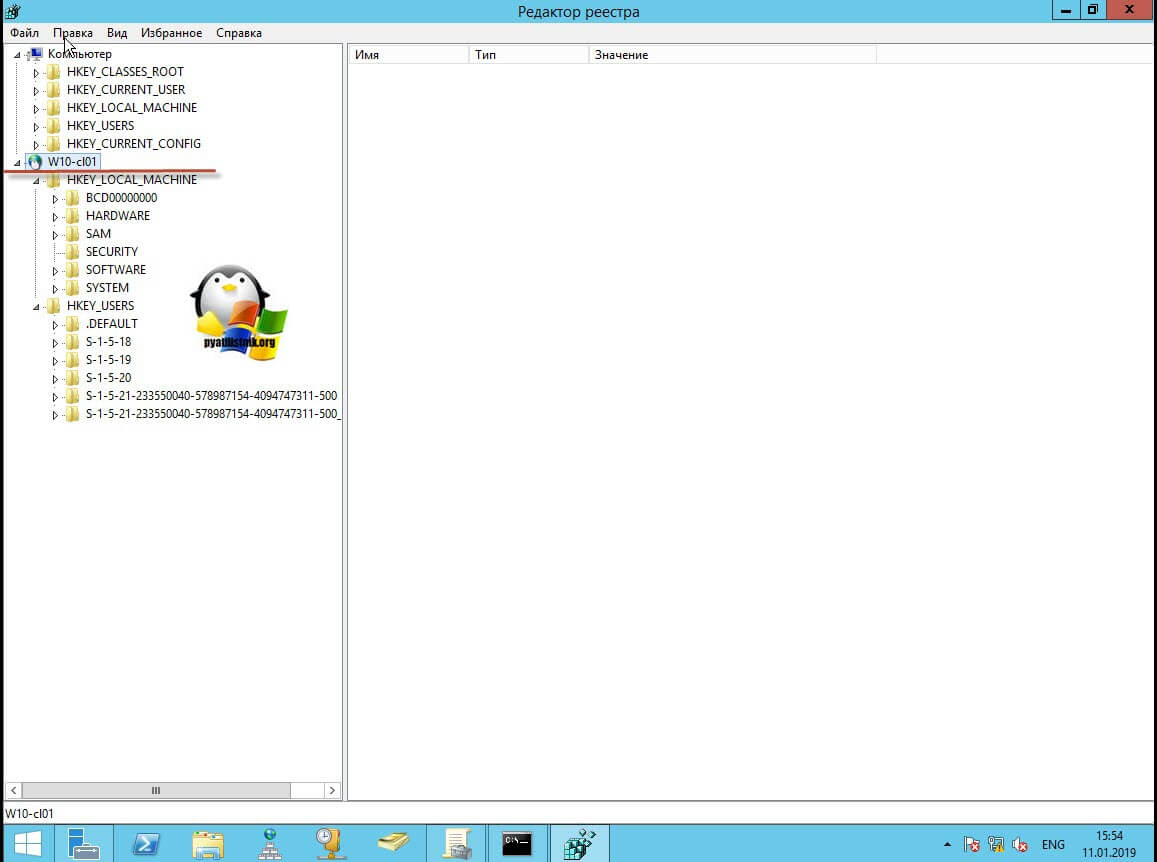
В итоге у вас в окне редактора реестра Windows появится еще один куст. Именно через данный реестр вы включите RDP службу на удаленной системе.
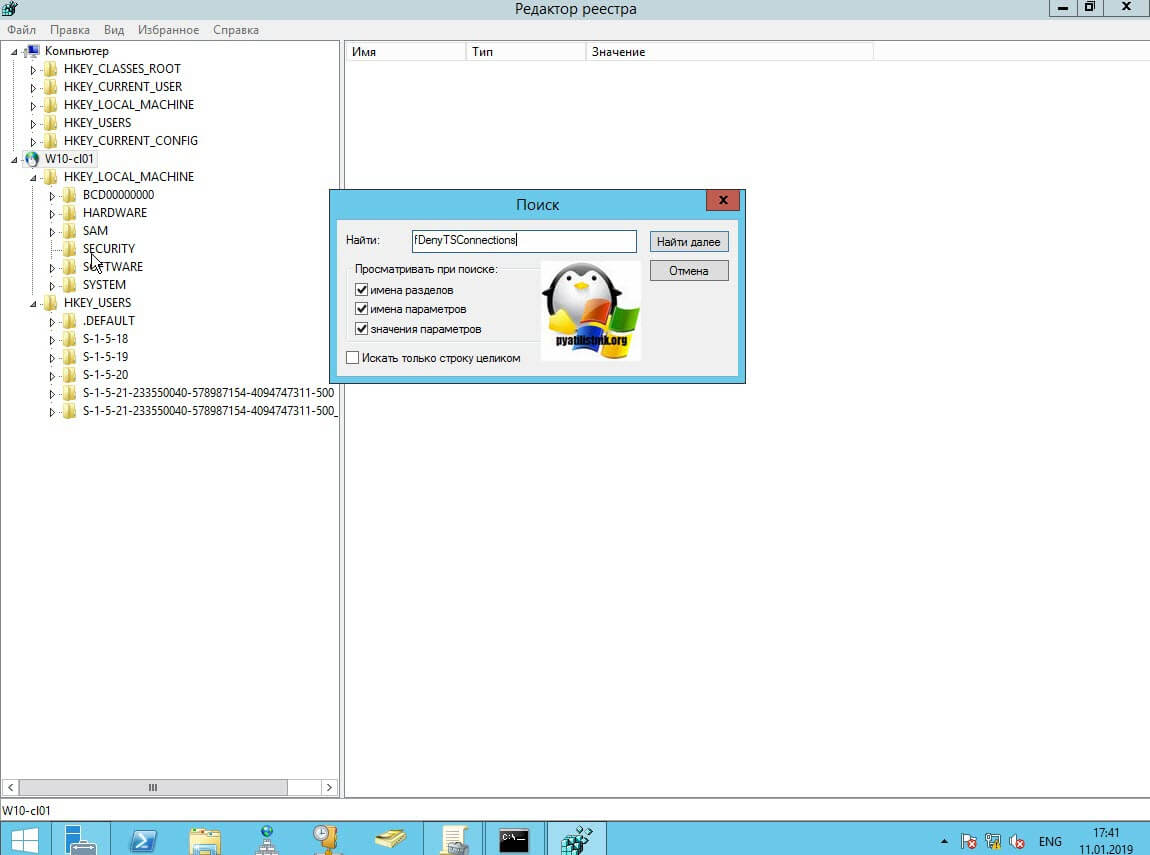
Теперь выбираем корень сетевого реестра Windows и нажимаем кнопку CTRL+F, у вас откроется форма поиска по нему. Тут вам необходимо найти ключ fDenyTSConnections.
Он также по сути должен лежать по пути:
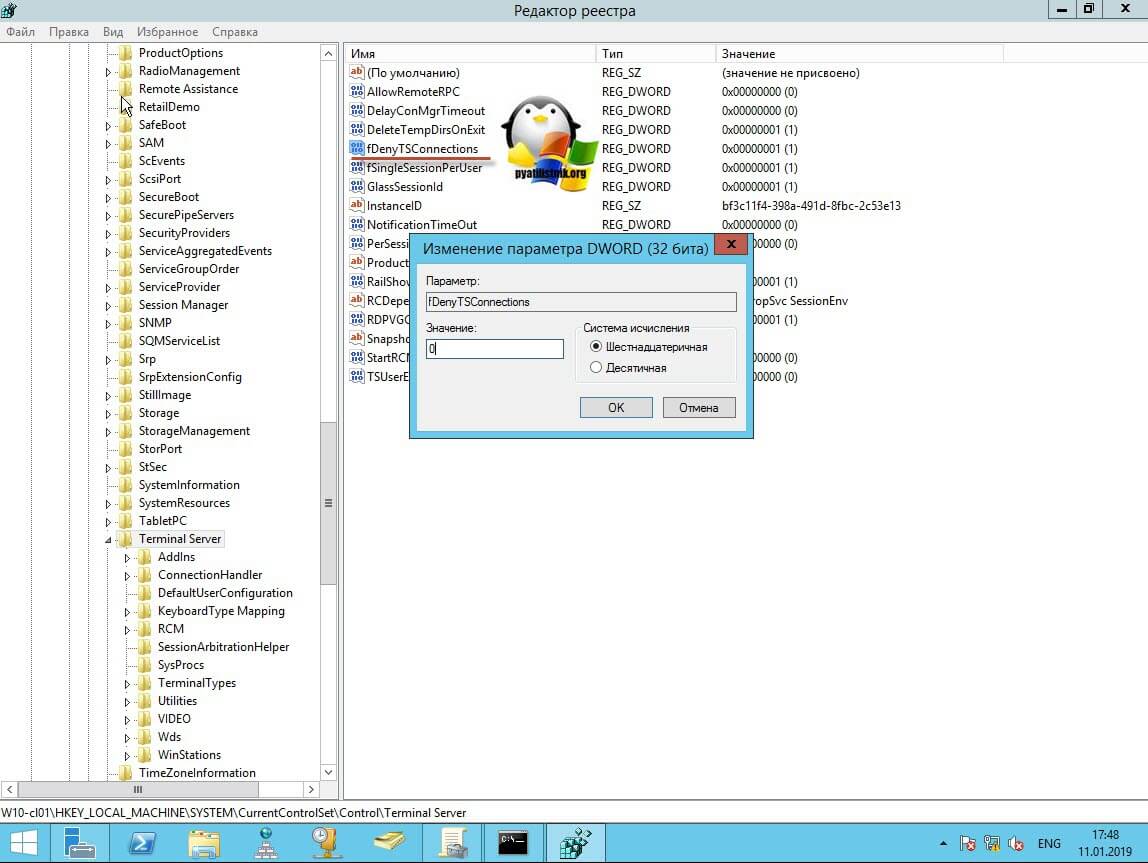
Где ключу fDenyTSConnections вам необходимо изменить значение с 1 на 0, чтобы включить RDP доступ к удаленному компьютеру.
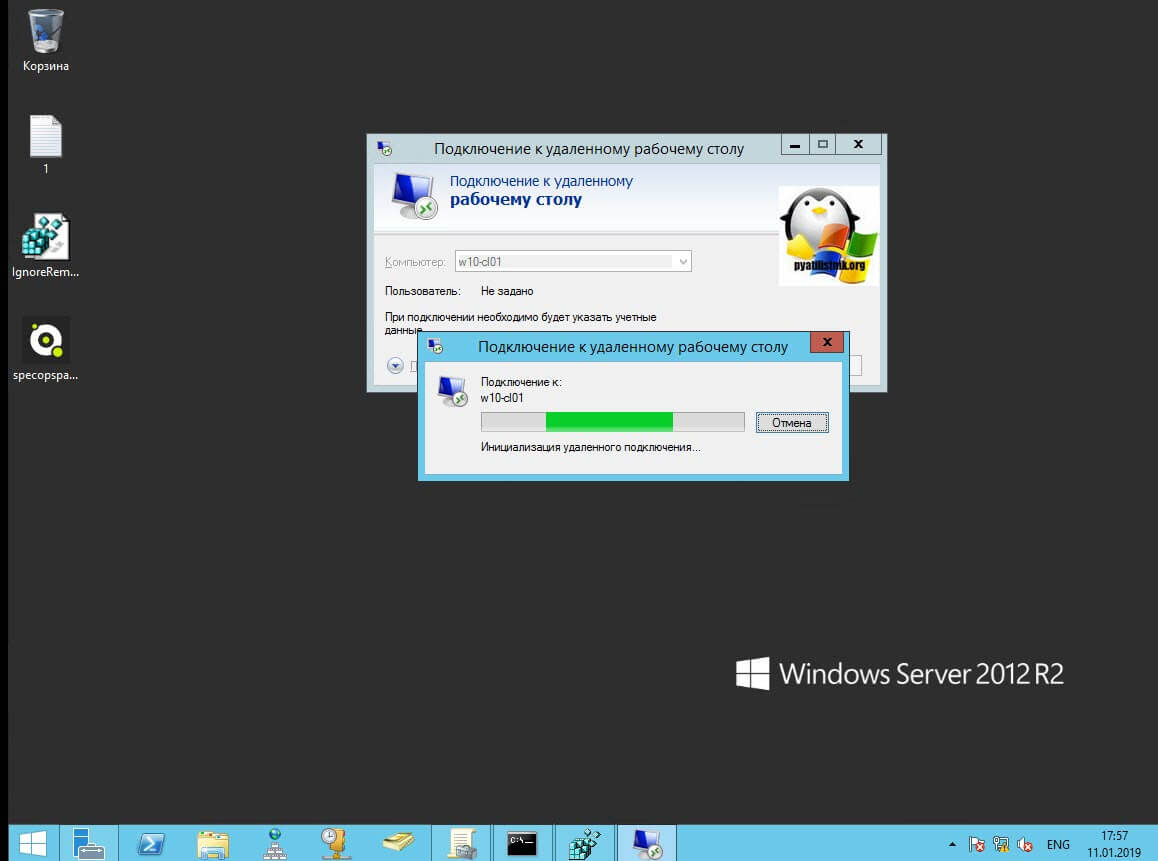
Пробуем произвести подключение, для этого откройте клиента подключения к удаленному рабочему столу (mstsc) и смотрим результат.
Если у вас будут закрыты порты, то вы увидите вот такую картину. При попытке подключиться у вас будет висеть инициализация удаленного подключения.
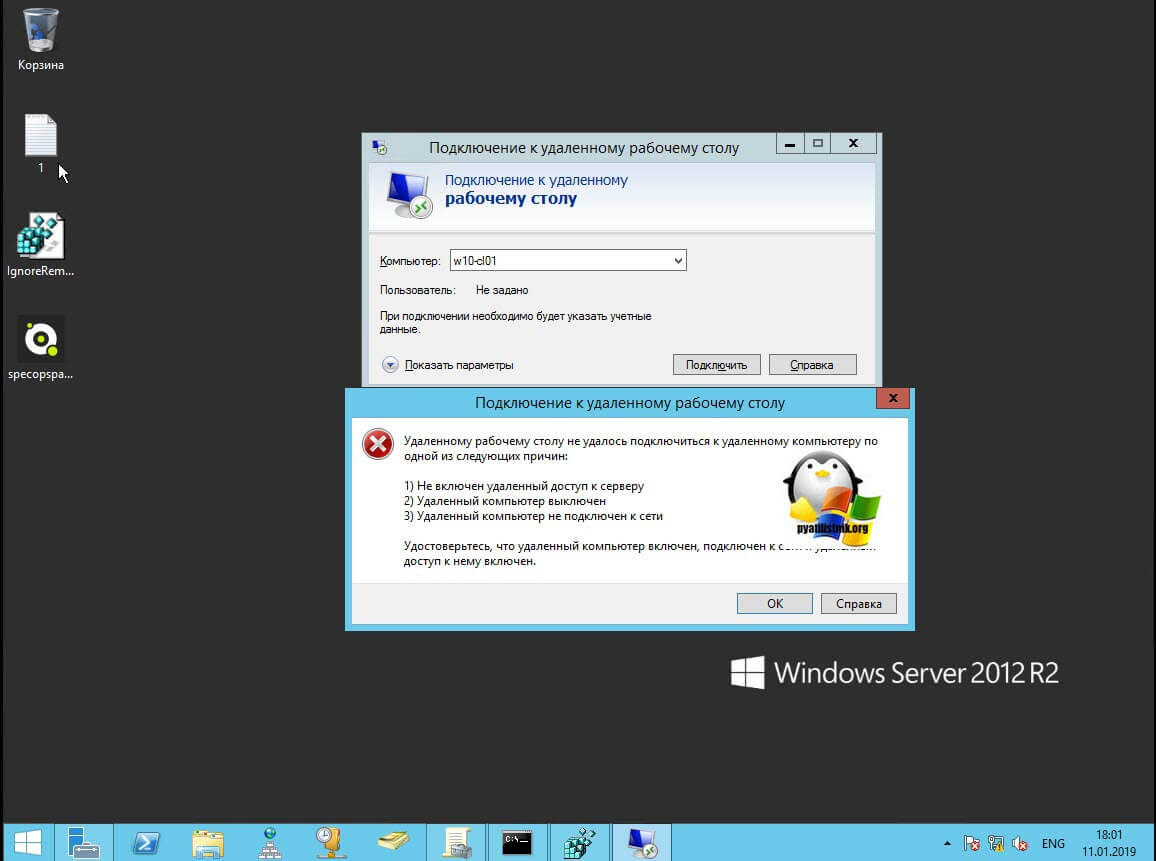
После чего вы увидите ошибку:
- Удаленному рабочему столу не удается подключиться к удаленному компьютеру по одной из следующих причин:
Не включен удаленный доступ к серверу - Удаленный компьютер выключен
- Удаленный компьютер не подключен к сети
Удостоверьтесь, что удаленный компьютер включен, подключен к сети и удаленный доступ к нему включен
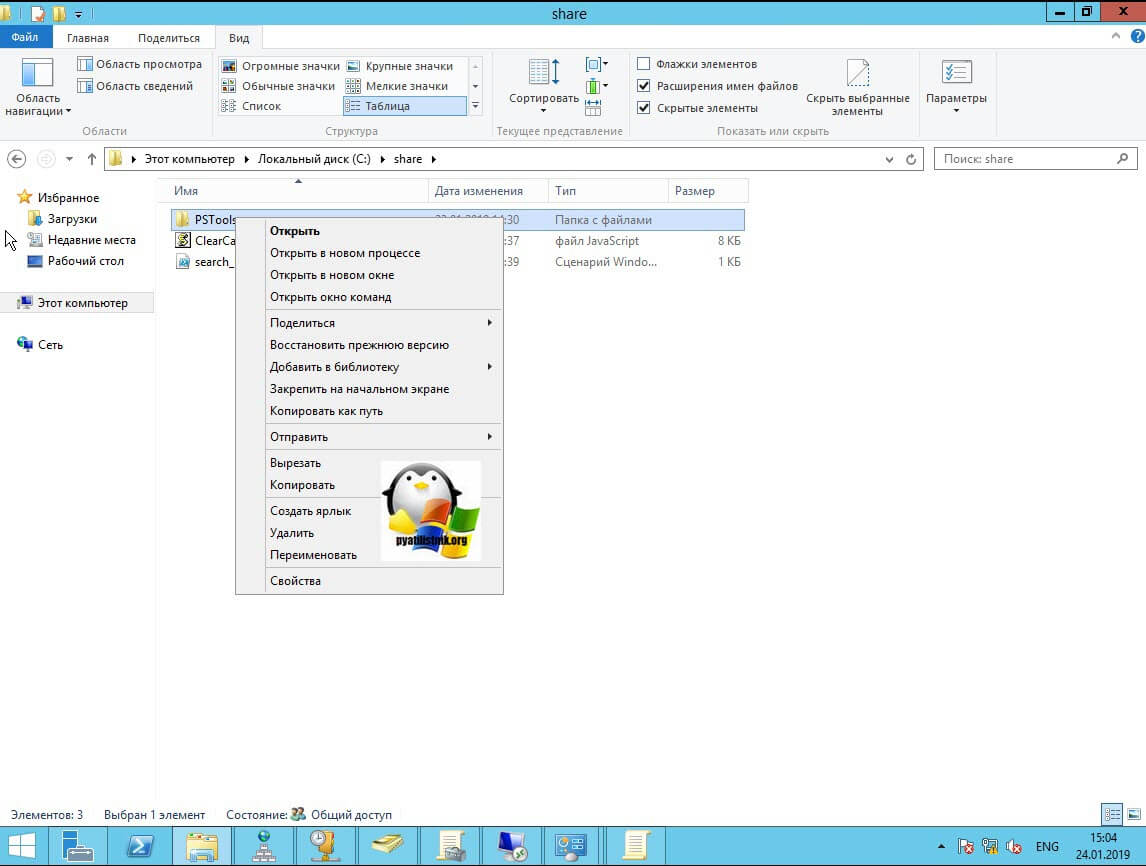
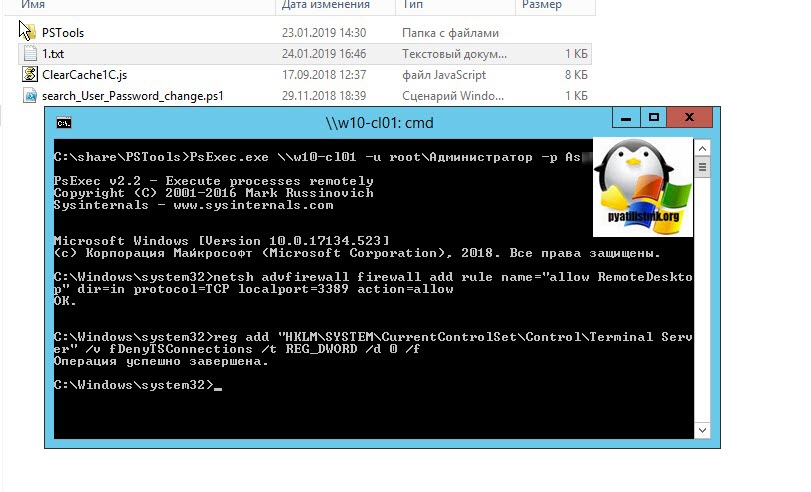
Напоминаю, что вы можете проверить доступность порта , через утилиту Telnet. Проверять нам нужно порт 3389. Вероятнее всего он не ответит. Как я и писал выше откроем порты и создадим правило в брандмауэре. Для этого мы воспользуемся утилитой PSTools.
На выходе у вас будет архив с утилитами, который нужно будет распаковать через архиватор. Когда вы распакуйте его, зажмите клавишу Shift и кликните правым кликом по папке PSTools. Из контекстного меню выберите пункт «Открыть окно команд».
Введите вот такую команду:
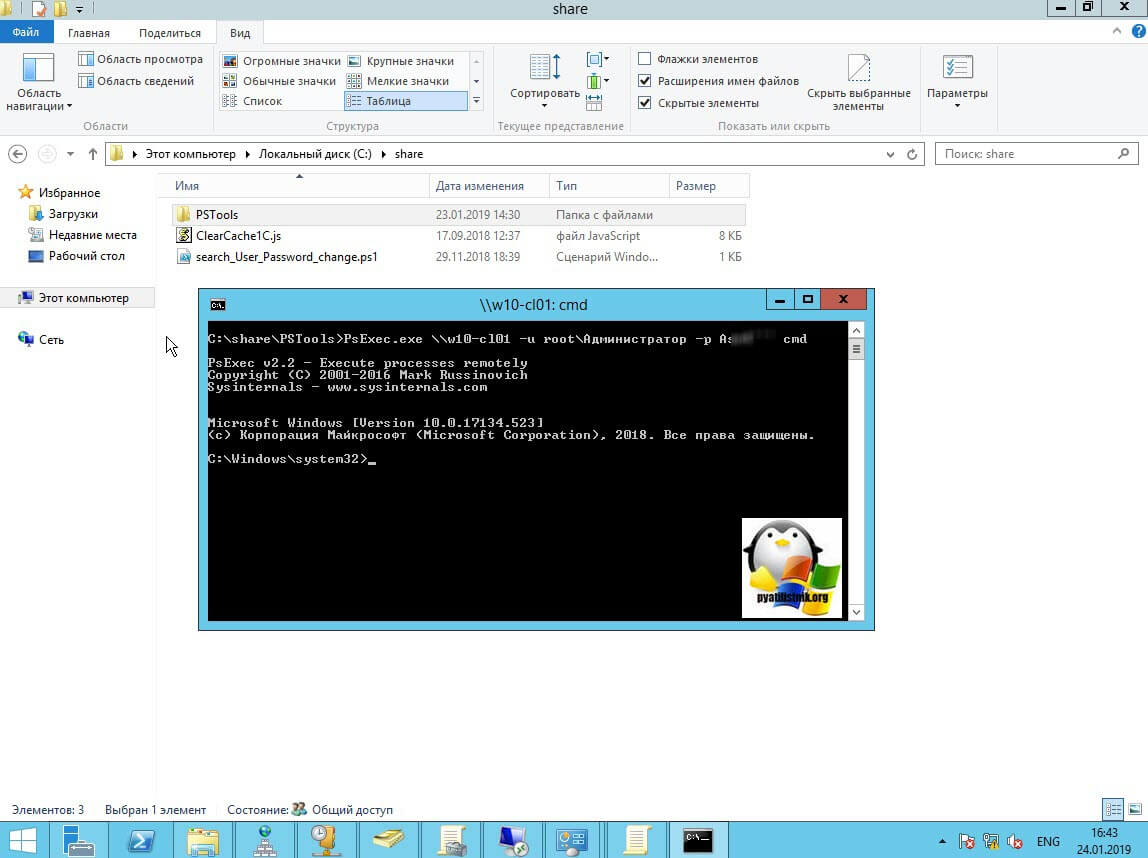
Мой пример: PsExec.exe \\w10-cl01 -u root\Администратор -p пароль cmd
В итоге у вас будет произведено подключение к удаленному компьютеру, вы увидите в заголовке \\dns-имя: cmd. Это означает, что вы успешно подключены.

Далее вступает утилита командной строки netsh, благодаря ей мы создадим правило разрешающее входящие подключения по RDP.
Если вы до этого не включали через реестр доступ к удаленному рабочему столу, то так же это можно выполнить в PsExec.exe:
По идее все должно работать сразу и без перезагрузки, но если она требуется, то выполните команду:
Классический метод включения удаленного рабочего стола
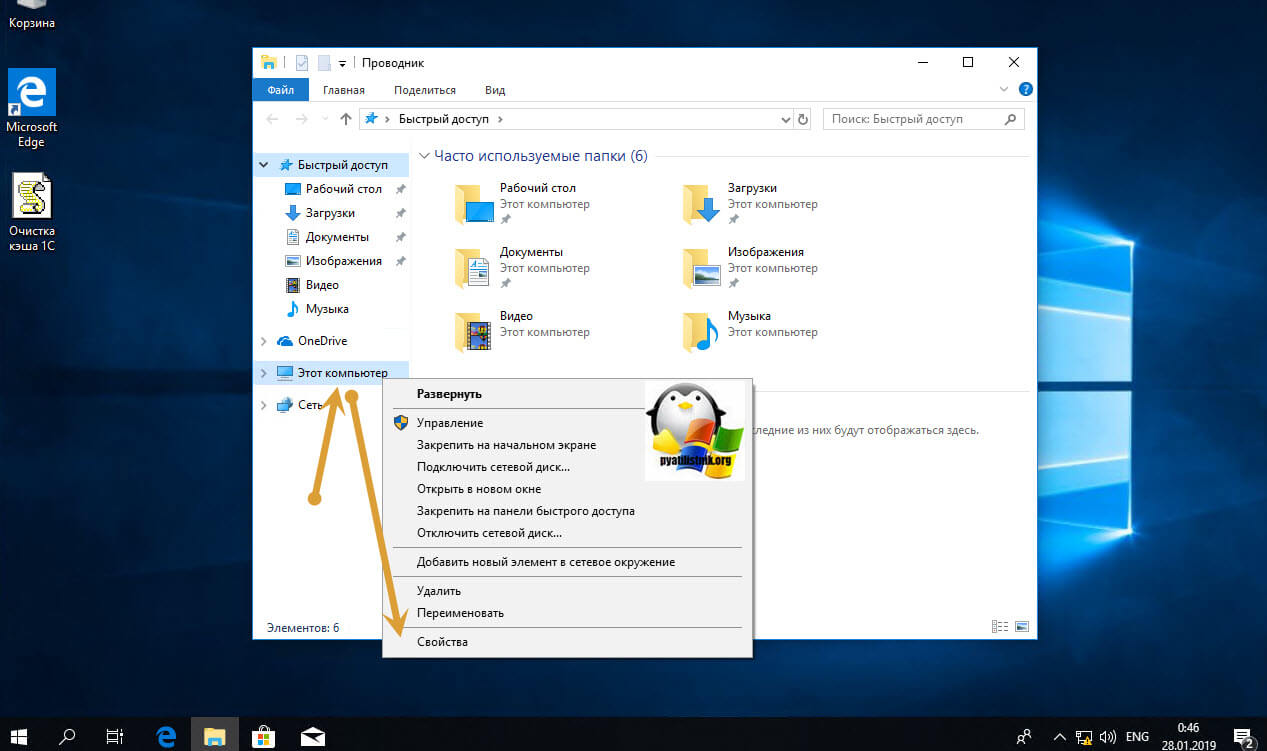
С удаленным включением служб RDP мы разобрались, теперь напомню для новичков, как можно локально его активировать. По умолчанию данная служба, как я и писал не работает. Чтобы это исправить есть два метода. Универсальный метод для любой версии Windows, я буду показывать на десятке, но для семерки, восьмерки, все будет одинаково. Откройте проводник Windows. Найдите в левой части объект «Этот компьютер (Мой компьютер)». Кликните по нему правым кликом и из контекстного меню перейдите в пункт «Свойства».
У вас откроется окно система. В правой части нажмите пункт «Настройка удаленного доступа», которое вызовет окно свойств системы. НА вкладке «Удаленный доступ», чтобы активировать службы удаленных рабочих столов Windows, вам нужно активировать пункт «Разрешить удаленные подключения к этому компьютеру». После этого у вас в системе сразу будет работать RDP доступ.
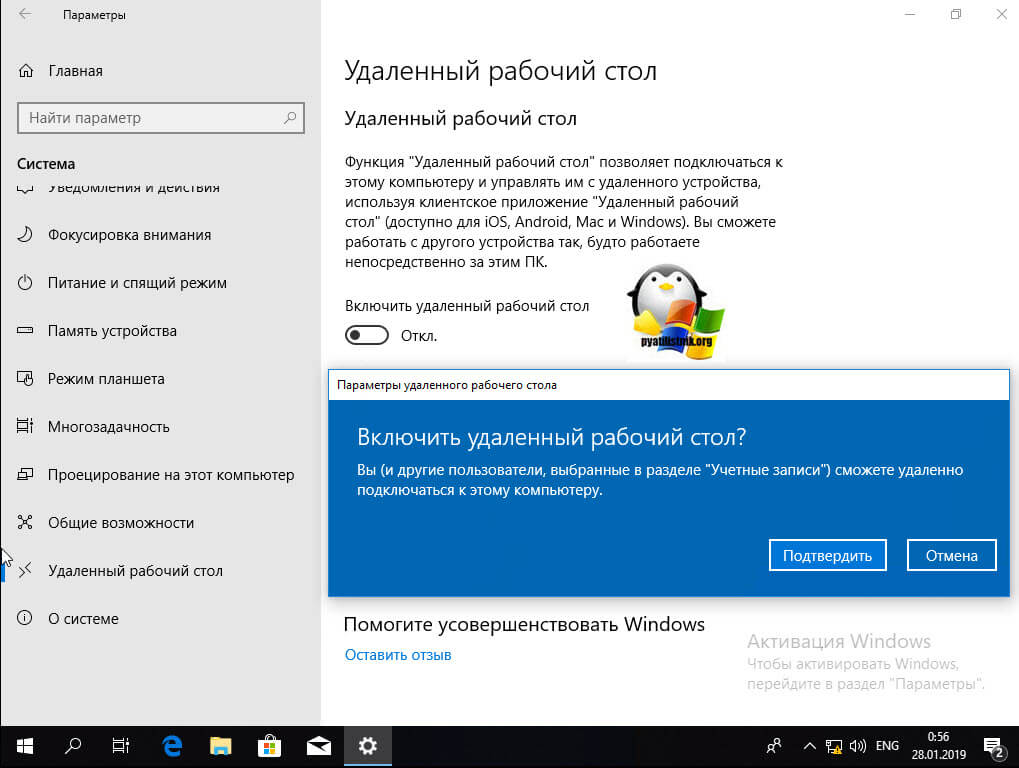
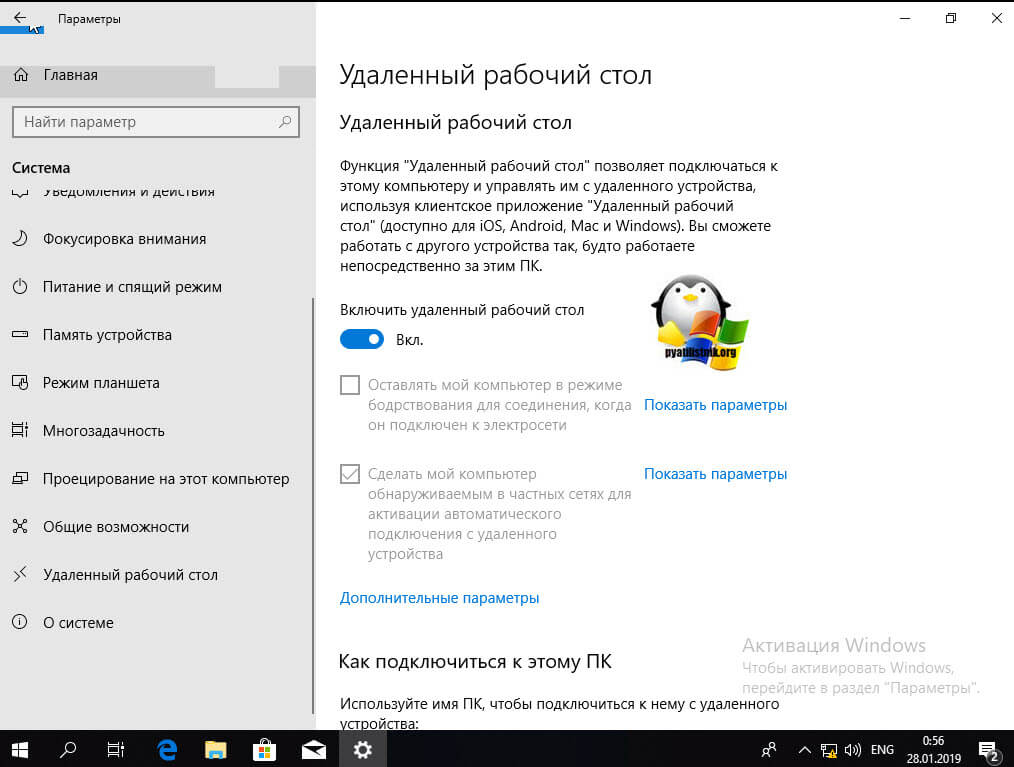
А вот метод исключительно для Windows 10 или Windows Server 2016 и выше. Вы открываете параметры Windows. Переходите в пункт система. В системе будет пункт «Удаленный рабочий стол». Активируем ползунок «Включить удаленный рабочий стол». Выскочит окно с подтверждением, говорим «Подтвердить».
Все функционал RDP активен, можно подключаться с других компьютеров. Данный метод по сути ставит все тужу галку, что мы видели и в классическом окне системы.
Этот подход можно с натяжкой назвать удаленным методом включения RDP, так как на той стороне вам потребуются руки которыми вы будите управлять по телефоны.
Как включить удаленный рабочий стол (RDP) через PowerShell
Открываем на компьютере, где необходимо включить RDP службу оснастку PowerShell.
(Get-WmiObject Win32_TerminalServiceSetting -Namespace root\cimv2\TerminalServices).SetAllowTsConnections(1,1)
Вторая команда активирует галку «Разрешить подключение только с компьютеров, на которых работает удаленный рабочий стол с проверкой подлинности на уровне сети»
(Get-WmiObject -Class «Win32_TSGeneralSetting» -Namespace root\cimv2\TerminalServices -Filter «TerminalName=’RDP-tcp'»).SetUserAuthenticationRequired(0)
Третья команда, включает правило в Брандмауэре
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup «Remote Desktop»
Данные команды вы можете собрать в скрипт и распространить его через групповую политику при включении компьютера или автологоне пользователя.
Как удаленно включить RDP через групповую политику
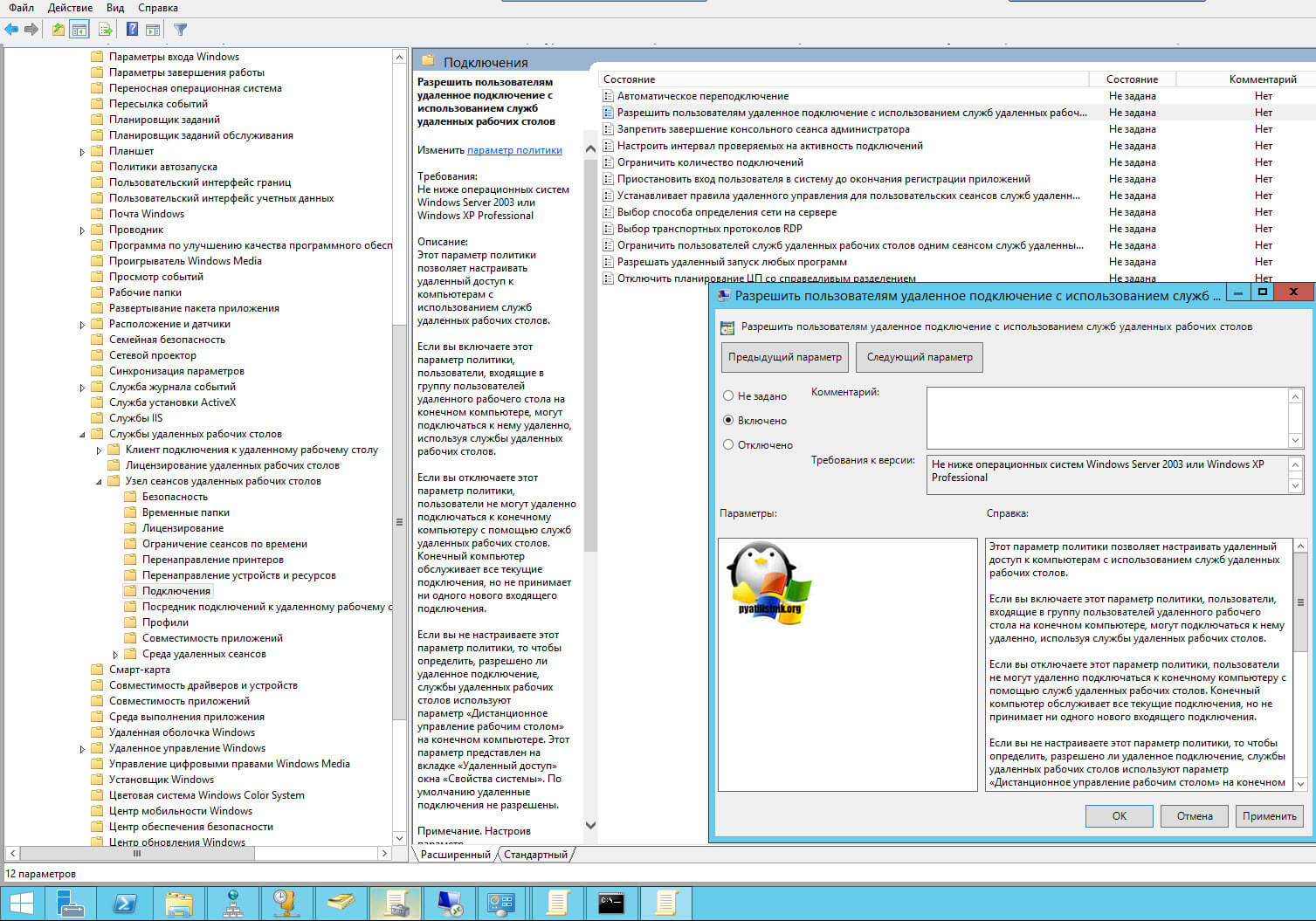
Данный метод включения удаленного рабочего стола на нужном компьютере возможен за счет домена Active Directory, благодаря централизованному управлению рабочих станций ваших сотрудников. Откройте редактор управления групповыми политиками. Создайте новую политику и прилинкуйте ее к нужному организационному подразделению, которое содержит нужный компьютер. После чего зайдите в свойства данной политики и измените ее настройки. Перейдите по пути:
Откройте эту настройку и включите ее. Не забываем после этого обновить групповую политику на нужном компьютере и не забываем там открыть порт для RDP. Так же политиками или локально.
Включив настройку вы можете указать конкретные ip-адреса откуда можно производить подключение или же ввести *, это будет означать, для всех.
General Remote Desktop connection troubleshooting
Use these steps when a Remote Desktop client can’t connect to a remote desktop but doesn’t provide messages or other symptoms that would help identify the cause.
Check the status of the RDP protocol
Check the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer
To check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer, see How to enable Remote Desktop.
If the remote desktop options are not available, see Check whether a Group Policy Object is blocking RDP.
Check the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer
Follow this section’s instructions carefully. Serious problems can occur if the registry is modified incorrectly. Before you start modifying the registry, back up the registry so you can restore it in case something goes wrong.
To check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer, use a network registry connection:
- First, go to the Start menu, then select Run. In the text box that appears, enter regedt32.
- In the Registry Editor, select File, then select Connect Network Registry.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, enter the name of the remote computer, select Check Names, and then select OK.
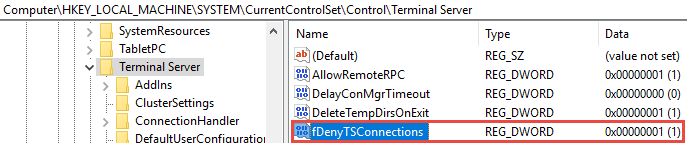
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server.
- If the value of the fDenyTSConnections key is 0, then RDP is enabled.
- If the value of the fDenyTSConnections key is 1, then RDP is disabled.
- To enable RDP, change the value of fDenyTSConnections from 1 to 0.
Check whether a Group Policy Object (GPO) is blocking RDP on a local computer
If you can’t turn on RDP in the user interface or the value of fDenyTSConnections reverts to 1 after you’ve changed it, a GPO may be overriding the computer-level settings.
To check the group policy configuration on a local computer, open a Command Prompt window as an administrator, and enter the following command:
After this command finishes, open gpresult.html. In Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections, find the Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services policy.
If the setting for this policy is Enabled, Group Policy is not blocking RDP connections.
If the setting for this policy is Disabled, check Winning GPO. This is the GPO that is blocking RDP connections.
Check whether a GPO is blocking RDP on a remote computer
To check the Group Policy configuration on a remote computer, the command is almost the same as for a local computer:
The file that this command produces (gpresult- .html) uses the same information format as the local computer version (gpresult.html) uses.
Modifying a blocking GPO
You can modify these settings in the Group Policy Object Editor (GPE) and Group Policy Management Console (GPM). For more information about how to use Group Policy, see Advanced Group Policy Management.
To modify the blocking policy, use one of the following methods:
- In GPE, access the appropriate level of GPO (such as local or domain), and navigate to Computer Configuration >Administrative Templates >Windows Components >Remote Desktop Services >Remote Desktop Session Host >Connections >Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services.
- Set the policy to either Enabled or Not configured.
- On the affected computers, open a command prompt window as an administrator, and run the gpupdate /force command.
- In GPM, navigate to the organizational unit (OU) in which the blocking policy is applied to the affected computers and delete the policy from the OU.
Check the status of the RDP services
On both the local (client) computer and the remote (target) computer, the following services should be running:
- Remote Desktop Services (TermService)
- Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector (UmRdpService)
You can use the Services MMC snap-in to manage the services locally or remotely. You can also use PowerShell to manage the services locally or remotely (if the remote computer is configured to accept remote PowerShell cmdlets).
On either computer, if one or both services are not running, start them.
If you start the Remote Desktop Services service, click Yes to automatically restart the Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector service.
Check that the RDP listener is functioning
Follow this section’s instructions carefully. Serious problems can occur if the registry is modified incorrectly. Before you starty modifying the registry, back up the registry so you can restore it in case something goes wrong.
Check the status of the RDP listener
For this procedure, use a PowerShell instance that has administrative permissions. For a local computer, you can also use a command prompt that has administrative permissions. However, this procedure uses PowerShell because the same cmdlets work both locally and remotely.
To connect to a remote computer, run the following cmdlet:
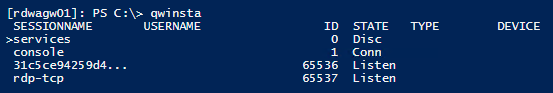
Enter qwinsta.
If the list includes rdp-tcp with a status of Listen, the RDP listener is working. Proceed to Check the RDP listener port. Otherwise, continue at step 4.
Export the RDP listener configuration from a working computer.
- Sign in to a computer that has the same operating system version as the affected computer has, and access that computer’s registry (for example, by using Registry Editor).
- Navigate to the following registry entry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp - Export the entry to a .reg file. For example, in Registry Editor, right-click the entry, select Export, and then enter a filename for the exported settings.
- Copy the exported .reg file to the affected computer.
To import the RDP listener configuration, open a PowerShell window that has administrative permissions on the affected computer (or open the PowerShell window and connect to the affected computer remotely).
To back up the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlet:
To remove the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlets:
To import the new registry entry and then restart the service, enter the following cmdlets:
Replace with the name of the exported .reg file.
Test the configuration by trying the remote desktop connection again. If you still can’t connect, restart the affected computer.
Check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate
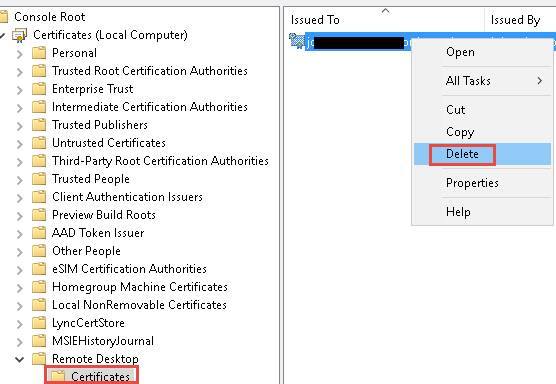
- If you still can’t connect, open the Certificates MMC snap-in. When you are prompted to select the certificate store to manage, select Computer account, and then select the affected computer.
- In the Certificates folder under Remote Desktop, delete the RDP self-signed certificate.
- On the affected computer, restart the Remote Desktop Services service.
- Refresh the Certificates snap-in.
- If the RDP self-signed certificate has not been recreated, check the permissions of the MachineKeys folder.
Check the permissions of the MachineKeys folder
- On the affected computer, open Explorer, and then navigate to C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\.
- Right-click MachineKeys, select Properties, select Security, and then select Advanced.
- Make sure that the following permissions are configured:
- Builtin\Administrators: Full control
- Everyone: Read, Write
Check the RDP listener port
On both the local (client) computer and the remote (target) computer, the RDP listener should be listening on port 3389. No other applications should be using this port.
Follow this section’s instructions carefully. Serious problems can occur if the registry is modified incorrectly. Before you starty modifying the registry, back up the registry so you can restore it in case something goes wrong.
To check or change the RDP port, use the Registry Editor:
- Go to the Start menu, select Run, then enter regedt32 into the text box that appears.
- To connect to a remote computer, select File, and then select Connect Network Registry.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, enter the name of the remote computer, select Check Names, and then select OK.
- Open the registry and navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\ .
- If PortNumber has a value other than 3389, change it to 3389.
You can operate Remote Desktop services using another port. However, we don’t recommend you do this. This article doesn’t cover how to troubleshoot that type of configuration.
Check that another application isn’t trying to use the same port
For this procedure, use a PowerShell instance that has administrative permissions. For a local computer, you can also use a command prompt that has administrative permissions. However, this procedure uses PowerShell because the same cmdlets work locally and remotely.
Open a PowerShell window. To connect to a remote computer, enter Enter-PSSession -ComputerName .
Enter the following command:
Look for an entry for TCP port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port) with a status of Listening.
The process identifier (PID) for the process or service using that port appears under the PID column.
To determine which application is using port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port), enter the following command:
Look for an entry for the PID number that is associated with the port (from the netstat output). The services or processes that are associated with that PID appear on the right column.
If an application or service other than Remote Desktop Services (TermServ.exe) is using the port, you can resolve the conflict by using one of the following methods:
- Configure the other application or service to use a different port (recommended).
- Uninstall the other application or service.
- Configure RDP to use a different port, and then restart the Remote Desktop Services service (not recommended).
Check whether a firewall is blocking the RDP port
Use the psping tool to test whether you can reach the affected computer by using port 3389.
Go to a different computer that isn’t affected and download psping from https://live.sysinternals.com/psping.exe.
Open a command prompt window as an administrator, change to the directory in which you installed psping, and then enter the following command:
Check the output of the psping command for results such as the following:
- Connecting to : The remote computer is reachable.
- (0% loss): All attempts to connect succeeded.
- The remote computer refused the network connection: The remote computer is not reachable.
- (100% loss): All attempts to connect failed.
Run psping on multiple computers to test their ability to connect to the affected computer.
Note whether the affected computer blocks connections from all other computers, some other computers, or only one other computer.
Recommended next steps:
- Engage your network administrators to verify that the network allows RDP traffic to the affected computer.
- Investigate the configurations of any firewalls between the source computers and the affected computer (including Windows Firewall on the affected computer) to determine whether a firewall is blocking the RDP port.
—>